Children's multidisciplinary medical center for children from 0 to 18 years old
10/11/2017 Natal injury of the cervical spine. What is hidden behind this diagnosis? What is the threat? And why is it important to perform an ultrasound of the cervical spine as early as possible.
It is not surprising that in the first year of life the child’s condition and development are closely monitored by a pediatrician and specialized specialists, because it is during this period that the child acquires and develops important skills, and so that nothing prevents the child from growing up healthy, it is important not to miss scheduled visits to doctors for up to a year ( at the age of 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, 12 months) . And if there is any pathology, then identify it as early as possible and eliminate the causes. Various laboratory and instrumental examinations help us with this. Along with routine (mandatory) examinations (such as ultrasound of the brain, abdominal cavity, heart, hip joints), parents need to remember the importance of conducting an ultrasound of the cervical spine (for some reason doctors often overlook this examination). Natal injuries of the cervical vertebrae are often encountered in neurological practice.
So, let's begin!
The human cervical spine is the thinnest, most mobile and sensitive part. In the fruit it is even more tender. For this reason, any forceful bending, stretching or twisting can cause injury.
The term "natal" means that the injury occurred during childbirth. Below are examples of how this or that injury to the cervical spine could occur.
The following types of cervical injuries occur during childbirth:
— Rotation injury — Distraction injury — Flexion-compression injury
A rotational injury to the cervical spine occurs when obstetricians help the baby move through the birth canal during childbirth. Manipulation is carried out by hand or obstetric forceps. Rotational movements of the child's head are performed, which can lead to subluxations of the atlas (first cervical vertebra), damage to the articulation of the first and second vertebrae. There may be displacement of the atlas and narrowing of the spinal canal, accompanied by compression of the spinal cord.
When a large fetus is formed, in some cases during natural childbirth obstetricians are forced to make excessive efforts. This is fraught with distraction injuries: separation of the vertebral bodies from the discs, rupture of ligaments in the cervical spine and damage to the spinal cord.
Flexion-compression injuries most often occur during rapid labor, especially if the fetus is large. The baby's head encounters resistance while moving through the birth canal, which can cause compression fractures of the vertebral bodies.
Even a small natal injury cannot go unnoticed; regardless of the severity, the injury will have its consequences. Damage to the cervical spine always affects the baby’s well-being, his behavior, and the state of his nervous system.
Symptoms:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- muscle hypotension;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle;
- anxiety;
- sluggish sucking;
- frequent and profuse regurgitation "fountain"
Upon examination you can identify:
- lengthening or shortening of the neck;
- tension in the muscles of the neck and back of the head;
- swelling of the neck muscles;
- torticollis
And if you don’t pay attention to this in time and start treatment, the problem itself will not go away, and the consequences can be unpredictable.
Sometimes there are no obvious consequences of the injury. This does not mean that the child is absolutely healthy. Damage to the cervical spine directly affects the blood supply to the brain. Due to impaired blood supply, the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to brain cells becomes difficult, which in turn can lead to hypoxic damage to the brain, as a result of which the baby may lag behind in development.
Some consequences generally appear only closer to preschool and school age. At that time, few people associate them with the trauma received at birth. Consequences such as delayed speech and/or psychomotor development, and at an older age headaches, scoliosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia, increased blood pressure, and hypotension appear. Also, a cervical spine injury leaves its mark on the child’s mental health.
When entering school, such children may experience problems in their studies, they can be both inhibited and hyperactive, which does not have the best effect on their communication with others, poor memory, low concentration, and decreased motivation for the educational process. Poor studies and behavioral disorders lead to a decrease in self-esteem and further aggravate negative processes in the nervous system.
- If a newborn has a natal injury to the cervical spine, the first and most important measure is neck fixation.
- In case of a dislocation, before fixing the neck, the orthopedist must set the cervical vertebrae in place. Fixation is carried out using a special swaddling method, when the neck is enclosed in a hard cotton-gauze roll. You need to swaddle in this way for at least 2-3 weeks.
- The doctor may also prescribe wearing a Shants collar. You need to select such a collar strictly individually, focusing on the weight and volume of the baby’s body. An incorrectly selected collar can only aggravate the problem of the cervical spine. 3-4 weeks after the start of treatment, the next stage begins, which is aimed at restoring muscle tone and normalizing the functions of the nervous system. At this stage, massage, various baths, and physiotherapy (electrophoresis) are performed.
Similar courses of rehabilitation therapy should be carried out 2-3 times in the first year of life. You can be registered with a pediatric neurologist and orthopedist for quite a long time, depending on how successfully the recovery goes.
Causes of vertebral displacement in a child
Most often, displacement of the cervical vertebrae occurs as a result of birth trauma.
The displacement of a vertebra is correctly called a subluxation. One or more vertebrae are displaced from their places, but without rupture of ligaments and muscles. This can occur in any part of the cervical spine, but the most vulnerable is the articulation of the atlas and the axial vertebra. This joint is one of a kind; it is subject to heavy loads when the head rotates. Its complete dislocation can cost the patient his life.
The most common types of subluxations in newborns:
- Rotational – associated with a sharp turn of the head in any direction. The neck takes a forced position, most often turning in one direction and tilting in the other, or just turning.
- Active - occurs due to an insufficiently tight connection between two adjacent vertebrae, the head can take any position, movement is painful.
The reasons for this phenomenon are congenital defects of connective tissue or incorrect actions of obstetricians during childbirth. The baby can get injured in the first days and months of life if parents allow themselves to treat him too harshly. A combination of several factors is possible - with congenital defects, displacement may not occur immediately, but it will easily develop against the background of any sudden impact.
In children beyond infancy, the main cause of subluxation is injuries during active games and sports.
There are several riskiest periods. When the baby begins to explore the world around him and tries to get out of the crib, he may fall to the floor upside down. The second period is 3-4 years, when the child learns to run and climb, then early school age, when children are often left unattended for a long time, and adolescence, which is conducive to active games and breaking prohibitions.
Prevention of vertebral displacement in children
Older children need to monitor their posture if there has been a previous neck injury.
To avoid displacement of the cervical vertebrae in newborns and not to treat them, you need to prepare for childbirth, undergo regular examinations and treat emerging pathologies. The main responsibility during childbirth lies with the medical staff - improper medical care is dangerous for the baby.
For parents of older children, the main means of prevention is to monitor their behavior. The older the child, the more important it is for him to know and follow safety rules, regardless of whether he is supervised by adults. It is also the parents' responsibility to explain these rules. A careful child is unlikely to get into a dangerous situation and get hurt.
Types and degrees of displacement
Depending on the direction of the displacement, it is customary to distinguish:
- ventrolisthesis - anterior displacement;
- retrolisthesis - posterior displacement.
Depending on the area of displacement, five degrees of pathology are distinguished:
- First degree - the displacement area does not exceed 25%, there are practically no pain symptoms, it manifests itself with intense movements and loads;
- Second degree - the displacement area ranges from 25% to 50%, pain occurs more often and lasts longer;
- Third degree - the displacement area ranges from 50% to 75%, severe pain occurs, limited movement, subsidence of the spine, pain radiating to the leg;
- Fourth degree - the displacement area exceeds 75%, is characterized by incessant pain, the inability to walk, sit, stand for a long time, numbness and weakness of the feet and hands appear;
- Fifth degree - there is complete displacement and prolapse of the vertebra.
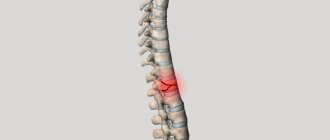
Complications
The consequences of vertebral displacement can be very serious, especially if you do not seek professional medical help in a timely manner. Complications are associated with the specific department in which the displaced vertebra is located.
So, if a cervical vertebra is damaged, the patient suffers from the following consequences:
- headache;
- insomnia;
- hearing impairment;
- private dizziness and fainting;
- blurred vision;
- thyroid diseases;
- hoarseness.
If there are disorders in the thoracic region, the following complications arise:
- labored breathing;
- cough;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- frequent bronchitis and colds;
- liver pathologies;
- frequent heartburn;
- rheumatism.
If the displacement occurs in the lumbar region, the reproductive system and intestines suffer due to complications. The patient begins to:
MRI of the spine
- Cost: 16,000 rub.
More details
- convulsions;
- colitis;
- menstrual irregularities (in women);
- impotence (in men);
- pain in the knees;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- feeling of weakness in the lower extremities, frequent cramps.
How does torticollis manifest?
With torticollis, its characteristic signs attract attention:
– the neck is deformed, the head is tilted; – mobility is limited, the child cannot hold his head straight or tilt it in the opposite direction; – the shoulder and shoulder blade on the affected side are higher than on the healthy side; – when trying to straighten the child’s head, he cries and resists; – facial asymmetry - the ear, eyebrow and eye on the affected side are lower compared to the healthy side. – already at 2–3 weeks of a child’s life, thickening and shortening of the sternocleidomastoid muscle can be felt to the touch.
By 1–1.5 months of life, the seal may disappear - it will become thinner and shorter than healthy. Therefore, attempts to straighten the child’s head will cause him pain and crying. This indicates that torticollis has become fixed and its treatment will require a special approach.
Facial asymmetry helps distinguish congenital torticollis from acquired. It takes time to form, so if the baby was born with asymmetry, then the pathology is congenital. If his face was normal and then changed - acquired.