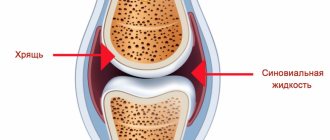
A decrease in bone density near the head of the humerus may be a manifestation of general (widespread) osteoporosis or a local process.
People at risk for general osteoporosis:
- there have been bone fractures of any location in the past;
- postmenopausal women (a year or more since the last menstruation);
- age from 65 years;
- smokers;
- weight up to 57 kg;
- hereditary predisposition to fractures due to minor trauma;
- taking drugs from the glucocorticoid group (prednisolone and analogues);
- low levels of sex hormones in men and women;
- nutritional disorders - lack of calcium, abuse of alcohol, salty and sweet foods, insufficient absorption in the intestines, the diet contains little or much phosphorus, protein, fats;
- vitamin D deficiency (rarely staying outdoors, living in northern regions);
- diabetes;
- kidney and lung diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- dysfunction of the thyroid and parathyroid glands.
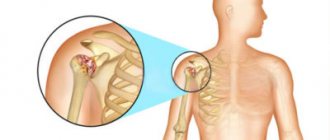
Osteoporosis of the shoulder joint
Local lesions:
- fracture;
- fixation of the joint in case of injury (long-term immobility);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- arthrosis;
- osteomyelitis;
- tumors or metastases;
- muscle weakness (for example, after a stroke);
- professional overload (athletes, hammer hammers, loaders, work with vibration mechanisms);
- gouty arthritis;
- osteoarticular tuberculosis.
Widespread osteoporosis with primary bone damage does not have typical symptoms and occurs latently until the time of fracture . The humerus breaks less often than the others. But its structure contains a lot of spongy substance, which quickly dissolves during illness.
Therefore, when you fall on your elbow, shoulder, or abducted arm, the following symptoms occur:
- sharp pain in the shoulder, especially when trying active movements, passive movements are limited, but less painful (especially with an impacted fracture);
- swelling;
- limb deformity.
With local osteoporosis, the underlying disease is most often arthritis of the shoulder joint. The development of osteoporosis in patients is preceded by clear clinical symptoms :
- prolonged pain, first with exertion, then at rest, intensifies at night;
- spread of pain down to the elbow joint and forearm, to the back in the scapular region;
- swelling of tissues, redness of the skin;
- limited mobility, in the later stages immobility occurs;
- crunching sound when moving;
- deformities of the upper limb.
Against the background of spinal osteochondrosis, glenohumeral periarthrosis occurs. It is characterized by a variety of pain sensations, and then comes a period of frozen shoulder, persistent limitation of movements in the joint.
Densitometry is used to study bone density . Based on its results, it is possible to detect loss of bone mineral mass starting from 2%. For comparison, measurements are required in the area of the shoulder joint, lower thoracic vertebrae, radius and femoral head. This will help estimate the prevalence of osteoporosis and the risk of fractures.
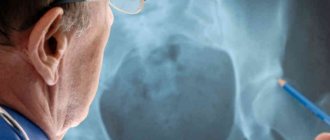
X-rays are prescribed for cases of trauma or inflammatory processes that have already occurred. Signs of osteoporosis are visible on photographs when bone density decreases by 30%. Using this method you can detect:
- decreased compactness of the spongy substance in the shoulder joint;
- thinning of the cortical layer (located near the periosteum);
- resorption of horizontal partitions, contrast of vertical ones;
- glass bone symptom with an emphasized outer contour;
- manifestations of arthritis due to a local process (narrowing of the joint space, marginal bone defects);
- formation of cystic bone changes near the articular surfaces.
X-ray of the shoulder joint
Blood tests can confirm the inflammatory process, the presence of an autoimmune disease, gout . To assess the risk of fractures, tests are prescribed for indicators of bone resorption (destruction) and osteogenesis (formation of new bone tissue) : calcitonin, osteocalcin, C-telopeptide, alkaline phosphatase. Deoxypyridinoline is determined in urine, studies of blood levels and urinary calcium excretion are also indicated
Before prescribing therapy, an analysis of the concentration of vitamin D, the level of thyroid and parathyroid hormones . If secondary osteoporosis is suspected, it is important to identify its underlying cause. This requires diagnosis of the condition of the kidneys, lungs, intestines, and carbohydrate metabolism.
For treatment, non-drug and pharmacological treatment is recommended . Patients need to stay in the sun for about 15 minutes in the summer (in mid-latitudes) with their face and arms open, and walk in the fresh air for at least half an hour. It is important to give up smoking, daily coffee, and alcohol.
A diet is prescribed. The most complete sources of calcium are dairy products, fish, nuts, seeds, especially sesame seeds . Every day the diet should contain at least 2 glasses of fermented milk drink, 300 g of cottage cheese, 50 g of cheese, 150 g of fish. For lactose intolerance, use special products from which it has been removed. Drinking tea and coffee, spinach, and beets at the same time as dairy products interferes with calcium absorption.
Without physical activity, osteoporosis progresses much faster. It is necessary to exercise regularly. Starting position - sitting on a chair with a straight back, hands should be placed on your hips. Each of the movements should be repeated at least 8 times:
- movements of both shoulder joints - moving forward, abducting back, then each separately;
- rotation forward first in two, then alternately and also in the opposite direction;
- shrug;
- lowering down to the maximum distance and holding in the lower position for 10 counts.
At the end of the complex, you need to let your arms sag in a relaxed state and swing them for 2-3 minutes without tension, then shake your hands.
Older patients are most at risk for bone fractures . Fusion takes a long time, sometimes with complete loss of ability to work. To prevent injury it is recommended:
- undergo treatment for visual impairment, vascular diseases of the brain that cause dizziness, unsteadiness when walking;
- wear shoes with non-slip soles that tightly secure the ankle joint;
- use a cane or walker if necessary;
- it is necessary to clear traffic paths from obstacles and have good lighting;
- avoid sleeping pills with a long period of action;
- Monitor blood pressure daily.
Medicines for the treatment of osteoporosis are indicated:
- after 50 years of age for patients with an identified fracture or a high risk of its occurrence;
- when bone density decreases to less than -2.5 according to densitometry results;
- in case of danger of bone destruction due to long-term use of hormonal drugs, endocrine pathology.
The following medications are prescribed:
- calcium with vitamin D – Calcemin, Calcium D3;
- bisphosphonates – Alendronate, Aklasta, Bonviva, Rizendros;
- strontium ranelate – Bivalos;
- denosumab – Prolia, Ixijeva;
- teriparatide – Forsteo.
All these remedies are used for a long period of time. To reduce the risk of fracture, women during menopause are prescribed hormone replacement therapy, and if there are contraindications to the use of female sex hormones, raloxifene .
Read more in our article about osteoporosis of the shoulder joint.
Causes of osteoporosis of the shoulder joint
A decrease in bone density near the head of the humerus may be a manifestation of general (widespread) osteoporosis or a local process.
Are common
This disease affects patients in the following risk groups:
- there have been bone fractures of any location in the past;
- postmenopausal women (a year or more since the last menstruation);
- age from 65 years;
- smokers;
- weight up to 57 kg;
- hereditary predisposition to fractures due to minor trauma;
- taking drugs from the glucocorticoid group (prednisolone and analogues);
- low levels of sex hormones in men and women;
- nutritional disorders - lack of calcium, abuse of alcohol, salty and sweet foods, insufficient absorption in the intestines, the diet contains little or much phosphorus, protein, fats;
- vitamin D deficiency (rarely staying outdoors, living in northern regions);
- diabetes;
- kidney and lung diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- dysfunction of the thyroid and parathyroid glands.
We recommend reading the article about osteoporosis of the hip joint. From it you will learn about the causes of osteoporosis of the hip joint, degrees and symptoms, as well as methods for diagnosing and treating osteoporosis of the hip joint.
And here is more information about massage for osteoporosis.
Local
Periarticular osteoporosis in the humerus area can also be associated with local diseases:
- Humeral neck fracture;
- fixation of the joint in case of injury (long-term immobility);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- arthrosis;
- osteomyelitis;
- tumors or metastases;
- muscle weakness (for example, after a stroke);
- professional overload (athletes, hammer hammers, loaders, work with vibration mechanisms);
- gouty arthritis;
- osteoarticular tuberculosis.
Treatment
It is very important to determine the causes of osteoporosis, since the entire treatment process depends on this
Treatment of osteoporosis of the shoulder joint should be comprehensive. It is based on medications, but exercise therapy, massage, traditional medicine and other techniques are used as an addition.
Drugs
The following groups of medications are used for medicinal purposes:
- Bisphosphonates. .
- NSAIDs.
- Muscle relaxants.
- Means to improve blood circulation.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Calcitonins.
- Female sex hormones for patients during menopause.
- Chondroprotectors.
As a rule, medications are prescribed in combination. Their dosage and duration of administration are determined by the doctor individually in each case. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Exercises, exercise therapy
Therapeutic gymnastics helps restore the motor function of the joint, as well as accelerate regeneration processes in it.
It is recommended to perform a general strengthening set of exercises, devoting special time to the arms, in particular the shoulder area. Rotational movements of the arms, which must be performed at a slow pace, have proven themselves well.
During classes, it is prohibited to use weights or make sudden movements. The duration of therapeutic exercise should not exceed 60 minutes.
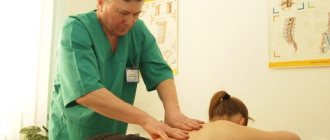
Massage
Massage is effective at all stages of pathology. It allows you to speed up blood flow, which helps restore bone tissue. In addition, massage effectively eliminates pain.
In the initial stages of pathology, massage is allowed to be performed independently, and movements should be smooth and without strong pressure. At the last stage of osteoporosis, massage can only be performed by a specialist, since the likelihood of fractures is increased.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is little used in the treatment of osteoporosis; they cannot replace drug treatment. Traditional methods are good only as a supplement. In the treatment of osteoporosis of the shoulder joint, the following recipes are most often used:
- decoctions, compresses and infusions of white cabbage;
- adding black pepper to all dishes, as well as preparing ointments based on it;
- soy lotions and decoctions;
- use of anti-inflammatory herbs;
- frequent consumption of carrots and parsley, as well as decoctions based on them.
The products used in traditional methods can be allergens, so before using them you need to make sure that there are no allergic reactions.
Diet
A diet for any location of osteoporosis involves daily consumption of foods containing calcium and phosphorus. These include cottage cheese, natural yogurt and cheese, milk, parsley, spinach, celery and nuts.
It is necessary to minimize the consumption of table salt, spicy and smoked foods, as well as baked goods and milk chocolate.
Joint replacement
Surgery is performed only when therapy methods are ineffective. Prosthetics involves partial or complete replacement of the affected area of the joint. An artificial joint allows you to completely restore the mobility of the limb. This operation is not recommended during pregnancy. In addition, it is better to postpone surgery in the presence of inflammatory processes in the joint and acute infectious diseases.
Symptoms in patients: pain, numbness and others
Widespread osteoporosis with primary bone damage does not have typical symptoms and occurs latently until the time of fracture. The humerus breaks less frequently than the femur, radius, and spine. Nevertheless, its structure contains a lot of spongy substance, which quickly dissolves during the disease. Therefore, when you fall on your elbow, shoulder, or abducted arm, the following symptoms occur:
- sharp pain in the shoulder, especially when trying active movements, passive movements are limited, but less painful (especially with an impacted fracture);
- swelling;
- limb deformity.
With local osteoporosis, the underlying disease is most often arthritis of the shoulder joint.
The development of osteoporosis in patients is preceded by clear clinical symptoms:
- prolonged pain, first with exertion, then at rest, intensifies at night;
- spread of pain down to the elbow joint and forearm, to the back in the scapular region;
- swelling of tissues, redness of the skin;
- limited mobility, in the later stages immobility occurs (joint contracture);
- crunching sound when moving;
- deformities of the upper limb.
Against the background of spinal osteochondrosis, glenohumeral periarthrosis occurs. It is characterized by a variety of pain sensations, and then comes a period of frozen shoulder, persistent limitation of movements in the joint.
Prevalence
Osteoporosis thins bone tissue and increases the likelihood of fracture
Osteoporosis of the shoulder refers to local varieties of the disease, when not the entire skeletal system suffers, but only its elements that form the shoulder joint. Pathology is divided into two types: diffuse and focal.
Diffuse
Diffuse osteoporosis is characterized by uniform damage to the bones involved. The progression of the pathological process occurs at high speed, so the bones quickly become fragile. With diffuse osteoporosis, the likelihood of fractures is higher than with focal osteoporosis.
Focal
Focal osteoporosis affects individual areas of bones, forming round or oval lesions of tissue loss. In the case of osteoporosis of the shoulder joint, the most common form is focal. With it, the likelihood of fractures and bone injuries is much lower than with the diffuse form.
Diagnosis of the condition
Densitometry is used to study bone density. It is based on the absorption of x-ray radiation by bone tissue. Based on its results, it is possible to detect loss of bone mineral mass starting from 2%. For comparison, measurements are required in the area of the shoulder joint, lower thoracic vertebrae, radius and femoral head. This will help assess the prevalence of osteoporosis and the patient's risk of fractures.
X-rays are prescribed for cases of trauma or inflammatory processes that have already occurred. Signs of osteoporosis are visible on photographs only when bone density decreases, starting from 30%.
Using this method you can detect:
- decreased compactness of the spongy substance in the shoulder joint;
- thinning of the cortical layer (located near the periosteum);
- resorption of horizontal partitions, contrast of vertical ones;
- glass bone symptom with an emphasized outer contour;
- manifestations of arthritis due to a local process (narrowing of the joint space, marginal bone defects);
- formation of cystic bone changes near the articular surfaces.
Blood tests can confirm the inflammatory process, the presence of an autoimmune disease, or gout. To assess the risk of fractures, tests are prescribed for indicators of bone resorption (destruction) and osteogenesis (formation of new bone tissue): calcitonin, osteocalcin, C-telopeptide, alkaline phosphatase. Deoxypyridinoline is determined in urine, and studies of blood levels and urinary calcium excretion are also indicated.
Before prescribing therapy, an analysis of the concentration of vitamin D and the level of thyroid and parathyroid hormones is carried out. If secondary osteoporosis is suspected, it is important to identify its underlying cause. This requires diagnosis of the condition of the kidneys, lungs, intestines, and carbohydrate metabolism.
How to treat osteoporosis of the shoulder joint
Non-drug and pharmacological treatment is recommended. Patients need to stay in the sun for about 15 minutes in the summer (in mid-latitudes) with their face and arms open, walk in the fresh air for at least half an hour, and exercise therapy. It is important to give up smoking, daily coffee, and alcohol. A diet is prescribed to improve bone ploidy.
Medical nutrition
The most complete sources of calcium are dairy products, fish, nuts, and seeds, especially sesame seeds. In order to get the daily norm, your daily diet should include at least 2 glasses of fermented milk drink, 300 g of cottage cheese, 50 g of cheese, 150 g of fish. For lactose intolerance, use special products from which it has been removed.
Drinking tea and coffee, spinach, and beets at the same time as dairy products interferes with calcium absorption.
Exercises for illness
Without physical activity, osteoporosis progresses much faster. It has been proven that those bone partitions that bear the least load are the first to collapse. Therefore, it is necessary to include exercises for the shoulder joint in therapeutic exercises every day.
Starting position - sitting on a chair with a straight back, hands should be placed on your hips. Each of the movements should be repeated at least 8 times:
- movements of both shoulder joints - moving forward, abducting back, then each separately;
- rotation forward first in two, then alternately and also in the opposite direction;
- shrug;
- lowering down to the maximum distance and holding in the lower position for 10 counts.
Watch the video about therapeutic exercises for the shoulder:
At the end of the complex, you need to let your arms sag in a relaxed state and swing them for 2-3 minutes without tension, then shake your hands.
Fall Prevention
Older patients are most at risk for bone fractures. They often experience prolonged fusion, limitation of movements, and sometimes loss of ability to work.
To prevent injury it is recommended:
- undergo treatment for visual impairment, vascular diseases of the brain that cause dizziness, unsteadiness when walking;
- wear shoes with non-slip soles that tightly secure the ankle joint;
- use a cane or walker if necessary;
- it is necessary to clear traffic paths from obstacles and have good lighting;
- avoid sleeping pills with a long period of action;
- Monitor blood pressure daily.
Wearing shoes with non-slip soles is a must to prevent falls.