Many people experience joint pain. But it always arises for a reason. Therefore, if you have pain in your joints or limited mobility, then you should not listen to others who claim that you simply slept in an uncomfortable position or the weather is changing and everything will soon go away on its own. Joints hurtDo you experience a crunch or limited movement when trying to bend or straighten a limb? Contact a specialist immediately. And we will help you decide which doctor you should make an appointment with.
groups of joint diseases
groups of joint diseases Joints belong to the structures of the musculoskeletal system of the human body. They have a rather complex structure, including connective tissue, bone tissue and cartilage. Due to the specificity of functional activity and structure, structures are often subject to the development of pathological processes. All diseases are conventionally divided into several main groups:
- Infectious processes affecting various tissues and leading to their inflammation (infectious arthritis).
- Autoimmune processes - a violation of the functional state of a person’s immunity is accompanied by the fact that immunocompetent cells “erroneously” produce antibodies to the body’s own tissues. As a result of the development of the pathological process, tissues of various structures of the musculoskeletal system are often affected with the development of long-term inflammation and damage.
- Degenerative-dystrophic conditions - age-related changes, inflammatory processes, regardless of their cause and origin, as well as post-traumatic conditions lead to disruption of the nutritional processes of structures, which primarily affects cartilage tissue. As a result, lesions gradually form, which then lead to an inflammatory response.
- Suffered injuries that cause mechanical damage and changes in the anatomical relationship of various structures.
Each group of diseases has its own specialization and a doctor specializing in joints.
What specialists treat?
The doctor responsible for the joints, as well as the diagnosis and appropriate treatment of pathological conditions, includes several specialties:
- An orthopedist is a specialist who diagnoses and treats inflammatory pathology of the structures of the musculoskeletal system, which is of infectious or aseptic (reactive arthritis) origin, as well as degenerative conditions (arthrosis). In large medical clinics, narrower specializations of orthopedists are separately distinguished; in particular, there is a doctor who treats knee joints, elbows, and small structures of the hands and feet. Typically, a narrow division into specializations is due to the fact that inflammatory processes in large and small structures develop differently and require certain therapeutic approaches.
- Rheumatologist is a specialty that often includes a doctor who specializes in knee joints. This is due to the fact that the development of autoimmune pathology is usually associated with symmetrical damage to large joints.
- Traumatologist is a separate specialization, which is a type of orthopedics; a joint doctor diagnoses and treats various acute or chronic post-traumatic conditions.
The identification of narrow specializations is important, since for each group of diseases or pathological conditions a treatment is determined that has fundamental differences.
A little about drug blockades
There is a period when basic therapy for the disease is most effective. It is called the “therapeutic window”. With arthritis, for example, it lasts about three months. The inflammatory process is in the primary phase. Sometimes at this stage it is enough to make one blockade and the pain syndrome will disappear forever.
Unfortunately, there is a strong opinion that the body gets used to drug blockades. There are doctors who convey a biased attitude towards this treatment method. The argument is that once you get used to it, the medications won't help anymore. Guided by this opinion, many people who have shoulder or knee pain refuse joint therapy at the initial stage and miss a very important period. The disease is progressing.
In fact, a timely and correctly performed blockade gives positive results. The technique is successfully used in Europe and Israel, and you should not be afraid of it if you trust your specialist. But only a few people trust it, because there are not many specialists in joint diseases.
In what cases should you consult a rheumatologist? We present the TOP 10 reasons in the video below:
Manifestations of pathology
The main manifestation of the pathology is pain. It can be localized in large or small structures. If large joints (knees) hurt, the doctor may suspect the development of arthrosis or rheumatism. The doctor regards damage to small (inflammation) joints as rheumatoid arthritis.
Infectious pathology is often accompanied by a deterioration in the patient’s general condition with the development of intoxication of the body. The injuries suffered are characterized by acute symptoms with intense pain and dysfunction of the damaged structure. Since the manifestations can be different, the doctor determines joint diseases using additional objective research methods.
Joint doctor
Joint doctor
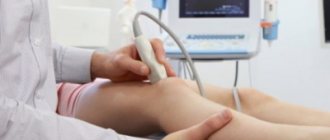
A doctor who deals with joints, namely inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic pathologies, is an orthopedist. He conducts consultations in specialized outpatient or inpatient medical institutions of various forms of ownership. To reliably determine the cause of the disease, the nature of the pathological changes, as well as the degree of their severity, he prescribes an objective examination, which usually includes various imaging techniques (ultrasound, tomography, arthroscopy).
Routine laboratory tests are required. After the diagnosis, the orthopedist prescribes appropriate treatment, which may include the use of medications or surgery. If necessary, during diagnosis and therapy, the orthopedist can prescribe a consultation with doctors of other specialties, in particular an infectious disease specialist, a dermatovenerologist, and a phthisiatrician. This is due to the fact that a significant number of arthritis can be the result of the development of specific infections (tertiary syphilis, tuberculosis, brucellosis). Very often, a doctor treating the joints of the knees, other structures of the legs and spine is faced with degenerative-dystrophic pathology.
Therapist
A therapist is also called one who treats diseases in the early stages of pathogenesis. As a rule, this specialist is well versed in all diseases. He knows a large number of symptoms and signs of a particular pathology, so this doctor should be at the top of the list of doctors to whom you should contact with osteoporosis. After contacting a therapist, the patient will have to collect an anamnesis (medical history, symptoms and complaints), undergo laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostics.
The therapist prescribes an MRI of the spine to examine the bone structures in several projections. This technique allows you to examine the bone, joint and soft tissues of the back.
Rheumatologist
A doctor who specializes in joints and the heart is called a rheumatologist. The peculiarity of the specialization is that the specialist deals with a wide group of pathological processes, the development mechanism of which is associated with a violation of the functional state of the immune system, they are called rheumatoid diseases.
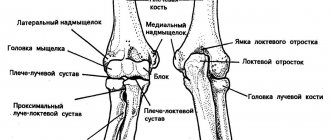
Typically, the triggering factor is a previous streptococcal infection, prolonged systematic exposure to the sun, the use of certain medications, as well as a genetic hereditary predisposition. In this case, immunocompetent cells produce antibodies to the body’s own tissues. Rheumatoid diseases occur with primary damage to the connective tissue of the structures of the heart and joints. The inflammatory process often develops symmetrically in large joints, so a specialist is also defined as a doctor for elbow joints and knees.
Diagnosis of the pathological process is carried out using modern imaging techniques, ECG (electrocardiogram), as well as laboratory tests to identify rheumatoid factors. Treatment of autoimmune pathology affecting the structures of the musculoskeletal system is predominantly conservative. It involves long-term (sometimes lifelong) use of hormonal anti-inflammatory medications.
Treatment methods and follow-up features
Treatment depends on the diagnosis. Orthopedic treatment options include, for example, limb immobilization, surgery, pharmacological treatment, as well as rehabilitation and physical therapy.
Physiotherapeutic procedures can be represented by an extensive list of techniques. Among them:
- Electrophoresis . The procedure is based on the use of weak electrical currents and injections of drugs into the affected area. The procedure allows you to enhance the effectiveness of pharmacotherapy by delivering medications to the diseased area, relieves swelling and pain, and improves metabolic processes.
- Medical massage . Relieves pain, helps accelerate regeneration processes and quickly alleviate symptoms.
- Exercise therapy . Helps restore joint mobility, promotes the formation of a strong muscle corset.
- Phonophoresis . The method involves delivering medications directly to the affected area. The procedure is non-invasive; pharmacological agents are introduced under the skin using ultrasound.
- Manual therapy . It has a powerful therapeutic effect, especially relevant for restoring the correct position of intervertebral discs.
Further observation in the case of chronic diseases should be continuous. The patient will be recommended moderate physical activity, proper nutrition while maintaining a normal weight, healthy sleep and rest patterns, etc. As with the treatment of other diseases, a comprehensive approach is critical.
Traumatologist
A joint and ligament doctor who diagnoses and treats injuries is called a traumatologist. He represents a narrower orthopedic specialization, therefore, if necessary (mainly in small medical clinics), he can deal with the problems of inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic pathology of the structures of the musculoskeletal system, with the exception of autoimmune rheumatoid diseases.
A specialized medical specialist treats injuries suffered on an outpatient basis or in a trauma hospital. Also, most public and private medical institutions have trauma centers where medical specialists provide urgent care. They work around the clock without holidays or weekends. In a trauma center, a primary diagnosis of the cause and nature of the injury is carried out using radiography, and first aid is provided.
In case of fractures or dislocations, it includes repositioning of fragments or reduction followed by immobilization (immobilization) of the limb. In case of severe injury requiring surgical treatment, the victim is hospitalized in a hospital.
Correct diagnosis
To determine the type of arthritis and arthrosis and which doctor treats this type of disease, you need to do a series of studies and collect anamnesis. The blood is checked for erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and the number of leukocytes and eosinophils is calculated. Based on the results, the doctor will understand whether a bacterial infection or allergy is present. For gout, a biochemical blood test is done. Checking immunological parameters will show the presence of rheumatoid arthritis.
X-ray examination will help determine joint degeneration and the stage of the disease. Ultrasound and computed tomography will show joints, especially large ones, in several positions, which will determine the condition of bone and muscle tissue. MRI is used in rare cases of spinal disc and ligament damage.
If necessary, arthroscopy is performed, taking a biopsy of tissue and fluid from the joint (usually the knee).
Joint doctor
Joint doctor
A joint doctor in Moscow conducts consultations in a specialized medical institution of state or private ownership. An orthopedist and traumatologist can diagnose and treat the corresponding pathology in a clinic and in the orthopedic and trauma department of a medical hospital.
The clinic usually sees outpatients with diseases or injuries that do not require hospitalization. The department treats severe pathologies that require constant medical supervision.
A medical specialist rheumatologist usually conducts consultations in large clinics. He also provides consulting assistance to doctors of other specializations. Patients with severe autoimmune rheumatic pathology are often treated in a cardiology or orthopedic hospital, but the attending physician is a knee and elbow doctor from the clinic.
Types of pain
The type and nature of pain depends on the cause that caused it.
Joints ache with the flu and acute respiratory infections against a background of high (up to 40 ⁰C) temperature. This pain goes away on its own as soon as the temperature returns to normal and does not require special treatment.
Arthritis pain:
- spicy,
- painful,
- pulsating,
- shooting,
- occurs at rest and intensifies when performing certain movements,
- sending out to neighboring areas,
- when palpated, it hurts everywhere, over the entire surface of the joint, but especially along the joint space.
Periarthritis is especially unbearable - inflammation of the tissues around the joint (its bursa, tendons and ligaments). How everything happens can be explained using the example of the shoulder joint (Fig. 2). First the joint begins to ache. The pain very quickly becomes excruciating, almost unbearable. It radiates to the shoulder blade and neck area, intensifies (and is often accompanied by a crunching sound) when trying to stretch your arms to the sides at shoulder level or bend them at the elbow and place them behind your back. There are pain points at the end of the collarbone, which rests on the shoulder joint in front, and in the same place at the back. When you press on them with your finger, the pain intensifies. With such acute sensations, the joint requires immobilization - you need to hang your hand on a scarf, try not to move it. This is an important condition for the success of treatment.
Figure 2. Humeroscapular periarthritis. Inflammation of the soft tissue around the joint causes severe pain, often causing disability. The prevalence of the disease is high and amounts to about 4-7% in the population. Photo: CC0 Public Domain
Important! quickly select adequate pain relief and anti-inflammatory therapy after the examination. This will reduce the severity of joint inflammation, reduce pain and improve the quality of life.
With arthrosis, joint pain is different:
- At first, the pain is not severe and intermittent, its character is wave-like - at certain periods it does not exist for weeks or even months. But over time, without treatment, the waves of pain become more severe and come more often, and the intervals between them become shorter.
- Pain at the start: it explodes during the first attempt to take a step, raise an arm, or bend over. Then the joints seem to develop, and the pain goes away.
- Mechanical rhythm - the joint begins to hurt when you load it. First, the pain appears during high loads - lifting heavy objects, running up the stairs, long walking, playing sports. Later, even minor movements echo with pain. But at the same time, unlike the discomfort of arthritis, the pain of arthrosis goes away when you give the joint a rest and provide it with peace. That's why doctors talk about a mechanical rhythm: movement provokes pain, and rest relieves it.
- Night discomfort. There is no pain at rest as such, but lying down is uncomfortable, I always want to change my position, to find a position in which I could forget about the joints and spine, but I can’t. My joints ache, that's all!
- The shackles of the morning: you woke up, there is no pain yet, but it’s as if you were shackled with a chain or tightly swaddled - your joints don’t obey, but little by little the feeling of stiffness goes away, the range of motion in the joint is restored.
- Protective posture. When a joint hurts, you want to take the so-called antalgic - anti-pain pose, in which it becomes easier. This is best seen in the example of the spine: it also consists of joints. When one of them jams, and along with it a nerve root gets caught in a bone vice, acute pain occurs due to radiculitis. Anyone suffering from radiculitis can be diagnosed by anyone who sees how the poor thing is twisted. In fact, with the help of this “distortion”, supported by muscle spasm, the body tries to reduce pain to a minimum.
Arthrosis of the hip and knee
Pain when the hip joint is affected (and it most often affects one side) is localized in the upper part of the thigh and radiates to the knee. He usually starts getting sick in the afternoon, when he has already worked quite a lot. The pain intensifies when walking, and at rest weakens and disappears.
Most often, both knee joints are affected at once. They bend easily, but begin to hurt when bent. Damage to the knees is characterized by the so-called staircase symptom. It becomes more painful to go down than to go up; patients do this by turning sideways. Sometimes a joint becomes jammed in a half-bent position due to a bone outgrowth (osteophyte) or its fragment (such a bone fragment “lost” inside the joint is called an “articular mouse”). Blockage of the joint is accompanied by increased pain when trying to bend or straighten it.
Knee mobility problems are not always due to arthritis. Sometimes joint jamming can be “false”. Some of the most common causes of knee pseudolock include:
- Swelling (excess fluid in the joint capsule can prevent full flexion and extension of the joint),
- Inflammation (inflammation of tissue in the knee, such as in rheumatoid arthritis and gout),
- Incorrect movement of the kneecap in the joint (accompanied by severe pain),
- Irritation of the tissue lining the joint
- Knee injury (any serious injury to the knee, such as a sprain, can cause muscle spasm).
Important! If the joint is jammed and active movements in the joint are impossible, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible from an orthopedic traumatologist - to an emergency room, hospital clinic. Do not hesitate to call an ambulance - this is a good reason to call it, because you won’t get far on one leg and you may not even get to the clinic yourself.
How to sign up?
A doctor who treats joints is a specialized medical specialist, so making an appointment differs depending on the type of ownership of the medical institution, as well as its specialization. To get an appointment with an orthopedist or rheumatologist for planned treatment, you need a referral from a general medical specialist (general practitioner, pediatrician, family doctor). In advance, he prescribes routine tests (clinical blood tests, urine tests), which saves time for a highly specialized specialist.
In a private healthcare setting, booking an appointment is easier and does not require a referral from a GP. Typically, a patient makes an appointment by contacting the clinic directly, by calling or filling out a special form on the official website. In an urgent situation, in particular by specialists from the trauma room, medical care is provided without an appointment.
Causes of arthritis
The causes of arthritis can be allergies, diseases of the nervous system, tuberculosis, gout, disruptions in the endocrine system, hormonal changes in the female body during menopause, lack of vitamins, alcohol and drug addiction. Arthritis can result from a simple bite of a poisonous insect into the joint cavity.
By analyzing all this, a specialist treats arthritis. Tests and studies will show which doctor the patient needs first. Therefore, it is impossible to answer this question unequivocally.
When choosing which doctor will treat the disease for arthritis, you need to correctly determine the cause of the disease and refer, in addition to the surgeon and orthopedist, to other necessary specialists.