Etymologically, the word “hyperlordosis” comes from the Greek language and means: hyper– (excessive), lordo– (bending) and – sis (disease, disorder).
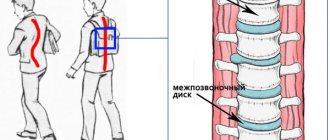
Lumbar hyperlordosis is an increase in the lordotic curve of the spine. Hyperlordosis of the lumbar region can be noticeable from the side in a relaxed standing position and is determined objectively by X-ray. A curve greater than 70 degrees is considered hyperlordic (measuring the angle between the surfaces of the L1 and S1 vertebrae).
Although the cause of lumbar hyperlordosis is unknown in most cases, it can result from shortening of the hip flexor muscles, particularly the iliopsoas muscle. This phenomenon is relatively often explained by a sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity, which is very typical for modern society. In a sitting position, the origin and insertion of these muscles come closer to each other). Over time, the muscles adapt to this position, shorten, and their ability to stretch decreases.
In the standing position, shortened flexor muscles pull on the pelvis, moving it into an anteversion position (2), predisposing the spine to hyperlordosis. Strengthening the lumbar lordosis contributes to the shortening of the paravertebral muscles, the iliocostalis muscle, the longus dorsi muscle and the quadratus lumbar muscle (3), which, in turn, helps to consolidate the change in the statics of this part of the spine.
- With age, physical activity decreases and muscles gradually weaken. This leads to a weak ability to hold the spine, which, coupled with the force of gravity, leads to increased physiological curves of the spine.
- As the volume of the abdomen increases, the pelvis shifts toward anteversion and the lumbar curve increases due to the shift of the center of gravity forward.
Development - forecast
- If you do not perform appropriate exercises to inhibit the development of lumbar hyperlordosis, the intensity and frequency of symptoms will increase over time. Prevention
- Moderate physical activity promotes the necessary tone and elasticity of the main muscles responsible for maintaining the spine.
- Performing special physical exercises given on page 212 is aimed at improving the statics of the lumbar and sacral regions.
- Compliance with diet.
General description of lordosis
This disease refers to a pathological protrusion of the vertebrae forward , which creates an uneven load on the entire body. Most often, such anterior bulging occurs in the lumbar region. The disorder is provoked by injuries, inflammation, infections, unsuccessful operations or congenital pathologies.
The curve in the lower back can either increase (hyperlordosis) or decrease (hypolordosis).
The disease manifests itself as a characteristic change in the curvature of the vertebra, severe wear of the discs, the appearance of pain and difficulty walking. Without treatment, the patient's condition will quickly deteriorate, which can lead to disability and problems with the reproductive and urinary systems.
Methods for diagnosing hyperlordosis
Hyperlordosis of the lumbar region is visible, as they say, to the naked eye. To clarify its degree, X-ray diagnostics are performed to determine the angle of deviation of the spine; for a more accurate study of the structures of the spine, ligamentous apparatus and muscles, MRI, CT, and in pregnant women, ultrasound, myoelastography, and neuromyography are performed. If necessary, the abdominal organs are examined.
Important!
Some consider hyperlordosis to be a feature of the constitution and posture. Only a doctor can determine this, so examination is necessary in any case.
Basic principles of treatment of lordosis
When treating this disease, any medications are rarely prescribed , since they are not able to correct the curvature of the spine. Typically, medications are used as pain relievers and strengthen bone tissue and joints.
To eliminate pain, the specialist suggests non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that have minimal side effects. These include Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen and others. They can be used in the form of ointments, injections and tablets. To strengthen joints and bones, medications are selected individually for each patient.
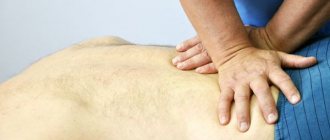
The main methods of treating lordosis are therapeutic exercises, massage and physiotherapy. In some cases, treatment is only possible with surgery, followed by long-term rehabilitation.
Attention! If non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs do not have any effect, your doctor may prescribe steroids. But they should be taken only under the supervision of a doctor and for a short time.
Reasons for development
The main causes of the disorder are damage to the vertebrae or pathology of the hip joints. Lordosis occurs as a result of:
- Developmental defects.
- Neoplasms.
- Inflammation.
- Spondylolisthesis.
- Torsion muscle spasms.
- Spinal injuries.
- Diseases such as polio, cerebral palsy, rickets.
- Systemic diseases that cause damage to muscles, cartilage, and bones.
- Poor posture during pregnancy (a temporary phenomenon that goes away after the birth of the child).
Pathological lordosis of the spine can occur in children for no apparent reason. This condition is corrected as the child grows older and does not leave any health consequences.
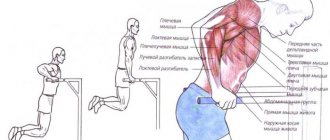
The use of exercise therapy for lumbar lordosis
Physical therapy plays an important role in the treatment of lordosis.
Pay attention to the positive properties of therapeutic exercises for lordosis of the lumbar spine. Thanks to properly selected exercises, you can achieve several positive aspects:
- improve the condition of the muscle corset;
- prevent early wear of joint tissue;
- prevent the occurrence of hernias and other neoplasms;
- increase the strength of the musculoskeletal system;
- relieve pain and discomfort in the affected area;
- protect the reproductive and other body systems from their dysfunction.
Attention! Physical therapy alone cannot provide optimal results. In order for it to help the patient as much as possible, it is also necessary to monitor nutrition and follow other doctor’s instructions. Exercise therapy should be used already at the first stage of pathology development.
Video: “Exercises to strengthen the lower back and abdomen”
Read more about the development of lordosis in each part of the spine:
- Thoracic lordosis of the spine - what is it?
- How to correct lumbar lordosis? More on this in the next article
- Read more about the symptoms, causes, treatment of neck lordosis on the page
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of lordosis or, after treatment, to prevent its development again, you should follow simple preventive tips.
- Firstly, carefully monitor your posture and avoid sitting for long periods in an uncomfortable position.
- Secondly, while working at the computer and doing any other “sedentary” work, try to do warm-ups, at least five minutes every hour and a half.
- Thirdly, engage in sports that are good for the spine: swimming, Pilates, yoga.
If you can’t exercise, then do exercises at home, such as “cat”, hip rotation. Take multivitamins and be sure to go to the clinic for a preventive examination every 6-10 months. These not the most difficult actions will help you maintain the flexibility of your spine.
The medical office will always be happy to provide all services for consultation and treatment of various diseases, including pathological lordosis.
Exercise therapy for the treatment of lumbar lordosis: technique
Did you know that...
Next fact
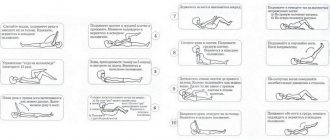
Exercise 1
To perform this complex, you need to place your feet shoulder-width apart and lower your arms. After this, you need to lean forward so that your hands reach your feet. When performing this exercise, it is important to ensure that your knees are straight. In this case, you need to lower while exhaling, and rise while inhaling.
Exercise 2
You need to stand against the wall so that your heels, gluteal muscles and shoulder blades touch the wall. After this, you need to try to bend the vertebra so that the lower back touches the surface of the wall. At first it will be difficult to do this, but gradually the pathology will be eliminated, which will allow everything to be done correctly. Breathing during this task can be voluntary.
Exercise 3
To perform the complex, you will need to stand straight, your legs should be together, and your arms should be lowered along your body. You need to lean forward so that you can wrap your arms around your legs. But you cannot bend your knees. You need to bend over so that your forehead eventually touches the surface of your knees. Once this has been done, you need to return to an arbitrary position. In this case, you need to breathe in any convenient way.
Exercise 4
In the starting position, you need to put your feet shoulder-width apart and lower your arms, they should be located along the body. As you exhale, you need to sit down and stretch your arms in front of you. While inhaling, the patient returns to the original position.
Exercise 5
To perform this task, you need to lie on a hard surface and stretch your arms along your body. It is important to relax as much as possible so that your lower back can reach the surface on which the patient is lying. There are no breathing recommendations in this case.
Exercise 6
You also need to lie down on a hard surface and place your palms down, arms straight out to the side. After this, you need to start raising your legs up, resting your palms on the surface as much as possible. You should try to throw your legs behind your head so that your fingertips touch the surface. You need to raise your legs as you exhale, lower them as you inhale.
Exercise 7
The patient also assumes a horizontal position. As you exhale, you need to take a sitting position, and you cannot help yourself with your hands. While inhaling, the patient returns to the starting position.
Exercise 8
The patient assumes a horizontal position. After this, you need to bend your knees and press them slightly towards your body. In this position, you need to lift the body as you exhale and return to the starting position as you inhale.
Exercise 9
As in the previous position, you need to lie on your back on a hard surface; it is better to choose an orthopedic mat. You need to spread your arms out to the sides and press your palms to the floor. After this, you need to take turns raising and lowering first the left and then the right leg. A minimum of 15 lifts are required for each leg. There are no breathing recommendations for this exercise.
Exercise 10
The complex is performed in a vertical position; this requires pressing against the gymnastic wall. Next, you need to grab the crossbar with your hands and hang on it. After 1-2 seconds, you should bend your legs and hold it for 3-7 seconds. For a good effect, you need to perform the task at least six times, you cannot rush, breathing is voluntary.
Attention! The described exercises are suitable for patients suffering from flattened lordosis. This condition means a slight deflection in the lumbar region.
When hyperlordosis develops, it is necessary to perform abdominal exercises. To do this, it is recommended to perform twisting exercises. In this position, the patient lies on his back and performs lateral lifts of the torso.
When doing abdominal crunches, you can use a special roller, this will help keep your lower back in the desired position.
For the best effect, you should try to perform 10-15 lifts in each direction. If this type of exercise is difficult, you can perform lower back lifts until the shoulder blades lift off. But for the best effect you need to combine these exercises.
In order for exercise therapy not to cause harm, it is necessary not only to pay attention to the technique of execution, but also to the following points::
- classes should begin with light movements, gradually loading the spine and lower back;
- the complex time also needs to be increased gradually;
- after exercise, the patient should feel slightly tired, but not exhausted;
When performing exercises for lumbar lordosis, the main thing is to avoid heavy loads on the spine; you cannot expose yourself to physical activity during the period of exacerbation of the disease or in the presence of severe pain; first, the patient needs to be stabilized;- The lower back should also be well insulated, clothing should not hinder movement, it is better to choose shoes with an orthopedic base;
- at the beginning, it is better to perform all complexes under the guidance of an instructor;
- before starting an active complex to eliminate lordosis, it is first recommended to stretch and warm up the muscles, this will minimize the chance of injury;
- in the room where the lesson takes place, the optimal temperature must be maintained;
- After performing exercise therapy, you should rest and cool down.
Attention! For the best effect, it is recommended to perform exercises daily for 15 minutes in the morning and evening, and not 2-3 times a week. This will avoid unnecessary stress on your back and give a more complete effect.
Diagnosis methods
The diagnosis is made after the patient approaches. The patient's complaint, medical history, visual examination and X-ray examination are taken into account. An external examination is carried out by a therapist, surgeon or traumatologist. During the examination, the patient’s posture is taken into account, and pain points are identified by palpation. The depth of the bend of the cervical lordosis is measured. To do this, the doctor uses two rulers. One is applied to the back of the sick person’s head with one end and to the upper part of the spine with the other. The second ruler measures the distance to the middle of the cervical spine.
With a strong degree of curvature, the distance will be about 3 cm. The exact depth of the bend and concomitant diseases: injuries, tumors, spasms are diagnosed using:
- radiography
; - computed tomography
; - MRI
.
Treatment is prescribed after diagnosis. You can also do a simple test at home. We have already mentioned it in this article. The patient should be asked to stand against the wall and press his back tightly. The second person should try to put their hand into the open space between the neck and the wall (if there is one at all). If this manipulation is difficult, then pathology is present. Only a specialist can determine its exact stage and level of damage. It is strongly not recommended to postpone your visit to him.
What exercises are contraindicated for lordosis?
With lordosis, any exercises associated with sudden movements or increased pressure on the lower back and neck . It is prohibited to perform complexes that involve lifting weights. Also, you should not perform the permitted exercises a large number of times, since moderation is important in any load.
You should not prescribe exercise therapy or any other procedures yourself, as it is necessary to exclude all contraindications and the presence of concomitant pathologies. In cases of lordosis complicated by other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, even the simplest physical activity and exercises may be contraindicated.
Video: “Exercises for lumbar hyperlordosis”
Symptoms
The disease is not that difficult to identify. Like any other curvature of the spine, it is characterized by pain in the back. When lordosis appears, you will probably notice an increase in the level of fatigue, difficulty performing certain movements, and most importantly, a change in posture. The stomach, head and shoulders now stick out more, and the chest seems to be pushed back and flatter. Sometimes changes affect the legs: the knees unnaturally point in different directions. The level of attentiveness and the ability to maintain attention for a long time are also significantly reduced. Lordosis can cause changes in the functioning of other vital systems: the chest and abdominal organs are at increased risk. Lordosis can also lead to many other spine diseases: vertebral instability, deforming arthrosis, pinched nerves, hernias, etc.
If everything is very clear in determining the presence of a disease in an adult, then with children the situation is a little more complicated. Kids don’t always make contact and say if something hurts. Moreover, very young patients may not even be able to do this. Due to the fact that many parents do not attach importance to this, the disease begins to progress rapidly: in this case, serious treatment of the spine is required. If you notice changes in your child's posture, immediately make an appointment with our specialist.