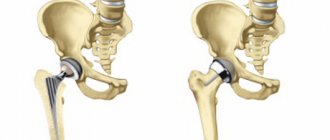
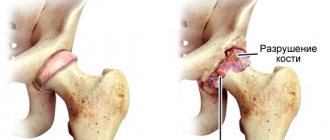
If you have a need for endoprosthetics (replacement) of a joint with an artificial one, then in Germany you will find the best specialists in endoprosthetics and get the most optimal result, which will improve your quality of life for a long time. For those wishing to undergo joint endoprosthetics (replacement), we offer our recommendations - clinics and endoprosthetics centers that operate at a high professional level and use the highest quality prostheses and materials.
The experience of the specialists presented here in the field of endoprosthetics is the richest in this field of medicine in Europe, because It was in Germany that endoprosthetics (replacement) of joints became widespread and has been constantly improved over the past 30 years.
If YOU doubt whether joint endoprosthetics (replacement) is really indicated for you, then you have the opportunity to get a paid second opinion. To do this, you can contact our consultants:
Call us today! or use it - we will call you back immediately.
+49 152 056 612 47 (phone and Whatsapp in Russian)
Leading orthopedic clinics and doctors
Endoprosthetics in Germany - estimated prices
| Orthopedic consultation and diagnosis | from € 300 |
| (order service) | from € 250 |
| Total hip replacement, replacement with an artificial hip joint | from € 10.700 |
| Surface replacement of the hip joint using the McMinn method | from € 11.500 |
| Revision hip replacement | from € 9.000 |
| Endoprosthetics (replacement) of the knee joint (partial or complete) | from € 10.500 |
| Endoprosthetics (replacement) of the elbow joint | from € 9.700 |
| Endoprosthetics (replacement) of the shoulder joint | from € 12.300 |
| Carrying out rehabilitation in rehab. clinic | from 180 €/day |
Call us today! or use it - we will call you back immediately.
+49 152 056 612 47 (phone and Whatsapp in Russian)
Types of prostheses
Depending on the degree of development of arthrosis, different types of prostheses are used. The standard is a total endoprosthesis that completely covers both articular surfaces, femoral and tibial. However, if arthrosis of the knee joint affects only a certain limited area, implantation of a partial prosthesis is possible.
Partial
In this case, we are talking about a unicondylar unilateral sliding prosthesis , with the help of which only one of the two condyles of the femur is changed. By replacing one section of the knee, they allow the majority of the joint to be preserved with limited damage to the cartilage. In partial knee replacements, as in total knee replacements, the femur component is made of metal. It is placed in such a way that it covers only one part of the femur. A metal part is placed on the side of the tibia, on which a polyethylene liner is located. The metal part slides along the liner like the runners of a sled.
Total:
- double-sided sliding prosthesis;
- prosthesis with axial stabilization.
The most commonly installed is a bilateral surface sliding prosthesis . In this case, all parts of the knee are replaced: the surfaces of the femur, the tibia, and sometimes the back of the kneecap. When installing such a prosthesis, the connecting ligaments of the knee are preserved.
If, in addition to cartilage and bone, the ligamentous apparatus of the joint is damaged, the only possibility of prosthetics is a prosthesis with axial stabilization , the so-called pedicled prosthesis. It fixes the joint along the longitudinal axis, which prevents lateral displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur. In this case, the interconnected parts of the prosthesis work like a hinge.
Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Dominicus Clinic, Berlin
Dr. honey. Sciences D. Flashmeyer Official website in Russian
In our department, patients with acute injuries and complications after injuries of all degrees of severity, as well as with orthopedic and traumatic diseases of the musculoskeletal system acquired as a result of sports, are treated according to modern standards and operated on using minimally invasive methods.
Special tasks of surgery are endoprosthetics (installation and replacement of hip, knee and shoulder prostheses), foot surgery, sports traumatology and orthopedics (arthroscopy, treatment of cartilage tissue), as well as spine and hand surgery.
In addition, our head of the department, MD. Dirk Flaschmeyer is a specialist in rheumatology. After clinical and imaging diagnostics (X-ray, CT, MRI), we offer you therapy that is optimally suited to your needs.
Medical services provided by our department:
- Hip replacement
- Knee replacement
- Knee ligament injuries
- Knee cartilage damage
In our state-of-the-art operating theatre, our experienced and motivated team can operate on you to the latest quality standards. For post-operative care as well as conservative treatment, our patients are supported by a team of highly educated and proactive patient care specialists and physical therapists.
Nearest airport: Berlin
Rehabilitation and life with a knee replacement
Already on the first day after surgery, they begin to carefully perform passive movements of the joint using an electric splint. On the second day, intensive physical therapy is included: the patient is taught to move with the help of crutches. On days 4-5, it is possible to walk up the stairs and be discharged home. Upon completion of inpatient treatment at the Nordwest Clinic, three to four weeks of rehabilitation follow, either on an outpatient basis or in a rehabilitation clinic.
Duration of the knee prosthesis
Modern knee replacements last 15–25 years.
The duration of use of the prosthesis depends on:
- Patient weight The lower the weight, the longer the prosthesis lasts.
- Activities The more physical activity the patient experiences, the greater the risk of wear and loosening of the prosthesis. Sports that place the least amount of stress on the knee joint, such as swimming or cycling, are ideal.
- Quality of the patient's bones The higher the bone density, the more firmly the prosthesis is attached. In patients with osteoporosis, the prosthesis lasts less than in patients with high bone density.
How can you increase the service life of a knee replacement?
- Perform gymnastic exercises after completing the rehabilitation period to prevent the development of joint stiffness.
- Wear flat shoes with soft insoles.
- If purulent infections occur (and in other parts of the body), draw the attention of a doctor to the presence of a prosthesis and take prescribed antibiotics.
- Avoid bending the joint more than 90 degrees.
- Do not lift or carry heavy objects.
- Avoid heavy physical work.
- Prefer sports that place the least stress on your knee joints, such as swimming, gymnastics or cycling.
- Avoid contact and traumatic sports such as football, tennis, running or horseback riding.
Traumatology and orthopedics in Berlin-Steglitz
Professor, dr. med. Dr. Wolfgang Ertel Read more
The Charité Clinic for Emergency and Reconstructive Surgery has a modern rescue station, where life-saving measures are carried out daily for seriously injured patients (polytrauma).
As a certified trauma center, the emergency clinic in Berlin's Steglitz district works closely with the Berlin rescue services. The Rescue Center offers a state-of-the-art emergency department, including a blood bank, ultrasound and X-ray equipment, and an integrated 80-line CT scanner.
Additionally included:
- 16 examination halls
- 3 operating rooms
- 8 monitoring stations
- 1 reception room with 10 beds
At the Traumatology and Orthopedics Clinic, a team of trauma surgeons and orthopedists, in collaboration with the departments of anesthesiology, cardiology, neurosurgery and thoracic, vascular and abdominal surgery, treat and save patients seriously injured in accidents and accidents: a team of expert traumatologists works around the clock to eliminate the consequences of the accident case and reconstructive surgery for the survival of the most seriously injured. This would not be possible without a highly qualified dedicated team - meet the team led by Prof. Dr. med. Sciences Mr. Ertel.
In addition to polytrauma care, the Department of Traumatology and Reconstructive Surgery in Berlin-Steglitz specializes in surgical interventions in the following medical areas:
- Spine surgery
- Endoprosthetics and joint surgery
- Hand surgery
As part of the renowned Charité University Hospital in Berlin, the department's orthopedic surgeons, under the leadership of Prof. Errtel, attach great importance to the continuous improvement of medical education. For example, the Department of Traumatology and Reconstructive Surgery trains future specialists in the field of orthopedics and traumatology.
Demographic changes not only lead to socioeconomic changes, but also have a significant impact on patient care. Therefore this change must be taken into account. In Germany, on average, about 300 hip replacements are implanted per 100,000 inhabitants.
This is why the Clinic for Traumatology and Reconstructive Surgery at the Charité Berlin-Steglitz is increasingly specialized in joint replacement and surgery, and the clinic team - doctors, nurses and physiotherapists - is aware of the particular importance of joints.
Main activities:
- Endorhesis: primary endoprosthetics for degenerative and post-traumatic arthrosis
- Revision endoprosthesis: surgery to replace prostheses or prosthetic components in the event of infection, fracture or loosening
- cartilage damage
- with pronounced signs of wear (arthrosis)
- weakening
Nearest airport: Berlin
Components of a knee replacement
At the Nordwest clinic, during a prosthetic operation, depending on the task at hand, various elements are used, which make it possible to replace partially or completely worn-out areas of natural tissue of cartilage or bone.
- Femoral component Consists of metal, covers the lower end of the femur and must strictly follow the paired cylindrical shape of the end of the femur (condyles).
- Tibial component Covers the head of the tibia, on which the femur slides at the knee joint. The cruciate ligaments and menisci stabilize and support the knee joint. The tibial component is also usually made of metal. To form a sliding pair with the metal femoral component, it is covered with an elastic, resistant layer of polyethylene.
- Artificial kneecaps are used quite rarely. If the back side of the kneecap is damaged by arthrosis, an artificial plate made of polyethylene is used to replace the worn back side of the kneecap.
All components are built in such a way that the metal surface slides over the plastic surface. This makes the artificial joint durable and prevents it from quickly wearing out.
HKF Orthopedic Center, Heidelberg
Professor, Dr. honey. Dr. Fritz Thorey Official website in Russian
The HKF Orthopedic Center is a specialized clinic for the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Up to 3,500 orthopedic operations are performed annually within the walls of this institution. The impeccable performance of the services of the clinic's orthopedics department is monitored by its head, Professor and Doctor of Medical Sciences Fritz Torey, who is a recognized specialist in the field of implantation of artificial joints and has more than 20 years of experience in the field of orthopedics. The FOCUS magazine published a list of doctors in which Professor Dr. Fritz Torey, MD, is recommended as one of the best orthopedists.
The main areas of work of the HKF Orthopedic Center are reconstruction and replacement of the knee joint.
The clinic provides the following types of surgical treatment in such areas of medicine as orthopedics in Germany:
- Knee joint: orthopedics in Germany specializes in knee joint prosthetics (resurfacing with or without preservation of the cruciate ligament, etc.), correction of the position of the knee joint;
Nearest airport: Frankfurt
Material for the manufacture of endoprostheses
The material from which the artificial joint is made plays an important role in the manufacture of prostheses. The quality of the material affects the service life of the endoprosthesis, the quality of performance of the replaced functions, the survival rate of the endorosis and the physical capabilities of the patient when returning to normal life after surgery. Artificial joints are made from:
- metal-polyethylene;
- ceramics-polyethylene;
- completely made of metal;
- entirely made of ceramics.
During human life, parts of the articular surfaces constantly rub against each other. Joints made from the above materials have a limited service life. In addition, during friction, metal particles are formed, which spread into the surrounding tissues, which leads to bone metallosis. It should be noted that due to the use of modern alloys for the manufacture of prostheses, cases of metallosis are extremely rare. However, in German clinics, to eliminate this problem, Dacron is used as a shell for endoprostheses. Prostheses made in this way last longer, and the metallosis process is minimized.
Orthopedic Clinic Markgröningen
Professor, dr. med. Sciences B. Fink
The Orthopedic Clinic Markgröningen (abbreviated as OKM) is a very modern and interregional center for orthopedics and endoprosthetics, with a full range of all areas of treatment of orthopedic diseases. With a total of more than 10,000 operations per year, the OCM Orthopedic Clinic is the largest in the south of Germany and is further on the path to expansion.
This clinic is certified as an endoprosthetics center with maximum operational support (German: Endoprothetikzentrum der Maximalversorgung).
This endoprosthetics center is also known for its revision prosthetics operations.
The medical director, Prof. Dr. med. Bernd Fink, of the endoprosthetics center at the Markgröningen Orthopedic Clinic is also the president of the association of endoprosthetics specialists; with his participation and under his leadership, more than 1,700 endoprosthetics operations are performed annually at the OKM Clinic.
Implantation of artificial joints in the OCM clinic is carried out using minimally invasive, gentle surgical methods. With such methods, soft tissues are preserved without damage, thus the recovery period after endoprosthetics becomes as short as possible.
The endoprosthetics center of the OKM clinic has gained international fame thanks to its success in complex and revision endoprosthetics. There are more than 500 such operations per year, with this being the largest number in the states of Baden-Württemberg.
Nearest airport: Stuttgart
Surgery to install a knee prosthesis
Only one skin incision is made to expose the knee joint. The surgeon then removes the damaged cartilage and bone tissue. Important ligaments of the joint are preserved, and the knee after implantation has the necessary stability and mobility. The surfaces of the femur and tibia are replaced with maximum bone preservation.
Next, special clamps are installed to check mobility and determine the size of the prosthesis. Finally, the implant can be fixed in the bones of the femur and lower leg.
In all cases, doctors try to preserve the existing knee joint and ligaments as much as possible, most often preserving the internal and external ligaments, as well as the posterior cruciate ligament.
The anterior cruciate ligament must be removed when installing a total knee prosthesis due to its geometric structure and the method of its installation. However, a knee replacement replaces her function. When installing a partial denture, the anterior cruciate ligament is not removed and thus the natural movement of the knee is maintained.
Clinic of Orthopedics and Surgery at the University Hospital Bonn
Professor, dr. med. Sciences D. K. Wirtz
Professor Dr. med. Dr. Kristan Wirtz is a recognized and widely known expert in orthopedics, emergency otropedic surgery and endoprosthetics. He has vast unique experience in practical and scientific activities with more than 20 years of experience. Every year, under the leadership of Professor Wirtz, more than 5,000 operations on various joints are performed at the Clinic of Orthopedics and Endoprosthetics at the University Center Bonn.
Nearest airport: Cologne/Bonn, Frankfurt, Dusseldorf
Causes and symptoms of joint disease
The causes of diseases are mainly age; these diseases are very common in older people; 70% of pensioners develop arthrosis. Other causes include overloading the legs or improper or uneven load, and arthrosis also develops due to lack of treatment for damage to the meniscus or cruciate ligament.
The first symptoms of the disease are pain during exercise or when climbing stairs, and shooting pains may also appear when squatting. The more the pain intensifies, the more the disease progresses.
Clinic CIM (Center for Integrative Medicine)
Dr. honey. Science Dirk Laue Read more
Dr. honey. Dirk Markus Laue is a specialist of the highest category in orthopedics and traumatology. Specialization: orthopedic surgery, endoprosthetics, sports medicine, physical therapy, osteopathy. Practical experience since 1994.
The endoprosthesis center of the CIM Clinic (Center for Integrative Medicine) covers a wide range of conservative and surgical treatment methods in the field of orthopedics and trauma surgery. The endoprosthetics center has two highly modern operating rooms at its disposal.
The priority area of work of the endoprosthetics center: knee and hip joint replacement, arthroscopic operations on the knee, ankle, shoulder and wrist joint. Thanks to numerous successful joint replacement operations, the Endoprosthesis Center of the SIM Clinic also enjoys well-deserved fame among foreign patients.
Nearest airport: Frankfurt
How is joint replacement surgery performed?
The endoprosthetics operation begins with a consultation of the patient with an orthopedic doctor, during which an anamnesis is collected and the necessary tests are prescribed. After the completed procedures, the type of prosthesis, its size and shape are selected. Advantage in choice is given to those types of endoprostheses that can subsequently provide patients with a return to a full life.
Joint replacement surgeries are usually performed using minimally invasive surgery.
After the examination, a preparation process takes place, during which the patient is examined by an anesthesiologist and the method of anesthesia is determined. The type of anesthesia is determined based on the type of joint to be replaced. After all the preparatory procedures, which last a couple of days, the patient is sent to the operating table. Surgery takes from one to three hours.
During the intervention, the diseased, destroyed joint is removed and replaced with a new endoprosthesis.
Joint replacement in Germany belongs to the category of complex high-tech operations. The developed algorithm of actions is mandatory for strict compliance by both the doctor and the patient at all stages of endoprosthetics without exception: starting with preoperative monitoring of the patient’s condition and the diseased joint, including the selection of an adequate type of individual endoprosthesis and ending with scrupulous compliance with the instructions after the intervention.
Endoprosthetics Center of the Bonn United Hospital
Dr. honey. Dr. Holger Haas Read more
Dr. med. Holger Haas is a specialist in orthopedics, endoprosthetics and accident surgery with 20 years of experience. The specialists working under his supervision offer medical care of a high level of quality.
The Center for Orthopedics and Endoprosthetics of the Bonn United Hospital is one of the largest institutions in Germany in this field of medicine: the department has 145 beds for patients. The Bonn Joint Hospital has 40 years of experience in performing endoprosthetics and is considered one of the founders of modern orthopedic surgery in Germany. About 1,500 joint surgeries are performed at the center every year. Directions of the clinic: endoprosthetics of the hip, knee, ankle and shoulder joints based on minimally invasive, gentle surgical techniques and interdisciplinary work.
Nearest airport: Cologne/Bonn, Frankfurt, Dusseldorf
Types of endoprostheses depending on the method of fixation
There are:
- Cementless endoprostheses, the fixation of which does not require the use of bone cement. All parts of the endoprosthesis are in close contact with the bone. The surfaces of the prosthesis are treated with a special coating, which ensures that the prosthesis grows into the bone, that is, the process of osseointegration occurs. In this case, native human tissue acts as a fixative. This design is more stable and durable.
- Cemented endoprostheses are fixed using bone cement. They are less popular in Germany. However, in some cases there is no alternative to their use. Thus, for older patients who have slow regeneration processes, which are necessary for the installation of cementless prostheses, cement prostheses are installed. Hybrid endoprostheses combine the two above methods. When installing them, one part of the new joint is secured with bone cement, the other with a cementless method.
Endoprosthetics Center of the Eduardus Clinic
Dr. honey. Dr. Jochem Schunk Read more
The endoprosthesis center of the Eduardus Clinic in Cologne, with its experienced specialists and innovative medical equipment, has gained an excellent reputation far beyond the country and provides a full range of services: joint treatment, knee and hip replacement, patella joint prosthesis, shoulder and ankle joint replacement.
The head physician of the department is Doctor of Medical Sciences Jochem Schunk, a specialist in endoprosthetics, orthopedics and traumatology. Under his strict leadership, more than 1,500 joint replacement surgeries are performed annually at the Endoprosthetics Center. The sufficient experience of our surgeons and high surgical results are appreciated by both German and foreign patients.
Nearest airport: Cologne/Bonn, Frankfurt, Dusseldorf
Endoprosthesis clinics in Germany
In Germany there are over 500 clinics where endoprosthetics operations are performed. Almost all clinics are certified as Endoprosthetics Centers (EndoProthetikZentrum) or Maximum Endoprosthetics Centers (EndoProthetikZentrum der maximalversorgung). Below is a list of the most mentioned in open sources.
Knee replacement in the Czech Republic: guarantees, prices, rehabilitation, reviews and statistics.
Find out more
Minimally invasive endoprosthetics in the Czech Republic: doctors, rehabilitation, terms and prices.
Find out more
Orthopedic clinic Gelenk-Klinik in Gundelfingen
Gelenk-Klinik.
Address: Gundelfingen, Alte Bundesstrasse 29
Website: https://ortoped-klinik.com
Tel. +49-761 55 77 58 309
Specialized orthopedic clinic operating in Germany since 1992. More than 20,000 patients are treated here annually and almost 2,500 operations are performed. The clinic has a rehabilitation department.
Peter Baum.
The founder of the Gelenk Clinic and leading orthopedic surgeon is Dr. Peter Baum. Under his leadership, endoprosthetics is performed by:
- Thomas Schneider;
- Sven Ostermeier;
- Martin Rinio;
- Bastian Marcas;
- Angelika Kruschke.
The clinic staff is fluent in English, and a translator is provided for Russian-speaking patients. The clinic provides comprehensive support to foreign patients, including assistance with visa applications.
Bethel Hospital in Berlin
Bethel Hospital.
Address: Berlin, Promenadenstraße 3-5
Website: https://www.bethelnet.de
Tel. +49 030-7791-23 21
Rüdiger Haase (right).
The hospital's endoprosthetics center performs all types of knee and hip replacement surgeries. The head of the center and leading orthopedic surgeon is Dr. med. Rüdiger Haase. Other doctors also perform operations: Uwe Cha, Carsten Höptner. The early rehabilitation of patients is carried out by a group of specialists: Karin Wald, Annette Becker, Cordula Hergesell-Kegel, Stephanie Ullmann. For questions about rehabilitation, call tel. +49 030/77 97 – 91 99.
Havelklinik
Havelklinik.
Address: Berlin, Gatower Straße 191
Website: https://www.havelklinik.de
Tel. +49 030 36 206-0
Havelklinik is one of the largest surgical clinics in Germany, which has been providing care to people for more than 45 years. According to sociological studies, Havelklinik has very high patient satisfaction rates.
Havelklinik
Havelklinik provides endoprosthetics to:
- Andreas Pingsmann - Head of the Endoprosthetics Center;
- Alexander Friedebold;
- Olaf Neubert;
- Andreas Pingsmann;
- Oliver Rehm;
- Cyrus Sarem.
Havelklinik has 91 beds for surgical and traumatology patients, and 350 joint replacement surgeries are performed here per year.
Diakonie Hospital in Bremen (Diakonie-Krankenhaus)
Diakonie-Krankenhaus.
Address: Gröpelinger Heerstraße 406-408
Website: https://www.diakobremen.de
Tel. +49 0421-6102-0
Diakony Hospital was one of the first in Bremen to receive the EPZmax certificate. The hospital performs all types of joint replacement, including those performed for emergency reasons. Considering that the hospital has intensive care units, even the most severely ill patient has the opportunity to receive an endoprosthesis after undergoing intensive treatment and stabilizing his condition.
Michael Bohnsack
The Endoprosthetics Center is headed by Professor Dr. Michael Bohnsack. Under his leadership, the center annually performs up to 1,700 joint replacement surgeries, including knee, hip, and shoulder. The hospital’s specialists perform not only primary prosthetics, but also revision ones. Operating doctors:
- Prof. Dr. med. Michael Bohnsack;
- Dr. med. Thorsten Berns;
- Dr. med. Jost Feldmann;
- Dr. med. Götz Kemper.
The clinic uses computer navigation during operations to reduce the number of complications.
Sana Medical Center Munich (Sana Gesundheitscampus München)
Sana'a Medical Center.
Address: München Steinerstraße 6
Website: https://www.sana-gesundheitscampus-muenchen.de/
Tel. +49 089 — 72 403-0
Robert Hube.
At Sana Medical Center Munich, up to 1,300 hip replacement surgeries and 2,500 knee joint surgeries (endoprosthetics, arthroscopy, meniscus interventions) are performed annually. The head of the department of orthopedics and traumatology is Professor Robert Hube, under his leadership the operations are carried out:
- Prof. Dr. med. Thomas Kalteis
- Dr. med. Alexander Kirgis
- Prof. Dr. med. Michael Dienst
Post-operative care and rehabilitation are handled by Nursing Director Monika Schnell. Contact phone + 49 089 72403-1000.
University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden (Universitätsklinikum Carl Gustav Carus Dresden)
Universitätsklinikum Carl Gustav Carus Dresden
Address: Dresden, Fetscherstraße 74,
Website: https://www.uniklinikum-dresden.de
Tel. +49 03 51 / 45 83 1370
The Carl Gustav University Hospital is currently considered the largest medical institution in Germany; it includes 26 highly specialized clinics, 5 research centers and 3 institutes. More than 300 thousand patients are treated here every year. Assistance to orthopedic patients is provided at the Endoprosthetics Center (EPZ certified). The head of the center is Professor of Medicine Jörg Lützner, under whose direct supervision high-quality operating orthopedic traumatologists work:
- Prof. Dr. med. Klaus-Peter Günther
- Dr. med. Albrecht Hartmann
- Dr. med. Jens Goronzy
- Dr. med. Anne Postler
- Dr. med. Markus Sensenschmidt
- Dr. med. Friedemann Steinfeldt
- Dr. med. Mike Stiehler.
Professors Klaus-Peter Günther and Jörg Lützner are members of the initiative group that once developed the German Endoprosthesis Register (EPRD). Professor Günther is also a member of the EndoCert certification committee.
Tabea Hospital Hamburg (Krankenhaus Tabea)
Krankenhaus Tabea.
Address: Hamburg, Kösterbergstraße 32;
Website: www.tabea-fachklinik.de
Tel. +49 0 40 86 69 22 41
Hamburg Tabea Hospital is a highly specialized center. The center's doctors specialize in two areas: surgical orthopedics and skin and vein surgery. The clinic has an EPZmax certificate, so it performs absolutely all types of endoprosthetics of both the knee and hip joint. The head of the center is Dr. Jan-Hauke Jens, a doctor with more than 20 years of experience. In addition to this, joint replacement is performed by:
- Dr. med. Christian Friesecke
- Dr. med. Verena Hilgen
- Dr. med. Nicolaus Siemssen
- Dr. med Florian Westphal
- Dr. med. Christine Wolff
You can make an appointment at the orthopedic surgery center by email or by calling 040 86692-241 / -245. The center’s specialists receive patients from Monday to Thursday from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m.
Schön Clinic in Hamburg-Eilbek (Schön Klinik Hamburg Eilbek SE & Co.)
Schön Klinik Hamburg Eilbek SE & Co.
Address: Hamburg, Dehnhaide 120;
Website: https://www.schoen-klinik.de;
Tel. +49 040 / 20 92 – 73 00
Awards.
The Schön Clinic, located in one of the districts of Hamburg - Eilbeke - is considered one of the largest hospitals in the city: it has 750 beds and employs almost 750 employees. The clinic performs endoprosthetics of all large joints: hip joint, knee, shoulder. The endoprosthetics center is licensed by EPZmax, the head of the center and chief orthopedic surgeon is Professor Dr. Frank Lampe. Other doctors also perform operations:
- Dr. med. Axel Radelhof;
- Dr. med. David Scheunemann;
- Dr. med. Anusch Sufi-Siavach;
- Dr. med. Karina Bohlen
- Arne Demming
- Prof. Dr. med. Oliver Dierk
- Dr. med. Ole Guderjahn
- Dr. med. Thomas Weber
Endoprosthesis centers of the Helios medical network
Helios.
The Helios group of clinics is the largest network of multidisciplinary hospitals in Germany, uniting 112 medical institutions throughout the country. This network includes 17 certified endoprosthetics centers: in Hamburg, Auey, Freital, Köthen, Attendorn, Munich, Pirna, Gotha and other cities.
Helios ENDO-Klinik Hamburg
Address: Hamburg, Holstenstraße2;
Website: https://www.helios-gesundheit.de/kliniken/hamburg-endo/;
Tel. +49 (040) 3197-0
Helios Clinic.
The largest endoprosthetics center in the Helios network is located in Hamburg. More than 7,000 thousand endoprostheses are installed there annually, and over the entire existence of the center, 140,000 people have been operated on. The clinic operates a large rehabilitation center, where patients have the opportunity to fully recover after surgery under the supervision of qualified specialists. The center willingly accepts foreign patients - transfer services are provided and visa support is provided.
The Center is headed by Professor Thorsten Gehrke, and the following employees work under him:
- leading orthopedist of the clinic, Dr. Alaa Aljawabra;
- Dr. Ralf Hempelmann;
- Dr. Götz von Foerster;
- Dr. Christian Ansorge;
- Dr. Jörg Neumann;
- Dr. Volker Jonen;
- Dr. Akos Zahar.
There is another clinic in the Helios network in Hamburg, where joint replacement surgeries are also performed:
Helios Mariahilf Klinik Hamburg
Helios Mariahilf Klinik Hamburg.
Address: Stader Straße 203c;
Website: https://www.helios-kliniken.de/index.php?id=9692;
Tel. +49 0 40 79 00 60
Matthias Seack.
This is a 176-bed hospital with 24-hour stay, almost half of which are for orthopedic patients. The prosthetics center at the clinic is headed by a doctor with 20 years of experience, Matthias Seack. The team of doctors involved in endoprosthetics includes responsible surgeons:
- Udo Brehsan;
- Henning Jeziorkowski
and assistants:
- Felix Behrendt;
- Christian Straub;
- Frauke Klaßen;
- BjörnGebhardt.
Consultations by phone +49 (040) 79006-360 from Monday to Friday, from 9-00 to 12-00.
Professor Eingartner, Caritas Clinic
Professor, dr. med. Dr. Christoph Eingartner Read more
Prof. dr. honey. Christoph Eingartner - Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology at the Caritas Clinic in Bad Mergentheim; Head of the Academic Hospital of the University Hospital of Würzburg. For 25 years, Professor Eingartner has been providing highly qualified medical care in the treatment of joint diseases: primary and revision knee and hip arthroplasty, total and partial joint replacement.
Prof. dr. honey. Christoph Eingartner is included in the list of “Best Doctors in Germany” for the treatment of diseases of the knee and hip joints (according to the German magazine “Focus”).
Nearest airport: Frankfurt
Bilateral hip and knee replacement
Joachim Pfeil, Philipp Höhle, Philipp Rehbein
SUMMARY
Background: In Germany, more than 300,000 joint replacement surgeries are performed every year. With the ever-increasing number of surgeries, simultaneous hip and knee replacements are being considered. This replacement is considered for bilateral symptomatic arthrosis.
Methods: This publication is based on a selective review of the literature and the results of our own prospective comparative studies of simultaneous hip replacement.
Result: During simultaneous hip replacement, there will be no difference in mortality and morbidity compared with unilateral surgery. Rehabilitation is easier after bilateral surgery. The slightly increased mortality rate (0.30% to 0.14%) relative to morbidity after knee surgery is no different compared to unilateral surgery.
During bilateral surgery, especially on the knee, there is a high need for blood transfusions.
For both hip and knee replacements, it is better to undergo bilateral surgery rather than a two-stage inpatient joint replacement.
Conclusion: When it comes to hip replacement, the safest option for patients, regardless of age or ASA score, is bilateral hip replacement. It also has a favorable rehabilitation process.
Because knee replacement carries a high risk of requiring a blood transfusion or death, the authors recommend bilateral joint replacement for patients in ASA categories 1 and 2. The cost of bilateral joint replacement is half that of two separate procedures.
Links:
Pfeil J., Höhle F., Rehbein F. Bilateral hip or knee arthroplasty. German International Medical Bulletin 2011;
108(■■): ■■–■■. DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2011.0nn
The Federal Quality Assurance Service recorded approximately 158,000 hip joint implantations and 147,000 knee joint implantations in Germany in 2008. This shows the quantitative value of endoprosthetics of these joints. Bilateral simultaneous prosthetics are not included in these statistics, since they represent a different group of cases (DRG, diagnosis of related groups). Some patients have indications for bilateral prosthetics. The decisive criterion in favor of simultaneous bilateral replacement is bilateral severe symptomatic osteoarthritis and the patient's desire to replace both joints. Through improved surgical planning, easier implant insertion and muscle-sparing surgical techniques, the choice of bilateral joint replacement is clear.
The purpose of this review is to examine the pros and cons for the patient of simultaneous and bilateral arthroplasty. There are no randomized controlled trials comparing bilateral joint replacement with two-stage surgery. For this reason, the evidence of the results presented is limited.
Methodology
This review article is based on a selective review of the literature and the results of our own prospective comparative studies of simultaneous hip replacement. The following are data from the orthopedic clinic "St. Joseph's Hospital" in Wiesbaden, prospective comparative studies of simultaneous hip replacement (30 bilateral and 30 unilateral patients) with evaluation.
There are no Cochrane selected approaches or guidelines for selecting a procedure for replacing bilateral joint wear yet.
Story
The history of large joint replacement began in the mid-20th century. Already in 1971, publications appeared that addressed the question of whether preference should be given to bilateral total hip arthroplasty for bilateral coxarthrosis.
The purpose of this study of 50 bilaterally operated patients was to find out whether the new treatment method is as successful as unilateral prosthetics, goes hand in hand, or even has an advantage in patients. The primary focus of this study was to evaluate functional or clinical outcomes. The results were promising. Many publications followed on the topic of simultaneous joint replacement of both the hip and knee.
The results obtained in recent years have provided answers to the questions raised here, based on some prospective comparative studies.
Bilateral Joint Replacement Rate
Whether simultaneous arthroplasty is offered to the patient will largely depend on the surgeon. Clinics with a large number of procedures often offer this option. The clinic in Wrightington in England has the highest percentage of unilateral hip replacements. Over a 20-year period, 13,000 operations were performed there, of which 405 were bilateral. This corresponds to 3.1% of patients and, accordingly, 6.2% of prostheses used.
In the last three years (2008-2010) at St. Joseph's Hospital in Wiesbaden, hip endoprostheses were implanted in 1,692 patients, and 62 simultaneous replacements were performed. It corresponds
3.7% of all patients with operated hip joints. In North America and Asia, the largest number of patients had knee replacements. In one retrospective Korean study report, Kim reported more than 2385 concurrent knee arthroplasties. How often simultaneous bilateral operations were carried out throughout the world is not known.
There are regional differences. In South America, unlike North America and Asia, this approach is little used. There are numerous publications on simultaneous hip or knee replacement. In contrast, there is little consideration of this procedure for ipsilateral osteoarthritis of the hip and knee or arthrosis of all four joints.
Figure 1 shows severe bilateral hip arthrosis in a patient who opted for simultaneous replacement of both joints. Figure 2 demonstrates digital preoperative planning with a scaled image depicting the virtual placement of prosthetic joints. Figure 3 shows the situation after simultaneous hip arthroplasty.
Safety of simultaneous prosthetics
Elective joint replacement is associated with a low mortality rate. Various collected studies have given numbers ranging from 0.14 to 0.3%. All published data - retrospective or prospective studies in context - regarding simultaneous hip replacement show no difference. There was also no difference in mortality between patients with low overall risk (ASA classification 1-2; ASA, American Society of Anesthesiologists) and high risk (ASA classification 3-4) in a large retrospective study. The ASA classification of patients operated on in Germany (2008) was published by the Federal Quality Assurance Service (BQS) and is shown in Table 1 below. A (retrospective) study of 450 unilaterally operated patients compared with 450 bilaterally operated patients undergoing surgery from 1970 to 1997 showed a higher rate of pulmonary embolism (1.6% versus 0.7%). Mortality within the first year after surgery is again higher in unilaterally operated patients (4% vs. 3.1%). All patients received Varvarin for prophylaxis before 1986.
Since 1987, prophylaxis on the day of surgery only has been provided with heparin, and only 325 mg of aspirin per day is prescribed for prophylaxis from the first postoperative day. So far, these data are not comparable to the four weeks of prophylaxis that is practiced in Germany, where low molecular weight heparin or new oral antithrombotic drugs are used.
Regarding the knee joint, there are various details regarding the threat to the patient's life during joint replacement. Again, many studies show no difference. In an analysis of all prosthetic knees supplied in the United States between 1998 and 2006, the mortality rate for bilateral surgery was 14%, compared with 0.30% for unilateral surgery (p < 0.0001). If the other side is operated on during the hospital stay, the morbidity and mortality risk increases. A prospective study of 70 patients who were over 70 years of age who underwent knee replacement was compared with a control group of 312 younger patients who had unilateral total knee arthroplasty. The risk of disease was comparable; the risk of mortality was not considered. The authors do not see older age as a contraindication for simultaneous bilateral arthroplasty. In addition, for simultaneous bilateral hip arthroplasty
A (retrospective) comparative study of patients who were 75 years of age or older (n = 43) and younger patients was published (n = 136). In this study, too, no difference was observed.
Complication rate
In joint replacement surgery, there are various possible complications, however, which are rare. A distinction must be made between thromboembolic events in general and specific complications associated with the relevant surgical procedure. Two potential comparison studies between simultaneous and unilateral hip replacement showed no difference in fat embolism and respiratory depression among the procedures. Interestingly, patients with bone marrow embolism had significantly lower oxygen saturation on the first postoperative day than patients without embolism (p = 0.017). However, this was the case in both groups. Several studies that have shown thromboembolic complications during simultaneous hip replacement have failed to find any difference. In the meta-analysis, which was based on 23 separate studies and 2063 bilateral hip replacements, no statistically significant difference was found (p = 0.365 and p = 0.268). In their own study of a total of 60 patients, no non-thromboembolic complications were observed.
Even for specific complications (infections, fractures, and dislocations), differences are not apparent in many studies. The largest studies of simultaneous knee replacement retrospectively analyzed 2385 bilaterally and 719 unilaterally knee replacement patients and found no difference. Berend
and others saw 1.4% (bilateral) versus 1.3% of deep infections associated with implanted hip joints. Infection rates are still low today. In summary, the authors of this study observed more than one thousand implanted hip joints over the past two years and found deep infections in only 0.4% of cases.
Blood loss and transfusion
The incidence of blood loss during bilateral prosthetics is logically higher than that of unilateral ones. In our own studies, the hemoglobin level was (with an average baseline hemoglobin level of 14.1 mg/dL) on the first day after surgery in the bilateral operated group on average 10.2 mg/dL compared with 11.0 mg/dL after unilateral surgery.
Four of the simultaneous and two unilateral patients received blood transfusions during hospitalization (Table 2). Increased transfusion rates can also be seen in other prospective studies. The transfusion rate for bilateral knee arthroplasty is higher than for bilateral hip arthroplasty. In summary, Peak et al reported that blood transfusions are given in 20% of hip transplant patients and 34% of knee transplant patients. With transfusion, the incidence of morbidity increases significantly when hospital treatment delays the operation.
Patient Assessment
The possibility of simultaneous joint replacement is unknown for many patients. After extensive consultation, most patients prefer this procedure. Video recordings of patients walking on crutches just a few days after surgery are useful in consultations. 29 of the 30 patients who underwent surgery in their own study would retrospectively decide to have the procedure performed again. Patients are often very happy that they chose bilateral prosthetics.
Rehabilitation
With bilateral arthrosis, after the first unilateral operation, the joint that causes pain remains and the contracture of the side that has not yet been operated on further prevents rehabilitation. Vykman and Olsson found that due to this fact, in bilateral coxarthrosis, an optimal result may not be achieved before joint replacement. Brand et al added that simultaneous bilateral total hip arthroplasty provides better conditions for clinical success because both sides will be weight-bearing during rehabilitation. Undesirable sparing of the operated hip joint is thus prevented. Even when the first operated hip shows an excellent functional result, the final satisfactory result can only be achieved after surgery for the contralateral painful hip. A simultaneous prosthetic procedure is desirable for optimal recovery and patient satisfaction. Consecutive unilateral arthroplasty represents a significant temporary, psychological and physical burden on the patient. Thus, the total burden of two operations, anesthesia, associated risks, two hospitalizations and two subsequent recovery periods must be taken into account. Also, the long-term result is an advantage for simultaneous replacement for bilateral arthrosis. Flexion was significantly better with simultaneous hip replacements compared with flexion after unilateral or staged hip replacements. This was also noted for indicators that quantify activities of daily living. There was no difference regarding limb abduction ability and pain data.
Economic aspects
Also, hospitalization time and recovery time are significantly shorter with simultaneous bilateral treatment compared to two unilateral surgeries.
This was observed in all studies, and the authors saw a clear cost advantage for concurrent operations. Thus, in our own study, bilaterally operated patients spent an average of 15 days in hospital treatment, while unilaterally operated patients averaged 12 days; This means that for two separate operations the patient spends 24 days in the hospital. The following statements are examples of economic differences.
Based on the average values of the state of the basic value (SZSBZ) catalog of the unified pricing system for medical services (INEK) 2009 Hesse, an account of the costs of simultaneous bilateral rehabilitation was compiled. The results are shown in Table 3. The benefits to payers are significant.
For the hospital, revenue is higher with simultaneous transplantation, but less than the sum of two unilateral operations. The cost of hospitalization and recovery is paid only once for a simultaneous approach and is only slightly higher than for single-stage surgical procedures.
Discussion and recommendations
Almost all studies compare bilateral replacement with unilateral replacement. Symptomatic bilateral osteoarthritis means the need for unilateral surgery on only one joint. It is logical that a bilateral joint replacement operation should be compared - in terms of risks - with the risks of two unilateral operations, since the patient must endure both of these procedures. Thus, simultaneous replacement is considered to be a particularly safe method of hip replacement in many respects. From this point of view, bilateral prosthetics, especially of the hip joints, are preferable. Simultaneous joint replacement is preferable to two-stage operations, in which a similar operation is performed on a different joint a few days later.
In every respect - but in particular because of the increased complications and increased incidence of blood transfusions - this two-stage procedure is inferior to simultaneous prosthetics and is therefore not used. Increasing the frequency of blood transfusion during simultaneous hip replacement should be discussed with the patient when considering the frequency of blood transfusion during bilateral surgery. With bilateral prosthetics, the frequency of blood transfusion increases significantly.
Even the small increase in mortality that corresponds to twice the rate of unilateral knee replacement. This should be taken into account when weighing simultaneous replacement. The patient's age is not critical for simultaneous bilateral replacement. The ASA classification is important. This is indicated in some studies, with different estimates made. The authors recommend bilateral prosthetics for patients with symptomatic bilateral coxarthrosis and ASA classification 1-3, which means more than 99% of patients (Table 1). For the most part, cementless implants are used today. However, thanks to modern surgical techniques and implant design, prosthetic joints can operate at full weight-bearing capacity. Doctors are very cautious about knee replacements in ASA3 patients. Increasing transfusion capacity should also be discussed. For the patient, simultaneous replacement is clearly beneficial. It consists of hospitalization and rehabilitation, which do not differ significantly in time from the rehabilitation of a unilaterally operated patient. Costs per patient and lost employment are lower. The functional result also indicates simultaneous bilateral prosthetics.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest within the meaning of the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors guidelines.
| Table 1 | ||
| TETS | TEX | |
| ASA 1 Normal healthy patient | 9,6 % | 6,0 % |
| ASA 2 Patient with mild illness | 59,8% | 59,4% |
| ASA 3 Patient with severe general illnesses and disabilities | 30% | 34,2% |
| ASA 4 Patient with inactivated general diseases, permanent threat to life | 0,6% | 0,5% |
| ASA 5 Patient is dying | 0% | 0% |
table 2
Comparison of bilateral (n=30) and unilateral (n=30) knee replacements - data from a prospective study at St. Joseph's Hospital
| one-sided | bilateral | |
| Gender distribution Female/Male | 15/15 | 16/14 |
| Average age (years) | 64 | 62 |
| Average weight | 80 | 81 |
| Average ASA score | 2,0 | 2,1 |
| Hospitalization time | 12 | 15 |
| Harris Ball before surgery | 41 | 39 |
| Harris score 6 weeks after surgery | 91 | 90 |
| VAS before surgery | 7,6 | 7,6 |
| VAS 6 weeks after surgery | 1,0 | 1,1 |
| Hemoglobin value before surgery | 14,1 | 14,1 |
| Hemoglobin value on the first day after surgery | 11 | 10,2 |
| Blood transfusion (patients) | 2 | 4 |
| Average operating time (minutes) | 75 | 100 |
| Complications | 0 | 1 postoperative femoral trochanter |
| Changes | 0 | 1 refixation of the femoral trochanter |
| Infections | 0 | 0 |
| Thromboembolism | 0 | 0 |
| Ability to walk (days) | 2,4 | 2,7 |
VAS, visual analogue scale: 0 (no pain) to 10 (severe pain);
All patients with bilateral simultaneous hip replacement who underwent surgery between 6/2006 and 3/2009 at St. Joseph's Hospital were included in the study.
Table 3
| Bilateral simultaneous prosthetics (DRG I36Z) | 2*Single-sided prosthetics (DRG I47B) | Difference | |
| LBFW (€) | 2 868,50 | 2 x 2,868.50 | |
| Rel. Weight x | 3,344 | 2,366 | – |
| Income (€) | 9 592,26 | 13 573,74 | 3 981,48 |
| INEC expenses (€) | – 8 765,76 | – 12 406,06 | 3 640,30 |
| Revenue (€) | 826,50 | 1167,76 | 341,18 |
Digital endoprosthetic planning for hip replacement.
Postoperative x-ray of cementless bilateral prosthetics.
Endoprosthetics: features of implementation in German clinics
Endoprosthetics (replacing a joint with an artificial implant) is a time-tested method, which is the replacement of joints damaged due to an accident or wear and tear with artificial joints. If there are necessary medical indications and with careful adherence to technology, long-term results can be achieved using endoprosthetics.
Please note: the quality of endoprosthetics in Russia and Germany varies significantly. In Russia, prostheses from an unknown manufacturer are often used, and even if a patient specifically orders and pays for an expensive prosthesis from a foreign manufacturer, there is no guarantee that it will not turn out to be a fake. It is quite obvious that the quality of the prosthesis determines its service life and the absence of complications after endoprosthetics surgery. In Germany, prosthetics from manufacturers are used for endoprosthetics, the quality of which is deservedly considered to be very high. Basically, for endoprosthetics operations in Germany, well-proven, high-quality prostheses from Swiss and American manufacturers are used.
An important success factor is that German endoprosthetics clinics and doctors have significantly longer experience installing prostheses compared to their Russian colleagues. In Germany, endoprosthetics have been around for 40 years. It is obvious that in addition to the quality of the implant, its service life is greatly influenced by correct installation, which, of course, depends on the experience and qualifications of the surgeon. In addition, the availability of the most modern equipment in the endoprosthetics clinic plays an important role. In Russia, especially in its regions, there are not enough large endoprosthetics clinics that are properly equipped; in addition, there are not enough qualified specialists with the appropriate level of training in the field of endoprosthetics.
In our clinic, the requirements for specialists who can perform such complex operations as endoprosthetics are very high: they need more than 5 years of experience in the field of traumatology or surgery, as well as training for successful endoprosthetics in training centers of leading companies - manufacturers.
— Privat-docent, dr. med. Sciences Holger Mellerovich -
Another factor that ultimately leads to the short-term service of prostheses installed in Russia, or even to postoperative complications, is the lack of a rehabilitation system for patients after endoprosthetics surgery. In Germany, after endoprosthetics, such patients always undergo at least two weeks of rehabilitation.
In German endoprosthetics clinics, the most modern VISIONAIRE computer technology is used, with the help of which each patient is implanted with an individually selected prosthesis. This guarantees the most comfortable shape and high durability of the endoprosthesis. 8 weeks before endoprosthetics surgery, an MRI examination of the knee joint is performed and pictures of the entire lower limb are taken. Based on the images obtained as a result of the examinations, individually adjusted resection blocks for sections are made.
In some endoprosthetics clinics in Germany, hip arthroscopy is performed, which allows you to preserve the natural hip joint for as long as possible. This type of operation is not offered in Russia.
Also in Germany they offer superficial hip replacement. With superficial hip replacement, the head and neck of the femur are almost completely preserved. The advantages of this arthroplasty method are the preservation of bone, as well as the preservation of normal force to move the femur.
Reasons for needing joint replacement
The main cause of joint dysfunction is diseases such as arthritis, arthrosis, gout. Other causes of disorders are infections, injuries, systemic diseases (rheumatism), and birth defects. As a result, the quality of life decreases, a person’s mobility is limited, and painful sensations appear.
Through diagnostic procedures, the degree of disease and the condition of the affected joint are determined. After the diagnosis, a set of therapeutic procedures is prescribed aimed at improving the functional abilities of the joints, stopping degenerative processes and eliminating pain.
If conservative treatment and arthroscopic procedures do not lead to improvement, to solve this problem it is necessary to replace the diseased joint with an artificial one.
Preparation for endoprosthesis surgery
Typically, you should stop taking the following medications two weeks before your arthroplasty surgery. Namely, drugs containing:
- acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin)
- clopidogrel (Plavix, Iskover)
- Coumarin (Marcumar): a special case - parallel administration of heparin
- voltaren, ibuprofen, paracetamol, novalgin or similar
- enzyme preparations, e.g. Wobenzym, Phlogenzyme
- pentoxifylline - trental and other medications, such as arnica, kolnik, gingko
Before you stop taking the above medications, we recommend that you consult with your doctor. You only need to arrive at the clinic for endoprosthetics one day before the operation, since the prostheses are not made individually for each patient, but are “adjusted” in accordance with his physical parameters using a special computer program.
Reasons for replacement
The need to replace joints arises when they are worn out or injured. Most often, doctors have to perform endoprosthesis replacement of large joints in the legs, since these are the areas that are subject to the greatest load and wear out over time.
Shoulder replacements are also quite common. In this case, doctors replace the upper surface of the main joint; its damage is explained by excessive mobility and individual characteristics - weakness of the ligaments.
Somewhat less often, doctors perform endoprosthesis replacement at other locations. The need to replace relatively small joints arises with arthrosis and arthritis, which are accompanied by pain and dysfunction of such areas of the musculoskeletal system. Joint surgery also helps to recover from an injury.
Replacement of worn-out artificial joints is very popular in German medical centers. After all, even prostheses made with the latest technology can wear out after years of use.
Clinics in Germany employ professionals - doctors who specialize in certain types of endoprosthetics. Our company will help you choose the right specialist even in difficult and unusual cases.
Endoprosthetics. Range of services
- Full range of services for hip and knee replacement, incl. operations to replace existing ones
- Cementless hip arthroplasty with a time-tested standard (Aesculap Bicontact type) and a modern rod system (short stem prostheses/Metha type)
- Bone-sparing stem replacement system (Metha short stem prostheses)
- Endoprosthetics using a cementless system for acetabular defects
- Ceramic sliding pair with high wear resistance (ceramics)
- Various knee replacement systems (unfixed, partially fixed and fixed, depending on need)
- “Sliding” endoprostheses for the internal side, installed using minimally invasive techniques
- Computer navigation systems for hip and knee replacement surgeries
- Hip replacement surgeries using minimally invasive and muscle-sparing techniques
- Complex operations for hip and knee replacement
- Endoprosthetics of intervertebral discs (see Spine surgery)
If you require treatment in Germany with endoprosthetics of the knee, hip or other types of joints, contact our specialists!
Call us today! or use it - we will call you back immediately.
+49 152 056 612 47 (phone and Whatsapp in Russian)
What is an endoprosthesis?
An endoprosthesis is an internal device that performs the function of a substitute organ.
Accordingly, a joint endoprosthesis is an internal device that ensures the function of the joint.
The current level of development of endoprosthetics in Germany provides the opportunity to replace any joints: hip, knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, fingers and toes. During the operation, damaged joints are removed and endoprostheses made from biocompatible materials are installed in their place. The entire joint can be replaced (called total replacement) or only the damaged parts of the joint (partial replacement).