until October 31
Appointment with a doctor based on the results of instrumental diagnostics with a 50% discount More details All promotions
Ultrasound of the hip joints is a painless and accessible method of assessing the condition and identifying pathologies of the joints themselves and the tissues surrounding them. In adult patients, this ultrasound examination is more likely to be an additional diagnostic method: it is rarely performed independently, more often as an addition to or MRI. However, ultrasound is recommended for patients with an artificial heart pacemaker or metal dental implants, since MRI is contraindicated for such people.
You can get an ultrasound of the hip joints at the clinics of JSC Family Doctor.
In what cases is ultrasound of the hip joints prescribed?
Diagnostics can be prescribed by a traumatologist, surgeon or orthopedist. Typically, ultrasound examination of the hip joints is indicated in the following cases:
- Limited mobility, difficulty getting out of bed after sleep;
- The appearance of stiffness when moving;
- Painful sensations;
- Suspicion of a dislocation or dislocations in the past;
- Change in skin color in the hip joint area;
- The appearance of a distinct crunch in the joint during physical activity;
- Frequent muscle spasms in the buttocks and thighs;
- Different lengths of the lower limbs.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to do an x-ray of the hip joint if:
- Pregnancy or lactation - radiation, although at a safe dose, can disrupt the intrauterine development of the fetus or lead to cessation of lactation.
- The patient is under 15 years of age (period of active growth).
- The patient is in serious condition – heavy blood loss, painful shock.
- Repeated X-rays taken within the previous year or several months.
There may also be a risk of using a contrast agent during x-rays. It is based on iodine, which is not advisable for diseases of the thyroid gland, allergies to iodine, severe renal and liver failure, and severe diabetes mellitus.
Advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound of the hip joints
Today, there are many different diagnostic procedures, such as x-rays, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Of course, these studies provide more detailed information, but such methods have a higher cost. Ultrasound examination, in turn, is cheaper, completely safe and allows you to identify pathological processes even in the early stages. In addition, the diagnostic result can be obtained within 10 minutes after the end of the examination.
Let's look at a few more benefits:
- The procedure is non-invasive;
- It is painless;
- It is also possible to study the condition of the blood vessels in the area under study.
FAQ
- Do I need to somehow prepare for an ultrasound diagnosis of a joint?
No special preparation is required for ultrasound examination of joints and soft tissues. A contraindication to an ultrasound examination may be the presence of a plaster cast, wound or abrasion.
- How often can an ultrasound be done?
The ultrasound diagnostic method is absolutely harmless; if necessary, it can be done as many times as necessary.
- Is it possible to consult a specialist after an ultrasound?
Yes, you can get advice from a specialized specialist - a traumatologist, orthopedist, physiotherapist or sports doctor. You can also undergo treatment with us, and you can start on the same day you contact us.
- Is it painful to have an ultrasound examination?
No, this is a non-invasive and painless diagnostic method.
- Does ultrasound replace radiography of the joint?
No, ultrasound does not make it possible to assess the nature of the bone fracture, the presence of fragments and displacement. Therefore, in case of injuries and suspected fracture, it is better to first conduct an X-ray diagnosis.
How is the procedure carried out?
The patient removes clothing below the waist (except underwear) and lies down on the couch. Diagnosis is made using a sensor, with which the doctor reads information about the condition and density of bone, cartilage and soft structures. To obtain a complete clinical picture, the doctor uses several access options.
Anterior approach
The ultrasound doctor asks the person to lie on his back, and a small cushion is placed under the femoral surface. This position helps to better examine the structural elements of the hip joint. By observing the image on the screen, the specialist receives information about the condition of the ilium, femoral head, ligaments, muscles and lymph nodes of the groin.
Rear access
For such an examination, the specialist asks the patient to lie on his side and bend his knees slightly closer to his chest. During the study, it is possible to identify the functioning and characteristics of the sciatic nerve, obtain information about the surface of hyaline cartilage, and examine the superficial and internal structure of muscle fibers in the gluteal region.
Medial access
The person lies on his back, bends the lower limb and moves it to the side. This position allows for a detailed examination of the pelvic flexor muscles and articular ligaments if a pathological process is suspected.
Lateral access
The person lies on his side, and the specialist asks him to rotate his hip inward. In this position, the protruding elements of the tibia and the trochanteric bursa are clearly visualized.
On average, this manipulation lasts no more than 30-40 minutes. The patient is given the results of the examination; in some cases, additional images are attached so that the doctor can independently assess the clinical picture.
Causes, symptoms and therapeutic measures
The main source of dystrophic-degenerative destruction in the joint is the changes in the body that occur upon reaching 65-70 years of age. With age, the necessary elements are synthesized in the joint fluid in a smaller volume, as a result, the joint tissue becomes less elastic and durable.
Drying particles of cartilage settle on the joint capsule, which is why the acetabulum cannot function fully. The inflammatory process and necrosis of rubbing areas lead to the appearance of unpleasant painful manifestations.
In some cases, a significant acceleration of the onset of degenerative processes is possible. This can happen in the background:
- congenital dislocation of the hip joint (dysplasia);
- shock-mechanical damage or fracture of the femoral neck;
- hereditary disorders of the musculoskeletal system in the pelvic region;
- psoriatic infectious or rheumatic inflammation;
- sedentary lifestyle or increased physical activity on the pelvic elements;
- hormonal changes in the body.
The manifestation of clinical signs of pathology is due to the severity of the inflammatory process:
- Arthrosis of the first stage is accompanied by painful discomfort that occurs against the background of physical overload or prolonged movement. A little rest helps relieve pain. Laboratory diagnostics can determine the presence of a slight narrowing of the gap between the joints and fleecy growths along the contour of the acetabulum.
- After arthrosis develops to stage 2, pain symptoms increase, and they are disturbing even when stationary. Motor activity decreases, changes in gait occur, and lameness appears. The main symptom of this form of the disease is the inability to completely abduct the hip to the side, and the patient experiences acute piercing pain at the time of movement. During the X-ray examination, it is possible to examine bone growths on the outer and inner sides of the acetabular notch.
- The most difficult and difficult to correct disease is stage 3 coxarthrosis. With this form of arthrosis of the hip joint, the patient is bothered by constant pain. There is complete limitation of motor activity in combination with a decrease in leg length. On an x-ray, you can see that the surface of the cartilage is completely destroyed, and large osteophytes (bone growths) are formed in its place. Due to this condition, a person may find himself completely immobilized.
According to clinicians, the development of such problems with the hip joint in men is much less common compared to women. The reason for this is the physiological characteristics of the female body.
The goal of therapy for coxarthrosis of the hip joint stages 1 and 2:
- relieve painful manifestations with the help of drugs that have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and analgesic effects - Ibuprofen, Voltaren in gel form, Diclofenac, Ketanol, etc.;
- activate the supply of nutrients to cartilage tissue and start blood circulation with the help of Teraflex, Hondrex, Mucosat, etc.
In some cases, injections into the joint are indicated. For this purpose, they use Osteonil, Fermatron, etc. Also, for arthrosis of the hip joint of stages 1 and 2, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed, namely magnetic therapy, paraffin, high-frequency electrophoresis, physical therapy and massage.
If the patient is diagnosed with stage 3 coxarthrosis of the hip joint, surgical intervention – endoprosthetics – is indicated.
Decoding the results
An orthopedist, surgeon, or orthopedic surgeon can interpret the results. The research protocol usually contains the following information:
- the presence of pathological processes, a detailed description of the deviation.
- congenital or acquired changes inside the joint;
- condition of ligaments and nerve bundles;
- increase in the thickness of the joint capsule;
- functioning of adjacent muscles;
- features of cartilaginous structures;
- the amount of synovial fluid inside the joint.
- the presence of neoplasms, if any, their shape, structure, size and individual characteristics;
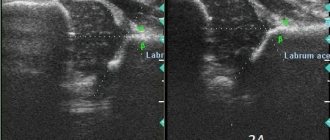
- information about the ilium, labrum and femoral head;
- metastasis of nearby tissues;
- presence of hematomas.
Please note that the result of an ultrasound examination is not a basis for making a diagnosis. If any inconsistencies or pronounced pathological processes are detected, it is additionally necessary to perform a computed tomography scan and pass various tests for laboratory research. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary (for example, if the doctor suspects a malignancy). The final diagnosis and necessary treatment are prescribed only after additional studies.
What are the advantages of the method
Since 1989, ultrasound has been used in pediatrics. It is noteworthy that the first studies were aimed at studying the hip joint. The problem of dysplasia was encountered everywhere, which means it required an effective solution and constant monitoring. Ultrasound examination still does not lose popularity and remains the safest, most informative and accurate diagnostic method. The production and use of ultrasound equipment is strictly regulated by the World Health Organization, so parents can be confident in their quality and functionality.
The main advantage of ultrasound is safety. Unlike X-rays or computed tomography, after which radiation doses accumulate in the body, ultrasound does not affect a person in any way. It is this type of diagnosis that is suitable for the most vulnerable categories of patients - newborns, pregnant/lactating women and the elderly.
The second advantage is maximum patient comfort. During the examination, the baby does not need to be fastened with soft belts or forcibly held in your arms for the device to record the state of the body. On the contrary, activity within normal limits will help the doctor better study the hip joint and will not darken the mood of the little patient. Additionally, a specialist can track the dynamics of changes, record inflammatory processes or defects in muscles, ligaments, tendons, joint capsule and cartilage.
Normal hip joints according to ultrasound
If the patient does not have various pathological processes, the protocol indicates that the hip joints have a clear and smooth surface, without deformations and bone growths. The joint capsules should have folds and branches; their structure is normally hypoechoic.
The following information is also usually indicated:
Right joint:
The bony part of the acetabulum is normal. No major changes. Rectangular bony protrusion. The overlap of the cartilaginous part of the roof of the femoral head is sufficient. The limbus is projected laterally from the femoral head, is presented, and has a normal angle of inclination. The head of the femur in the acetabulum is located correctly. The ossification nucleus is located. Angle a is less than 60 degrees. Angle b is greater than 55 degrees.
Left joint:
the roof of the acetabulum is moderately flattened, without structural changes. The femoral head is centered correctly. The ossification nucleus is located. Angle a is more than 60 degrees. Angle b is more than 55 degrees. The angular parameters of the joint are not changed. When performing functional tests, the joint is stable.
Please note that these indicators may vary depending on age - deviations from them do not always indicate the presence of diseases or some problems.
Restrictions
The diagnostic capabilities of modern ultrasound machines make it possible to clearly visualize the cartilage and soft tissues (muscles and tendons) surrounding the joint, but examination of the pelvic bones using ultrasound is difficult. The fact is that the ultrasound beam cannot pass through the bone, so damage to bone structures during this diagnosis will be poorly visible, and the patient will be referred for further examination using an X-ray or CT scan.
Initial appointment with an ORTHOPEDIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
What pathologies can be identified
Most often, during an ultrasound examination of the hip joints, the following diseases are detected:
- Arthrosis (it develops as a result of congenital dislocation of the hip, a disturbance in the circulatory system, or as a result of a fracture of the femoral neck);
- Arthritis (may occur due to infection of joint joints by pathogens);
- Synovitis, which is characterized by inflammation and fluid accumulation inside the joint;
- Necrosis of bone tissue (can occur due to frequent fractures, dislocations, bruises);
- Tears and spasms of muscle fibers;
- Swelling of the joint.
The hip joints are most susceptible to various pathological processes. Diseases can be either congenital or acquired. If you visit a medical facility as soon as the first symptoms appear, you can hope for a favorable outcome and complete recovery. Otherwise, your doctor may recommend surgery.