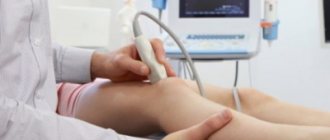
Establishing a correct diagnosis requires high professionalism and the use of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods. X-ray examination allows us to determine the destruction of cartilage, ligament ruptures, and deforming processes. In some cases, it is advisable to perform magnetic resonance imaging. MRI images allow you to visualize changes in the structure of the synovial membrane, bone marrow swelling, and pathological processes in soft periarticular tissues.
Laboratory blood tests show levels of specific inflammatory markers. Analysis of the effusion of the joint capsule makes it possible to establish the infectious nature of the disease.
At the Center for Restorative Medicine in Naberezhnye Chelny, professional neurologists, orthopedists and traumatologists conduct a comprehensive examination for complaints of pain in large and small joints of the upper, lower extremities, and hip joints. A modern laboratory with the latest equipment allows you to examine biological fluids for elements of inflammation and infection.
Causes of joint pain
The causes of joint pain can be either mechanical or infectious. After an injury, no one is surprised by pain when moving. But when pain occurs for no obvious reason, the patient does not understand how to act to get rid of the problem.
However, a bacterial infection can cause pain. When pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the synovial fluid, they infect nearby soft tissues. An infection can get into a joint in several ways:
- As a result of prosthetics, due to poor quality sterilization of materials.
- Due to deep tissue damage due to skin infections;
- After any surgical intervention performed in violation of the rules of antiseptic treatment.
In addition to bacteria, the joint is also threatened by fungus. These microorganisms also enter the synovial fluid as a result of infection obtained during surgical interventions.
Few people associate stomach disease or bladder damage with pain in the knee or elbow joint. However, there is a connection. When the gastrointestinal tract is affected by a bacterial infection, toxins and colonies of microorganisms enter the bloodstream and move through the body with the bloodstream. Some of them settle in the joint cavity. Joint risks include:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- damage to the urinary system;
- venereal diseases;
- rubella;
- angina;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- pneumonia.
This suggests that improper treatment of infectious diseases can lead to more serious consequences than one might imagine. For example, late diagnosed tonsillitis, or the patient’s refusal of prescribed antibiotics can lead to disability. This is due to the fact that streptococcus, which causes tonsillitis, is recognized by the immune system in the same way as cells from the heart valves and intra-articular tissue. If antibiotic therapy is not used as the primary treatment, the immune system itself will destroy the joint tissue while fighting the infection.
Viral infections also affect joints. These are diseases such as:
- rubella;
- hepatitis C;
- hepatitis B;
- herpes.
Humanity has not yet come up with a proven effective medicine that would fight viruses. The only exception is the drug Acyclovir, which is effective against the herpes virus. Other diseases of viral etiology can only be defeated by the human immune system. To protect yourself from infections that can destroy joint tissue, you can arm your immune system with vaccination. Vaccinations against rubella and hepatitis are included in the mandatory calendar.
Diseases that can cause joint pain in the legs
Diseases and injuries of the leg joints often lead to disability, and in many cases this is not due to the severity of the pathology itself, but solely to the patients’ reluctance to visit a doctor on time and unsuccessful attempts at self-medication in the early stages of the disease. In diseases, this leads to severe destruction of articular joints, and in injuries, to improper fusion of damaged areas.
If your leg joints hurt, treatment will depend on the reasons that led to the discomfort. The main types of pathologies that cause pain in the legs:
- infectious;
- autoimmune;
- metabolic;
- degenerative-dystrophic;
- deforming.
Also, the appearance of pain can be associated with injuries: fractures, sprains, bruises or dislocations. Often, swelling and hematoma do not appear immediately after injury, but only after several hours, and sometimes even days. Hypothermia and excessive stress contribute to the exacerbation of chronic joint diseases: arthritis, synovitis, arthrosis and others. If discomfort always occurs after physical activity or long walking, you should consult your doctor. This will allow you to timely diagnose articular pathology and begin its treatment.
Degenerative-dystrophic diseases With arthrosis, articular joints gradually become deformed and mobility decreases. This pathology is characterized by moderate pain, crunching when walking and changes in gait (usually lameness). Metabolic disorders Often pain in the leg joint near the foot is caused by gout. This pathology is associated with a metabolic disorder, due to which uric acid crystals gradually accumulate in the joints. They injure and destroy tissue, cause inflammation, which causes swelling, “bone” growth, and periodic severe pain attacks, during which the temperature may rise and blood pressure may change sharply. Under the skin, and then on the internal organs, tophi form - gouty nodules with accumulations of uric acid. Gout is a dangerous pathology that can lead to kidney damage and other serious complications, so if you have pain in the joints of your feet, be sure to consult a doctor: he will order an examination and tell you how to treat this disease. Inflammatory joint diseases Arthritis and synovitis most often lead to pain in the leg joints. Often these pathologies worsen after acute respiratory viral infections and other infectious diseases, with severe physical exertion or hypothermia. These pathologies are accompanied by fever, intoxication, swelling and redness of the skin. Arthritis most often affects the hip joints. With coxarthritis, the patient experiences severe pain in the hip joint when walking, and in advanced cases, surgical treatment may be required. Synovitis usually affects the knees. Without treatment, tissue death occurs, pus accumulates in the joint cavity, and sepsis is possible. In severe cases, complete or partial replacement of the joint is required. In the early stages, arthritis and synovitis can be successfully treated with medications, physical therapy and exercise therapy.
How to relieve pain
Orthopedists use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as a symptomatic treatment for joint pain. Among them, the following are particularly pronounced in relation to joint pain:
- Diclofenac;
- Nimesulide;
- Ketorol;
- Ketoprofen;
- Ibuprofen.
If the pain is unbearable, you will need to contact a specialist who will install a blockade. This is a procedure that allows you to inject anesthesia into the joint itself and into the radicular zone of the nerve endings. But this solution to the problem is temporary. After 10-16 hours, the patient’s condition will return to its original position.
Gout
Gouty joints usually involve paroxysmal episodes of pain, stiffness, inflammation and redness in the joints. The reason for this lies in the excess production of uric acid, which is not completely utilized by the kidneys and is deposited in the form of crystals in the joints, which leads to inflammation. As a rule, this disease develops after 50 years. Therefore, it must be remembered that with age, the excretory function of the kidneys may decrease, which can lead to gout. Gout usually affects the feet, but if left untreated, other joints can also be affected.
What does crunching in joints mean?
Crunching in the joints can be caused by several reasons. On the one hand, the crunch indicates that the intra-articular substrate is depleted as a result of a violation of the water-salt balance. On the other hand, a single crunch, which can be heard when bending or straightening a joint to its maximum position, is the sound made by gas bubbles bursting inside the joint fluid.
If there is a constant crunching sound when moving, you need to reduce the load on the moving part. It is better to eliminate the cause through the office of an orthopedic traumatologist. Self-administration of advertised medications not only will not help, but can also cause harm. An x-ray will show the condition of the bones and interarticular cartilage. If it turns out that it is depleted, individual recommendations will be given. If you treat the pain with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs when you have worn out cartilage, you will only be able to reduce the sensitivity in the joint while continuing to use it. Over time, thin cartilage causes inflammation of the intra-articular tissue, which will lead to arthrosis.
Self-help during attacks of gout, arthritis and synovitis
Take a pain reliever or use an ointment with an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Secure the joint with an elastic bandage, try to move as little as possible, and use support when walking. Avoid eating fatty, spicy, salty and spicy foods.
If you have already been diagnosed with one or another, you can take medications previously prescribed by your doctor to eliminate the cause of the pain attack. For example, during an exacerbation of gout, it is necessary to take medications that help remove excess purines from the body. If you have a high temperature and very severe pain, call an ambulance.
Arthritis or arthrosis
For those who do not have a medical education or have not personally encountered problems with bones and joints, the two concepts: arthritis and arthrosis seem exactly the same. The similarity of the names is explained by the fact that all diseases associated with joints have the root “art”. The prefix “it” indicates an inflammatory process. This can be seen in the example of other terms: rhinitis - inflammation of the sinuses, bronchitis - inflammation of the bronchi; otitis – inflammation of the ear. However, the term does not indicate the causes of inflammation, which means it cannot be a diagnosis. Bronchitis, for example, can be both viral and bacterial. This means that treatment tactics in both cases are completely different. Arthritis is inflammation in a joint, without a description of the cause.
Arthrosis is a disease that affects the interarticular cartilage. Prolonged unexamined arthritis sooner or later leads to arthrosis. Inflammatory processes in the joint disrupt metabolism, due to which the tissues do not receive proper nutrition and become thinner. This is where the destruction of cartilage tissue occurs.
Arthrosis of the ankle joint
Surgical treatment may be indicated for patients with severe osteoarthritis or in cases where conservative treatment is ineffective. There are several different options for surgical treatment of osteoarthritis.
Arthroscopy . Arthroscopic procedures include synovectomy and debridement (cleaning of the joint), removal of loose intra-articular bodies, excision of osteophytes (bone spines) and chondroplasty (cartilage replacement). The high effectiveness of arthroscopic interventions in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the ankle joint has been confirmed in many studies. In patients with widespread degenerative joint disease, arthroscopy can achieve long-term positive effects. Arthroscopy may also be effective in patients with focal osteochondral lesions of the talus.
Osteotomy of the tibia . In some cases, osteoarthritis of the ankle joint is caused by deformities of the tibia, which lead to improper distribution of loads in the ankle joint. In such cases, osteotomy eliminates deformity and optimizes load distribution. It is indicated primarily for young patients with varus or valgus deformity of the lower limb and associated minimal or moderate osteoarthritis of the ankle joint.
Arthrodesis of the ankle joint . Arthrodesis of the ankle joint (tibiotalar arthrodesis) is one of the most predictable interventions for relieving pain caused by severe degenerative damage to the joint. Arthrodesis can be performed openly or arthroscopically. In this case, all remnants of cartilage covering the articular surfaces are removed, and the articular ends of the bones are fixed to each other with a plate and/or screws in order to create conditions for their fusion. The probability of forming a bone block created in this way with both methods reaches 80-90%, and the choice of a specific method of joint arthrodesis is determined by such factors as the severity of the deformity, the condition of the vessels and skin of the limb, and the quality of the bone tissue. The main disadvantage of ankle arthrodesis is the loss of dorsiflexion and plantarflexion. Most patients tolerate this quite well, but this in turn accelerates the development of degenerative changes in other joints of the foot, in particular in the subtalar joint. In order to ensure maximum mobility of the remaining joints of the foot after arthrodesis of the ankle joint, the latter is fixed in a special position.
Rice. Arthrodesis (closure) of the ankle joint.
Total ankle replacement . During this operation, the damaged articular surfaces of the tibia and talus are replaced with artificial components. This operation is ideal for elderly and senile patients with a normal body mass index, in advanced stages of osteoarthritis, minimally severe deformities, a satisfactory range of motion and good quality of soft tissue in the surgical area. Its effectiveness in relieving pain is similar to arthrodesis, and the advantage is maintaining mobility of the ankle joint and thereby reducing the load on the remaining joints of the foot. The main disadvantage of ankle replacement is that the artificial joint is a mechanical device and wears out over time, gradually leading to the need for replacement. The need for revision of the prosthesis due to its wear usually occurs earlier than the need for similar revisions after knee or hip replacement, however, according to modern research, the survival rate of ankle joint prostheses at 8-10 years after surgery reaches 85-90%.
Rice. Total ankle replacement.
Subtalar arthrodesis . Arthrodesis of the subtalar joint is the most effective treatment method and the method of choice in cases where conservative treatment of arthrosis of this joint is ineffective. The operation involves removing the articular cartilage and subchondral bone of the articular surfaces that form the subtalar joint and fixing them with staples or screws. If the shape of the articular surfaces does not allow for close contact between them, bone grafting is performed using auto- or allo-bone, which fills existing defects, thereby creating conditions for the formation of bone fusion. The principle inherent in arthrodesis of any joint (getting rid of pain at the cost of loss of movement) is also true for this operation. The scope of the operation can be expanded by simultaneous arthrodesis of the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints. This operation will be called “three-joint arthrodesis.” It is most often used to correct hindfoot deformities.
Rice. Subtalar arthrodesis.
Debridement and microfracture . This method is most often used to treat small (less than 1.5 cm in diameter) cartilage defects of the talus. Unstable fragments of cartilage are removed arthroscopically, and the bone base is processed and many holes (microfractures) are formed in it using an awl or drill to stimulate bleeding and the subsequent formation of a fibrin bundle. The fibrin bundle fills the defect and then transforms into fibrocartilage. The operation is effective in approximately 90% of cases of cartilage damage.
If the articular cartilage is not damaged, and the damage is located under it, it is possible to drill out the defect from the side of the bone, and not from the side of the articular surface, the latter remaining intact (the so-called “retrograde tunneling”).
Osteochondral transplantation (cartilage transplantation) . This is the replacement of the damaged articular surface with grafts consisting of bone and cartilage tissue.
Options for such transplantation are osteochondral auto- or allotransplantation (OCAT), as well as autochondrocyte implantation (ACI). Such operations are usually indicated in cases of ineffectiveness of previously performed debridement and microfracture, as well as in cases of significant osteochondral damage.
During OHAT, a cylindrical block consisting of cartilage and bone is taken from the condyle or trochlea of the femur and transplanted into a bone bed formed of the same shape in the area of the osteochondral defect.
IAC involves taking the patient’s own chondrocytes, culturing them in the laboratory, and then implanting the thus enlarged cell mass into the defect area and covering it with a patch of periosteum or collagen matrix.
Prevention of joint disease
Proper nutrition ensures health to all body systems. A sufficient amount of protein, calcium, iron and vitamins allows you to provide cartilage tissue, ligaments, synovial fluid and bones with everything they need.
In addition, an active lifestyle will keep your muscles toned, thanks to which they provide additional support to the entire skeleton in general, and joints in particular. And in order to protect yourself from dangerous viral infections that affect the joints, you need to be vaccinated in a timely manner.
Bursitis
This disease is often confused with arthritis, although with bursitis it is not the joint that is inflamed, but the joint capsule. Bursitis can cause discomfort, stiffness and pain in the joint area. Symptoms are associated with inflammation of the synovial membranes of the joint, usually caused by improper movement, compression or injury. Most often, bursitis develops in the shoulder, knee or hip joints. One type of bursitis, called maid's knee, develops due to prolonged pressure on the knee joint on a hard surface.
Vascular pain
Pain in the legs of vascular origin is most often associated with obliterating endarteritis, varicose veins of the lower extremities, and thrombophlebitis.
With endarteritis, pain occurs during exercise and goes away after rest or if the legs are lowered down. Approximately the same symptoms accompany atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, when the lumen of the vessels narrows and the tissues suffer from a lack of oxygen6.
Thrombophlebitis and varicose veins often accompany each other. Due to the weakness of the vascular wall, the veins expand, become deformed, and blood flow in them is disrupted. There is pain, a “humming” sensation, and heaviness in the legs. By the end of the day, the legs swell, but when you lift them up, it becomes easier7.
Thrombophlebitis is an acute dangerous condition in which pain in the leg occurs suddenly and has a bright, burning, pulsating character. At the site where the blood clot appears, a dense formation is felt inside the vein. The temperature may rise and the area of the leg may turn red. In this condition, you need to urgently contact an angiosurgeon8.