The spine is the axial skeleton of the human skeleton. This bone structure is shaped like the letter S. Thanks to physiological curves, the spinal column is more elastic, this allows it to soften shocks and vibrations during movement, and maintain stable balance of the body.
The sections of the spine consist of a different number of vertebrae and perform important functions. Ligaments and muscles support the vertebrae, allow rotation and bending of the torso, and also limit movements that could damage this bone structure. Every person should understand what structure the spine has and how it functions in order to notice problems in time due to injuries, diseases or natural changes in the body.
General information about the structure of the spine
The spine is a long column curved in several places; it consists of 32 - 34 interconnected small bones called vertebrae. The elements of the spine are connected to each other. Between the vertebral bodies there are intervertebral discs that connect them. In appearance, it is a round flat pad made of connective tissue, which has a complex structure. Discs also play a big role in shock absorption of the spine, softening shocks during walking, running, and jumping.
The structure of the spinal column
To further stabilize the spine, its elements are connected by ligaments. These are dense connective tissue cords that fix the bones in the correct position and relieve some of the load from the spine. Tendons are the final structure of muscles by which they are attached to bones. Facet joints, located between adjacent vertebrae, connect them to each other. These bony connections provide movement in the intervertebral space.
Inside each vertebra there are holes that are located one above the other. They are called the spinal canal, in which the spinal cord lies. This is an organ of the central nervous system, in the gray matter of which a large number of bundles of neurons are located. They are the ones who send and receive signals from the brain to various organs. The spinal cord is divided into 31 segments, from which the same number of nerve roots emerge. Nerve branches exit the cavity of the spinal canal through the foraminal openings (the lumen that forms the vertebral body, its arch, and the pedicles of the arch).
Some people don't know how many sections there really are in the human spine. There are 5 segments:
- Cervical.
- Chest.
- Lumbar.
- Sacral.
- Coccygeal
All parts of the human spine consist of a certain number of elements.
Table of the structure of spinal segments:
| Spinal segment | Number of vertebrae |
| Cervical | 7 vertebrae (C1 – C7) |
| Chest | 12 bone elements (Th1 – Th12) |
| Lumbar | 5 dice (L1 – L5) |
| Sacral | 5 elements (S1 – S5) |
| Coccygeal | From 3 to 5 vertebrae (Co1 – Co5) |
Reference. In adults, the coccygeal vertebrae fuse into a single bone structure.
To better understand how the spine is structured, you need to consider the structural features of its different sections.
As already mentioned, the spinal column has a curved shape in several places. If you look at it from the side, it resembles the letter S. These physiological curves are called lordosis (bending forward) and kyphosis (bending backward). Lordosis is observed in all people in the cervical and lumbar segments. Kyphosis forms in the chest and sacrum area.
With the help of these bends, a person is able to maintain balance when walking upright. During dynamic, sudden movements, they spring, softening vibrations.
The spinal column performs the most important functions: it supports the head, as well as the body in a vertical position, and is a support for other bone structures. In addition, the spine protects the spinal cord from damage.
No ads 1
Human spine and lumbar region: its anatomical structure
The lumbar region includes the 5 largest vertebrae, increasing in size from the first to the fifth. Due to the need to maintain the body in an upright position, they bear the greatest burden. Therefore, in size and shape they differ significantly from the others - they are more massive, shorter, and more developed in width. Despite their massiveness, their connecting segments are quite mobile, which in turn ensures the mobility of the body and the possibility of various turns and tilts of the body.
Important: Despite the massiveness of the connecting elements of this section, it is considered the most vulnerable! Excessive load on the lower back, hypothermia, mechanical displacement of the discs - all this can lead to inflammation of segments of the human spine. In addition, even excess weight often leads to similar problems. Disc herniation often occurs in this section at the L4-L5-S1 level, namely in 94%.
Structure of the lumbar spine
Anatomy of the cervical spine
The spinal segment is the initial section of the spinal column. As already mentioned, the number of vertebrae of which it consists is seven. They have the following medical designation - from C1 to C7. In this area there is a bend that is directed forward. The mobility of this section is the highest, thanks to which people can move their neck in different directions, tilt it, and turn it.
Inside the transverse processes of the vertebrae of the neck there are openings in which the vertebral arteries are located. They transport blood to the brain. When vertebrae are displaced, protrusions or hernias form in this area, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted due to compression of the vertebral artery. Then the following symptoms occur: headache, vertigo (dizzy), visual disturbances, impaired coordination of movements, speech. This is how vertebrobasilar syndrome manifests itself.
The cervical spine begins from the atlas and axis. The structure of the upper vertebrae is different. The first consists of an anterior and posterior arch, which are connected on the sides by bone thickenings, while the vertebral body is absent. The second has a tooth (process) in front, which is attached by ligaments to the vertebral canal of the atlas. Thanks to this structure, a person can rotate his head in different directions.
The cervical segment is considered the most vulnerable to traumatic effects, unlike other structures of the spine. This is due to the weakness of the neck muscles, the small size of the bones, and their low strength.
Most often, the cervical segment is damaged by a direct blow with a blunt object, excessive flexion or extension of the neck (during an accident or diving). With such injuries, the spinal cord can be damaged, and this can lead to dangerous complications, including death.
[node:field_similarlink]
Treatment tactics
After all the necessary examinations, treatment tactics are selected.
If conservative (non-surgical) treatment is possible, a corset is selected for the patient, and primary rehabilitation is carried out (the abdominal and back muscles need to be strengthened).
If a decision is made to undergo surgery, the doctor will determine the type of surgical treatment. You can read more about this in the section “For persons with medical education.”
Thanks to reliable and proven methods, the experience of surgeons, as well as modern technologies, patients recover quickly.
Thoracic region
Not everyone knows how many vertebrae there are in the thoracic area. Their number is 12, they are designated as follows - Th1 - Th12, T1 - T12 or D1 - D12. It has a physiological bend directed backwards.
The thoracic segment is an integral part of the posterior wall of the chest. The bodies and transverse processes of the vertebrae are attached to the ribs by joints. From the spine, the ribs extend to the sternum, this is how the rib cage is formed.
The thoracic segment is the least mobile. This is explained by the fact that its vertebrae are connected by discs, the height of which is minimal. In addition, its motor activity is limited to the spinous processes of the vertebrae and the chest.
Reference. The cavity in the spinal column of the thoracic segment is quite narrow. This leads to the fact that when even small hernias, tumors or bone growths appear, the nerve bundles and spinal cord are damaged.
How to help your spine last longer
Exercise
Physical exercises help maintain the flexibility of the spinal column and strengthen the muscles that hold it, but remember, not all exercises are useful, it is better to engage in complexes created by therapeutic physical education (PT), they are safe and created specifically for the prevention and elimination of problems with posture.
Exercises that strengthen the muscles of the back and abdomen are suitable, as they stabilize the spine. Exercises with lifting the body while lying on your stomach and back (on your abs) are suitable; it is also necessary to stretch the spine. Yoga classes provide an ideal load; they not only strengthen the muscle corset, but also stretch it; swimming is also perfect. Be sure to exercise at least 2-3 times a week.
The ideal exercise for relaxing muscles and relieving pain during spasms is the child's yoga position. Starting position: sitting on your knees, chest resting on your knees, neck relaxed. You need to sit in this position for about three minutes, breathing slowly through your stomach.
If you already have serious problems with the spine (hernia, scoliosis or others), a set of exercises should be compiled by a movement specialist and performed under his supervision. Incorrect technique or unnecessary exercises can aggravate problems and worsen the condition of the musculoskeletal system.
Avoid Toxin Accumulation
Food affects not only the digestive system; the normal functioning of the spine depends on the quality of the food. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor your diet.
It is best to exclude from your menu all harmful and unhealthy foods: those with excess cholesterol, salt and sugar. Frequent consumption of fast food has a negative effect on the condition of the spine.
Poor nutrition contributes to the accumulation of harmful toxins that destroy the spinal column.
To maintain health, it is important to drink enough water (at least 1.5 liters of water per day), eat plenty of vegetables and herbs, and drink freshly squeezed juices. This helps rid the body of toxins.
Keep your weight normal
Almost everyone whose weight is above normal has spinal injuries. The reason is that with increasing mass, the load on the spinal column increases, because of this the vertebrae suffer, the discs between the vertebrae become thinner, and displacements occur.
If your body mass index is higher than normal, be sure to lose a few pounds - this will keep you healthy and allow you to move freely.
Do local massage
You can prevent back problems and pain with massage. But remember: for acute pain, massage is contraindicated. It is best to do a course of massages (when you do it weekly for 1 or 2 months in a row). This will prevent back pain, relax muscles, and improve blood circulation.
Massage increases the distance between the vertebrae, promotes their realignment, and rids the body of toxins.
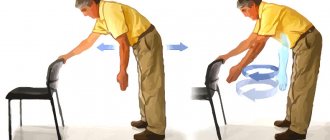
Don't lift heavy things
If you are unable to refuse the lift, do it in the correct position.
Doctor's opinion:
Vladimir Yurievich Voronov
Traumatologist with 20 years of experience in a regional hospital
Ask a Question
It is necessary to take the correct position: squat as low as possible, knees bent, back straight. Take the object, if possible, hug it. Gently straighten your knees, making sure that your lower back does not bend back.
If you often have to carry heavy objects, be sure to purchase and wear a special corset. Even if you rarely lift heavy objects, do it carefully so as not to harm your back.
Lumbar segment
The largest vertebrae are located in the lumbar region.
Reference. Normally, the lumbar segment of the spinal column contains 5 vertebrae. However, this section may differ in the number of vertebrae in different people. We are talking about a congenital pathology called lumbarization. Then, in the lumbar region during intrauterine development, an additional vertebra (L6) is formed, which appears from the first sacral one. This bony element is partially or completely separated from the sacrum.
In a healthy person, there is a bend in the lower back directed forward (as is cervical lordosis).
The lumbar segment connects the sedentary thoracic and immobile sacral regions. This area of the spine is subject to enormous stress, as the entire body presses on it. When a person lifts or carries heavy objects, the pressure on the lower back increases even more. For this reason, the cartilage pad in this area wears out faster. Under pressure from the vertebrae, cracks appear on the surface of the disc, which increases the risk of rupture of the outer shell and loss of the nucleus pulposus. This is how a disc herniation occurs, which can compress nerve branches, causing pain and neurological disorders (numbness of the buttocks, groin, legs).
No ads 2
The sacrum or sacral region of the human spine
The human spine below has 5 fused vertebrae that form the sacrum - a single massive triangular-shaped bone, with its apex facing down and having a bony connection with the pelvic bone. It is worth noting that in women it is shorter, but wider and not so curved.
Front and back view
Vertebral structure
The vertebrae are the connecting elements of the spine. The anterior thickened part of the cylindrical bone is called the vertebral body. It is this part that bears the main load. On the back of the vertebral body there is an arch with processes. Between the bodies and arches there is the spinal canal, which is the receptacle of the spinal cord, blood vessels, nerve bundles, and fatty tissue.
Vertebral structure
In addition, the posterior longitudinal and yellow ligaments are located inside the spinal canal. The first fixes the vertebral bodies, and the second fixes the arches.
The spinal canal contains the longitudinal and yellow ligaments
When degenerative changes in the cartilage pads and joints of the vertebrae become unstable, the ligaments in the spinal canal thicken to hold them in place. When the spinal canal is narrowed, even small formations cause compression of the spinal cord.
Reference. MRI can help identify narrowing of the spinal canal in the early stages. To expand the lumen of the spinal column, spinal decompression is performed.
From the vertebral arch there are 2 transverse and 4 articular processes (upper and lower), as well as one spinous one. Ligaments and muscles are attached to the spinous and transverse processes, and the articular ones form arcuate (facet) connections. The arch is fixed on the vertebra by legs.
Nerves and vessels of the spinal cord exit through the foramen
The arch processes facing each other form facet joints. Between the bones there is cartilage, which reduces friction. The ends of the processes are enclosed in an articular capsule, which produces articular fluid, which is responsible for the sliding of bone surfaces. Facet joints provide additional flexibility to the spine.
The pedicles, bodies and articular processes of adjacent vertebrae form the foraminal opening. It is through them that the nerve processes and vessels of the spinal cord gain access to the periphery.
The vertebrae are covered on the outside with a dense cortical layer, and on the inside they are filled with loose tissue, which is filled with bone marrow, which performs a hematopoietic function.
Moment of truth
There are from thirty-two to thirty-four vertebrae in the human spine, which include:
- seven cervical vertebrae;
- twelve thoracic vertebrae;
- five lumbar vertebrae;
- five sacral vertebrae, considered one bone;
- from three to five coccygeal vertebrae.
The structure of the spine is quite complex, and if any part of it is damaged, the entire human body will cease to function normally. Therefore, it is important to monitor your health and not endanger your musculoskeletal system.
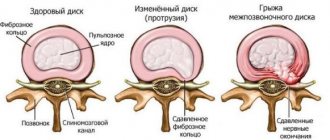
Intervertebral disc structure
The anatomy of intervertebral discs is quite complex. It looks like a round gasket that connects 2 adjacent vertebrae. The outside of the disc is covered with a fibrous ring, inside of which there is an elastic nucleus pulposus. The outer shell holds the nucleus pulposus and does not allow the vertebrae to move. And the inner part serves as an additional shock absorber.
Intervertebral disc
The cartilage lining of an adult human lacks blood vessels, so it absorbs nutrients from the blood vessels of nearby vertebrae.
Reference. Most medications do not reach the intervertebral disc. To restore its structure, laser thermodisplasty is performed.
In a healthy person, the annulus fibrosus disc consists of strong fibers. However, there are cases when, under the influence of negative factors, the tissue of the outer shell is replaced by useless scar tissue. Then the likelihood of violating the integrity of the fibrous membrane increases.
Possible diseases
The spine of a modern person is subject to a number of unfavorable factors that provoke the development of a variety of diseases. This is a sedentary lifestyle, constant stay in an uncomfortable position, poor nutrition, deficiency of calcium and other nutrients. As a result, the following pathologies may appear:
- Ankylosing spondylitis. It provokes the covering of bone tissue with calcium growths, which limits its movement and leads to disability. It occurs more often in men, but it is also diagnosed in women.
- Intervertebral hernia. One of the most common pathologies of the spinal column. It is provoked by obesity, lack of moderate physical activity or excessive sports training. Leads to loss of the nucleus from the annulus fibrosus. It can be treated traditionally or surgically.
- Oncology education. It is a dangerous pathology that is becoming more common in the modern world. Appears in different departments and without surgery poses a serious threat to life and health.
- Osteochondrosis. It occurs in almost every modern person in the initial stage. It can develop unnoticed for a long time and provoke the development of serious complications. It manifests itself as back pain, poor posture or loss of sensitivity in a certain area.
- Osteoporosis. The gradual leaching of calcium from bones makes them brittle and brittle. In later stages, it occurs mainly in older people. Manifested by problems with teeth or nails. It is treated with specific exercises and vitamin complexes.
You can prevent the occurrence of any types of spinal diseases by taking good care of your health. To do this, people at any age are recommended to play sports, or at least do simple exercises every day in the form of exercises. And it is also important to remember about the correct position of the back during work, high-quality nutrition, taking vitamin complexes, monitoring normal body weight, and avoiding excessive physical activity.
The spine is a support for the whole body; it is a complex structure that is subject to daily stress and negative factors. It is divided conditionally into several departments, which are assigned certain functions by nature. They differ from each other in the structure of their vertebrae.
Spinal cord
Coccygeal spine
The structure of the spinal cord is segmental, it consists of millions of nerve fibers. This organ is surrounded by 3 membranes: soft, arachnoid, and hard. The outer hard shell consists of dense fibrous tissue, inside of which there is the spinal cord and a large number of nerve roots, washed by cerebrospinal fluid.
The spinal cord emerges from the brain and ends at the level of the 1st - 2nd lumbar vertebrae. A bundle of nerve fibers departs from it, which form the cauda equina underneath it (4 lower lumbar, 5 sacral and coccygeal nerves, filum terminale of the spinal cord). It is responsible for the innervation of the lower extremities, as well as the pelvic organs.
Nerve roots exit the spinal canal through the foramina. Each section of the spinal cord transmits a nerve impulse. For example, the nerve roots of the cervical segment of the spine are responsible for the innervation of the neck and arms, the thoracic - the chest, abdominal organs, the lumbar and sacral - the lower extremities, and pelvic organs.
The spinal cord sends signals along peripheral nerves to various organs, in this way it regulates their functions. Next, information from the tissues enters the central nervous system via sensory nerve fibers.
Radiculopathy
The term radiculitis (radiculopathy) is widely used and means root compression. Radiculitis can occur in both the lumbar and cervical spine, or much less frequently in the thoracic spine. Root compression occurs when there is excess pressure on the nerve root. Excessive pressure can come from both bone tissue and soft tissue (muscles, cartilage, ligaments). This pressure disrupts nerve function, causing pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness.
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bone tissue, including the vertebrae, weakens, which increases the risk of vertebral fracture, even with minor loads. Vertebral compression fractures are the most common type of fracture caused by osteoporosis, and hip and wrist fractures are also possible with osteoporosis. These vertebral fractures can change the shape and strength of the spine, especially in older women, who often develop spinal deformity as a result of such fractures. The spine becomes excessively tilted in the thoracic region (kyphosis) and the shoulders bulge forward. With severe osteoporosis, even simple movements such as bending forward can lead to vertebral fractures.
Muscles and ligaments of the spine
The muscle fibers located around the spinal column stabilize this bone structure and make it possible to perform various movements of the body (turns, bends). The muscles are fixed to the processes of the spine.
Often, painful sensations in the back are associated precisely with muscle damage. During physical activity, diseases or injuries of the spine, the likelihood of sprain or spasm increases. In the latter case, an involuntary contraction of the muscle occurs, then it cannot relax.
Reference. When the intervertebral discs, ligaments or joints of the spine are damaged, the muscles that surround it reflexively contract to stabilize the damaged area.
During muscle spasm, lactic acid accumulates in the fibers as they compress the blood vessels. This process is accompanied by painful sensations. When the muscles relax, the lumen of the blood vessels expands, lactic acid is washed out by the blood and the pain syndrome disappears.
The ligaments of the spine are divided into short and long. The first include - yellow, interspinous, supraspinous, nuchal, intertransverse, and the second - anterior and posterior longitudinal. They are located on the front and back surfaces of the vertebrae, as well as on the sides.
Muscles and ligaments fix the spinal column in a vertical position. In addition, they restrain the vertebrae from sudden movements, protecting them from injury.
No ads 3
Can a person move or walk after a fracture of the human spine?
Despite the great importance of such an element of our body as the human spine, in case of a fracture, recovery is still possible in 80% of cases. Of course, a lot depends on the severity of the injury. If the spinal cord is damaged or ligaments are torn, such an injury can lead to paralysis or even death.
- Compression fractures are considered the easiest, relatively speaking, when cracks occur along the vertebrae or their size decreases. But the explosive or splintered type is no less dangerous
- Flexion-extension fracture - the vertebral element splits into small parts with possible damage to the ligaments or spinal cord
- The most severe injuries are considered to be rotational ones, when there is rotation along the axis or significant shift with possible fragmentation.
In addition, they are divided by the number of damages and by departments. The sacrum and coccyx should not be overestimated - these areas are directly connected to the rectum and reproductive function, and therefore often have complications of this nature.
Classification
A person can move with a fracture! But this does not mean that he will be able to walk or sit, because... the pain will be felt strongly in the damaged area and radiate to other parts of the body. For example, with a fracture of the thoracic region, numbness of the arms may occur, while the lumbar region may impair the movement of the toes. If you observe symptoms of a vertebral fracture, you should provide first aid and urgently call an ambulance! Because there is a high chance of internal bleeding.
Human spinal defects
Protrusion and herniation of the intervertebral disc
Spinal defects
Connection of vertebrae with various organs
The spine is a strong frame that unites not only all the bones of the skeleton, but also many organs. Nerve branches extend from it, thanks to which the brain regulates the functioning of the entire body. If there are disorders in the spinal column, the nerves that innervate a certain organ transmit incorrect information, then its functionality is impaired.
The bone elements of the spine are associated with certain organs:
- C1 – C7 are responsible for the normal functioning of the organs of hearing and vision, and are connected to the brain. Excessive tension in the muscles of the cervical spine can cause headaches, hearing and vision problems.
- C7 is associated with the functioning of the thyroid gland. And C7 and D1 – D3 are involved in the work of the heart. With degenerative changes in these vertebrae, the likelihood of pressure surges, angina pectoris, and arrhythmia increases.
- D4 – D8 are associated with the gall bladder, liver, stomach, pancreas, duodenum, spleen.
- D9 – D12 are responsible for the normal functionality of the adrenal glands and kidneys. If discomfort occurs in this area, you should visit a urologist, since it is quite difficult to independently determine whether the kidneys or spine hurt. The 12th vertebra affects the functioning of the large and small intestines. If the 9th vertebra is damaged, allergies may occur.
- L1 – L2 is responsible for intestinal function; if it is damaged, the likelihood of digestive disorders increases. The lumbar vertebrae are related to the genitourinary organs and lower extremities.
- The vertebrae of the lumbosacral region receive signals from the genital organs. With the development of inflammatory diseases in this area, discomfort occurs.
As you can see, the spine is connected with the work of many organs. Therefore, if discomfort appears in a certain area, you should not make a diagnosis yourself; go to the doctor immediately.
Anatomy in Chinese
Several thousand years before humanity invented radiography, Chinese doctors already knew about the connection between human internal organs and the spine.
If we are based on the theory of acupuncture, then the main knowledge that we received from the ancient Chinese is knowledge about bioactive points that have a direct effect on internal organs. These points are located near the spine.
Atlas of acupuncture
Depending on the location of the pain, we can talk about the disease itself. To recover from it, you need to influence the sore point. This can be achieved using hands (massage) or various means (for example, special needles).
Acupuncture
Video – Acupuncture
The ideas of Chinese doctors of that time about the connection between internal organs and vertebrae are completely similar to the map of segmental innervation that modern doctors have.
Moreover, Chinese scientists back in ancient times came to the conclusion that emotions affect physical condition. They were able to create a system for detecting diseases based on emotions. The main emphasis is on which emotional component harms a particular organ.
Table No. 3. Chinese health card.
| Place | Organ(s) | Symptoms | Emotion as a root cause |
| Third thoracic vertebra | Lungs | Breathing disorders | Sadness |
| Fourth and fifth thoracic vertebrae | Heart | Painful sensations | Rage, aggression |
| Ninth and tenth thoracic vertebrae | Liver and gallbladder | Discomfort and pain | Anger, bile |
| Eleventh thoracic vertebra | Spleen | Performance deterioration | Doubt, oppression, depression |
| Second lumbar vertebra | Kidneys | Impaired functioning | Fear |
Modern medicine, on a scientific basis, fully confirms all the knowledge that Chinese scientists of ancient times shared with us.
Main conclusions
The spine is the most important bone structure of the body. It consists of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. If the position of the vertebrae is incorrect, the functionality of the organs with which they are connected is impaired. Unfortunately, the spinal column is prone to wear and tear (especially the cervical and lumbar spine), which increases the likelihood of destruction of the intervertebral discs and the bones themselves. To avoid osteochondrosis, the formation of protrusions, disc herniations or osteophytes, you need to be able to unload the spinal column and strengthen the muscle corset.
Osteochondrosis?
Synonyms: radiculitis, salt deposits. Between the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae there is an intervertebral disc that performs 3 functions: shock absorption, holding adjacent vertebrae, ensuring mobility of the vertebral bodies. With osteochondrosis, the intervertebral disc loses its elasticity, becomes less durable, and therefore cannot perform its functions. Salts are deposited at the junctions of the vertebrae, bone growths appear, which, together with the discs, can shift and compress the nerve roots. This causes pain.
Manifestations of osteochondrosis are herniated intervertebral discs. A lumbar hernia causes pain in the back, buttocks, sacrum, and can spread to the legs. If you have any of these symptoms, it is necessary to undergo an examination, which includes not only x-rays, but also magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). When determining treatment tactics, we rely on MRI data. If an MRI reveals a disc herniation, the patient is most often frightened by this “terrible” diagnosis - not surgery! It must be said that for surgery for a herniated disc at the lumbar level, good reasons are needed. The patient makes the final decision after consultation with a neurosurgeon - vertebrologist.
A disc herniation causes severe pain, even with slight exertion, which interferes with life and work. If the patient wants to significantly improve the quality of his life, he will choose surgical treatment that will permanently rid him of this disease.
Another question arises: Where to have surgery? What to look for when choosing a medical institution?
To successfully perform an operation, in addition to the knowledge and skills of the surgeon, you need appropriate equipment in the operating room (Electro-optical converter (EOC) - a special X-ray unit, a powerful operating microscope, a special set of microsurgical instruments). The operating rooms in our clinic meet all these requirements and are fully equipped with everything necessary for spinal surgery.
A question that people leading an active lifestyle ask: How many days will the hospital stay take in case of surgery? Before surgery – from 2 to 5 days. After surgery – up to two weeks. The patient gets up on the second day and is discharged after the stitches are removed. He is offered a special rehabilitation program that will allow him to recover as soon as possible and return to an active lifestyle.
Theory - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
VertebrologistOrthopedist
Gromov Ilya Sergeevich
Moscow, st. Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 (Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth)
+7
Registry
0 Write your review
VertebrologistOrthopedist
Kudryakov Stepan Anatolievich
Moscow, st. Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 (Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth)
+7
Registry
0 Write your review
Orthopedist