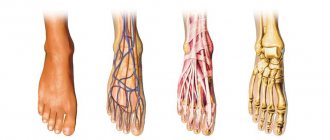
The most common areas of pain on the foot
Pathologies often develop in areas of protruding bones due to a number of factors:
- The projections are the attachment sites for large muscles. If the muscle is in hypertonicity, it pulls harder on the bone and tears its shell-periosteum. It is in the periosteum that pain receptors are located, but they are not normally found in the bone itself.
- There is no protective fat layer on the “bones”; only thin skin separates them from the environment. Any blow, even a small one, directly hits the same particularly sensitive periosteum.
- The more fat and muscle there are around, the greater the blood circulation in the bone. Where there is little other tissue around the bone, blood flow is weaker. And this in turn slows down regeneration and healing.
Typical sites of pain in the foot include the bony prominence of the ankle (ankle), the styloid process of the fifth metatarsal on the outside of the foot, and the head of the first metatarsal at the base of the first toe. All of them can disturb, become inflamed and affect gait. Despite the fact that each problem has its own characteristics, any pain in the “bones” can have very typical causes.
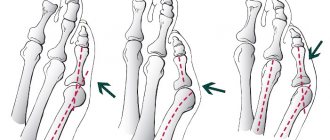
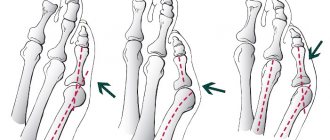
Valgus deformity of 1 toe (Hallux abducto valgus)
Surgical treatment:
Operations for hallux valgus have been known since the time of Hippocrates.
Throughout the history of orthopedics, there are more than 300 different surgical techniques for treating hallux valgus. Of course, many of them today are considered ineffective, many are very traumatic (sometimes crippling). These operational techniques are becoming a thing of the past, although it can be stated with regret that “old-time” operations are still widely used (our country is no exception). Well, let's not talk about sad things... After all, the 21st century is here! The choice of surgical treatment method depends on the degree of valgus deformity of the 1st toe and is always purely individual for each patient. It is an individual approach and careful preoperative planning that ensure a positive outcome of the operation.
In my practice of surgical treatment of feet, I used various types of surgical tactics for reconstruction of hallux valgus deformity of the 1st toe. At the beginning of his surgical career, he used operations performed only on the soft tissues of the foot, without sawing through the bones or using any fixators (for example, the MacBride operation). But such operations turned out to be completely ineffective, since there was a high percentage of relapses (repeated deformities of 1 finger).
Mini-invasive (percutaneous, percutaneous) surgery for hallux valgus deformity of the 1st toe: This method of surgical treatment of hallux valgus is based on the elimination of hallux valgus deformity of the 1st toe without skin incisions (mini-punctures). The essence of this technique: the “bone” is removed from small punctures using bone drills; in certain places, the bones of the foot are sawed off, thereby reducing the deformation of the first toe. This technique does not require any internal fixation (no screws, no knitting needles, no staples).
These are low-traumatic operations with a high cosmetic effect (no wounds or scars).
After analyzing the results of the operations, I came to a disappointing conclusion: it is impossible to completely eliminate the deformity of the first toe, make the foot narrower and more graceful with the help of such operations. It turns out that this is just a cosmetic semi-operation; in the future, the growth of the “bone” is inevitable... Therefore, I refused to use a mini-invasive technique when reconstructing the hallux valgus deformity of the 1st toe; I believe that this method does not provide a 100% correction effect for hallux valgus. Yes, I use minimally invasive techniques in forefoot surgery. They have proven themselves to be excellent for deformities of small toes (hammer deformities of 2-3-4 toes), metatarsalgia, corns, or in combination with open operations for severe deformities of all toes.
Well, now about removing the “bone” with a laser!!! I didn’t want to write about this, but half of the patients, having read on the Internet, ask about this “wonderful” method of surgery... I want to reveal a terrible secret and convey it to everyone: laser surgery to remove a “bone” on one finger does not exist!!! This is either PR or a laser called a mini-invasive method for reconstructing hallux valgus deformity (I wrote about this method above).
In principle, in medicine there is laser surgery, which is used, for example, in ophthalmology, dermatology, urology... But sawing through a bone with a laser is already fantastic! In a word, STAR WARS! Therefore, my dears, do not believe everything that is written on the Internet!
Causes of pain in a bone in the leg
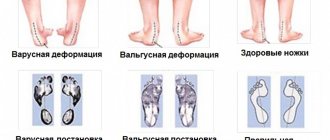
Most chronic foot diseases are caused by mechanical imbalances. The innate position of the bones is designed for their proper use and loading. Diseases, overload, and incorrect shoes adversely affect the position of the foot and lead to pathologies.
Excessive pronation, that is, “rolling” the entire foot inward, overloads the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Over time, a “bone” or “bump” grows there - the body’s attempt to increase the area of contact of the joint with the surface. Pronation also changes the condition of the ankles: the inner ligaments are stretched and the outer ones are compressed.
The appearance of pain in the area of the styloid process of the metatarsal bone along the outer edge of the foot is an indicator of overload of the lower leg muscles. The condition is characteristic of hypopronation or supination - “rolling” the foot outward. If the position of the foot is not corrected in time, the bony protrusion may even come off due to awkward movement or constant microtrauma.
Effective Treatments
The basis for treating problems with protruding bunions is correcting the position of the foot to reduce the load on its individual areas. There are active and passive correction. Active includes improving muscle function through exercises, passive includes any orthopedic devices to change position or eliminate symptoms. According to reviews from patients and clients, the following help best:
- Exercises on a balance pad. Strengthen the muscles of the lower leg and foot, improve blood circulation and tone for any foot problems. An indispensable method of active correction.
- Walking on orthopedic mats. Stimulates the active points of the feet, engages proprioception - the correct sense of the position of body parts.
- Wearing orthopedic insoles. Factory insoles are useful for prevention, and individually made insoles are useful for treatment.
- For pain at the base of the first toe, valgus splints are indispensable, and in the ankles - special ankle braces. For many problems, special products have been developed that are very effective when selected correctly.
- Massagers act directly on pain. Mats and rollers with needles, embossed papillae, and protrusions stimulate mechanoreceptors and block the conduction of pain impulses.
You can solve the problem of pain in the bones at Medtechnika Orthosalon. After consulting your doctor, our consultants will select the most appropriate solution, taking into account the doctor’s recommendations, the characteristics of the problem and the condition of the legs. Each salon has foot analysis equipment and a full range of effective medical products.
With us you can also use the service of individual custom-made insoles:
Why does a formation occur on the top of the foot?
The appearance of a lump on the top of the foot is associated with existing general and local risk factors that have a long-term effect on the body.
In women, the main reason is the constant wearing of tight, narrow-toed shoes with heels up to 15 cm in height. The load is distributed unevenly: the pressure of the entire body weight falls on the fingers. This leads to deformation of the foot, causing the development of curvatures and growths. With prolonged high loads, the metatarsal bones diverge, horizontal flat feet develop, and compactions occur.
Diagnostic methods
To effectively treat the pathology that leads to the formation of a bunion, to get rid of any protrusion that makes the top of the foot uneven, it is necessary to accurately determine the disease in the early stages.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following studies are necessary:
- x-ray of the foot;
- Ultrasound of a changed joint is an additional diagnostic method used to examine a child;
- CT;
- MRI;
- laboratory tests to exclude gout, rheumatism, arthritis and arthrosis of other etiologies.
Prevention
Even after successful treatment, a person may develop a bunion on their foot again. This is due to many factors. In order to prevent repeated curvature of the foot bones, it is recommended to adhere to several mandatory rules:
- Wear comfortable shoes made from natural materials with low heels (4–6 cm). Use a soft liner where the cone comes into contact with the shoe.
- During heavy physical activity at work, take breaks to rest your legs.
- Use orthopedic shoes that reduce the load on the foot, since the foot is securely fastened with rigid fixing inserts.
- If you have a sedentary lifestyle, do gymnastics: regularly do a set of exercises to strengthen muscles and ligaments.
- In case of traumatic injury, be sure to consult a doctor.
- To improve blood circulation, walk more barefoot on sand, small pebbles, and use special massage mats in winter.
- Take multivitamins and calcium in courses.
- Eat right: include vegetables, fruits, fish in your diet (it contains substances that are beneficial for joint function).
- Begin treatment of diseases of bones, joints, and blood vessels in the early stages.
To prevent deformities, it is important to maintain foot hygiene. If discomfort, pain or lump formation occurs, it is recommended to consult a doctor promptly. Only a specialist will help cure the pathology in a short time and explain how to prevent the development of complications.
Types of formations
The localization, structure and clinical manifestations of neoplasms on the instep of the foot are different and depend on the causes that caused them. Several types of pathological changes in the upper part of the foot have been described:
- A hygroma is a cyst on a tendon that can grow in the middle of the bend of the foot.
- Exostosis is a single or multiple benign growth on the surface of the bone. It can develop and grow from cartilage tissue, which ossifies over time. Often appears on the ankle. Passed on by inheritance.
- Lipoma is a wen.
- Fibroma is a neoplasm of connective tissue.
- Thrombophlebitis is inflammation of the wall of a venous vessel.
- Keratoderma (diffuse or focal) is a violation of keratinization of the skin, predominantly the growth of the epidermis occurs on the sole.
- Phlegmon is an acute purulent-inflammatory phenomenon in soft tissues.
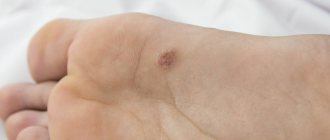
- A wart is a disease caused by the human papillomavirus.
- A callus is a keratinized area of skin that is the result of prolonged friction or pressure from shoes on the foot.
- Keller's disease is a growth on the bend of the foot that occurs due to progressive degenerative processes in bone tissue. Complicated by aseptic necrosis.
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is inflammation of the vein walls followed by the formation of a blood clot. It is characterized by compaction and hyperemia along the venous vessels with the development of dark blue nodules. When pressure is applied, pain occurs, followed by swelling and a local increase in temperature.
Thrombophlebitis is a common pathology and is one of the complications of varicose veins. After a stroke or major surgery, when the patient does not get out of bed for a long time, the pathology develops over several days. A lump on the rise is a characteristic symptom of thrombophlebitis. In addition to the tumor developing as a result of inflammation of the vein, other clinical signs appear:
- hyperemia or cyanosis of the skin;
- pain when pressed;
- pigmentation associated with impaired blood circulation at the site of the affected vein.
Such symptoms are characteristic of inflammation and the development of a blood clot in the superficial veins.
Deep vein thrombophlebitis develops acutely and requires emergency hospitalization. The pathology is treated using therapeutic methods, but in some cases surgical intervention is necessary.
Indications for surgery are:
- ascending inflammation that spreads along the veins;
- high probability of developing PE (pulmonary embolism);
- a history of severe attacks of acute thrombophlebitis;
- detachment of a blood clot with the likelihood of it reaching the site of reunification of the superficial veins with the deep ones.
The operation is contraindicated if:
- severe vascular or cardiac pathology;
- pregnancy at any stage;
- infectious skin inflammation (erysipelas, eczema);
- varicose veins in the later stages.
Hygroma
Hygroma is a benign formation filled with transparent contents of a jelly-like consistency (mucus or fibrin). It is a cyst associated with a tendon or joint capsule. Bounded by its own strong connective tissue membrane. It looks like a dense lump, rising in the middle of the ankle, ranging in size from 3 mm to 7 cm. It is formed under the influence of various factors, including heredity. Frequent causes are constant physical activity (in athletes), traumatic joint damage.
When a cyst appears, there are complaints about an unaesthetic appearance and discomfort in the leg. If the hygroma reaches enormous sizes, it compresses small blood vessels and nerve endings.
Due to progressive tissue compression, inflammation of the tendon and joint capsule, the following occurs:
- pain in and around the lump when pressing or walking;
- stiffness of movement (prevents you from climbing stairs and bending your foot when walking calmly);
- hyperthermia (temperature rise to 40°C) with developing purulent inflammation.
Hygroma develops as a result of an inflammatory lesion:
- synovial membrane of muscle tendons (tenosynovitis);
- mucous membrane of the periarticular bursa (bursitis).
Due to frequent injuries and disruption of the integrity of these membranes, the epithelium, consisting of secretory cells, is replaced by fibrous tissue. A scar is formed: it fills the resulting defect, but cannot withstand high pressure, heavy loads and spreads beyond the capsule. Gradually, a hygroma forms - an additional cavity. In the structure of its walls there are 2 types of pathological cells:
- fusiform - form a hygroma capsule;
- spherical - secrete fluid that fills the cyst.