Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine affect 75%-80% of the population of socially active age (30-60 years), 80% of 100% of those examined are people diagnosed with intervertebral hernia of the lumbar or lumbosacral region.
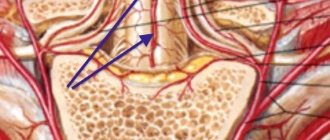
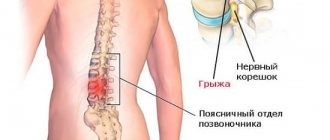
A feeling of numbness, heaviness, nagging pain in the lower back, a feeling of pain or weakness, paresthesia in the leg - these are the main symptoms. Unpleasant sensations arise not simply due to the development of deformation in the disc, but due to the fact that herniation affects and irritates the nerve roots, which are in great abundance in the lower parts of the column.
Neurological symptoms depress not only a person’s physical abilities, but also their psychophysiological state. According to statistics, hernias are the result of advanced osteochondrosis: about 50% of people with a history of osteochondrosis experience a hernia.
It is necessary to start therapeutic measures as early as possible, before the disease reaches the stage where it will be impossible to help conservatively. The basis of any conservative therapy for a diagnosis of intervertebral hernia is physical exercise - physical therapy. It is also indicated after surgical treatment.
What exercises are recommended for people with lumbosacral hernias, how to perform them, what is the essence of popular techniques, what is strictly contraindicated to do? We have prepared comprehensive material that will become your true guide in achieving victory over the painful manifestations of the disease.
The importance of exercise
Thematic sites post video exercises, visual illustrations, and advice from Sergei Bubnovsky and his colleagues. All this, of course, is wonderful, but remember one thing: we are not all the same! Even the same disease in each individual person has its own cause of development, nature of the course, location, severity, etc.
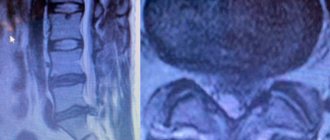
With a hernia like the one in the picture, gymnastics will not help.
Therefore, a therapeutic and prophylactic set of exercises, intensity, frequency and duration of loads should be developed by your attending physician together with a physical therapy instructor. A kind of exercise is a simple remedy for Schmorl’s hernia of the lumbar region, dorsal, foraminal, diffuse form. But only the right gymnastics will allow you to:
- reduce pressure in the area of the hernial protrusion, and the pathological effect on the nervous structures, spinal canal and vertebrae will be reduced;
- activate blood circulation, eliminate and prevent congestion and inflammation in the weak part of the spine and other segments;
- improve local metabolism and nutrition of intervertebral discs and joints, thereby stopping or significantly slowing down the progression;
- distribute the load evenly across departments, while safely strengthening the affected area;
- restore the previous mobility and flexibility of the spinal column;
- strengthen the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the back, normalize muscle tone;
- prevent the appearance of pain, achieve stable remission of the pathology, perhaps even its regression;
- if surgery was performed, quickly recover and return to a normal rhythm of life, prevent relapse of the disease;
- restore psycho-emotional comfort, establish healthy sleep.
First, perform strictly under the supervision of a rehabilitation trainer. You can practice calmly at home later, when you have mastered the technique perfectly. There are a number of movements that are strictly forbidden to do with a lumbar disc herniation. They will be discussed in our article.
What are the benefits of exercise therapy for the lumbar region?
Nowadays, almost everyone has heard about spinal osteochondrosis. According to the World Health Organization, 80% of the Russian population has pathologies of the musculoskeletal or musculoskeletal systems. This applies not only to older people, but also to the younger generation aged 29 to 49 years.
Many people feel back pain. It causes discomfort and reduces performance. After therapy, some patients never manage to return to their previous lives, because the disease becomes chronic. This significantly interferes with the return of performance to the previous level or even provokes its cessation.
Back pain is most often related to osteochondrosis. The pathology is very common and can affect anyone.
Osteochondrosis is accompanied by metabolic disorders in intervertebral cartilage and discs. As a result, the muscular and skeletal systems change. It has been proven that the spine has a significant impact on the internal organs, which means they are also subject to pathological transformations. Many doctors say that the most effective therapy for osteochondrosis is physical activity. Therefore, we advise you to pay special attention to exercise therapy for the lumbar spine.
How does osteochondrosis develop?
The spine contains from 33 to 35 vertebrae, and between them are elastic discs. Due to them, it has flexibility and elasticity. The disc has a core covered with cartilage above and below, and along its contour there is a fibrous ring.
Osteochondrosis negatively affects blood circulation and metabolism in the spine. In this regard, the discs dry out, decrease in height, and become less durable and elastic. The fibrous ring does not cope with its function of holding the spine, which leads to its protrusion. In addition, a rupture may occur, resulting in an intervertebral hernia. The consequence of these disorders can be mobility and curvature of the spinal column.
A healthy spine is a reality, but only with an active lifestyle and moderate sports activity. Considering that the age of modern technology forces us to spend most of our time sitting at a computer, do not forget about exercise therapy for the lumbar region. After all, this is the most effective method of treating spinal diseases, as well as their prevention.
Therapeutic exercise has a positive effect on the trophism of elastic discs. As a result, joint mobility improves, the spine is saturated with blood, and its bone components are destroyed more slowly. Exercise therapy for the lumbar region helps to recover after surgery and helps strengthen the back muscles.
Physical therapy is especially recommended for the following population groups:
- Elderly people.
- For those who have previously had vertebral injuries.
- People diagnosed with flat feet and club feet.
- For those who are constantly in a non-standard position.
- People with weak muscles and ligaments.
Osteochondrosis according to the place of occurrence can be classified into osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral spine.
Effective exercises
Physical exercises should be done exclusively outside the exacerbation phase; only in the absence of pain is it possible to begin them gradually. You can't force physical. loads, deliberately increasing the pace, duration, and number of approaches. They must be dosed, feasible, performed calmly and smoothly, and not provoke a painful syndrome. The wrong approach can make you feel worse.
Goal setting: muscle development
It has been established that normal muscle tension is the leading factor in resisting pathological changes in the spinal motion segment and protecting against injury. A lot depends on the condition of the muscles. Musculo-ligamentous dysfunction negatively affects flexion/extension, turns, rotation of the back, stability of the correct position of the spinal axis and the nutrition of the intervertebral discs.
The primary task is to strengthen, normalize tone, and increase the endurance of muscle structures. The main therapeutic measures are aimed at restoring the deep layers of the muscles of the back and abdomen. And the correct body position for performing exercise therapy is of great importance, so as not to overload the patient level.
The importance of exercising under medical supervision
Each disease and its corresponding rehabilitation treatment are deeply individual. A set of exercises is selected for each patient in accordance with pathologies, their severity, age, physical fitness and concomitant diseases. During classes, the doctor monitors progress, pays attention to the impact of exercises on the patient and adjusts the program based on individual characteristics, because the speed of recovery is different for each person. He also monitors the correct execution, range of movements, and determines the optimal number of repetitions and approaches.
Important! In order not to harm yourself, you need to increase the load gradually.
Correct body position
The lowest intradiscal pressure is observed in the supine position, the degree of load corresponds to 25 kg. For comparison, when a person just stands, it reaches 100 kg, and when sitting – 140 kg. With physical activity, the initial values increase significantly. In a supine position during exercise therapy, it is possible to achieve isolated strengthening of the necessary muscle elements without harming the problem area. Therefore, the main exercises for patients with lumbosacral hernias are those that will be performed in the following positions:
- lying on your back;
- lying on your side;
- on the stomach;
- On knees.
By doing gymnastics in the listed starting positions, the weak section will be unloaded, and physical training will take place in a safe and productive manner, since we will protect the lower level of the back from additional axial load and pressure above the parts of the body located above.
Of value are tasks for natural traction of the spine, performed on an inclined surface, which allow you to expand the interarticular distance and reduce mechanical compression of nerve fibers, as well as relieve swelling and inflammation, normalize blood flow and metabolic processes in the problem area.
What you need to know about exercise therapy for the lumbar region
The basic requirements for physical therapy are as follows:
- Classes can be started only after pronounced pain has been eliminated.
- During an exacerbation of osteochondrosis, it is recommended to do only simple movements.
- Training should be carried out on a regular basis during remission of the disease.
- Increase the range of motion and number of repetitions gradually.
- Watch your breathing, it should be measured and calm.
- Movements should be smooth. If you feel pain, you should end the session.
- The first training should be carried out strictly under the supervision of an instructor.
- Before classes, contact a specialist for advice and a program.
- Wear only breathable clothing.
If you have problems with the lumbar spine during exercise therapy, it is prohibited to:
- Use maximum loads at the very beginning of your workout.
- Make movements that lead to painful sensations.
If osteochondrosis worsens, perform exercises only in bed.
During exercise therapy for hernias and protrusions of the lumbar and sacral regions, it is contraindicated to lift weights while standing, do leg presses while lying down, jump and run.
A set of exercises for lumbar hernia
Strength loads with resistance, using additional weight, for endurance require caution. They will lead to injuries, generalization of disc prolapse, compression and damage to nerves, vascular formations, the spinal cord and other dangerous reactions. In mild stages, strength training is sometimes allowed, but only on medical advice. In case of serious displacements of the nucleus pulposus, a strict taboo is often placed on them. Be that as it may, completely avoid independent experiments, entrust the choice of any training to a doctor!
- Lie on your back, bend your knees. The feet are completely on the surface, arms along the body. As you inhale, draw in your stomach, tensing your abdominal muscles. Having reached the maximum point of retraction, record this result for 10 seconds. As you exhale, relax your stomach. Repeat 8-10 times.
- I.p. the same. Raise your upper body about 30 degrees (you can put your hands behind your head for convenience). Stay in this position for 7-10 seconds, then smoothly return back. Rest for the same number of seconds, then complete the task again. The number of repetitions is similar to exercise. No. 1.
- Lying on your back, bend your lower limbs at the knees. Very carefully and smoothly pull your knees to your stomach one by one, helping yourself with your hands. When you feel muscle tension in your back, fix the pose, and on the count of ten, return to i. p. Do 10 times with each limb.
- The starting position is the same. Raise one limb up, straightening it at the knee joint. Keep your straight leg up for about 7 seconds. Then we slowly lower it, returning it to the original position of the bent knee with support on the foot. Perform identical actions with the opposite leg. Repetition frequency – 8-10 times.
- Lie on your stomach. Hands are pressed to the outer thigh. Raise your head and chest above the surface to a distance that is acceptable for you. Hold this position for about 8 seconds. Slowly lower yourself to the floor and relax. After a 10-second break, repeat. Number of sets – up to 10 times.
- I.p. - lying on your stomach. Arms extended forward, legs together. Lift your right arm and left leg off the floor at the same time. Pull the toes of the foot back, the tips of the fingers of the palm forward for about 10 seconds. The chest is raised, do not throw your head back. We perform a similar action with the left leg and right arm.
- Get on all fours. Support in the legs: on the knees and the front of the legs. Support in the hands: on the palms, arms straight. This type of charging is similar to the previous one. Raise your straightened right arm and, on the opposite side, your left lower limb so that they are level with your back. We pull the toe (back) and hand (front) in different directions. Do not raise your chest or head.
- It is useful for lumbar intervertebral hernia to walk around the room on all fours for several minutes. Keep your back level (do not bend or bend), make sure that your arms do not bend when moving.
- Exercising in the pool has a beneficial effect. This could be aqua gymnastics or swimming. There are practically no restrictions on such activity in water, but the value is great: the lower back is unloaded and the spine is tactfully stretched, at the same time blood circulation is restored, metabolic processes are activated and the muscles are strengthened non-traumatically. But know that it is preferable for you to swim on your back or crawl style; it is not advisable to use other types.
The effectiveness of exercise therapy for the lumbar region and the main contraindications
During movement, the lumbar and sacral regions of the spine receive the main load. The vertebrae of the first zone are very mobile, unlike the vertebrae of the second zone. The latter are a fixed articulation of five vertebrae. Exercise therapy for the lumbosacral region helps strengthen the muscle corset, helps muscles that are constrained by spasms, and relieves pain in them after a pinched nerve.
Gymnastics alternately relaxes and tenses the muscles, which leads to improved blood flow. After an illness, the tissue receives stress and becomes stronger. Classes involve performing various exercises to train specific muscle groups. Exercise therapy is used for hernia of the lumbar spine.
Carrying out physical therapy of the lumbar region on a regular basis contributes to:
- Relief from lower back pain.
- Training of spinal muscle tissues.
- Normalization of joint mobility and blood flow in them.
- Relaxation of spasming muscles.
- Improving blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
- Increasing immunity and general tone of the body.
Exercise therapy for the lumbar region will be effective only if the exercises are performed correctly. Let's look at the basic rules:
- If you are doing physical therapy for the first time, be sure to contact an instructor. Your goal is the right exercises, not quick results.
- In case of exacerbation of the disease, you need to adhere to a special training program and only under the supervision of a trainer.
- Warm up your muscles and ligaments thoroughly before starting exercise. Massage the sacrum, because it bears the greatest load.
- Increase the difficulty gradually. The first workout should include a warm-up and the simplest movements. Duration no more than 20 minutes.
- It is not recommended to eat 1–1.5 hours before class.
- Perform exercise therapy for the lumbar and sacral region on a regular basis. Avoid long breaks. Only in this case can the disease be overcome.
Recommended articles on the topic:
- How to massage the abdomen for weight loss: different techniques for health and beauty
- Stone massage: description, benefits, methods
- MRI of three parts of the spine: when is it necessary and what are the features of the procedure
Undoubtedly, physical therapy is very useful, but not for everyone. Exercise therapy for the lumbar region has a number of contraindications:
- Any bleeding of the body, including uterine.
- The presence of malignant tumors.
- Increased body temperature.
- The period of exacerbation of any chronic disease.
- Swelling and cramps, poor circulation in the legs.
- In the presence of an inflammatory process of any organ. May be accompanied by general malaise or fever.
If, while performing exercise therapy for the lumbosacral region, you notice at least one of the symptoms listed below, consult a doctor immediately. The lesson plan may need to be adjusted:
- Sharp pain.
- Receiving microtraumas and other damage.
- Malaise and deterioration of health.
- Exacerbation of a disease associated with the spine or lumbosacral region.
Choosing a rehabilitation center
The domestic rehabilitation system is in a deteriorating state. In Russia there is very little assistance in the physical rehabilitation of such patients. Accordingly, the indicators of positive dynamics are too low, and our doctors do not even deny this. Not everything is going well with conservative and surgical therapy either. In this regard, a flow of people travels abroad for treatment. The Czech Republic inspires particular confidence, where the field of orthopedics and traumatology is developed on a global scale.
In the Czech Republic, prices are the most affordable abroad, and the quality of any medical service is excellent.
Prohibited exercises for lumbar disc herniation
- “Clean” vertical hanging and pull-ups on the bar. Since the spine will experience a significant load of body weight, due to the weakness of the ligamentous apparatus, pathological stretching may occur, which will have the opposite effect.
- Work with additional weight on the lower limbs and lower torso. Lifting weights with your legs, pressing limbs against resistance, squats and bends with dumbbells, kettlebells, or lifting heavy equipment from the floor with your hands. The danger lies in overstraining the spinal and abdominal muscles and increasing compression in the lumbosacral region.
- Torso twisting. To put it simply, it is forbidden to pump the press in any way. When performing a crunch, the lumbar region is critically overworked in your case. Moreover, twisting can displace the hernia and cause pinched nerves and compression of the spinal canal.
- Run, jump. You should avoid all situations where you need to run, jump or jump from some elevated object. Fast walking is also not recommended. The listed types of activity reduce the depreciation resource of the intervertebral discs, and, therefore, are fraught with aggravation of their morphological condition and the appearance of pain.
It is worth warning you against trying to do swings with the lower limbs, “mill” with the arms, all kinds of lunges on one leg, deep bends of the body down and to the sides from a standing position, circular rotations at the waist.
Rules for performing exercises
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is divided into 3 periods:
- for severe pain (acute period);
- subacute period (gradual reduction of pain);
- period of remission (pain is minimal or absent).
It is imperative to develop a clear lesson plan and divide the exercises into blocks that must be performed sequentially, without mixing. You can perform exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar region at any convenient time, the main thing is to take a break after eating, one hour or more.
Gymnastics for lumbar osteochondrosis gives maximum effect in the following cases:
- gymnastics is performed regularly every day;
- You need to do the exercises smoothly, concentrating on the work of the muscles;
- you should breathe correctly;
- You should periodically report the results of gymnastics to your doctor.
Yoga for lumbar hernia
It is worth taking into account that all these unconventional tactics for the spinal system should not be regarded as the main treatment, since they are not recognized by official medicine. And after removing the pathological formation, don’t even think about them at all; operated patients are not restored using dubious methods! Well, now let’s briefly look at each of the popular methods.
All non-traditional tactics should not be regarded as the main treatment, since they are not recognized by official medicine. And after removing the pathological formation, don’t even think about them at all. Yoga will in no way renew already degraded cartilage tissue, will not resolve the hernia and will not set it back. But it can relieve stress, increase flexibility and stabilize the spine.
Asanas consist of twisting the body, deep flexion and extension of the body, which is strictly contraindicated for this medical problem. Breathing and meditation tactics are allowed. Safe asanas:
- Lie on your back. Arms along the body, lower limbs lie freely. We bring our feet together, pull our toes toward ourselves, and push our heels back. Then, while inhaling, we slowly raise our arms up, moving them as far behind the head as possible, opening them slightly wider than the shoulder line. At the same time, we try to press the lower back with our stomach to the surface of the floor. Fix the pose for 3 seconds, continuing to pull your hands and heels in different directions. As you exhale, release the tension and return to the starting position, relaxing all parts of the body.
- Sit on all fours, standing on your knees and straight arms. Inhaling, slowly lower your head, pointing it towards the pelvis. At the same time, round your back like a cat. When you reach the highest point of the deflection, a short fixation of the pose is required, we return the head to i. p., straighten the back and bend it in the thoracic region. In the second approach, do not overextend your lower back and do not throw your head back.
Non-standard poses with insufficient flexibility of the musculoskeletal frame can end badly, even leading to complete paralysis of the legs. Especially with extrusion or with a sequestered form of protrusion, “turn on” your mind, these workouts are not for you. When using this approach for protrusions, monitor the sensations very carefully! Don't do anything that forces you past your fitness threshold. If you feel increased paresthesia or pain, even of a mild nature, retreat from the idea of training in a non-trivial way, and urgently notify your orthopedic doctor.
Attention! The long-term hernia of Schmorl L1 and others extremely thins the bone tissue of the vertebrae. Having done the asana, it is possible that a compression fracture of the vertebral body will follow. This outcome will add even more physical suffering and difficulties in treating the spine.
Pilates technique
The fashionable fitness trend is actively promoted on the Internet as a remedy for disc herniation. Experts are not against such classes, but they warn that they should only be taken under the guidance of a trainer with a higher medical education who understands what is good and what is bad for you. The principles of Pilates for the sacral and lumbar segment are completely different than for the neck or dorsal region.
Even if you choose the simplest exercise in terms of technical understanding, for example, the plank, keep in mind that its incorrect variation and inaccurate execution will not end well.
A plank from this fitness category is often recommended for protrusions and hernias. This is a static exercise, that is, you need to take an immobilized position and hold in the desired position. This technique has a comprehensive effect on the condition of the back, maintaining elasticity and tension of the muscle-ligamentous fibers, straightening and stretching the spine along its entire axis.
Example:
- take a pose as for push-ups from the floor (stand with outstretched arms);
- hands should be positioned strictly shoulder-width apart, legs at hip level, legs resting on the toes of the feet, heels do not touch the surface;
- the back is straight, the lower and upper limbs are straight;
- the pelvis, head, neck, lower limbs coincide with the line of the spine, hence the name of the “plank” technique (imagine that they are connected by one even string);
- hold the position as long as your endurance allows it (physically strong people are allowed to stay in this position for 30-60 seconds);
- most importantly, do not allow your back to sag, then most of the load will shift to the lumbar and sacral area, that is, the epicenter of gravity will be concentrated in the most vulnerable place.
There are other poses, for example, creating support in your hands on your forearms. Every day, increase the duration of the emphasis by a few seconds, as a result, stop at a maximum of 2-3 minutes.
Bubnovsky's exercises
A famous doctor says that it is necessary to treat the cause, not the consequences of the pathology. The problem is shortening, weakness and tightness of the muscles of the body, due to which the spinal elements do not receive the necessary nutrition, and the vertebral chain is destabilized and degenerative changes occur. Frankly speaking, this is not news for orthopedics, and all rehabilitation specialists offer exercise therapy based specifically on working out muscles and ligaments.
The well-known Shamil physical education technique or Dikul gymnastics also involve working with muscles, when the spinal column is aligned, the distance between the vertebrae increases, the load balance is adjusted, disc decompression and, as a result, neurological signs disappear. We present for your information Bubnovsky’s program, which, as a specialist says, will help you forget about a hernia without surgery or medications. But it is advisable only for non-advanced forms of pathogenesis. It is also useful as a good prevention of the development of degenerative diseases.
Exercises to do at home:
- Lie on your back, bend your legs at the knee joint. The soles of the feet are completely on the floor, arms along the body. Leaning on your shoulders and feet, while inhaling, raise your pelvis high. As you exhale, slowly lower your pelvis to the floor.
- Take a horizontal position, stomach up. Place the palms of your hands under your head, pressing your chin to your chest. Point your elbows up and at the same time bend your knees.
- Let's complicate the previous task. We try to reach our bent knees with our elbows, raising our head and upper back.
- Sit on the floor. Legs straightened, hands clasped at the back of the head. We bend the knee with each leg in turn, then extend it in an elevated position and lift the straight limb to the maximum distance from the surface.
- Lying on your back, spin the “bicycle.” Leg movements should be measured, without sudden jerks, breathing should be uniform.
- Sit on the floor, cross your arms behind your head. Lifting your buttocks one by one, move forward. Now we need to go back using a similar principle.
If you have already been recommended surgery, it is naive to think that physical education, whatever it may be, will replace it. Perhaps it will help delay the time before surgery for a short time. There are no other ways to solve the problem of large disc protrusion, which pinches the neurovascular plexuses to a critical level and ultimately compresses the spinal cord. By delaying the removal of herniation, you risk becoming wheelchair-bound due to the death of nerve tissue and damage to the main organ of the central nervous system - the spinal cord. And then surgery will no longer be effective.
How to prepare for lumbar exercise therapy
Physical therapy may be prescribed by a doctor after the results of the examination. Don't forget about the rules that will help you make it effective:
- The best time for classes is before lunch. The last meal should take place 1.5 hours before they start.
- Every workout should start with a warm-up. It helps warm up muscles and ligaments, prepares the heart for stress.
- During the exercise, use a roller under your knees at the correct height (the thigh and shin are perpendicular to each other).
- Record the exercises you perform in your diary and monitor the results.
For osteochondrosis, there is a whole complex of gymnastics. Exercises vary in difficulty and stages. Follow the lesson plan without combining them with each other.
The lumbar exercise therapy program is divided into blocks that are intended for a specific stage.
The first stage is carrying out exercise therapy in the acute period . As simple and slow movements as possible.
The second stage is the subacute period . If the pain has decreased, you can increase the load, but gradually.
The third stage is remission . The pain has stopped, complex exercises are included.
Choose loose clothing that will not interfere with your workout. We recommend paying attention to a cotton T-shirt or tank top, shorts or sweatpants. If you exercise outside in cold weather, use woolen items.
Inventory you will need:
- Gymnastic ball.
- Swedish wall.
- Pillow for the knees.
- Fitness mat.