Article updated 01/28/2020
Who does not have spinal osteochondrosis? It feels like everyone has it. In general, according to WHO statistics: 80% of people have various disorders of two systems - the musculoskeletal and motor systems. And what’s sad is that the majority of those suffering are of working age: from 29 to 49 years. That is, the majority of the population is diagnosed with certain pathologies of the spine and joints, and this is data only for Russia.
Back pain is felt by many people at different stages of life. When therapy for these pains has brought a successful outcome, most patients return to normal life and continue their professional activities. In some cases, the disease takes on a chronic form, leading to a decrease in performance, and for some, to its cessation altogether.
The widespread prevalence of back pain is the scourge of our century. And, perhaps, one of the most common pathologies associated with back pain is osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis affects the intervertebral cartilage and discs. Their metabolism is disrupted. This causes the development of changes in the skeletal and muscular systems of the spine. But this is not the only reason why osteochondrosis is dangerous.
Dystrophic changes in the spine can lead to pathological changes in the internal organs, since the relationship between the health of the spine and the internal organs of a person has been proven. By working with our spine, we heal the entire body. For this reason, it makes sense to take exercise therapy seriously for osteochondrosis, because many doctors claim that physical methods are the most basic therapy for osteochondrosis.
Mechanism of development of osteochondrosis
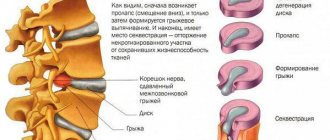
The spine has 33–35 vertebrae, with elastic discs between them. They give the spine elasticity and flexibility. Each such disc contains a core framed by an annulus fibrosus and covered above and below with cartilage.
With osteochondrosis, blood circulation in the spine itself and metabolism in it suffer. The elastic discs that are located between the vertebrae begin to dry out, their elasticity and strength are lost, and their height decreases. Gradually, the fibrous ring loses its ability to support the loaded spine, and it protrudes. It happens that the fibrous ring ruptures, and this leads to an intervertebral hernia.
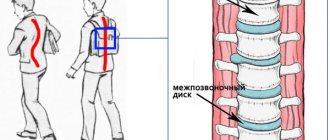
Due to such disorders, the mobility of the entire spinal column may be affected and its curvature may occur.
A favorable environment for spinal health is an active and sporty lifestyle with moderate load and without overexertion.
In our age of computerization, a person’s lifestyle is mainly sedentary. Prevention and treatment of problems with the spine is physical therapy (physical therapy), which improves the trophism of the discs between the vertebrae, because of this, joint mobility improves; blood saturation of the entire spine also improves, the muscular system of the back is strengthened, and the destruction of the bone components of the spine is slowed down.
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis is especially useful for people with predisposing factors:
- Elderly age.
- People who are constantly in an unusual body position.
- People with weak muscles and ligaments.
- Who has flat feet and club feet.
- With existing vertebral injuries.
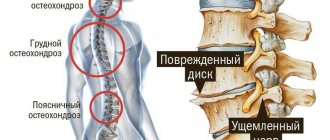
Osteochondrosis of the spine has different localization and is divided into osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, thoracic and lumbosacral spine.
Causes of shoulder osteochondrosis
More often, shoulder osteochondrosis develops as a result of lesions of the cervical spine. Therefore, doctors usually use the term cervical-brachial syndrome. The impetus for development can be any factors that provoke osteochondrosis:
- sedentary life with low physical activity;
- genetic predisposition;
- constant work at the computer, prolonged stay in a static position;
- poor posture;
- malnutrition, deficiency of vitamins and microelements;
- injuries (dislocations, fractures, sprains) of the anatomical structures of the shoulder;
- unevenly distributed physical activity (mainly on one shoulder).
- infectious diseases (osteochondrosis of the shoulder can be complicated by sexually transmitted infections, streptococcal infections or tuberculosis);
- overweight, obesity;
- arthrosis (in older people).
As a result of the changes occurring, muscles and nerves in the cervical region are pinched, which provokes circulatory disorders. The structure of the joint tissue of the shoulder is the first to be affected. A lack of chondroitin, vitamins, glucosamine and nutrients causes a disorder in the glenohumeral region, which entails atrophy and the transition of the pathology to a chronic course.
General principles of exercise therapy for any osteochondrosis
- Physical education should take place in a room with good ventilation; an excellent option is outside.
- Classes are held only during the period of remission of the disease (when there are no symptoms).
- Clothes for exercise therapy classes are expected to be wide, not restrictive, and breathable.
- All movements are smooth, the amplitude and number of repetitions gradually increase.
- If painful sensations begin, you should stop exercising immediately.
- The classes are preceded and completed by measuring blood pressure and pulse. When these indicators differ from normal, the load should be reduced.
- It is advisable to listen to your breathing throughout the session, this will increase efficiency. All stretching exercises are performed while exhaling.
- It is very important to gradually increase the load and number of repetitions; this will reduce the risk of injury and prevent overwork.
- It is important to do the exercises regularly, so you can achieve the fastest results.
- Before starting independent exercises, you must consult your doctor and agree with him on a set of exercises.
It should be remembered that exercise therapy is not carried out when signs of exacerbation begin: pain. After a complex of exercise therapy, they can intensify and cause inconvenience.
When gymnastics is contraindicated
If you feel unwell, gymnastics is prohibited. Training is contraindicated at elevated temperatures, rapid or slow heartbeat, and sudden changes in blood pressure. You cannot exercise after a recent operation, during respiratory, intestinal infections, exacerbation of osteochondrosis or other chronic diseases.
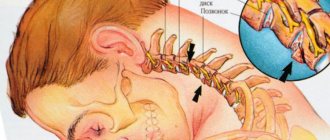
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the upper (cervical) spine
The cervical segment of the spine is intensely saturated with vessels that feed the brain. Therefore, to a greater extent, manifestations of osteochondrosis are caused by poor blood supply to the head.
There are some neurological syndromes associated with osteochondrosis:
- Scapulohumeral periarthritis syndrome.
In this case, the shoulder joint, shoulder and neck suffer the most. Often patients develop neurogenic restriction of movement of the shoulder joint; it protects the axillary nerve from irritation. That is, it manifests itself as pain in the back, arm, and the inability to use the arm on the affected side due to terrible pain.
- Radicular syndrome (cervicobrachial radiculitis).
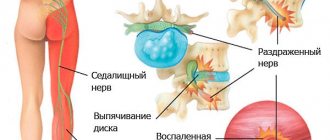
The roots of the spinal nerves are compressed because the intervertebral foramina are reduced, since the height of the intervertebral discs also decreases.
Symptoms: intense pain, the condition worsens when moving the head. The neck muscles are tense.
- Cardiac syndrome.
It is similar to angina pectoris, since there is pain in the area of the heart, but without changes in the heart itself. Other manifestations: tachycardia and extrasystole due to irritation of the spinal nerve roots.
- Vertebral artery syndrome.
Characterized by headaches, dizziness with staggering and loss of balance, nausea, vomiting; vision deteriorates, spots appear before the eyes; pain and sensitivity disturbances occur in the pharynx, hard palate, tongue, accompanied by a hoarse voice or it may disappear completely. It also manifests itself as pain or burning on the back of the neck and in the occipital region.
Characterized by sleep and memory disorders, mood swings and anxiety, irritability, resentment, weakness, lethargy and a feeling of heaviness in the head.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis should include both medicinal and physical treatments.
One of the physical methods for the treatment and prevention of osteochondrosis is therapeutic exercises.
In what cases are exercises contraindicated?
Performing exercises for osteochondrosis helps improve well-being and stop degenerative changes. But there is a certain list of contraindications for exercise therapy:
- acute period of the disease;
- severe myopia, high intraocular pressure;
- postoperative, beginning of the rehabilitation period;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus;
- hypertension, arrhythmia, tachycardia;
- neurological pathologies combined with incoordination of movement;
- threat of bleeding;
- severe forms or periods of exacerbation of any disease (malignant neoplasms, myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, infectious pathologies).
Exercises for osteochondrosis are not recommended to be done immediately after meals, on an empty stomach or after physical fatigue.
Exercise therapy complex for cervical osteochondrosis
When working on the cervical spine, it is important not to overload the neck muscles, so we use a complex of exercise therapy with the participation of other muscle groups. The complex uses both rest and switching actions. The exercise therapy complex has preparatory, main and final parts. Preparatory work is a warm-up to get the blood flowing. The main one is exercises directly for the neck, the final one is relaxation and distraction.
Exercises while lying on your back
- IP - lie on your back, legs straight, arms along your body. Raise and hold your head in this position for 3–7 seconds. Repeat 1-3 times.
- Hands at the shoulders: circular movements with the elbows in one direction and the other 4 times, repeat 2-4 times.
- Arms along the body, legs bent at the knee joints. Walking lying down - 30 seconds. Repeat 2-4 times.
- Arms extended toward the ceiling, alternately stretch your arms toward the ceiling, lifting your shoulder blade off the floor. Repeat 6–8 times.
- Arms along the body, move your arms up to the sides - inhale, pull your knee to your chest - exhale, without lifting your head from the floor. Repeat 4-6 times.
- Hands along the body - press the back of the head onto the floor, hold for 4 counts. Repeat the exercise 4–6 times.
- Raise your head from the floor, turning it slightly to the right (at the level of the middle of the collarbone) and hold in this position for 4 counts, lower it, relax. Repeat the exercise 4-6 times, then do the same in the other direction.
- Hands on the belt. Bend your legs at the knee joints - inhale, straighten them with relaxation - exhale. Repeat 4-6 times.
- Hands along the body. Bring your shoulder blades together, pressing them to the floor, and hold this position for 4 counts. Relax. Repeat the exercise 4–6 times.
Physical therapy, lying on the right side
- The right arm is extended, the right ear rests on it, raise the right arm along with the head, hold the position for 4 counts, lower and relax. Repeat 2-4 times.
- Left arm along the body, raise your left arm up, inhale, lower, exhale. Repeat 2-4 times.
Perform the same exercises while lying on your left side.
Exercise therapy for cervical osteochondrosis, lying on the stomach
- Head resting on the forehead, hands on the back of the head, elbows parallel to the floor. Raise your head with your hands from the floor, hold this position for 4 counts, lower it and relax. Repeat 2-4 times.
- Head resting on the chin, palms under the chin. Stretch your arms forward one time, spread your arms to the sides for two, stretch your arms forward three times, start position four. Repeat 2-4 times.
- Arms extended forward. Swimming crawl style, repeat 4–8 times.
Exercise therapy for cervical osteochondrosis in the “sitting” position
All exercises are performed slowly until pain is felt.
- With the right palm we press on the right knee, holding 4 counts. Same with the other hand. Then do the same with both hands. Repeat with each hand 4-6 times.
- We pull the right shoulder to the right ear, then the left shoulder to the left ear. Repeat the exercise 4–6 times.
- We pull both shoulders towards the ears, repeat 4-6 times.
- Circular movements first with the right shoulder, then with the left, then with both. Repeat 8 times in each direction.
- Hands to the sides - inhale, hug your shoulders - exhale. Repeat 3-4 times.
- We sit on the right side of the chair: - Hand up and down,
- - “cutting wood” - hand back and forth,
- - hand up - we describe circles clockwise and counterclockwise,
- - raise your hand up and down and shake.
Lifestyle with cervical osteochondrosis
In order to live fully and without pain, and periods of remission were long, and exacerbations were less frequent, it is necessary to follow the general principles of exercise therapy, which were described above.
It is important to remember that it is better not to make circular rotational movements with your head, as this can lead to neck injury.
Prevention of the development of cervical osteochondrosis
- Regular visits to an orthopedist from early school age. If necessary, correct spinal curvatures and postural abnormalities.
- Play sports, primarily swimming, to form a muscle corset.
- Eat foods that bring calcium and magnesium into the body (fish and seafood, spinach, beans, nuts, seeds, peas, wholemeal bread, dairy products, cheeses).
- Avoid accumulating excess weight.
- You cannot hang bags on your shoulder; it is advisable to wear backpacks.
Exercise therapy AFTER OPERATION
After any surgical intervention, especially after surgery for joint replacement or hernia excision, bed rest is required.
Rehabilitation can take from two weeks to several months. As soon as the patient’s well-being is restored, he is prescribed exercise therapy. After surgery, physical therapy helps prevent congestion, restore full functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, prevent the formation of blood clots, and restore muscle tone.
In the early postoperative period, light physical exercises in combination with breathing exercises are prescribed.
In the later recovery period, specialized physical education is necessary, taking into account the current condition of the patient. Exercise therapy after surgery is required to restore vital functions of the body.
Many patients experience deceptive fear after undergoing surgery. In an effort to protect the affected joint or spine from stress, they refuse the ability to walk independently and perform everyday activities for longer than necessary. Ultimately, excessive caution will play a cruel joke: fear will take root, muscles will lose their shape, atrophy, and correct motor stereotypes will be lost.
To prevent this from happening, we recommend that you contact the rehabilitation specialists at Doctor Ost MC as soon as possible after the operation. Here, highly qualified rehabilitators are professionally engaged in restoring motor activity using the latest equipment. The Exart simulator, the Motomed simulator and others allow you to distribute the load in doses even to overweight patients, carefully and in a controlled manner to include joints, ligaments and muscles in the work.
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Most often, due to the characteristics of the anatomical structure and functional load, the lumbar spine is affected.
Neurological manifestations of lumbosacral osteochondrosis: pain of various types in the lower back and lower extremities. Pain occurs as a result of irritation of the spinal nerve roots. Swelling appears around the affected area of the root, which increases the pain; the surrounding muscle tissue is involved in the painful process. A muscle spasm occurs, which puts pressure on the affected root, resulting in a vicious circle. To stop this, it is necessary to influence the muscular system, prevent or reduce spasms of the deep back muscles, and strengthen the muscle corset.
To do this, it is necessary to conduct physical therapy classes, self-massage, and behave correctly in everyday life.
In case of severe pain in the lumbar spine and lower extremities, a complex of exercise therapy using a gentle regimen (in easier positions) is recommended.
Objectives of exercise therapy during this period:
- stretching and relaxing pathologically tense back muscles;
- increased blood and lymph circulation in the lumbar spine.
When performing exercises, you should follow the general principles of the exercises described above.
Complex of therapeutic exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis
Gentle mode.
Lying on your back
- Arms along the body, legs together. Raise your hands up - inhale, lower - exhale. Repeat 4-5 times.
- Bend and straighten your feet while squeezing and unclenching your fingers. 10 times.
- Circular rotations of the feet 4–6 times in each direction. Repeats 2.
- Alternately pulling your knees to your chest. 6-8 times.
- Alternate abduction to the side of the right hand - right leg, left hand - left leg. 4–6 times.
- Hands in a “lock” behind your head. Raising your head, pull your toes towards you. Repeat 8 times.
- Hands along the body. Raise your arms up, at the same time pull your toes away from you - inhale, return to IP - exhale. Repeat 8 times.
- Bend your legs at the knees, place them shoulder-width apart. Use your right knee to touch your left foot, then touch your right foot with your left knee. Repeat 4-6 times.
- Simulation of riding a “bicycle”. 5 laps in each direction.
- Place your hand on your stomach. Take a deep breath into your belly, then exhale slowly. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Left hand along the body, right at the top. Alternately changing the position of the hands. Repeat 10-12 times.
- Feet shoulder-width apart, arms spread to the sides. With your right hand, reach for your left hand, return to the position, then with your left hand reach for your right hand. Repeat 6–8 times.
- Alternately pulling your knees to your chest using your hands. 6-8 hands.
- Bend and straighten your feet while squeezing and unclenching your fingers. 10 times.
Physical therapy, lying on your side
- On the left side . Swinging movements of the arm and leg upward. 4-6 times.
- Pulling the knee to the chest. 6–8 times.
- Swing your leg back and forth. 6–8 times.
On the right side, repeat all the exercises that were done on the left side.
Exercises on all fours
- Alternately abducting straight arms to the sides. 10–12 times.
- Alternate swinging movements with a straight leg backwards. 8–10 times.
- Alternately pulling the right knee to the left hand and then the left knee to the right hand. 6–8 times.
- Pull your right knee to your chest, round your back, tuck your chin to your chest. Return your leg to the IP and sit with your buttocks on your heels, pull your arms forward. Same with the other leg. Repeat 6–8 times.
- Alternate swinging movement with the straight leg up and the opposite arm up. Then repeat with the other arm and leg. 6–8 times.
- “Step over” with your hands to the right and left, your legs remain in place. 5 times in each direction.
- Sit on your heels without lifting your hands from the floor (at a slow pace) and stretch your arms forward, arching your back down towards the floor. 6–8 times.
- Transition to a sitting position on the right and then on the left buttock, without lifting your hands from the floor. 6–8 times.
- Place your straight arms on the floor and raise your head. Lowering your head to your chest (without bending your arms), arch your back (especially at the waist), then bend over. Perform slowly, 8-10 times.
Training mode
(in addition to the exercises of the gentle training regime).
For minor pain and beyond the acute stage, therapeutic exercises according to a training regimen are recommended.
Tasks:
— complete the formation of the muscle corset;
— normalize the range of motion in the joints of the lower extremities;
- perform strictly dosed exercises related to movements in the lumbar spine.
Lying on your back
- Starting position - legs bent at the hip and knee joints, feet resting on the support. Hands in a “lock” behind your head. Raising your head and shoulders off the floor. 6–8 times.
- IP - shins rest on a support, a heavy ball is clamped between the feet. Carrying the ball right and left. 6–8 times.
- The shins rest on a support, and there is a heavy ball between the feet. Pulling your knees to your chin, lifting your head off the floor. 6–8 times.
- Hands with dumbbells are moved to the left side, knees tilt to the right, and vice versa. 6–8 times.
- Arms along the body, legs straight. From the sides, pull your arms up behind your head at the same time as your feet point towards you, inhale. Arms down and feet relaxed - exhale. Repeat 4 times.
Lying on your stomach
- Arms extended forward. Raise your head and shoulders, move your left arm back to the side, turning your torso to the left. Repeat the same with your right hand.
- Moving your straight arms back, lifting your upper body, raise your legs bent at the knees. 6–8 times.
- Alternate flexion and extension of the legs at the knee joints. 15–20 times.
When performing exercises, you need to monitor your heart rate. For the intensity of the load to be optimal, the pulse should not exceed 120–140 beats per minute. Heart rate measurement is carried out at the beginning and at the end of the lesson.
Rules of conduct in everyday life for lumbar osteochondrosis
To prevent osteochondrosis from worsening, you need to avoid physical actions and back positions that lead to a sharp contraction of the lower back muscles.
The lying position reduces the load on the lumbar region (it reduces the pressure inside the disc by 50%), but sitting with such osteochondrosis is important as little as possible. In a standing position, it is necessary to change your position more often and transfer the load from one leg to the other.
You should also avoid a prolonged semi-inclined position of the body - in this position the discs experience maximum load. To do this, every quarter of an hour we straighten up, make several movements in the lower back and very smoothly several turns of the body, as well as a little bending back and forth (3-5 minutes; without tension or effort).
When walking, it is important to avoid sudden movements and steps. It is better to ride while standing in public transport.
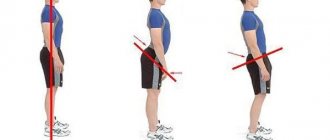
When working sedentarily, the patient needs to monitor his posture and control it with volitional effort - straighten his back, do not forget about regular straightening and smooth bends.
It is important for drivers to consider how to position their seat to provide maximum lumbar support. A 5-minute break after 2–3 hours of constant driving is mandatory, during which they do a warm-up.
Standing work requires optimization of the workplace to avoid bending towards it. To do this, you can increase, for example, the height of the table or lengthen the mop. If you need to reach down, it is important not to bend over, but to squat with a straight back .
It is also recommended to avoid lifting heavy objects, use a lumbar corset during physical work, and, of course, perform daily exercise therapy for osteochondrosis.
An active lifestyle as the main measure for the prevention of osteochondrosis
Prevention of osteochondrosis is primarily movement. Sports, walking, therapeutic exercises, and simple exercises help relieve stress on the intervertebral discs and strengthen the back muscles. The main reason for the development of the disease is that in ordinary life people move incorrectly, which creates unbearable loads on the spine. Prolonged sitting, standing, carrying bags on one shoulder and lifting heavy loads put stress on the back, mainly the cervical region.
You should know moderation in everything: excessive physical activity is just as harmful as its absence. Improper muscle contraction, for example, when playing tennis, volleyball, basketball, on the contrary, creates conditions for the development of osteochondrosis.
What to do when you don’t have enough time for exercise therapy?
The complexes compiled above make it possible, when performed correctly, to guarantee improvement of the condition and prevent complications of osteochondrosis. Naturally, this requires a certain amount of time. In addition, most often, osteochondrosis is present in all parts of the spine at once. In a hospital setting, exercise therapy is performed only for the most affected part. However, it is completely logical that the entire spine needs to be treated.
If you perform all the specified complexes, then the patient will develop a muscular corset, and - attention - a bonus: a toned figure will appear. For people with a sedentary lifestyle, there is no need to invent additional stress on the body. Although these complexes will not replace the gym (there will be no muscle relief, of course), the deep muscles will be strengthened, which is very important for the healthy functioning of not only the musculoskeletal system, but also the internal organs.
When there is no time for a full complex, but you need to exercise to improve your condition and feel lightness in the spine, a five-minute exercise therapy complex consisting of the most important basic exercises is proposed.
Precautionary measures
At first, exercise therapy consists of simple exercises that do not require additional physical skills. The selected activities must strictly correspond to their purpose. If during the implementation of the treatment complex the patient notices increased pain or lack of benefit, then it is necessary to consult a doctor.
During the first three workouts, mild pain is possible. Afterwards, the body adapts to unusual loads, which makes it easier to perform physical techniques. In the future, you should not ignore pain during exercise, as it is the main warning sign.
Before starting exercise therapy, it is necessary to prepare the body well and warm up the area of the thoracic spine, the clavicular-scapular area. 5-15-minute water procedures with 37°C water are excellent for this. You can also apply a dampened towel or heating pad to the desired area of the body. Sometimes a folk remedy is used to warm up the muscles - compresses with dimexide.
Do not overdo it from the first minutes of training. The exercises should be carried out smoothly and unhurriedly, excluding jerks and sudden movements. Dynamics and amplitude should increase gradually. Regular monitoring of equipment will reduce the likelihood of exacerbation of an existing condition or injury.
Exercise therapy complex - FIVE MINUTES FOR CERVICAL OSTEOCHONDROSIS
All exercises are performed sitting, preferably in front of a mirror to control your body, head straight, chin parallel to the floor; hands on the belt, knees together, emphasis on the feet.
- Slow turns of the head to the right and left, with a delay in the final positions as you exhale. When you inhale, return to the starting position - head straight, chin parallel to the floor. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Slowly tilt your head to the right and left shoulders (do not raise your shoulders!) with a delay in the final positions as you exhale. While inhaling, return to the starting position. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Slowly tilt your head down, reach your chin towards your chest (teeth are closed, mouth does not open), stretch as low as possible while exhaling. Return to IP - inhale. Don't throw your head back! Repeat 3-4 times.
- Slowly pull your chin to the middle of the right collarbone, then straight ahead to the middle of the left collarbone. Repeat 4 times.
- Slowly tilt your head down and “draw” a semicircle with your chin from one shoulder to the other and back (teeth closed, mouth does not open). Repeat 4 times.
- Pull your head up, hold for a few seconds and relax your neck. Repeat 2-3 times.
- Place your fists on your chin and press down on your fists for a few seconds. Repeat 2-3 times.
- Counter-resistance exercise: hands in a “lock” position, placed on the forehead. Press with your palms on your forehead and your forehead on your palms, hold for a few seconds. Repeat 2-3 times.
- Same with palms on the back of the head.
- Likewise, placing your palm on the side of your head. Tilt your head to the side, offering resistance with your hand.
- Also, palm on the temple area. Turn your head to the side, offering resistance with your hand.
- IP - arms bent at the elbows, palm over palm, at chin level. Reach your palms alternately with your forehead, chin, right ear, left ear. Repeat 1 time.
Exercise therapy-FIVE MINUTES FOR THORACIC OSTEOCHONDROSIS
- I.P. - sitting, arms along the body. Raising your hands up - inhale, lowering your hands - exhale. Repeat 2-3 times.
- I.P. - the same. Raising and lowering the shoulders with tension. Repeat 4–6 times.
- Sitting, palms to shoulders. Circular movements in the shoulder joints. 10 times in each direction.
- Sitting, palms to shoulders, elbows to the sides. Bring your elbows in front of you, tilt your head forward, round your back - exhale; move your elbows back, bend in the chest, head straight - inhale. Repeat 3-4 times.
- I.P. - sitting, arms straight to the sides. Horizontal scissors. Cross your arms straight in front of you and spread them to the sides. Repeat 10–12 times.
- I.P. - sitting - vertical scissors: right straight arm above, behind the head, left straight along the body. Changing the position of the hands. Repeat 10–12 times.
- I.P. - sitting, arms to the sides, circular movements with straight arms forward and backward. Repeat 10–12 times in each direction.
- I.P. - sitting, arms along the body. Torso tilt to the right. Then in the other direction. Repeat 4-6 times in each direction. This exercise can be done while sitting.
Preventive exercises
Preventive exercises for spinal osteochondrosis at home will help prevent pain from a sedentary lifestyle, and will also help improve concentration, intelligence and give a boost of vigor.
- Self-massage. Periodically knead the cervical or lumbar region with your hands using circular pressing movements.
- Sitting or standing straight, raise and lower your shoulders, bring them together and spread them apart. Do everything 10 times.
- Sitting, fix your knees and pelvis, turn in different directions, trying to twist as much as possible in the thoracic region. 10-15 times.
- Lying on your back, put your hands behind your head and lift your straight legs one by one. 15 times.
Back exercises for osteochondrosis at home will not take much time, but will protect you from back pain.
Exercise therapy-FIVE MINUTES FOR LUMBAR OSTEOCHONDROSIS
- I.P. - lying on his stomach. Arms are bent at the elbows and pressed to the body, legs are straight. Raise your upper body with straight arms, look to the right - to the left, turning your head. Return to IP, relax. Repeat 2-3 times.
- Arms extended forward, legs straight. “Crawl” with your hands, lifting your body. Repeat 4-6 times.
- I.P. - also, “Breaststroke” with hands. Repeat with each hand 4-6 times.
- Hands under the chin, we crawl “on our bellies”, alternately pulling the knee to the elbow. Repeat 4-6 times in each direction.
- Same thing, legs straight. Alternately raising your legs up, the toe “looking” at the floor. Repeat 4-6 times with each leg.
- Arms and legs are straightened. At the same time, raise your straight arms and legs up, hold for a few seconds, lower and relax. Repeat 3-4 times.
Author: adaptive physical education specialist Ekaterina Shishulina
Article updated 01/28/2020
Please note that the information presented on the site is for informational and educational purposes only and is not intended for self-diagnosis and self-medication. The selection and prescription of medications, treatment methods, as well as monitoring their use can only be carried out by the attending physician. Be sure to consult a specialist.
Exercise therapy at MC DOCTOR OST
Physical therapy is used in a number of medical centers and even in sports clubs. Before making a choice about whom to entrust your health to, you need to make sure that the rehabilitation specialist is qualified, has the appropriate level of equipment, and has a license for this type of activity.
You need to understand that it is impossible to overcome diseases of the spine or joints with the help of exercise therapy alone. Therefore, it would be correct to engage in physical therapy in combination with therapeutic measures and under the supervision of the attending physician.
“Doctor Ost helped my daughter cope with grade 3 scoliosis. They prescribed traction on the Elite robot and exercise therapy. After the first course of treatment, we found very noticeable changes; my posture became much straighter!”
Read full review
Doctor Ost MC is an expert in the treatment of various lesions of the musculoskeletal system, including the most severe ones. Experienced doctors at the Doctor Ost center work systematically, together. They regularly confirm their medical certificates and undergo training in the latest techniques.
In addition, the Doctor Ost MC has the latest robotic technologies and simulators that will help restore health to the spine and joints in the shortest possible time.
how much does it cost? The cost is indicated in the “rehabilitation” section of our price list. Follow the promotions, don't miss out on the best price!