Kyphosis is a curvature of the upper spinal column. The spine is characterized by some deviation from the vertical axis in the thoracic region, but in the presence of risk factors, the angle of curvature increases. If left untreated, the patient develops a pronounced hump. Kyphosis responds well to treatment with conservative methods if therapy is started in the early stages. The main element in the treatment complex is exercises for kyphosis.
What is kyphosis?
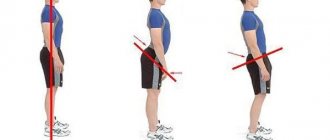
Kyphosis is a curvature of the spinal column in the anteroposterior plane. Visually, in a person it looks like an arched back, the upper part of which seems to be tilted forward (like a normal stoop), the stomach protrudes slightly forward, and the vertebra in the thoracic region seems to move back. Hunchback is the most severe form of kyphosis.
Typically, the deformity occurs in the thoracic spine, so the word “kyphosis” is often added to “thoracic kyphosis” or “thoracic kyphosis.” Kyphotic curvatures in the neck or lumbar region are rarely encountered in medical practice.
The most common type of kyphosis is acquired kyphosis. The causes of this type of disease are incorrect posture, back injuries, the presence of diseases such as tuberculosis, rickets, etc.
A rarer form of kyphosis is the congenital (or hereditary) form .
It must also be said that all people have some curvature of the spine (the so-called physiological), this is completely normal and there is no need to be alarmed. But if the angle of inclination is 40 degrees or more, then this is already a significant violation. Quite often, kyphosis is combined with varying degrees of scoliosis.
Pathological kyphosis is diagnosed when the angle of curvature is more than 30 degrees.
From the point of view of symptoms, kyphosis manifests itself, firstly, visually (deformation of the back: its tilt forward or backward) frequent back pain is also characteristic symptoms . If the disease is in an advanced state, then a strong pathological displacement of the vertebrae may occur, which means that the patient may often experience attacks of suffocation, numbness, and muscle weakness . Sometimes there may be difficulties with independent movement .
Video: “What is kyphosis and what are its consequences?”
Taking medications
Many medications that are used to eliminate the symptoms and consequences of kyphosis strengthen bones and have a preventive effect on bone tissue. Kyphosis can cause damage to various organs and systems, so all medications should be selected depending on which internal organ suffers from spinal curvature. However, all drugs for the treatment of kyphosis are presented:
- painkillers;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antispasmodics;
- as well as chondoprotectors that restore bones and cartilage;
- local agents that have a warming effect;
- vitamin complexes, the main task of which is to maintain immunity;
- biologically active substances that improve metabolism.
Traditional treatment for kyphosis
Traditionally, kyphosis is treated comprehensively. The complex includes:
- drug treatment;
- physical therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- orthotics (wearing special belts, corsets that support posture);
- massotherapy;
- surgical intervention (extreme case, used very rarely).
Drug treatment is usually used when the patient has severe pain. In this case, he is prescribed weak analgesics, or, in extreme cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Important! Analgesics are rather insidious drugs, many of them are addictive and can also lead to the opposite effect. Therefore, you should take any medications during treatment only after consultation with a doctor and under his strict supervision.
Physiotherapy is a standard item of any treatment complex concerning the treatment of the spine, joints or muscles. This is a kind of auxiliary technique. It helps strengthen muscles and eliminate their dystrophy. Physiotherapy can also improve the contractile function of the muscular corset, and, therefore, remove blocks on the spinal segments and relieve pain. Your attending physician will select a set of physiotherapeutic procedures for you, based on your medical history.
Pay attention to the main methods of treating hyperkyphosis. Orthotics is a technique in which the patient is selected with a special corset or belt (or other orthopedic device) that can keep the posture in the correct state, as well as reduce the load on the back. The general name for such devices is orthoses. They are fixative and corrective. The orthopedist will select the type you need when he examines and prescribes treatment.
Therapeutic massage and manual therapy are also good helpers in the fight for a healthy spine. The main thing to remember is that massage (and manual sessions) should be carried out only on the recommendation of a doctor, and the sessions themselves should only be carried out by professionals. No unauthorized or inexperienced massage therapists!
Surgery is a fairly rare type of treatment. An operation is prescribed to a patient only when the benefits of surgery outweigh all possible risks. Most often, this happens when no conservative methods help the patient, the pain becomes stronger, and the deformities become so severe that the risk of paralysis or disability increases.
Video: “What to do to correct the spine with kyphosis?”
Find out more about spinal kyphosis - methods of its diagnosis and treatment:
- Kyphosis in children: causes of the disease
- How the angle of curvature of the spine is measured with kyphosis can be found here
- Find out whether kyphosis can be cured at home by clicking on the link
Causes of pathology
Doctors have identified the following causes of curvature of the ridge in the thoracic region:
- Defects in the development of the fetal spinal column in the womb.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Mechanical injuries of the spine.
- Incomplete or complete paralysis of the back muscles due to poliomyelitis or cerebral palsy.
- Spine operations.
- Poor posture, inactive lifestyle.
- A spinal fracture accompanied by compression of one or more vertebrae.
- Pathologies of the spinal column, which are characterized by degenerative changes in its elements (for example, osteochondrosis, spondylosis, osteoporosis).
- Weak back muscles.
- Rickets in children.
- Psychological reasons. If a person is embarrassed by his height, then he constantly slouches, causing curvature.
- Tuberculosis of bone tissue.
In rare cases, kyphosis may occur after radiation therapy in children.
No ads 2
The use of physical therapy for thoracic kyphosis
Physical therapy is one of the most effective ways to correct kyphosis today. As part of the complex treatment described in the previous paragraph, exercise therapy is the leading method of treatment.
The main thing is to choose the right set of exercises, perform them strictly according to the instructions and under the supervision of your doctor. In the early stages, kyphosis can be overcome by using only exercise therapy (without medications, physiotherapy and other elements of the treatment complex).
At what stage can exercise therapy be used?
Therapeutic exercise for thoracic kyphosis can be used at all stages of the disease , with the only difference being that at the initial stage the doctor usually prescribes a basic set of exercises (with the addition of some individual elements that will be effective specifically in your case).
In advanced cases, exercise therapy is prescribed strictly individually by your attending physician (hence, the exercises are selected only by him and no one else), as well as in combination with other therapeutic methods (such as massage, physiotherapy or wearing orthoses).
Contraindications for use
With kyphosis, exercise therapy has virtually no contraindications. Unlike many other diseases of the spine, physical therapy for kyphosis does not have many contraindications.
However, be sure to consult with your doctor before starting exercise; there may be individual characteristics of the body that prohibit the performance of certain exercises.
General contraindications:
- high body temperature;
- unbalanced psycho-emotional state, stress or fatigue;
- high blood pressure;
- poor blood clotting;
- inflammatory processes in the body.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of kyphosis appear, you should consult an orthopedist, traumatologist or vertebrologist. The doctor asks the patient about the symptoms present, then conducts a visual examination. The specialist’s goal is to find the location of painful sensations, determine their nature, and detect neurological disorders (if any).
During the examination, the doctor uses the following methods:
- Palpation (feeling) of the thoracic segment of the spine.
- Test to detect skin sensitivity.
- Listening to heartbeat, lungs.
In addition, to identify violations of bone structures and surrounding tissues, radiography, and in some cases computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, is performed. These studies will help identify the cause and degree of kyphosis.
Physical therapy exercises for correction of thoracic kyphosis
Therapeutic exercise is one of the most effective means for restoring the spine, as well as for improving the general well-being of the patient. It can strengthen the muscle corset, improve blood circulation, and restore tone to the body.
However, remember that a set of physical therapy and yoga exercises for kyphosis should be selected only by your attending physician.
You also need to perform gymnastics based on certain rules:
- The exercise therapy complex should include both dynamic and static loads;
- The load should be increased gradually and be dosed. Also, do not forget about the individual characteristics of the patient and select the level of load for him personally;
- The pace and load should be increasing and gradually (you should start from a minimum);
- The duration of the complex should last no more than 30 minutes;
- Be sure to relax a little before starting gymnastics. Take a bath or meditate. If possible, get a massage;
- Watch your posture while doing the exercises. It must be correct;
- It is prohibited to lift any weights;
- Monitor your well-being. If you experience discomfort, cramps, nausea or dizziness during the exercises, you should immediately stop the session and contact your doctor;
- Do not exceed the load prescribed by your specialist;
- No running, no exercises on the horizontal bar! These types of exercises are prescribed only by a specialist and only strictly individually;
- The average number of approaches should be 2 or 3 (10-15 times each). Rest between sets, let your muscles relax a little;
- If you feel numbness in your legs, you should do a relaxing exercise with a fitball. Sit on the sofa, put your feet on the fitball and roll it slowly;
- At the end of the session, therapeutic walking should be performed;
- Some orthopedists advise carrying out physical exercises in an orthopedic corset (at or at the stage of the disease). Consult your doctor regarding this matter;
- The room in which the gymnastics session will be held must be well ventilated and also have enough space for exercise. It’s also worth taking care of a gymnastics mat in advance;
- Sportswear should be made from natural fabrics, “breathe”, and not restrict movement.
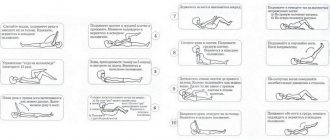
Main block of exercises
Did you know that...
Next fact
Exercises for spinal alignment usually consist of three blocks. In medical practice, there is a classification of exercises prescribed for kyphosis. All exercises are divided into lightweight , active , passive and dosed exercises.
Usually the doctor tries to select mixed complexes that will include different types of exercises. But there are also complexes of the same type, consisting of only one class of exercises.
Lightweight exercises are usually selected for patients with thoracic kyphosis. Such exercises can relax the muscle frame.
Active exercises can speed up blood circulation in tissues and muscles and increase the tone of the muscle corset.
Dosed exercises usually involve overcoming some kind of obstacle, an external force. For example, the hands of a trainer.
Lightweight gymnastics for the thoracic spine:
| Exercise name | Execution technique | Number of repetitions |
| Squats with a stick | Take a stick and place it behind your back at the level of your shoulder blades (horizontally). Straighten your chest and start squats from this position. The main thing is that your heels do not come off the floor surface. | Do 2 sets of 15 reps each. |
| Bends with a stick | Take the same starting position as in exercise 1. From this position, slowly and carefully stand on your toes. Heels should not touch the floor. Make several bends to the sides (while pressing your heels to the floor). | Also do 2 sets of 15 reps each. |
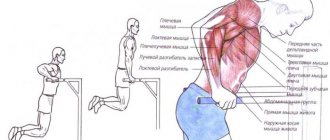
| Wall bars exercises | Hang on the wall bars for 3-5 minutes. Important! Such an exercise should only be included in your complex by a doctor; if he did not allow this, then under no circumstances should you perform such exercises yourself. | The duration of the exercise should be increased gradually as the muscle frame strengthens. The first exercise is 3 minutes, then 4 minutes and so on. |
| Chair exercises | Take a chair with a backrest. Sit on it and lean your spine on the back, lower your arms. From this position, arch your chest for 5-10 seconds. | Do several approaches. |
Exercises for extension of kyphosis of the thoracic spine (active complex):
| Execution technique | Execution duration |
| Stand up straight, straighten up, hands on your waist, shoulders down. Extend your chest as wide as possible. Hold in this position for 3-8 seconds (gradually increase the time each gymnastics session). | Do 2 sets of 15 times each. |
| Lie on your back. From a lying position, lift your straightened legs up, stretch your arms along your body. Cross your legs alternately in the air. | Do this exercise in 2 sets of 10 times each. |
| Lie on your back. From a lying position, place your legs approximately 25 centimeters apart. Then lift them up and do the bicycle exercise. Make movements slowly, carefully, take your time. | Do 10-15 times. |
| Lie on the floor, on your back. Arch your chest so that an arch is formed. | Hold this position for 10-15 seconds, then slowly lower. |
| Exercise “cat”: get on all fours, stretch your arms forward, lean on them. Arch your spine. | Stretch for about 10-15 seconds. |
Children's gymnastics
The child’s musculoskeletal system is very flexible, so with regular and proper exercise, you can completely get rid of the disease.
Exercises:
- Perform light head rotations and turns left and right.
- Rotate your arms back and forth.
- Take a gymnastic stick, pull it back with outstretched arms, and bend over.
- Take a stick in your hands, lift it up, and bend to the sides.
- Sit on your heels, put the stick in front of you, grab it by the edges. Reach forward, stretching your back.
It is advisable that the child perform all of the listed exercises under the supervision of parents or a doctor, so that all movements are correct and moderate.
Operational approach
Surgical intervention is indicated in the following cases:
- Pain syndrome that is not relieved by conservative methods.
- Rapid progression of kyphosis.
- The disease disrupts the functioning of internal organs (heart, lungs) or causes neurological disorders.
Many patients decide to undergo surgery to get rid of a hump, which looks unsightly and interferes with physical activity.
Reference. Surgery for kyphosis is contraindicated in old age, with stage 3 hypertension, severe arrhythmia, diabetes mellitus, oncological pathologies, etc.
Kyphoplasty will help correct the shape of deformed vertebrae
If there are no contraindications to surgical treatment, then it is performed to correct the angle of inclination of the thoracic spine and stop the development of the disease. During the procedure, the surgeon tries to release nerve bundles pinched by the vertebrae and prevent their compression in the future. This is a rather complex operation that is performed under general anesthesia. Often the patient needs repeated surgery.
During the treatment of kyphosis, 2 surgical techniques are used:
- Osteotomy. During the operation, the doctor corrects vertebral deformities, fills the resulting cracks with artificial grafts and biological fluids, and then fixes the spine with metal structures (screws, plates).
- Kyphoplasty. Small incisions are made in the skin over the damaged area, a balloon is inserted into them, which is inflated inside the vertebra, correcting its shape, then the cavity is filled with a quickly hardening material.
Surgical treatment of kyphosis is performed only in patients over 25 years of age.
After surgery, the patient must wear a corset, perform special exercises, go for massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, swim, eat well, and rest.
Workout
This type of exercise therapy has its own characteristic features. For health training, you will need special equipment, for example, a ball, mat or gymnastic stick. The main rules of gymnastics for kyphosis:
- It is necessary to control the duration of classes. On average they take from half an hour to 40 minutes. This time is enough to complete the required number of approaches without unnecessary overexertion.
- A tracksuit should be comfortable and not restrict movement.
- Before you start exercising, you need to do a warm-up.
- Classes should be carried out constantly, but it is better to do exercise therapy every other day to provide the muscles with time to rest.
- There should be no pain during exercise. Their occurrence means that some actions are being performed incorrectly.
- The number of approaches should be increased gradually.
Contraindications:
- fatigue or recent stressful situations;
- increased body temperature;
- inflammation;
- hypertension;
- hemophilia or other bleeding disorders.
Classification of the disease
There are several types of kyphosis:
- compression;
- senile;
- genotypic;
- mobile;
- total (when the entire spine is curved, occurs in newborns);
- rachitic form;
- corner
According to the severity of the pathology, kyphosis is divided into three stages:
- The first, mild stage is when the spine is curved by 30 degrees;
- The second, moderate stage in which the curvature is 30-60 degrees;
- The third, severe stage is a curvature of 60 degrees or more.
The causes of kyphosis include hunching, all kinds of back injuries, and progressive osteochondrosis. Elderly people are also at risk.
Yoga
Yoga is good because it helps stretch the spine and chest, and also allows you to use even the smallest muscles that you cannot feel. Pay attention to the following exercises:
- You need to stand straight with your feet hip-width apart. As you exhale, bend forward and bend at the waist, squeeze your buttocks and extend your arms straight to the sides. As you exhale, return to the starting position.
- Lie on your stomach with your legs together. Focus on your arms, bend your back, stretching your spine as much as possible.
- You need to get on all fours, exhale, squeeze your shoulder blades together, keeping your back straight. Stay in this position for several counts.