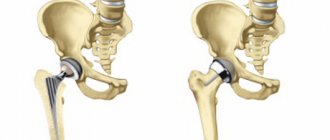
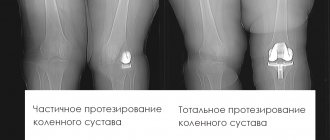
Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint in Samara
To relax spasmodic muscles and increase blood flow in the hip joint, shock wave therapy and peripheral magnetic stimulation are used. To reduce inflammatory changes and pain, carboxytherapy is used on the hip joint area, hydrocortisone ultraphonophoresis, and Khivamat electrostatic therapy. After the acute manifestations of inflammation have been relieved, it is advisable to carry out post-isometric muscle relaxation and manual joint techniques aimed at restoring the range of motion in the joint.
And at the final stage - physical rehabilitation, which implies at least minimal exercise, and ideally - a full 1-hour workout! For life!
Be healthy!
If you need help, call for residents of Samara and Kazakhstan.
Teraflex
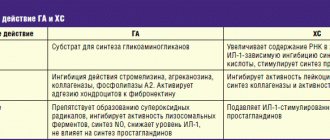
Problems with joints, one way or another, threaten almost every person: when a certain age is reached, the cartilage tissue of the joints loses the ability to self-heal and its wear becomes irreversible. And this is where medications such as Teraflex come to the rescue. This “impact” ligament in the form of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine, due to its active participation in the formation of connective tissue and the protection of cartilage from destruction, significantly expands the capabilities of cartilage tissue in terms of regeneration, which makes this combination an effective weapon in the fight against osteoarthritis. Thus, additional “feeding” of the body with glucosamine stimulates the synthesis of the cartilage matrix and provides the cartilage with reliable protection from damaging factors, including its protection from the destructive effects of other drugs (glucocorticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). In addition, glucosamine has a moderate anti-inflammatory effect.
If glucosamine is a catalyst for the formation of the cartilage matrix, then chondroitin sulfate acts as an additional substrate for this process. In addition, it is involved in the formation of hyaluron (in the form of acid, this substance is the main component of intra-articular fluid), proteoglycans (form the basis of connective tissue) and collagen.
Chondroitin sulfate maintains the required consistency of intra-articular fluid, stimulates cartilage regeneration processes and suppresses the action of “unfriendly” enzymes to cartilage, such as hyaluronidase and elastase.
Theraflex is available in capsules, taken with a small amount of liquid, regardless of meals. The regimen for taking the drug in adults and adolescents over 15 years of age is as follows: 1 capsule 3 times a day (in the first 3 weeks), 1 capsule 2 times a day (all subsequent days). Teraflex is a drug for long-term use: the optimal duration of the therapeutic course is from 3 to 6 months. In a number of situations, in consultation with the doctor, it is possible to repeat courses of treatment with Teraflex, the duration of which is decided on an individual basis.
The appearance of side effects from the digestive tract is not a reason to completely discontinue the drug: it is enough to reduce its dose by half. And only if there is no improvement, the course of treatment is stopped. Theraflex can be combined with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticosteroids. Moreover: when taken together, it reduces the need for the former.
Our specialists
Mizonov Sergey Vladimirovich
The doctor is a neurologist. Chiropractor. Osteopath. Physiotherapist. Experience: 8 years.
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Ogurtsov Denis Alexandrovich
Traumatologist - orthopedist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.
Joint pain
Joint pain (or as it is otherwise called - arthralgia) is an important symptom in the diagnosis of many diseases. She is the first to say that serious changes have begun at the junction of the bones. Joint pain is not always accompanied by swelling, curvature, severe pain when palpated, or redness. The patient also does not complain about significant restrictions in the mobility of large joints. It also happens that even an X-ray examination does not allow signs of inflammation to be seen. But this does not make joint pain an innocent symptom: it can signal severe organic lesions and even pathologies that are not related to the condition of the joint itself.
As statistics show, sharp pain in the joints of the arms and legs begins to bother every second person over the age of 40-50 years. In people who have crossed the 70-year mark, diseases of the musculoskeletal system are even more common - in 90% of cases.
Read also
Periarthrosis or periarthritis?
Let's imagine that you are driving a luxury car along our wonderful roads and suddenly notice that something persistently creaks in the area of the front wheel on the right.
Moreover, this creaking intensifies periodically,… Read more
Elbow pain
Clinical manifestation of elbow pain This symptom can occur in the segments controlled by the ulnar nerve. If this is due to Guyon's stock, which is being pressed by a tubercle, rupture or damage in ...
More details
Pain in the gluteal region
Clinical manifestation of pain in the gluteal region Pain in the gluteal region is quite common. Although this pain can be caused by a number of reasons, it is most often associated with thoracolumbar syndrome,...
More details
Arm and neck pain
A man's neck hurt. He walks, periodically independently twists it from side to side, kneads it with one hand, then with the other... Brings his neck to the extreme degree of tilt to the left... then to the right... slowly... and...
More details
Patellar tendinopathy
Patellar tendinopathy is pain in the knee joints and patella. This painful condition often occurs in young people involved in sports. Tendinopathy occurs due to excessive stress...
More details
Expert recommendations
Some of the best drugs for treating OA pain are NSAIDs. Unfortunately, patients who have had a myocardial infarction or heart surgery, or who have high blood pressure (very high or high risk of cardiovascular disease) should avoid using any NSAIDs. In this case, it is possible to take paracetamol, and in the presence of severe pain, after consultation with a doctor, tramadol or drugs of other groups.
For patients at low risk of developing cardiovascular and low or moderate risk of gastrointestinal complications, any NSAID may be recommended. Their choice can be determined depending on the presence of acute or chronic pain and the severity of the inflammatory process. Although all NSAIDs are considered equally effective at maximum permitted doses, their effects on the rate and duration of pain relief vary. The most powerful analgesic potential is diclofenac potassium and ketoprofen.
If patients with OA have even moderate risks of developing complications from the cardiovascular system or gastrointestinal pathology, taking NSAIDs is unsafe, and the choice of drug should be agreed upon and prescribed by your attending physician!
According to evidence-based medicine and the opinion of international experts, complex therapy for OA should include agents that affect inflammation and metabolic processes in cartilage tissue and chondrocytes (glucosamine sulfate or glucosamine hydrochloride, chondroitin sulfate, a combination of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride, unsaponifiable compounds of avocado and soy, diacerein and hyaluronic acid). Summarizing the findings of most RCTs, from a practical point of view, these drugs have a reliable analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect; increase functional activity; reduce morning stiffness and starting pain.
A number of studies have shown the effect of unsaponifiable compounds from avocado and soy (Piascledine 300) in reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In a domestic study, it was shown that unsaponifiable compounds of avocado and soy lead to a decrease in markers of systemic inflammation (TNF-α, IL-1β, R-IL2, CRP) by an average of 30% over 3 months of therapy, and also demonstrated a leveling of clinical symptoms of OA , primarily pain, as well as a decrease in the intensity of endothelial dysfunction due to the addition of the drug to the main therapy of cardiovascular diseases. It has been shown to reduce the need for NSAIDs and maintain the functional activity of the affected joints.
Do not cancel therapy with these drugs if they were previously prescribed to you by your doctor!
Local therapy for OA includes intra- or periarticular administration of glucocorticoids, intra-articular administration of hyaluronic acid preparations, as well as local application of NSAID-based ointments (creams, gels) to the joint area.
However, intra-articular glucocorticoids should be avoided during the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition to the risk of being in a health care setting, there is also a hypothetical risk that exposure to an intra-articular glucocorticoid may weaken the immune response of patients with OA.
Local application of creams and gels with NSAIDs (arthrosilene, ketonal, fastum-gel, voltaren, etc.) will help you reduce pain and improve joint function.
According to modern data, obesity is a risk factor for OA and many other diseases associated with metabolic disorders, and dysfunction and disability, as a rule, accompanying OA, in turn lead to an increase in body mass index and induce the development of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Now is the time to start reducing your weight by reducing calories and doing exercise!
Chew your food thoroughly (the feeling of hunger and satiety occurs much faster, you can limit the amount of food consumed). Reduce portions to fit your fist! Distribute meals evenly over 4-5 times a day, the last meal should not be later than 3 hours before bedtime.
Causes of joint pain
Age-related changes
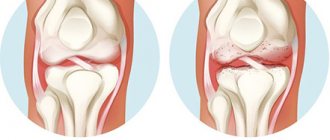
Possible causes of pain include age-related changes in the joints: cartilage tissue becomes thinner and loses elasticity, which causes pain and stiffness of movement. There is also less and less production of synovial fluid, which fills the “capsule” around the bone junction and lubricates the joint. As a result, the articular surfaces may begin to touch and the joint may begin to wear out. Without proper protection and support of cartilage, osteoarthritis and other diseases that accompany acute pain can develop. The process of age-related changes in the joint is aggravated by poor nutrition, weak muscle tone, previous injuries, a sedentary lifestyle or, conversely, excessive physical activity. It is noteworthy that discomfort in the joints due to the age factor often intensifies in the fall and spring.
Physical exercise
Increased physical activity can be considered as an independent reason, in which even young people can experience aching or acute pain in the joints. Intense training at the limit of capabilities and hard physical labor one way or another have a negative impact on the musculoskeletal system. Even in the absence of injury, excessive stress can cause problems with blood flow in the synovium surrounding the joint. Because of this, the cartilage tissue ceases to receive “nutrition” and becomes thinner without the possibility of normal regeneration. Professional athletes and people of certain professions often face this problem - builders, miners, mechanics, etc.
Diseases
Various diseases can also “hit” the joints. Thus, joint pain often confirms the presence of rheumatic processes in which the connective tissues of the body are affected. In this case, the pain syndrome is pronounced in the morning and tends to decrease in the evening. A person feels the most severe discomfort in the small joints of the hands and feet. In the mornings, the patient often suffers because he cannot immediately get up and walk quickly - his body is stiff.
Some patients have joint pain after suffering an inflammatory disease of the musculoskeletal system. In this case, you just need to wait until the discomfort goes away on its own.
If the pain is paroxysmal, arose unexpectedly, intensified during the day and persists for several days, while only one joint on the big toe aches, you can suspect gouty arthritis, in which uric acid crystals accumulate in the joint structures.
If the pain increases very slowly, the inflammatory process has affected the pelvic area, knees, symptoms intensify during physical work and weaken at night, then the presumptive diagnosis is “deforming osteoarthritis.”
Infectious diseases are also among the causes of joint pain; for example, after intestinal diseases, a person may experience discomfort in which all joints of the body ache. Mobility in them remains, but the unpleasant symptom lasts for several days.
If there are pockets of chronic infections in the human body, it can also cause pain in the joints.
The list of less common causes of joint pain is long and includes:
- weather dependence;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- post-allergic reactions;
- psychosomatic disorders.
Classification of joint pain
There are several classifications of joint pain. According to the localization criterion, the following are distinguished:
- monoarthralgia - in this case, only one joint is affected;
- oligoarthralgia - different joints hurt at the same time, but no more than four;
- polyarthralgia - discomfort is felt in more than 4 joints of the body.
According to the nature of the lesion, the pathology can be non-inflammatory and inflammatory in nature. Post-inflammatory arthralgia and pseudoarthralgia are divided into separate groups.
Joint pain occurs under different circumstances. A person feels starting pains at the very beginning of movement - when trying to change the position of the limbs, stand up or walk at a different speed. Night pains occur during the period of night rest, when a person is at rest. Such discomfort often causes sleep disorders and greatly impairs the quality of life. Referred pain can be noticed in areas where there is actually no painful deviation from the normal state. There are also mechanical pains that occur during or after performing certain exercises or activities.
In addition, joint pain varies in nature. They are:
- dull and sharp;
- permanent and transient;
- weak, moderate and intense.
This classification is largely subjective and depends on the individual characteristics of the human body.