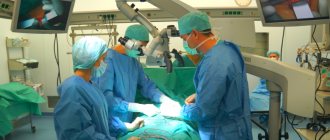
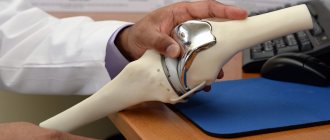
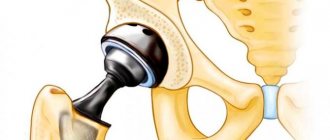
Arthrodesis is a surgical operation aimed at restoring the supporting ability of a limb affected by a particular disease or susceptible to injury. Among them it is customary to highlight the following:
- pathological dislocations;
- improperly healed fractures;
- complications of pathologies that lead to dysfunction of the limbs and pronounced pain (arthrosis, arthritis, etc.).
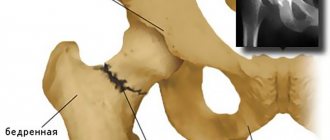
The arthrodesis operation involves complete immobilization of the joint by fusing adjacent bones. In this way, artificial bone ankylosis is created, in which the joint is fixed in the most favorable position.
At CELT you can consult an orthopedic traumatologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Arthrodesis of the joints of the limbs - 150,000 - 200,000 rubles.
Indications
Arthrodesis is performed if the following indications exist:
- Dislocations with displacement.
- Severe stage of arthrosis with decreased joint mobility.
- Incorrect healing of bones after a fracture.
- Deforming arthritis.
- Floppy joint syndrome.
- Inflammatory processes in the joint capsule.
- Clubfoot.
Contraindications
- Chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Age up to 12 years or over 60 years.
- Allergic reaction to local anesthesia and general anesthesia.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Joint diseases in the acute stage.
- Lesions of the joint capsule with a large accumulation of pus.
- Increased thrombus formation.
In what cases is endoprosthetics indicated?
The upper ankle joint, formed from the ankle joint itself, the tibia and fibula, is susceptible to arthrosis. In advanced stages, patients suffer from chronic pain and are unable to move normally. If conservative therapy fails, they are recommended to undergo upper ankle joint replacement. After operation:
- the pain subsides;
- gait normalizes, although it is impossible to completely restore mobility;
- the patient can perform daily tasks again.
About 90% of patients are satisfied with the results of ankle replacement
Types of ankle arthrosis
Arthrosis of the ankle occurs not only due to age-related changes in the joints. It can be triggered by cartilage injury, sprained ligaments, valgus flatfoot, and rheumatism. Osteoarthritis is also caused by a crooked position of the leg axis, metabolic disorders, rheumatism and other pathologies.
There are several types of arthrosis of the ankle joint. Depending on its type, the patient is selected a suitable method of surgical intervention.
- With concentric arthrosis, the talus bone is located in the center.
- When eccentric, it is displaced.
- There is also rear and front centering.
- Valgus and varus arthrosis.
If the disease is accompanied by bone necrosis and has reached an advanced stage, endoprosthetics is pointless. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor makes a decision, assesses the condition of the ligaments, the position of the hindquarters and arch of the foot: surgery is not always indicated and does not help everyone.
You need to seriously prepare for ankle replacement surgery.
Advantages and limitations of the method
The widespread use of arthroscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of wrist pathologies is facilitated by the following advantages of this method:
- the ability to observe the problem area from the inside, which facilitates the diagnosis of diseases and surgical procedures;
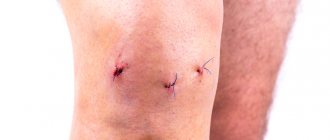
- minimal damage to healthy tissue and, therefore, a short rehabilitation period;
- small size of incisions, after healing of which barely noticeable scars remain;
- low risk of developing postoperative complications (bleeding, inflammation, etc.)
The complexity of performing arthroscopy of the wrist joint places higher demands on the qualifications of the doctor and the technical equipment of the clinic in which the operation is performed. Accordingly, the price of this service increases.
What are the treatment options?
For ankle arthrosis, the following types of joint replacement are practiced:
- Installation of a titanium prosthesis with a movable polyethylene core. This option is suitable even if the cartilage is completely worn out. The technology of ankle replacement has greatly improved over the past 10 years and has gradually begun to replace the “gold standard” (arthrodesis).
- Arthrodesis is therapeutic immobilization to relieve pain when putting weight on a joint. After surgery, gait is disrupted and the load on the hip and adjacent ankle joints increases. The rehabilitation period is at least 4 months. Arthrodesis comes to the rescue if endoprosthesis replacement is contraindicated.
- Osteotomy is a modification of the talus and calcaneus so as to move healthy cartilage to the area of the main load and preserve the joint.
Which is better – ankle replacement or arthrodesis? The expert’s reasoning is in the video:
Arthrodesis of the subtalar joint
Indications for arthrodesis of the subtalar joint are pathologies and lesions that can ultimately cause disability. These include:
- fractures accompanied by severe pain;
- fracture-dislocations due to a pathology such as arthrosis of the talocalcaneal joint;
- a whole range of orthopedic diseases, from clubfoot to foot deformities.
Surgical intervention in this case is aimed at the following:
- eliminate signs of foot deformity;
- eliminate pain;
- restore the functionality of the foot.
The positive effect of the operation is as follows:
- absence of pain symptoms;
- minimal shortening of the limb, or even its complete absence;
- the ability to wear regular shoes;
- good appearance of the lower leg after surgery.
Features of the modern approach to ankle replacement
During endoprosthetics, a small part of the talus is removed, and the cancellous bone tissue fuses with the surface of the endoprosthesis. The denser the bone, the more stable the prosthesis will be.
In recent years, the possibilities of endoprosthetics have expanded, and surgical methods for treating osteoarthritis have become more progressive. Orthopedic surgeons resort to accompanying measures for improved fixation of the prosthesis. These include correction of the support, plastic surgery of the tibial collateral and external ligaments, refixation and tightening of ligaments, and other operations that improve stability in a standing position, with maximum load on the prosthesis. Similar events are carried out several months before endoprosthetics.
In order for the prosthesis to last as long as possible, at the preparatory stage, surgeons eliminate deformations resulting from accidents and injuries. The more deviations of the axis from the norm, the faster the wear of the prosthesis will occur. Therefore, doctors strive to correctly align the hindfoot and get rid of deformities.
Our doctors
Samilenko Igor Grigorievich
Traumatologist - orthopedist, doctor of the highest category
24 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zubikov Vladimir Sergeevich
Traumatologist-orthopedist, Doctor of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category, professor
44 years of experience
Make an appointment
Marina Vitaly Semenovich
Traumatologist-orthopedist, head of the minimally invasive traumatology and orthopedics service
Experience 36 years
Make an appointment
Poltavsky Dmitry Ilyich
Traumatologist-orthopedist
Experience 28 years
Make an appointment
How modern ankle endoprostheses work
Previously, patients had metal prostheses installed that did not adhere well to cement and did not give the desired result. Today, orthopedic surgeons use only third-generation prostheses, which completely fuse with the bone and are securely fixed, providing the joint with natural biomechanics.
- A special metal cover is placed on the talus bone.
- The surface of the tibia is covered with a metal plate.
- The third component of the prosthesis is a freely moving polyethylene core.
You will be able to drive a car no earlier than 2 months after surgery.
Rehabilitation
After ankle arthrodesis, starting from the first day, exercise therapy classes are prescribed. Exercise prevents muscle atrophy, prevents blood clots, and eliminates congestion in the lungs. With prolonged immobilization and little activity of the patient, the results will be disastrous.
At first, exercise therapy consists of breathing exercises. The patient also performs isometric exercises that help strengthen the thigh and calf muscles. Classes are conducted under the supervision of a specialist. Over time, the load increases and new exercises are added.
During rehabilitation, drug treatment is prescribed:
- drugs against the development of infections;
- symptomatic remedies;
- drugs against thromboembolic complications.
Starting from the second day, the patient is allowed to take a vertical position. You can walk using crutches; putting pressure on the damaged surface is not allowed. Only when the first signs of bone fusion appear (after about 6 weeks) is axial load on the leg possible. A person will be able to walk normally 4-6 months after surgery. After 6-12 months, removal of metal structures is prescribed. Internal fixators do not require removal. Full recovery occurs after 15-18 months.
To speed up tissue healing, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed: UHF, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy.
How is the operation performed?
Endoprosthesis replacement is performed under general or local anesthesia. The patient lies on his back. The leg is tightened with a cuff to prevent the flow of blood (if the operation is protracted). To obtain an instant image, the surgeon uses a mobile X-ray device under a sterile coating, which allows you to monitor the progress of the operation and the localization of the prosthesis.
- The surgeon makes an incision along the front of the joint and extends it down to the back of the foot.
- The tendons above the joint are moved to the side.
- The joint capsule is opened and part of the bone tissue is removed to get a good view.
- Using an X-ray machine and special instruments, the axis and position of the hindfoot for implantation are determined.
- The talus is covered with a metal cap (there are metal pins inside it that allow movement).
- The surface of the tibial joint is covered with a protective metal plate, and both components are also covered with a special layer for reliable fusion of the bone tissue.
- A movable sliding core is installed.
After endoprosthetics, the patient spends 5-7 days in the hospital
The essence of the method
The wrist joint is formed by 8 small bones arranged in 2 rows, as well as numerous ligaments that provide flexion and extension of the hand, and its rotation around the longitudinal axis. Such a complex design significantly complicates the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies using indirect methods - MRI, radiography, external examination, etc. Therefore, the “gold standard” is arthroscopy of the wrist joint - a minimally invasive surgical operation that allows you to observe the problem area from the inside.
The procedure is carried out using an endoscope (arthroscope) - a thin surgical instrument that is inserted into the cavity of the affected joint through a small (up to 1 cm) incision (port) in the covering tissues. It is equipped with an optical system or a miniature camera that transmits a video signal to the monitor, as well as a backlight.
With the help of an endoscope, the surgeon can directly observe all elements of the joint structure, such as bones, ligaments or muscles.
Atroscopy has been practiced in medicine since the beginning of the 20th century, but such an operation on the wrist joint was first performed only half a century later, and it became widely available to surgeons already in the 90s. This is due to the high complexity of the joint itself, which required a more delicate approach and, therefore, the use of high-precision tools.
The following types of arthroscopy differ in purpose:
- Diagnostic.
It is carried out in cases where the cause of the pathology of the wrist joint cannot be accurately determined using indirect methods (MRI, CT, radiography, external examination), as well as when conservative treatment is ineffective. During diagnostic arthroscopy, the surgeon inserts only the arthroscope into the joint cavity, since the main goal of this operation is to make an accurate diagnosis, and not to treat the disease. - Therapeutic.
This operation is performed for surgical treatment of already identified pathology. The doctor makes several cuts in the skin over the joint. Through one of them, he inserts an arthroscope to observe the problem area and control his actions. The remaining ports are intended for the introduction of a thin arthroscopic instrument, which is used to perform surgical manipulations (for example, excision of cartilage) and a cannula - a hollow, blunt-nosed needle for supplying irrigation fluid into the joint cavity, increasing the intra-articular space for more convenient surgery.
The introduction of arthroscopy into medical practice also had general scientific significance. With its help, doctors received a more accurate understanding of the structure of the wrist joint and its biomechanics. Thanks to this, it was possible to develop more accurate, effective and gentle methods of treating diseases of this joint.
Is it possible to play sports with a prosthetic ankle?
After endoprosthetics, the patient is given a number of restrictive recommendations. The most important thing is to avoid lifting weights over 20 kg. It is advisable to wear special shoes that will provide stability when walking, especially at first. During the recovery period, physiotherapeutic procedures and lymphatic drainage may be prescribed.
At the end of the recovery period, as a rule, the following is allowed:
- ski;
- swim;
- ride a bike;
- jog;
- go trekking;
- to play golf.
After endoprosthetics, you will have to forget about football, tennis or high-speed slalom
Let's sum it up
Arthroscopic operations are effective for stage 2-3 gonarthrosis, when the axis of the lower limb is preserved. They allow you to improve the functional state of the knee and temporarily get rid of the symptoms of arthrosis. But most likely in a few years the knee joint will still have to be replaced. Therefore, arthroscopy should be considered only as a temporary measure to postpone arthroplasty.
Patients with advanced osteoarthritis should consider other surgical treatment options. The most effective operation in this case is total knee replacement.
What are the forecasts?
Despite the latest operating technologies, the prognosis is not very encouraging. In 90% of cases, the prosthesis lasts no more than 8 years. Repeated operations are performed infrequently - only in 6-8% of cases. This means that after this time the patient will again experience pain and remember limited mobility.
There are also complications after endoprosthetics. The wound over the new prosthesis does not heal quickly, the lower leg swells, suppuration, the formation of blood clots and thrombosis are not uncommon. Sometimes the prosthesis spontaneously loses its fixation, sags and wears out unexpectedly quickly. Therefore, experienced doctors recommend that patients think carefully before deciding to undergo surgery. In many cases, you can get rid of pain and restore joint mobility with the help of a synovial fluid prosthesis, without surgery.
Arthrodesis of the knee joint
An operation such as arthrodesis of the knee joint is practiced only in extreme situations. Indications:
- severe deforming arthrosis, accompanied by severe pain;
- instability of the knee due to paralysis of the femoral muscles.
The rehabilitation period in this case depends on the individual characteristics of the body and is carried out in a hospital. Contraindications to the procedure include:
- age under 12 and over 60 years;
- the danger of the appearance and development of inflammatory processes in the area of surgical intervention;
- the presence of fistulas of non-tuberculosis nature.