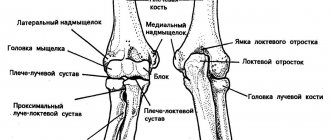
So, the proximal row is located on the side of the radial and ulnar hands. It includes 4 bones:
- The scaphoid is the first on the side of the thumb. Contacts the scaphoid and three of the second row. The flexor carpal tunnel is attached to it. This bone is more susceptible to fractures than others.
- The lunate is the second bone from the scaphoid. Above are the hamate and capitate bones. The lunate bone is often dislocated.
- Triangular - in contact with the lunate, but located slightly upward. Joins with the hamate bone from the upper row. The triquetrum bone forms part of the arch, within which lies the carpal tunnel. It rarely breaks.
- Pisiform - comes into contact only with the triquetral bone. Forms the border of the carpal tunnel on the side of the elbow.
The other row, the distal one, is located on the palm side and consists of the following bones:
- Trapezius - located above the scaphoid bone, under the thumb, so its ability to move depends on it. The trapezium connects to the triquetral and capitate bones.
- Trapezoid - located near the trapezium, responsible for the work of the index finger.
- Capitate - controls the work of the middle, partially ring finger. It comes into contact with the trapezium, scaphoid, lunate, and hamate bones. The capitate bone rarely breaks because it is located in the center of the wrist and is well protected.
- Hook-shaped - located under the little finger, ring finger. The bone is extreme, therefore prone to fractures, and does not heal well due to poor blood supply.
Why do my hands hurt in the folds of my wrists?
Many vessels, nerves (radial, ulnar, median), and their branches pass through the wrist. Joints ensure normal movement of bones relative to each other. Flexor muscles are responsible for mobility. When these structures become damaged, the hand hurts when you bend the wrist.
At risk are athletes (hand injuries are common in many sports, occur after a blow (volleyball, basketball), due to monotonous repetitive actions (tennis); people whose work involves monotonous hand movements (typing on a computer, embroidery, hair cutting); patients with diabetes, obesity, arthritis, gout; pregnant women (when a woman is pregnant, the volume of water in the body increases, the tissues swell and put pressure on the nerves of the wrist).
Injuries. The wrist of the left hand hurts when bent due to sprain, dislocation, fracture after falling on the hand. An acute pain appears, which subsequently dulls and becomes aching. After an injury, the hand cannot bend, the wrist hurts, swells, and a bruise appears. An x-ray will help determine why the wrist of your left or right hand hurts when bent. A sprain requires a bandage. The dislocation is reduced, the hand is fixed. If there is a fracture, the doctor will apply a plaster cast.
Occupational diseases. Any work involving repetitive movements in the wrist can cause microdamage and, as a result, inflammation of the tissues around the joints. The most common are Kienböck's disease, carpal tunnel syndrome, and stenosing tenosynovitis. A stress fracture is also possible if a person does the same movements for several hours in a row without a break.
Tunnel syndrome. The disease develops in people whose work involves monotonous movements of the hands (artists, musicians, office workers). Carpal tunnel syndrome can also be a consequence of arthrosis, diabetes, hormonal imbalances, and renal failure. Alcoholism, tumor, pregnancy (2nd trimester) can also contribute to the development of the disease in the presence of a traumatic factor. Carpal tunnel syndrome develops due to compression of the median nerve between bones, tendons, and carpal ligaments. Symptoms of the pathology are pain, numbness in the hands, it is difficult for the fingers to hold objects or fasten buttons.
Kienbeck's disease. Avascular necrosis occurs in workers engaged in heavy manual labor (carpenters, mechanics, hewers). The disease rarely affects both hands; usually the working limb is affected. The cause of the disease is compression of the lunate bone, which provoked a disruption of the blood supply with subsequent deformation of the articulation.
Crunching in the joints: stop worrying.
- Crunching is absolutely normal, there is no harm. But also benefits.
- “The ability to crack your knuckles may be related to joint health,” says study author Kauchak.
- Does not cause arthrosis. It is a popular belief that crunching is deliberately harmful and can cause various diseases of the musculoskeletal system (arthritis, osteoarthritis). A recent X-ray study of 215 people found that there was no difference in the risk of joint disease between people who crack their knuckles and those who don't. It also does not matter the frequency with which this manipulation is performed.
- Don't panic. If a crunch in a joint is not accompanied by pain, swelling, or fever, then there is definitely no reason to panic. If any of the above symptoms are present, you should consult a doctor.
- Shnobel. Dr. Donald Unger conducted his own experiment. He cracked the fingers of only one left hand every day for 60 years, after which no differences in the hands were detected. The scientist received the so-called Ig Nobel (not Nobel!) Prize for this work in 2009.
- Desire to crunch. If crunching causes discomfort, or the desire to crack a joint arises as a way to relieve discomfort in the joint, it is worth finding a specialist who can assess the functional state of the joints (usually an assessment of biomechanical chains is needed, not just one joint) and the muscles involved in their movement (orthopedist, doctor Exercise therapy, rehabilitation therapist, competent fitness trainer). A constant desire to stretch indicates numerous muscle spasms.
- Neurotic crunching of fingers. Another study found that the habit of cracking your knuckles may correlate with the presence of habits such as smoking, alcoholism or nail biting, i.e. be of a neurotic or stressful nature. This is also worth paying attention to.
Symptoms and causes of wrist pain
The main manifestations of the pathology are symptoms such as constant pain in the bend of the hand, which intensifies with load, as well as in the wrist of the left or right hand when bent back.
De Quervin's disease is known as trigger finger. Seamstresses, telephone operators, pianists, and laundresses who constantly wring out wet laundry often encounter this pathology. The cause is inflammation of the tendon bursa of the muscles that control the movements of the thumb. Stenosing tenosynovitis develops against the background of trauma, followed by the addition of a bacterial infection (staphylococci, streptococci).
The finger bends freely, but when straightened, discomfort occurs. It gets stuck, clicks, and sometimes takes a long time to straighten. The skin is often inflamed and the wrist hurts when touched. Scar tissue forms and can be felt as a dense swelling. The finger in a passive state does not hurt, but it “shoots” in the wrist when the hand is moved to the side and the fist is clenched.
If your right wrist hurts when you bend it, osteoarthritis may be the cause. The cartilage located at the junction of the bones is destroyed. Osteoarthritis is rare, mainly in people with a history of severe hand trauma. Most cases of osteoarthritis affect one limb.
Pain is common with rheumatoid arthritis. The immune system is experiencing disruptions. It mistakes healthy body cells for enemy agents and sends antibodies to destroy them. The disease affects the wrists of both hands.
Poor blood flow. Numbness and tingling are observed if a person lies on one limb for a long time, with the hand bent unsuccessfully. Due to unnatural compression of the blood vessels, blood did not flow to the palms, causing numbness and tingling. The situation quickly improves when a person removes the weight from the arm - blood flow is restored and the limb returns to normal. These symptoms can also warn of heart and vascular diseases. When the myocardium does not work well, it ejects blood poorly, and the plasma does not reach the fingers in the required quantity.
A similar picture is observed in atherosclerosis, when cholesterol plaques narrow the lumen of blood vessels, thrombosis of small veins and arteries. Nutrients and oxygen do not reach the palms, and cells begin to die. Tissue necrosis develops. This is a dangerous condition, see a doctor immediately.
Treatment of the wrist joint
As a rule, treatment of pain in the wrist joint consists of a whole range of procedures, including:
- massage;
- reflexology;
- kinesiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- dirt, etc.
In addition, complete protection of the affected joint by the patient himself is required.
The hand should absolutely not be overloaded. When working with heavy physical exertion, you need to protect the joint with special orthopedic devices, for example, wristbands.
These are only possible methods used to treat joint problems; only a doctor can prescribe the exact treatment!
How is the disease diagnosed and treated?
If the pain does not go away, you should seek medical help. The doctor will examine the patient, ask about symptoms, evaluate nerve conduction, and prescribe the following tests:
- X-rays, CT scans show the condition of the bones.
- MRI - detects pathologies in soft tissues.
- Arthroscopy - the doctor makes a small incision in the wrist through which a camera is inserted. The image is projected onto the screen, allowing the doctor to assess the condition of the tissues.
- Puncture - the fluid located inside the joint is examined (if osteoarthritis is suspected).
Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory and painkillers. Ointments and antiseptic solutions have a good effect. They penetrate the tissues, relieve inflammation and pain. Surgery may be necessary to eliminate tumors and growths.
Physical therapy will improve blood flow around the wrist, which promotes healing. Exercise therapy will help restore hand mobility during the recovery period.
In a word, take care of your wrist, do not load your hand, and if necessary, immobilize it with a splint or bandage. Change your occupation to an activity that does not require stress on your hand. If this is not possible, take a 10-minute break once an hour while working.
Why do my joints crack?
The reasons for this phenomenon have not been studied for certain and there is no clear answer as to why this phenomenon occurs. For those who are faced with this annoying disease, it is extremely important to understand what led to its appearance, since this is the only way to get rid of the problem. In addition, in the fight against a disease, nothing is more effective than prevention, which is also impossible without understanding the causes of the development of pathology.
Causes of crunching in joints
Modern medicine has proposed several options for the causes of crunching in the joints. Thus, the most popular version is considered to be the accumulation of gas in the liquid that surrounds the joint capsule. When moving, the liquid is compressed and gas bubbles burst, producing an unpleasant crunch. As a rule, in such cases there is no reason for concern, the mobility of the limbs is not limited and no pain occurs. Secondly, crunching in the joints may occur due to the development of serious diseases, including osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis. Inflammatory processes, disturbances in metabolic processes and the composition of bone tissue, or a decrease in the amount of synovial fluid also provoke the appearance of crunching and creaking. And finally, the cause of the crunch can be a banal injury, hypothermia, or the individual characteristics of the body.
What to do if you experience crunching in your joints
The first step to solving a joint problem should be a visit to a specialist, since self-diagnosis is even more dangerous than dubious treatment methods. Only a doctor will select the optimal treatment regimen and offer the safest complex of therapeutic exercises. However, in any case, it is recommended to normalize the diet, enriching it with protein foods rich in calcium and phosphorus, eliminating coffee and alcohol at least for the duration of treatment. In this case, be sure to take chondroprotectors - dietary supplements that restore joint strength, relieving inflammation and increasing the elasticity of ligaments.
It is also important to move more, not neglecting walking and exercises aimed at increasing joint mobility. Be sure to make it a rule to do gymnastics immediately upon waking up and warm up several times during the day. However, sports feats in the presence of crunching in the joints are not appropriate and all loads should be moderate. If pain occurs during exercise, you cannot refuse them at all; you just need to reduce activity and give the sore joints the opportunity to rest and recover. It makes sense to use fixing bandages and support bandages.
When should you see a doctor with wrist pain?
You should immediately consult a doctor if:
- your wrist hurts for more than two days;
- Wrist pain accompanies stiffness, swelling of the joint and/or abnormal shape of the hand;
- it is impossible to carry out normal physical work;
- after physical activity, the pain intensifies, there is a loss of sensitivity in any part of the arm;
- Wrist pain combined with shortness of breath or chest pain may be a symptom of a heart attack. In this case, urgent medical attention is needed!