- November 29, 2018
- Orthopedics and traumatology
- Svetlana Pavlova
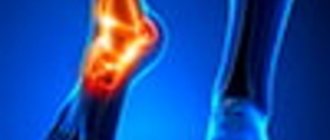
The knee is one of the important and complex joints of the human body. Movement, and therefore quality of life, is related to its health and functioning. Often, with increased physical activity, pain in the knee joint appears. They occur on both the outer and inner sides of the knee and can vary in intensity and frequency of occurrence. Let's look at why pain occurs in the knee on the inside and on the side and how to deal with it.
Briefly about the structure of the knee
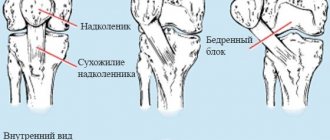
In the human body, the knee joint is the largest.
It consists of three bones:
- femoral, located above;
- tibial, located below;
- kneecap - in front.
Bone joints are protected by interarticular cartilage and menisci: lateral and medial. The entire joint is housed in a joint capsule, covered with a membrane that contains synovial fluid. It serves as a lubricant for cartilage, facilitating gliding. The ligaments, tendons and muscles located in the knee joint provide it with mobility and strength.
The structural features and harmonious operation of all parts of the knee ensure its reliable functioning. But if any disturbances occur in the functioning of the joint, then the person experiences pain.
Causes of pain
The most common causes of knee pain on the inside side can be:
- Injuries are the most common source of pain.
- Arthrosis – damage occurs to the cartilage and ligaments of the knee joint, causing crunching and clicking during extension and flexion, and pain.
- Arthritis – inflammation of the joints, rapid development of the disease, severe night pain.
- Damage to the meniscus often occurs for no apparent reason and causes severe pain.
- Inflammation of the knee tendons - periarthritis "crow's feet". Often suffer from women whose knee hurts on the inside during physical exertion on the joint.
- Rickets is a disease that affects children and causes bone softening and destruction.
- Rheumatism is inflammation of the joints as a consequence of acute infections.
- Baker's cyst - forms in the popliteal fossa; when it grows, it disrupts blood circulation, interferes with bending and straightening the knee, causes swelling and thrombophlebitis.
Treatment of Medial Knee Pain
Treatment varies depending on the doctor's diagnosis and the type of complication. The orthopedist may ask for an X-ray or MRI to accurately diagnose the cause of the pain. But this is not always necessary, and based on your examination and medical history, your doctor can prescribe the best treatment for you. While some patients think the treatment is just surgery, knee surgery is a last resort after taking medications and proper exercise. In addition to specific medications, the following exercises are also very effective in treating pain and should be performed under the supervision of a physical therapist:
- ATV Stretch
- Hamstring stretch
- Half Squats
- Heel and calf stretch
- Calf lifts
- Hamstring curl
- Raises straight leg
- Swimming
- Yoga
- Stationary cycling
Knee injuries
The most common knee injuries are:
- Bruise – sharp, sometimes unbearable pain occurs. The color of the skin changes and swelling appears.
- Damage to the ligaments - the pain is acute, swelling appears, mobility is limited, pain is felt when touched, it is difficult to walk on the leg.
- Damage to the meniscus - you can get such an injury even if you turn your leg incorrectly. In this case, after running, the knee hurts on the inside.
A damaged meniscus makes itself felt by painful sensations during physical activity, difficulties arise when going up and down stairs due to the accumulation of fluid in the joint capsule and the appearance of a tumor.
When providing first aid for injuries, apply cold to the sore spot, limit the load, make a tight bandage, and give painkillers in case of severe pain. Take the patient to the emergency room or call an ambulance.
Causes of Medial Knee Pain
Various factors cause medial knee pain, which varies from person to person. But sports injuries, falls, and sudden increases in knee activity are common causes of pain. The causes of medial knee pain in children may differ from those in adults. For example, patellar tendinitis, patellar subluxation, and Osgood-Schlatter disease are the most common causes of this pain in children. Additionally, the main causes of medial medial knee pain are related to anatomical injuries to the medial knee, some of which are described below.
1.Injury to the Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
This injury is generally recognized as the most important cause of medial knee pain. First of all, it is better to know what the “Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)” is. The MCL is one of the most important ligaments in your knee that connects your tibia to your femur. This ligament holds the knee stable and controls the lateral movement of the knees. A sprain or tear of this ligament is one of the main causes of internal knee pain that athletes, especially rugby players, often experience more frequently. This results in an MCL injury when the impact pushes the knee inward into the opposite knee. Additionally, various factors such as twisting the knee while skiing or falling can damage this ligament.
Symptoms of MCL Injury
Depending on the severity of the injury, you may experience mild or severe knee pain. If the blow is severe, you may not be able to walk or even touch the affected area. According to the experience of injured people, you may hear a popping sound during the impact and the area will swell, which does not vary from person to person. Knee locking and medial knee pain when bending are other common symptoms of medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury.
Possible treatments: knee brace, PRICE (protection, rest, ice, compression and elevation)
2. Rupture of the medial meniscus
What is Meniscus? The meniscus is a C-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure that acts as a shock-absorbing structure between the femur (femur) and the shinbone (tibia). There are two meniscus cartilages in each knee (one meniscus on each side), and a tear is one of the common causes of medial knee pain. Knee rotation and pressure can cause this injury, especially during sports activities such as football and basketball. This rupture is not limited to athletes, and older people may experience it when subjected to light impacts.
Symptoms of a medial meniscus tear
The cool thing about a torn meniscus is that you can hear the pop and continue walking without pain. But what about the day after the accident? You will likely wake up with pain and swelling, and the pain will gradually get worse. Other symptoms include:
- Rigidity
- Catch or lock
- Feeling imbalanced
- Sharp pain inside the knee
Possible treatments: Surgery, Exercise and PRICE
3.Osteoarthritis (OA)
Let's say you experience pain inside your knee without swelling while sitting, walking, or lifting up and down. In this case, you are more likely to develop osteoarthritis. This is a degenerative disease that usually causes loss of cartilage between joints in people over 50 years of age. As a result, you may have difficulty moving your knee and numbness when you first stand up for less than 30 minutes in the morning. Older people, women, obese people, gardeners or runners are at high risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Possible treatments: medication, acupuncture, injections and knee braces
4.Bursitis
Bursae are thin tissue sacs that contain small amounts of slippery fluid. The bursa allows tissue to move easily on both sides of the sacs. The bursa between the MCL and the three tendons in the knee is collectively called the " Pes Anserinus ". Sometimes, various causes such as osteoarthritis, obesity and medial meniscal tears cause excessive fluid secretion and inflammation of the bursa, which is called bursitis.
Symptoms of knee bursitis
- Pain approximately 2-3 inches below the knee joint
- Redness
- Difficulty walking
- Edema
- it hurts to lie on your thigh
- thickening of the bursa
Possible treatments: corticosteroid injections, strengthening exercises, rest and ice
5.Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
This condition is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the joints and usually causes internal knee pain. Arthritis affects various areas of the body, but the joints most affected are the elbows and knees. Severe pain and tightness in the knee in the morning are symptoms of arthritis that improve throughout the day.
6. Medial Plica Syndrome
Sometimes part of the synovial membrane folds into the joint space, forming a synovial fold. This fold, also called the plica, is located inside the knee and is very effective in stabilizing the knee joint. Excessive use of the knee in activities such as running, cycling or climbing and descending can cause friction, irritation and inflammation of the knee.
- Symptoms of Medial Plate Syndrome
- Hear a clicking sound when bending the knee
- painful rather than sharp or feverish
- uncomfortable sitting for a long time
- Severe pain when going up and down
- catching or snapping your knee when you bend your leg
Possible treatments: Anti-inflammatory drugs such as Celecoxib and Diclofenac.
All of these factors are significant causes of medial knee pain and associated symptoms. There are many other factors associated with this problem that orthopedic surgeons look for. Keeping your knee healthy should be very important to you because minor injuries can have a significant impact on your life. If you have one or more of the above symptoms, do not treat it arbitrarily and be sure to consult a doctor. You might be wondering when is the best time to see a doctor for internal knee pain treatment?
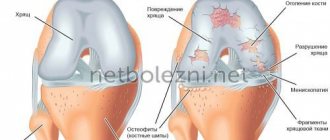
Arthrosis
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a disease associated with wear and tear of the cartilage layer. It develops slowly and appears in people with metabolic disorders and excess weight. In the initial stage, painful sensations arise only after physical exertion, then the pain intensifies and, finally, torments even at rest. The joint becomes deformed and its mobility is impaired.
Pain in the knee joint on the inside occurs in people who also suffer from flat feet or club feet. In this case, the load on the inside of the joint increases and it wears out more quickly.
Treatment is mainly aimed at eliminating pain. In the initial form, complete recovery can be achieved. For this purpose, drugs are used to nourish and restore cartilage. Massage, manual therapy and physiotherapeutic treatment are widely used.
Prevention
It is always easier to prevent pathology than to treat it later. To prevent pain on the outside of the knee, follow these rules:
- Never start training abruptly. Start with small loads and increase them gradually.
- During high physical activity (for example, competitions or intense training in powerlifting, long training in football, hockey), wear an elastic bandage on your knees.
- When running long distances, wear orthopedic shoes.
- Avoid gaining excess weight, as it creates additional stress on all joints, including the knee.
Arthritis
Arthritis develops when there is an imbalance in the processes of synthesis and degeneration in cartilage and bone tissue, which results in the destruction of cartilage. The main causes of the disease are injuries, inflammation of connective tissues and joints.
A characteristic feature of arthritis of the knee joint is the rapid onset of the disease with severe swelling, and the pain in the knee on the inside intensifies at night, when the joint is at rest. This progressive chronic disease occurs in waves, periods of remission alternate with exacerbations, which are provoked by physical activity or environmental factors. Growths called osteophytes may appear in the joint cavity. When a small piece is torn off, unbearable pain occurs.
Treatment of the disease is complex: correction with medications, physiotherapy, lifestyle changes. The patient is often prescribed:
- non-steroidal drugs for pain relief;
- anti-enzyme - to prevent the development of the disease;
- anabolic, promoting the restoration of damaged tissue;
- antispasmodics to relieve muscle spasms.
If therapy is ineffective, surgery is recommended. Knee replacement can completely eliminate arthritis.
Rheumatism of the knee joint
The joint apparatus of the knee begins to be affected by an inflammatory process in the synovial membrane: thickening occurs, swelling occurs, and fluid accumulates in the joint. Then the inflammation spreads to the cartilage tissue, changing its structure and leading to destruction. Subsequently, the destruction of bone tissue begins, leading to stiffness and immobility of the joint.
The patient experiences acute pain when bending the inside of the knee, visible swelling and redness. As it progresses, restrictions in joint mobility occur. The causes of the disease are most often previous streptococcal infections: otitis and tonsillitis, against the background of weakened immunity. The risk of morbidity is especially high in children aged 7 to 14 years.
In the treatment of rheumatism, antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticoids are used, and physiotherapeutic procedures also play an important role.
Treatment methods
Treatment tactics will depend on what kind of disease caused the pain in the outer part of the knee.
The possibility of a complete cure and the prognosis for recovery depend on the specific pathology that provoked the pain:
- If the outer side of the knee hurts due to iliotibial band syndrome, the prognosis is good. Complete relief from pain is possible.
- In case of injuries, it is also conditionally favorable. After complete healing, the pain goes away.
- The only injury that is very difficult to treat is a meniscus tear. Pain may remain even after recovery.
- Ailments such as bursitis and tendovaginitis are also completely curable.
- If the symptom arose against the background of osteoarthritis, the pain will periodically bother the patient during periods of exacerbation. The disease itself is incurable.
Relieving pain symptoms
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for symptomatic treatment. They have an analgesic effect. They are produced in the form of tablets or ointments.
Popular drugs in this group:
- Diclofenac;
- Nise;
- Dolaren.
Ointments without NSAIDs can also be used for pain relief, such as:
- Viprosal - based on viper venom.
- Capsicum with turpentine and camphor.
They have a warming effect that helps relieve pain.
However, they should not be used in the first days after injury. Ointments with a cooling effect - menthol ointment, menovazin, gevkamen - will be good helpers here.
Basic treatment
Treatment of various pathologies accompanied by knee pain:
| Pathology | Treatment methods |
| External meniscus tear | Applying a bandage to the knee, gentle on the joint Physiotherapy Chondroprotectors are medications that have a beneficial effect on cartilage tissue and promote its restoration. Physiotherapeutic procedures that improve blood circulation and speed up the healing process If conservative treatment is ineffective, then surgery is performed Surgical intervention can be carried out using 4 methods: stitching, cutting, complete removal, removal with replacement with an artificial one |
| Popliteal bursitis | Performing a puncture to remove effusion Physiotherapy – ultrasound therapy, laser therapy, shock wave therapy, magnetic therapy, electrotherapy are especially useful |
| Gonarthrosis (osteoarthritis of the knee joint) | Taking chondroprotectors Physiotherapy Exercise therapy is the basis of treatment |
| Tenosynovitis of the semimembranosus tendon | To eliminate inflammation - NSAIDs After its removal - physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises |
| External collateral ligament injury | Wearing an elastic bandage, which relieves increased stress on the joint and periarticular tissues, speeds up the healing process If a ligament rupture occurs, then only surgical treatment is possible - its stitching or plastic surgery |
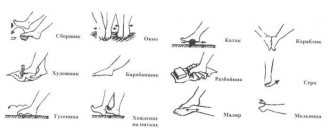
Click on photo to enlarge
Rickets
Rickets affects only children under three years of age. The disease is provoked by a lack of vitamin D in the body, which interferes with normal phosphorus-calcium metabolism. As a result, disturbances in the growth of bone tissue and weakening of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus occur. In a neglected state, the bones of the legs become bent and cannot withstand the load and flat feet develop. And from this, when walking, the child experiences pain in the knees on the inside and possible cramps in the limbs.
The main treatment is proper nutrition for the nursing mother and baby, frequent walks in the fresh air, massage and therapeutic exercises. Among medications, vitamin D, Calcium D3 Nycomed, and Ergocalciferol are used.
Inflammation of the knee tendons - periarthritis "crow's feet"
With periarthritis, inflammation of the periarticular apparatus occurs, while the joint itself remains unaffected. It occurs on the inside of the knee where the sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus tendons attach, forming a triangle similar to a crow's foot.
The cause of inflammation can be intense sports, excess weight, bruises and sprains, arthritis and arthrosis extending beyond the joint, and the presence of infection.
Knee pain on the back side occurs during physical activity or after intense physical activity. Walking calmly on level ground does not cause any discomfort. It should be noted that the painful sensations are concentrated only on the inner surface and do not spread to the entire knee. In the chronic course of the disease, pain occurs periodically.
For therapy, analgesics, short courses of glucocorticosteroids, ointments and gels are used.
What does Internal Knee Pain mean?
It may be important for you to know which parts of the knee are most susceptible to medial knee pain. So to make this clear, you first need to know where the medial side of the knee is. The medial sides of your knee point to the right side of your left knee, and the left side of your right knee points to the middle of your body. Thus, you will feel pain in these areas, which usually affects your daily activities. To better understand, it is best to have an overview of the anatomy of the internal parts of the knee.
- The quadriceps tendon connects the quadriceps muscle to the kneecap
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL)
- The medial meniscus is a thick, elastic, crescent-shaped band of cartilage attached to the tibia.
- A plique is a fold in the thin fabric that forms the joint of your knee.
- Between your bones and tendons, the bursa acts as a cushion and reduces friction.
These areas are among the most susceptible and vulnerable areas where internal knee pain is usually caused by damage or complications in one of these areas. Accidents, sometimes a little carelessness and poor lifestyle choices can easily damage your knee health. Who do you think experiences medial knee pain most often?
Everyone can experience knee pain throughout their lives and at different ages. For some people it is temporary and goes away after a while; for others it becomes a lifelong problem. Athletes and adults over 60 years of age are at high risk, while youth and children are at low risk in terms of susceptibility to injury. In general, the following people are more likely to experience internal knee pain:
- Footballers, skiers, rugby players. The estimated rate of knee pain in former football players was 52.2%, compared to 26.9% in the general population. (Reliable source)
- People who suddenly increase their physical activity
- Cyclists or breaststroke swimmers. because these people use their knees too much
- Older people due to osteoporosis or falls
But do not forget that anyone, young or old, can suffer from this disease, so you should take care of your health.
Baker's cyst
Baker's cyst is a tumor-like formation located in the popliteal fossa. This is a secondary disease after pathologies of the knee joint, which may include: injuries, damage to the meniscus and cartilage, arthritis, arthrosis and chronic synovitis.
The disease manifests itself as pain when bending on the inside of the knee, discomfort and the appearance of a tumor. When the knee is straightened, the cyst can be easily felt by palpation; over time, it disappears on its own or remains for several years.
Treatment is divided into conservative and surgical. With conservative therapy, a puncture is performed, pumping out the contents with a syringe, and then steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are injected into the cavity.
After such treatment, relapses often occur, and pain in the knee on the inside reappears. If inflammatory processes of the underlying disease occur, non-steroidal drugs, physiotherapy and drug blockade are prescribed. If flexion functions are limited and the cyst is large, surgical intervention is performed to excise it.
Associated symptoms
Various pathological conditions are accompanied by various additional symptoms, in addition to pain.
The nature of the pain may also differ.
Pathologies and symptoms:
| Disease | Signs and characteristics of pain |
| External meniscus tear | At the time of the injury, the pain is strong, sharp, mobility in the joint is limited Sometimes there is swelling The pain becomes less intense over time, but is still present |
| Popliteal bursitis | Slight tenderness in the outer part of the knee, swelling |
| Gonarthrosis (osteoarthritis of the knee joint) | The pain is localized not only in the outer lateral part of the joint, but throughout the entire knee There is also a feeling of stiffness and, later, limited movement. |
| Tenosynovitis of the semimembranosus tendon | Aching pain that intensifies when bending the knee Redness, swelling |
| External collateral ligament injury | If it is stretched or torn, you will experience pain, swelling, and limited movement. If it is torn, then in addition to the listed symptoms, there will also be increased mobility of the knee |
Meniscus injury
Two menisci - lateral and medial - are shock-absorbing pads between the bones of the thigh and lower leg. Their injury occurs when they move incorrectly: inexperienced athletes who do not follow safety precautions when doing alpine skiing, weightlifting, and overweight and elderly people often suffer.
When the meniscus ruptures, a click is felt in the joint and the knee begins to hurt on the inside side (where the meniscus is located), preventing you from bending and straightening the leg. To quickly relieve pain, apply cold to the injured knee and provide complete rest. Sometimes the pain goes away and the person can walk normally, but with physical activity it returns. The pathological process in the joint that has begun continues to develop.
Treatment can be conservative, including physical therapy and physiotherapy, but the problem is not radically solved. If the meniscus is damaged, surgery is prescribed to stitch it together or remove it. In modern conditions, the arthroscopic method is low-traumatic and does not cause postoperative complications.
First aid
If your knee hurts on the inside and you feel severe discomfort, then before consulting a doctor you should:
- Create rest for the lower limb.
- To reduce the load, lean on a cane.
- If an injury occurs, apply ice and try not to bend the limb at the knee.
- For inflammatory processes accompanied by joint pain, use painkillers “Indomethacin”, “Voltaren”, “Ibuprofen”, “Diklak gel”.
It is not recommended to do massage, compresses and baths.
When should you seek help?
Pain in the knee on the inside side can occur instantly and be a response to strong physical activity, incorrect movement or for no apparent reason, and sometimes it bothers you constantly or, conversely, periodically, from time to time. When should you see a doctor? A visit should be made when:
- any persistent or recurring pain;
- visible swelling of the knee;
- joint deformities;
- difficulty getting up on your feet;
- elevated temperature in the knee joint;
- increase in general body temperature.
Don't delay visiting a doctor. Timely treatment will lead to a quick recovery.