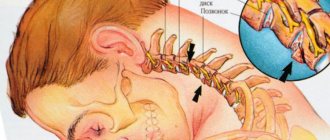
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the spine, characterized by compression of the intervertebral discs and their nuclei, resulting in deformation of the spine and impaired mobility. The disease is accompanied by pain, and in the absence of proper treatment, it significantly worsens the quality of life.
Osteochondrosis can develop in one or more parts of the spine. The type of disease that affects the cervical spine is called cervical osteochondrosis.
Description of the problem
- The disease begins with dehydration of the nuclei of the intervertebral discs; as a result, the nuclei become flattened, the vertebrae move closer together, and the spinal column itself “settles.”
- At the next stage of the disease, spondylolisthesis occurs - displacement of the cervical vertebrae, ligaments and muscles change their position. Neck mobility is limited and pain appears.
- The third stage of cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by the appearance of intervertebral protrusions (hernias) and the occurrence of arthrosis.
- At the fourth stage of cervical osteochondrosis, osteophytes appear - bone growths, with the help of which the body tries to compensate for the lost support function. The spine is practically immobilized.
What is osteochondrosis?
Content
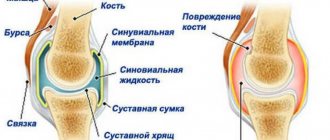
The spine is made up of vertebrae, 24 of which are involved in almost all movements of the body. It is divided into cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions. There is a hole inside the vertebra. The openings of all the vertebrae on top of each other form a canal that contains the spinal cord. Between the individual vertebrae there are small openings through which nerves from the spinal cord reach the body.
The stability of the spine is maintained by ligaments, tendons and many muscles along the vertebral bodies.
To buffer shock and vibration, intervertebral discs are located between the vertebrae. They consist of a gelatinous core and a continuous fibrous ring. Like all organs, intervertebral discs are subject to degenerative changes or, more simply put, signs of wear. They begin as early as age 30. The jelly-like core loses liquid, this leads to loss of strength of the MD. As a result, the distance between specific vertebrae decreases, and the spine as a whole becomes more unstable. To restore stability, the vertebral bodies form small bony edges (ostephytes) on the side.
Degenerative changes in the spine are among the most common symptoms in the musculoskeletal system worldwide.
The meaning of exercise therapy
Exercises with a stick are one of the effective methods of preventing and combating osteochondrosis. Exercise therapy is especially effective in the early stages of the disease. In order to prevent further damage to the spine, you need to perform the exercises prescribed by your doctor with a gymnastic stick regularly.
Therapeutic exercise helps both relax tense back and neck muscles and strengthen them. The spine takes a physiologically correct position, pain decreases, and posture improves. Thanks to exercises with a stick:
- blood supply to the brain is normalized;
- fatigue goes away;
- one feels a surge of strength and energy.
The best exercises with a gymnastic stick
The main advantage of training with a stick is that it is almost impossible to get injured. To do this you need to try very hard. We can say that when working with body steam, you perform warm-up exercises of increased complexity. Accordingly, there is no need to warm up before such a workout.
Moreover, such training is available to people of any gender and age. So your problems with the spine and excess weight are completely solvable.
The most effective exercises with a gymnastic stick:
- Body twists are the simplest but most beneficial movement for the spine. Place the body pair on your shoulders and grab it with your hands. Straighten your back and place your feet shoulder-width apart. Rotate your body as much as possible. Don't forget to breathe properly.
- Bringing a stick behind your back is an exercise that gymnasts often perform. You need to take the body pair with a wide grip, lift it above your head and begin to lower it back. At the lowest point, your hands with the stick should be behind your back at the level of your buttocks. This movement is excellent for developing the elasticity of your shoulder joint.
- Ab crunches are performed in the same way as usual. Only here you must put the stick on your shoulders and grab it with your hands. This allows you to exclude all muscles from work except the abdominals. This exercise is not recommended for beginners. However, for people with a high level of physical fitness, it is very effective.
- Squats and lunges with the body pair raised up. When your arms are raised and you are holding a body pair in them, your back automatically becomes straight. This means that the technique of doing squats and lunges becomes ideal, and most importantly, does not harm your spine.
- Bend forward, hands with a stick below. In the starting position, your hands should be behind your back and hold the body pair. Your task is to lean forward and stretch your arms up as much as possible. This allows you to develop flexibility in your back and lumbar joint.
- Press up - here we need a rubber band, which can be purchased complete with a body steamer. You tie it to a body pair. After which, you stand on it and take the stick in your hands. In the starting position, you hold it at chest level. Your task is to squeeze it up like a barbell. This exercise will increase your muscle strength and reduce the risk of shoulder injury if you are involved in bodybuilding.
- Raising the stick forward is also performed with a rubber band. The difference from the previous exercise here is that at the bottom point you hold the body pair at hip level. And at the top point you should lift them so that they are parallel to the floor. An excellent exercise for the muscles of the arms and shoulders.
- Side bends are a very simple, but at the same time effective exercise. It perfectly accelerates blood in the lumbar and pelvic areas. Your task is to hold the body pair at the top with straight arms, and bend to the sides as low as possible. Mentally, you should strive to reach the end of the stick to the floor. This is almost impossible, but you should think about it to maximize the flexibility of your lower back and obliques.
- Hyperextensions - here you will need the help of another person. Your task is to lie on a bed or other support so that your body is under load and your legs are supported. Your companion should hold your feet. And you must bend forward and then rise. This exercise perfectly develops the lower back muscles. Doctors recommend performing it for people who have problems with the spine. When performing this exercise with a stick on the shoulders, all muscles will be isolated, and the movement will be carried out only due to the efforts of the lumbar muscles.
- Shoulder rotations - take the body pair in your hands. At the lowest point, it should be at the level of your stomach, and your arms should be bent at the elbow joint at an angle of 90 degrees. Your task is to raise your hands. At the top, your forearms should be parallel to the floor. This exercise develops the rotator cuff, the most traumatic part of the shoulder joint. The average weight of a body pair is 1 kilogram, which is enough to perform this exercise.
Naturally, these are not all the exercises that can be performed with a stick. But they are the most effective. If these are not enough for you, watch a video on the Internet, where a professional will tell you about other exercises and the nuances of performing them.
When can it be used?
The doctor prescribes exercise therapy for spinal osteochondrosis, taking into account the individual data about the patient’s disease. You can perform exercises only in the remission stage, that is, when there are no symptoms. Before starting, you need to measure your blood pressure and pulse, especially in elderly patients. If the indicators deviate from the norm, you should not engage in exercise therapy.
Indications
Exercise therapy is prescribed as therapy and for the prevention of disease in patients:
- Suffering from osteochondrosis of the thoracic, lumbosacral and cervical spine.
- Elderly people.
- Those with spinal injuries.
- Working at a computer.
- People with weakness of muscles and ligaments.
- Having flat feet.
Contraindications
You cannot engage in exercise therapy for certain diseases, so as not to cause deterioration of the patient’s condition and complications. Such diseases include:
- Malignant tumors and metastases.
- Hypertension.
- Thrombosis.
- Increase in ESR.
- Heat.
- Bronchopulmonary diseases.
- Threat of bleeding (internal or external).
Some patients may exercise with limited exercise . These are people suffering from diseases such as:
- Mental disorders.
- Physical disability.
- Lesions leading to deformation of bone tissue.
- Aortic aneurysm.
Pregnant women can perform physical therapy exercises depending on the duration of pregnancy, the characteristics of its course and the patient’s well-being.
You cannot engage in physical therapy if there is a threat of miscarriage, placenta previa or fetal growth retardation. In case of polyhydramnios and severe toxicosis, you should also refrain from doing exercises.
What is osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that affects the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs. It can be cervical, thoracic and lumbar, depending on location. Lumbar osteochondrosis is the most common. But the most difficult is the complex lesion, which is difficult to treat.
The disease has four stages:
| First stage | involves mild symptoms, the patient feels a general malaise, often attributing it to other diseases. |
| Second stage | accompanied by severe pain, the cartilage tissue in the spine begins to deteriorate. Symptoms bring discomfort, and the person consults a doctor. |
| Third stage | suggests more serious changes in the spine, a hump or curvature occurs. |
| Fourth and final stage | these are irreversible changes. A person can feel severe pain even with minimal movements. |
The sooner you identify and begin to treat osteochondrosis, the easier it will be to do this. Therapy must be comprehensive. It usually includes special therapeutic exercises.
General recommendations for implementation
- You need to do physical therapy in a well-ventilated area, or better yet, outside.
- Clothing for classes should be loose and not restrictive.
- You cannot exercise during periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- If during the exercise the patient feels pain or his health worsens, he must stop the exercises.
- The load increases gradually, as does the amplitude of the movements.
- It is important to control your breathing while doing exercises.
- Be sure to coordinate exercise therapy sessions with your doctor.
Subtleties
Exercise therapy exercises should be performed smoothly and without sudden movements. This pace helps to relax and stretch “tight” muscles. A gymnastic stick holds the patient’s hands in the desired position and prevents them from moving to the sides. Thanks to this, the load on the muscles is distributed correctly.
To complicate the workout, over time, you can place your hands closer to each other. It is important to hold the gymnastic stick correctly, your arms should be straight. The result of the exercise directly depends on the technique of execution.
How to do physical therapy for the elderly and children?
For elderly and young patients, the load when exercising with a gymnastic stick should be small and feasible. When performing exercises for people of retirement age, you need to:
- Monitor blood pressure and pulse readings.
- Consider the patient's general well-being.
- Consider the presence of chronic diseases.
- Make movements smoothly, without jerking.
- Maintain a small range of motion.
- Start with a small number of repetitions of the exercise, gradually increasing to 20 repetitions.
The purpose of exercise therapy in old age:
- development of joints and muscles;
- maintaining spine flexibility;
- increased endurance.
Don't focus on strength exercises. To avoid injury, the load should be as gentle as possible.
The rules for conducting exercise therapy classes for children are similar. When performing exercises, you need to monitor the signs of fatigue and the child’s well-being. Young children do not understand the purpose of doing the exercises. You can conduct classes with them in the form of a game or a fairy tale. The emphasis is on increasing endurance, strength, flexibility, and improving coordination of movements. At the initial stage, training time should not exceed 20 minutes , then you can gradually increase the duration of the session.
A little about the gymnastic stick
A gymnastic stick is the simplest sports equipment that allows you to correct a crooked spine, strengthen your lower back and perform complex gymnastic elements. It should be used in training during classes:
- Pilates.
- Gymnastics.
Pilates is a system of exercises that allows you to get muscular joy.
It should not be confused with ordinary muscle tension in bodybuilding. Have you ever felt a pleasant sensation throughout your body after doing physical exercise? This is exactly the effect Pilates gives. To perform some exercises in Pilates, you need a gymnastic stick. Some elements in gymnastics require increased flexibility and mobility of your shoulder joint. This can be achieved using a gymnastic stick. Therefore, if you decide to take up gymnastics, you first need to purchase it.
Its cost usually does not exceed 300 rubles. If you buy a complete set, which includes a rubber band and a massage surface, then its price will not exceed 1 thousand rubles. You can buy it at any sports store. The material of the product will not affect the quality of your training in any way, so you can save money on it.
The length of such sticks varies from 70 to 120 centimeters. You can buy a stick of any length to suit your taste. However, it is better to purchase a projectile with the maximum length. Because thanks to this, you will have access to many more exercises.
Overview of gymnastics classes
Exercise therapy classes for osteochondrosis consist of a warm-up, main and final parts. At the warm-up stage, exercises are performed to warm up the muscles, joints are developed, and the body is prepared for the load. The basic position is standing, feet shoulder-width apart, hands on the belt. The range of movement should be small.
The main part includes exercises using a gymnastic stick, which are performed standing or lying down:
- bends;
- body rotations;
- abduction of arms with a gymnastic stick forward;
- up or down;
- placing a gymnastic apparatus behind the back.
The final part of the physical therapy exercise complex consists of stretching and muscle relaxation exercises.
Find out more about the types of exercises for SCH that you can do at home here.
Charger
During the preliminary stage - exercises or warm-up - perform the following exercises:
- The chin stretches up, then drops.
- The head describes a semicircle from one shoulder to the other.
- Rotation of the arms in the shoulder joints.
- Rotation of the arms at the elbow joints.
- Rotation of the knee joints.
- Turns the body left and right.
- Body tilts to the right and left.
- Rotation of the ankle joints.
- Walking on the outside and inside of the foot.
- Front and side lunges with emphasis on stretching the thigh muscles.
Basic elements for the neck in the supine position
The main part of the exercises is performed mainly while lying on your back or stomach.
“Berezka” – shoulder blade stand:
- The arms are straight, the stick is held with a wide grip.
- Pull your knees to your chest, hold your hands with a stick under your buttocks.
- Hands with a gymnastic apparatus on the floor, legs straightened, stretched upward.
- Slowly lower your legs.
- Repeat 2-3 times.
Lying on your stomach, perform the “Boat” exercise:
- Gymnastic stick in hands with a wide grip.
- Hands with the projectile stretch forward and upward as much as possible.
- The head and upper part of the body are raised.
- Smoothly lower your arms and body.
- Repeat the exercise 5-10 times.
For back and neck
Exercise therapy for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis is performed in a standing, sitting or lying position and includes turning, bending and lifting the body. The back should be as straight as possible.
Approximate complex
- Standing, feet shoulder-width apart. The stick is placed behind the back, resting on the shoulders, hands on top of the stick. The body rotates right and left.
- While standing, the stick is placed behind the back and parallel to the lower back. Body rotations are performed.
- While standing, the stick is extended upward with straight arms. The body leans forward until it is parallel to the floor.
- Sitting on a chair, the stick is placed behind the back and is located in the area of the shoulder blades, parallel to the floor. The head goes down and returns to its original position.
- From the same position, the head moves forward as much as possible, returns to its original position and moves back as much as possible.
- Lying on your back, stick on your arms outstretched in front of you. Body lifts are performed.
- Sitting on the floor, straight legs extended forward, a stick in your hands in front of you. Reach your whole body towards your legs, try to reach your feet with a stick.
According to Shishonin
A set of exercises for the neck, developed by the famous rehabilitation physician Dr. Shishonin, is aimed at strengthening the muscle corset and restoring the flexibility of the spine.
These exercises have been successfully used in the correction of cervical osteochondrosis since 2008. It is advisable to perform gymnastics according to Shishonin at stages 1 and 2 of the development of osteochondrosis ; at the last stages, the exercises are no longer effective. The complex includes seven basic exercises.
Read more about the features of Dr. Shishonin’s gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis in this material.
Metronome
The exercise is performed while sitting on a chair. The back is straight, the head is held level.
- A smooth tilt of the head to the right shoulder is performed, the position is held for 30 seconds.
- Then the starting position is taken and the same is done in the other direction.
Heron
Starting position: sitting on a chair, hands on your knees.
- The arms go down and are pulled back a little.
- The head goes up. This position is maintained for 30 seconds.
Goose
- Stand straight with your chin parallel to the floor.
- The neck is pulled forward, while the chin remains in place in an unchanged position.
- Then the neck turns to the left, goes down and returns to its original position.
- Repeat the action in the other direction.
Looking to the sky
- The head smoothly extends forward to the maximum possible distance.
- Then the neck turns to the left and down, the head returns to its original position.
Frame
Starting position: sitting on a chair, back straight.
- The right hand is placed on the left shoulder, the left hand lies on the left knee.
- The neck turns to the right side.
- The position is fixed for 30 seconds.
- Then the exercise is repeated in the other direction.
Fakir
- The arms are raised above the head, slightly bent at the elbows.
- The fingers are clasped together.
- The head turns right and left, each position is fixed for 30 seconds.
Spring
- Sit up straight.
- Lower your chin down and hold the position for 5 seconds.
- Then raise your chin, stretch it first forward, then up.
Gymnastics according to Dikul
Exercise therapy according to Dikul includes several groups of exercises, including stretching exercises and strengthening the neck muscles. Gymnastics according to Dikul is easy to perform, does not take much time and can be done daily:
- Starting position: standing straight, arms relaxed, feet shoulder-width apart. As you inhale, your head leans forward as much as possible, your chin touching your chest. As you exhale, the head tilts back.
- From the same position - while inhaling, the head tilts towards the shoulder. As you exhale, it returns to its original position. Then the exercise is repeated towards the other shoulder.
- Slowly rotate your head in a circle.
- Turns the head to the right and left, as if trying to look behind one’s back. The chin is parallel to the floor.
A complex that can be done at the workplace
When working at a computer or staying in a static position for a long time, it is recommended to do a simple warm-up from time to time. Exercises that can be done right at the workplace are a good prevention of cervical osteochondrosis , relieve muscle spasms and give a surge of strength. Gymnastics is performed sitting on a chair, with a straight back:
- Smooth turns of the head from right to left.
- Pull your chin forward and back.
- Lower your head as low as possible.
- Place the elbow of your right hand on the table, place your palm on your right temple. Tilt your head, providing slight resistance with your hand. Repeat on the other side.
- Place your palm on your forehead and tilt your head, overcoming the resistance of your hand.
- Raise your shoulders as high as possible, hold in this position for 10 seconds, then lower down.
- Massage the back surface of the neck and back of the head with your fingertips with intense, but not sudden movements (for more details on how useful it is to knead the neck for osteochondrosis and how to do it correctly, read this material).
Other options
Lunges and squats are performed with a gymnastic stick pulled back or holding it in front of you. These exercises are used not only for rehabilitation of osteochondrosis, but also to maintain good physical shape.
Performance:
- Standing, one leg is fixed in place, the other moves forward as much as possible.
- The stick is held from behind with support on the shoulders or in front, with outstretched arms parallel to the floor.
- From this position, perform a slow squat.
- We return to the starting position.
- The same leg is moved back as far as possible.
- A slow squat is performed.
- The exercise is repeated in the same way for the other leg.
Preventive
- Starting position: standing, legs apart. Press your forehead onto your palm and hold the position for 7 seconds. Do it 3 times.
- From the same position: press the back of your head onto your palm. Perform 3 times for 7 seconds.
- Press your left temple onto your left palm. Then with the right temple on the right palm. 3 times for 7 seconds.
- Tilt your head back slightly. Then press your chin to your chest. Do it 5 times.
- Slow turns of the head to the right - left.
- Lower your chin to your neck. Slowly turn your head to your right shoulder, then to your left.
- Throw your head back. Try to reach your right shoulder with your ear, then the left.
Gymnastics with a stick and its benefits for osteochondrosis
Exercises for osteochondrosis using a gymnastic stick are selected by a vertebrologist using a special technique based on the patient’s capabilities, taking into account the stage of the disease, the extent and area of the lesion. Gymnastics with a stick allows you to strengthen the muscle corset, relax the muscles, improve blood circulation in the joints, the state of the peripheral and autonomic nervous systems, increase the intervertebral space, and improve immunity.
Therapeutic exercise with a stick is an excellent alternative to get rid of an illness with minimal investment. Exercising with this gymnastic apparatus progressively increases the load on the muscle tissues of the abdomen and lower back, complementing the full range of therapy for the back with more complex, varied exercises.
Rules and features of exercise therapy
Proper breathing will increase the effectiveness of exercises.
The length of the gymnastic stick must be chosen correctly. The recommended length of the projectile is 10 centimeters less than the distance from the floor to the xiphoid process (lower end of the sternum). A set of exercises with a gymnastic stick differs in the method of execution, the level of load when performing the complex, which depends on the location of the problem, purpose, and stage of the disease. But there are training principles that are common to all, adherence to which will preserve the results obtained for a long time:
- Carry out only medical prescriptions after diagnosis and follow the instructions for their implementation.
- The first stage is carried out under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor.
- Perform gymnastics in the morning in a well-ventilated area.
- Regularity of execution: 4-5 times a week.
- Clothing should be comfortable and moisture-wicking.
- Start each movement with an inhalation and end with an exhalation.
- Increase the load gradually.
- Do not exercise if you have acute pain.
- Work through the movements smoothly, measuredly, without haste.
- Avoid forward lumbar deflection when performing a complex for lumbosacral chondrosis.
- Reduce the distance between the hands on the stick in order to increase the load during the period of remission.
Exercises for cervical osteochondrosis
Physical exercise will improve blood supply to the brain.
Perform pole training, which improves memory, blood circulation in the brain and overall performance. Such exercises are the main component of therapy for glenohumeral periarthritis (osteochondrosis of the shoulder joint). You need to start with a minimum load of 5-7 repetitions. Gradually increase the number of movements up to 10 times, execution time - up to 20 minutes. Exercises to stretch and relax the neck muscles will relieve swelling and inflammation in the intervertebral discs and tissues. Exercises for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are done while standing, and the exercises are as follows:
- Elbows bent at the elbows. Extend and bend at chest level.
- Extend your arms with the stick in front of you. Perform rotations along the axis.
- Lower the stick from above your head to your shoulders.
- Slowly lean to the sides. In this case, the hands with the stick are raised above the head.
- Raising your arms above your head, bend down, trying to reach the floor.
- Holding the projectile with your elbows behind your back, turn your upper body in different directions without stopping.
Complex for the thoracic region
Monitor your posture while performing the exercise.
- Pressing the projectile against your back with your elbows, roll it up and then lower it down as much as possible. Maintain proper posture.
- From the hand-down position, raise the stick to the chest, place it behind the head and lower it to the lumbar region. In this position, bend forward, while stretching your arms up as much as possible. The smaller the distance between the upper limbs, the greater the load on all muscle groups.
- Crossing your arms straight at the elbows, rotate the stick left and right.
- Sitting on a chair and holding the upper end of the stick with your hands, bend forward as you inhale, trying to lower your head between your hands. At the same time, the knees are widely spaced, the feet hold its lower end.
Exercises for the lumbosacral area
The complex is used during the period of remission.
- Feet shoulder width apart. Perform body turns in different directions with straight arms raised at chest level.
- Perform squats, raising your outstretched arms.
- Lie on your stomach, legs together. With arms extended forward, ride back and forth, like in a boat.
- Position: lying down. Holding the stick behind your back with straight arms, bend back while inhaling and raise your shoulders. Hold for 5 seconds. Perform 10 times.
Possible complications
If the exercises are performed incorrectly, the effect of physical therapy will be negative. This is due to the fact that the training takes place under heavy load, at an inappropriate pace, or the muscles were not warmed up and were not ready for exercise.
Complications may be the following:
- Increased pain . Causes: excessive effort when performing exercises, injury as a result of sudden movements.
- Muscle spasms can also be the result of overexerting yourself or due to a lack of proper stretching at the end of a workout.
- Sprained ligaments: the reasons are the same - too much effort and training with tense muscles.
- Spinal instability, blockages, fractures are the consequences of incorrect exercises and repeated repetitions.
A simple gymnastic complex for osteochondrosis
Exercises from the complex:
- The lower back and shoulder blades are on the floor. The legs are bent at a right angle, the arms are pressed to the floor. You need to stretch your arms up, slightly spreading them to the side.
- Scissors. The lower back and shoulder blades are pressed to the floor, the legs are crossed 10-15 times.
- Raise your legs and bend your knees, pressing your lower back to the floor. Stretch your shoulders towards your raised legs, while tensing your abs.
- From a lying position, pressing your shoulders and lower back to the floor, lift your chest and slightly move your shoulder blades towards each other.
- Deflection The pelvis must be raised without lifting the shoulders and legs from the floor.
- Bend your legs at an angle of 90 degrees and raise your torso by tensing your abs.
It is recommended to perform gymnastics in comfortable cotton clothes. It should not restrict movement. A gymnastic mat is also necessary, since classes are carried out in a lying position.
What's the use?
Opinion of doctors and patients
Doctors unanimously say that movement is the most effective remedy in the fight against osteochondrosis. Many famous doctors speak about the benefits of exercise therapy in the treatment of osteochondrosis. For example, Dr. S. M. Bubnovsky speaks highly of this method, calling therapeutic exercises using a stick a simple but effective combination of exercises that gives maximum effect in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis (read more about Dr. Bubnovsky’s exercises and exercises here).
Feedback from patients after completing a course of exercise therapy:
- Elena, 30 years old: “I work at the computer.
One day I noticed that my shoulders began to hurt, and there was fatigue and tension in my neck. I went to the doctor, he ordered an x-ray. As a result of the examination, it turned out that I have cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. The doctor prescribed me a special diet and therapeutic exercises using a special stick (body bar). At first I did the exercises with difficulty, then they began to come to me easily and even with pleasure. After about two weeks of daily practice, I noticed that there was ease in my movements, my neck and back hurt less. I will continue to do physical therapy!” - Pavel, 40 years old: “Working as a driver caused me to have back problems. The doctor said that I need to do physical education, exercise therapy. I set aside time in the morning to exercise. I did special gymnastics for 20 minutes. Now it's much easier for me! It’s good that I was prescribed physical therapy on time, otherwise I would have had to take pills.”
What does Dr. Shubin say?
The famous neurologist and chiropractor, Dr. Dmitry Nikolaevich Shubin, is entirely in favor of physical education, and is himself a supporter of a healthy lifestyle. However, the doctor says that running and jumping negatively affect the spine. These exercises are contraindicated for people diagnosed with osteochondrosis, as they put a shock load on damaged vertebrae and discs, contributing to the destruction of damaged tissue.
But swimming and walking have a beneficial effect on the spine and help correct degenerative changes in it.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical and any other type of osteochondrosis are necessary. This is the best remedy for maintaining a healthy spine and beautiful posture for many years. Physical education maintains a high quality of life in old age. Gymnastics is very useful for children. If there are no contraindications to performing therapeutic exercises, do not neglect the exercises.
To treat osteochondrosis, Alexandra Bonina’s gymnastics, Butrimov’s exercises and yoga are used, which you can read about in more detail on our website.
Solutions
Maintaining correct posture is a preventive measure against osteochondrosis. Don't sit in one place for hours. When working sedentarily, it is recommended to do a warm-up every 40-60 minutes, or better yet, a small set of exercises for the back.
Important! With healthy posture, a person in a standing position should experience tension in the area of the shoulder blades, buttocks and abdomen.
In addition to daily exercise, people at risk of developing osteochondrosis need to eat well and regularly attend physiotherapy and therapeutic massage sessions.
Starting your workout
Experienced athletes know that it is impossible to jump up and immediately begin performing any exercise, since this can lead to serious consequences. In such cases, a clear sequence is required. The optimal time for gymnastics is early in the morning, since during morning workouts it is easier to tone the back muscles. In addition, the body will be able to receive a greater charge of energy, which is necessary to carry out normal activities. It is strictly not recommended to exercise on a full stomach, so training should begin approximately 40-60 minutes before meals.
Warm-up
All types of training should begin with a warm-up, as the body needs to warm up well before further physical activity. The warm-up complex includes:
- jumping rope – 5-7 minutes;
- squats – 15 times;
- running in place (no more than 7 minutes);
- gentle stretching of all muscle groups, starting with the legs and ending with the neck muscles;
- light warm-up of the lower and upper limbs.
As noted earlier, all elements of exercise therapy should be accompanied by a gradual increase in the load on the body. That is, the number of approaches and repetitions should increase at a slow pace so that the muscle tissue can get used to a certain load. Also, to achieve a greater effect from training when performing different exercises, you need to independently strain and control the work of the muscle group being worked.
Set of exercises
When performing the exercises given below, you must be guided by the following rules: from a standing position, your feet should be placed shoulder-width apart, all movements should be performed while exhaling, and the number of repetitions in each exercise should be at least 6 times.
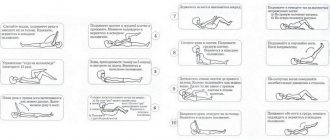
Table. Gymnastics for the back with a gymnastic stick.
Standing position, place your feet wider than your shoulders and lift the stick above your head. The grip should be wide. Slowly rotate your arms in a horizontal plane without releasing the gymnastic stick. After crossing completely, return your arms to the starting position. Keeping your legs straight, tilt your body forward and rest your hands on the stick, which should be perpendicular to the floor. Your arms should also be straight. Gently rock up and down.
Place the stick vertically in front of you.
Hold it with your hand and swing your foot over the stick, first one way and then the other. After 6-7 repetitions, change legs. Lie on your back and, leaning on a stick in a scapular stance, lift your legs up. Then tilt your torso back and forth without lifting the gymnastic stick from the floor surface. Take the stick with a wide grip and lift it above your head. Do alternating lunges, moving the stick back as far as possible, thereby bending your body. Raise the stick up above your head using a medium grip. Keeping your back straight, gently bend at the waist and return to the starting position.