The spinal column serves as the central axis of the body. This structure protects the spinal cord and ensures the function of upright posture. The main elements are the vertebrae and the discs between them.
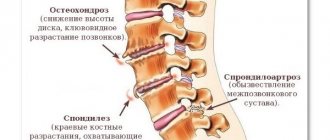
During life, the human body is exposed to various adverse effects, combined with the natural aging processes leading to the development of diseases. The most common degenerative changes in the spine are: osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis. Pathologies are accompanied by structural and functional disorders. The consequences of degenerative diseases are protrusions and herniated discs, spondylolisthesis, and stenosis of the spinal canal. Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to visualize all structures of the spine, diagnose degenerative processes in the early stages of development, and detect complications.
MRI scan of the neck
What it is?
Degenerative-dystrophic processes are changes that occur in the intervertebral discs . They are directly related to human aging. After all, over time, cartilage structures wear out, so the elasticity of the intervertebral discs deteriorates.
Metabolic processes are disrupted, nutrition of cartilage and bone structures becomes inadequate. Cracks appear on the cartilage, intervertebral protusions and hernias occur, and nerve endings are pinched. The pathology is accompanied by the appearance of pain and impaired mobility.
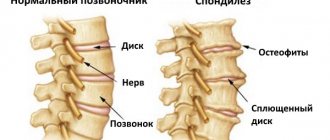
Destructive disorders begin with cartilage tissue
Picture of the course of the disease
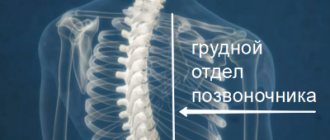
In the thoracic spine, trophic changes begin due to disrupted nutrition . The substances necessary for cartilage are supplied from the synovial fluid through diffuse processes. Nutrients enter the synovial fluid from the blood.
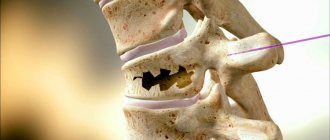
When trophic changes occur (deterioration of the nutrition process), lack of amino acids that are required for the synthesis of cartilage tissue, intervertebral discs are destroyed. Degenerative processes are observed. Cracks and erosive changes appear on the cartilage.
This leads to the following consequences:
- reduction in the height of intervertebral discs;
- the appearance of protrusion (protrusion);
- the appearance of an intervertebral hernia (in which the integrity of the disc fibrous ring is disrupted).
Such changes in the thoracic region provoke a decrease in the diameter of the holes through which the spinal roots emerge. They are compressed and the patient begins to feel pain.
Degrees and classification
Depending on the characteristics of the course of degenerative-dystrophic processes, there are:
- osteochondrosis;
- spondylosis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- local tendinosis, ligamentosis.
When the cartilage located between the thoracic vertebrae changes, osteochondrosis is diagnosed. In the later stages of the disease, protrusions and herniations of intervertebral discs appear. But in the thoracic region, changes most often begin in areas located between the processes of the vertebrae. As a result, the distance between the bone structures decreases and the spinal roots are pinched.
Dystrophic changes such as Forestier's disease (fixing hyperostosis) and osteopenic dystrophy . Dystrophy develops against the background of hormonal, endocrine pathologies, various diseases of internal organs, including medicinal ones.
Prevalence
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the thoracic spine are much less common than similar pathologies in the cervical and lumbar spine. This is due to its limited mobility and high stability .
People of different age groups can encounter the disease, but it most often occurs in people over 35 years of age.
Video: “Lecture on degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine”
Structural features
The intervertebral disc is a gel-like core surrounded by cartilage tissue and fibers of the fibrous ring. The discs are located between the vertebrae, providing the human body with flexibility. For the spinal column, the discs act as shock absorbers. The discs do not have their own blood supply, so they are restored very slowly, and with age they are completely “erased” (this is why older people become shorter). Therefore, the consequences of any changes in the design of the disc cause pain and can cause illness.
Risk factors and causes
A sedentary lifestyle is the main factor in the appearance of disorders in the spine. In the absence of health problems, the spine is able to withstand significant loads. But modern people are exposed to many factors that worsen its condition.
The main risk factors include:
- passive lifestyle;
- decreased physical activity;
- alcohol consumption;
- smoking.
This leads to obesity and weakening of muscle structures.
People who spend the whole day at the computer, neglect the need to walk, do morning exercises, and eventually face diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Tall people with an asthenic build are more prone to developing degenerative-dystrophic changes.
Among the main reasons are:
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the ridge, due to which blood circulation is impaired;
- incorrect posture;
- diseases in which the nutritional process of cartilage tissue is disrupted, including hereditary ones;
- thoracic spine injuries;
- hormonal imbalances;
- infectious, inflammatory diseases affecting the spine;
- excessive loads that provoke the appearance of microtraumas.
An improperly organized workday and chronic lack of sleep can provoke problems with the innervation of blood vessels. They will ultimately lead to impaired blood circulation, including in the tissues of the spine.
Consequences
Degenerative-dystrophic changes are not noticeable at the initial stages. Pain in the thoracic region occurs extremely rarely, so the disease is diagnosed when the process of pinching nerve endings begins due to narrowing of the intervertebral canals. Nerve roots swell, their conductivity deteriorates. Patients often complain of a feeling of numbness in the limbs, a feeling of fatigue in the back and shoulders.
Due to compression of nerve endings, people develop symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia . It manifests itself as headaches, dizziness, and in severe cases, fainting is possible. Due to chronic fatigue, some people experience panic attacks.
Lack of timely treatment leads to progression of the disease. As a result, in addition to constant pain, a person experiences increased fatigue . Degenerative-dystrophic changes can be complicated by arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondropathy, intercostal neuralgia . Weakening of the muscle corset provokes the appearance of scoliosis; in some people, the vertebrae even become displaced. In severe cases, paresis and paralysis occur.
Video: “Symptoms, consequences and treatment of osteochondrosis”
Diagnosis of thoracic spondylosis
Specialists who diagnose and treat spondylosis of the thoracic spine are neurologists, neurosurgeons, orthopedists, physiotherapists, and exercise therapy doctors.
Thoracic spondylosis can be diagnosed using a physical examination and medical imaging techniques:
- The doctor will take a medical history and medical history, as well as a detailed physical examination of the spine and neurological tests.
- To confirm the diagnosis, imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs of the thoracic spine may be ordered to determine the extent of thoracic spine degeneration
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Did you know that...
Next fact
The appearance of degenerative-dystrophic changes can be suspected based on the signs characteristic of the pathology.
Most often, people come to doctors with complaints about:
- pain in the back and chest, intercostal space;
- deterioration of mobility;
- numbness of the limbs and other parts of the body;
- decreased mobility;
- a feeling of discomfort in the area where the internal organs are located;
- sexual dysfunction.
Doctors send patients with the described complaints for radiography and myelography.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes are indicated by the proliferation of osteophytes. To clarify the nature of changes in the discs, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed.
The following signs indicate the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes::
- deformation of processes;
- reduction in disc height;
- osteophytes;
- vertebral subluxations.
Myelography is performed to detect spinal canal stenosis.
More informative diagnostic methods are tomography.
Dorsago and dorsalgia
Dorsago is a symptom manifested by sharp acute pain in the chest, the so-called lumbago. Usually this feeling occurs after working for a long time in a static position. During such an attack, the patient experiences difficulty breathing. The pain increases with rotation of the upper body.
Dorsalgia is pain of moderate intensity that manifests itself in the area of affected intervertebral discs. This pain syndrome begins gradually and lasts up to 2-3 weeks. Unpleasant sensations intensify with deep inhalation and exhalation, as well as bending in different directions. There is also the impression of lack of air. The peak of pain occurs immediately after waking up and decreases after a short walk.
Treatment
The tactics of therapy when identifying pathology depends on the severity of degenerative changes.
Treatment is directed to:
- pain relief;
- stopping or reducing the speed of destructive processes;
- restoration of bone tissue, cartilage structures;
- return of mobility.
The doctor prescribes medication in combination with a diet. If necessary, doctors recommend wearing an orthopedic corset. After acute symptoms are relieved, they give a referral for massage, physiotherapy, and exercise therapy. In advanced cases, surgical treatment is indicated.
Drugs
During drug therapy, medications are prescribed to improve the patient's condition.
Doctors prescribe:
| nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
|
| muscle relaxants that relieve muscle spasms |
|
| analgesics |
|
| vitamins |
|
| vascular drugs |
|
| chondroprotectors |
|
Analgesics are used for a short course, provided that NSAIDs do not help relieve pain. Most often they do blockades. They simply alleviate the condition without eliminating the cause of the pain. .
Surgery
In advanced cases, when conservative therapy does not give the desired result , surgery is prescribed. It is necessary to eliminate compression of a nerve root, remove a hernia that is bothering the patient, or replace a joint. In some cases, during the operation, the spinal column is fixed with special metal structures or grafts are installed.
Exercise therapy and massage
After the acute stage under the influence of medications has passed, doctors recommend massage to patients and give directions to therapeutic exercises. Massage allows you to tone relaxed muscles and relax tense ones. As a result, the muscle corset is strengthened and pain is reduced.
At first, exercise therapy is carried out under the supervision of a specialist. The exercises are designed to eliminate stiffness, strengthen muscles, and increase mobility . With the help of gymnastics, the process of supply of nutrients to the intervertebral discs improves, correct posture returns, and the elasticity of the intervertebral joints increases.
Treatment at home
If pain occurs, you should visit a doctor. The doctor will make a diagnosis and select treatment tactics. Inpatient therapy is necessary only in extreme cases. All treatment takes place at home. The patient takes prescribed medications, wears a corset, and does gymnastics.
But some recommend using alternative medicine to speed up recovery. You can use an infusion of celery root, a decoction of sunflower roots. It is recommended to smear problem areas with a prepared ointment made from pork fat, wax, fir oil and ammonia.
Prevention
Every person can avoid the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine. For this
Prevention of degenerative-dystrophic changes occupies the main place in the treatment of the disease, doctors recommend following the established rules.
Necessary:
- avoid hypothermia;
- Healthy food;
- maintain physical fitness;
- control weight;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- watch your posture;
- sleep on a hard mattress.
Moderate physical activity helps maintain the spinal column in the correct position throughout life. This is the main method of preventing diseases.
Treatment of spondylosis of the thoracic spine
Conservative treatment
Symptoms of thoracic spondylosis can range from mild and occasional discomfort to intense and chronic pain. Spondylosis affects the facet joints in the spine, significantly reducing mobility in motion segments. Fortunately, most people with thoracic spondylosis do not require surgery. The most common conservative treatment methods are:
• Acupuncture
is a popular treatment used to relieve back and neck pain. Tiny needles, about the size of a human hair, are inserted into specific points on the body. Each needle can be twisted, electrically stimulated or heated to enhance the treatment effect. Acupuncture is thought to work (in part) by stimulating the body's production of certain chemicals that help relieve pain.
• Bed rest
: In severe cases of spondylosis, bed rest may be required (no more than 1-3 days). Long-term bed rest should be avoided as the risk of deep vein thrombosis increases.
Use of corsets
: Temporary bracing (1 week) may help relieve symptoms, but long-term brace use is not recommended. Corsets worn for long periods of time weaken the back muscles and can increase pain if not worn continuously. Physical therapy (physical therapy) is more beneficial as it strengthens the muscles.
• Manual therapy
: Chiropractors believe that a healthy nervous system is synonymous with a healthy body. Subluxation or misalignment of a vertebra can lead to nervous system disorder and development of back and neck pain. Spinal manipulations, which a chiropractor performs with his hands, can eliminate subluxations and increase the mobility of motion segments.
• Lifestyle modification
: Losing and maintaining a healthy weight, eating healthy, nutritious foods, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking are important “healthy habits” that help support spinal function at any age.
Medicines
- Muscle relaxants: Muscle relaxants help relieve muscle spasms and pain.
- Drugs (opioids) may be prescribed for short periods of time to relieve acute pain.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) relieve inflammation, which often contributes to pain.
It is not recommended to take NSAIDs on your own, especially for a long time, as this can lead to serious side effects and adverse effects on the body.
• Physical therapy
- combines passive treatment with therapeutic exercises. Passive treatments include heat/ice, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation to relieve muscle spasm and pain. Therapeutic exercises allow the patient to increase flexibility and range of motion while building muscle strength.
Patients should not be afraid of physical therapy. Even patients who experience pain and difficulty walking have found that isometric exercises have some effectiveness.
• Spinal injections
: There are many types of spinal injections, including epidural steroid injections and facet joint injections. These injections use a combination of local anesthetics and steroid drugs to reduce inflammation in nerve tissue and thus often help reduce pain.
•Hydrotherapy
: By harnessing the soothing effects of water, hydrotherapy can treat a variety of bone and joint pain. It differs from swimming in that it involves exercises that the patient does in warm water, usually at a temperature of 35-37 degrees.
•Taping
: This is a technique that is used for injury prevention or rehabilitation. Exercise therapy professionals are specially trained to effectively apply tape to the skin to help maintain the stability of specific muscles or bones. The benefits of using this treatment include:
- Injury Prevention
- The ability to quickly return to sports or work
- Protection of damaged soft tissues such as ligaments, tendons or fascia
- Improved mobility
- Pain reduction
- Reduced risk of re-injury
- Improving joint stability
- Reducing swelling
•Postural restructuring
: If symptoms are the result of years of poor posture, spinal bone realignment combined with postural exercises may help reduce back pain. This often involves assessing your current posture, helping to identify any tight or weak muscles that may be causing back pain. Next, the doctor gives tips on how you can make changes in your posture—sitting, standing, and handling objects properly. A selection of exercises is also carried out to stretch and strengthen the back muscles, which helps improve posture.
•Effect on soft tissues
: Involves the evaluation and treatment of any soft tissue injury causing pain and dysfunction. Soft tissue includes ligaments, tendons, muscles and fascia. Types of soft tissue treatments include myofascial release, massage, heat therapy, stretching and electrotherapy.
Benefits of soft tissue treatment include:
- Faster recovery from injury
- Reduced risk of re-injury
- Increased functionality
- Accelerated healing process
- Increased mobility
- Increased muscle strength
- Reducing swelling
- Increasing the length of soft tissues
- Increased range of motion
- Pain reduction
Recovery prognosis
It is possible to say how the disease will develop only after a full examination and an accurate diagnosis. For example, it is impossible to completely get rid of grade 2–4 osteochondrosis . But properly selected therapy can relieve inflammation and stop further development of the disease. With proper treatment, long-term remission can be achieved . It is possible to prevent the occurrence of complications and stop the progression of degenerative-dystrophic changes if you do not forget about prevention.
Prevention
Due to the high incidence and prevalence of DDSD, all patients are advised to adhere to certain preventive measures during preventive examinations and after treatment. They will prevent the occurrence of back diseases and complications in the presence of chronic pathologies.
Such recommendations include: avoiding excessive physical exertion and heavy lifting, following physical therapy exercises, regular sports (swimming, gymnastics, yoga), alternating working hours with rest, doing a short warm-up every hour of working time.