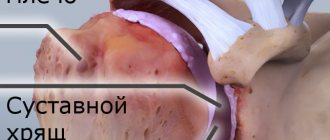
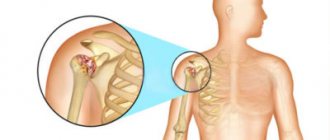
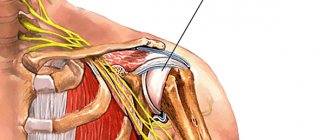
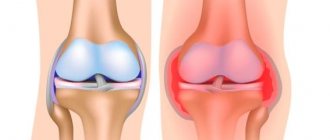
Contracture of the shoulder joint is a tightening of the soft tissues of the shoulder by the resulting scars, resulting in impaired mobility of the limb. The immediate cause of the development of such a disease is scarring of the joint capsules, tendons, or tightening of the subcutaneous tissue or skin. Contracture of the shoulder joint often appears after injuries associated with damage to the integrity of the joints. Burn scars also cause the skin to tighten.
Muscle atrophy and myogenic contracture are possible when wearing a cast for a long time. Neurogenic reflex contracture is caused by nerve damage. Acute inflammation is characterized by rapid development of contracture, while chronic inflammation is characterized by slow development.
Causes
To understand what contracture of the shoulder joint is, it is worth analyzing the main causes of its occurrence? This pathology can be caused by prolonged immobilization of the limb, damage to the articular surfaces, or a disease with an inflammatory process.
The main causes of shoulder contracture include the following factors:
- Various shoulder injuries;
- The appearance of scars on the skin after a burn;
- Surgical operations in the cervical and shoulder areas;
- Improper immobilization for a fracture;
- Neurological pathologies in the form of stroke, tabes dorsalis, syringomyelia, cervical osteochondrosis with transition to scapulohumeral periarthritis;
- Pathological formations that compress blood vessels;
- Development of joint ischemia due to atherosclerosis;
- Diseases accompanied by inflammation;
- Age-related pathologies, for example, arthrosis;
- Mental disorders;
- Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system at birth.
Contracture of the wrist joint after a fracture
Contracture of the wrist joint is one of the complications after a fracture. The wrist joint is a complex anatomical complex formed by a large number of bones; the full functioning of the joint is carried out by various connective tissue structures and muscles. The most common fracture of the radius occurs near the synovial joint, resulting in contracture. It is not the fracture of the wrist bone itself that causes damage to the joint, but damage to the connective tissue structures involved in the functioning of the joint. Contracture can be caused by an intra-articular fracture, which is accompanied by damage to the articular cartilage tissue, ligaments and capsule.
Classification
Contractures of the shoulder joint can be structural (passive) or neurogenic (active). The neurogenic form is characterized by a change in the innervation of the elbow joint. Active contractures are:
- Psychogenic nature – hysterical contractures;
- Central neurogenic contractures: spinal or cerebral;
- Peripheral contractures, which occur when the peripheral system is disrupted.
Pathology of this form can be provoked by mental experiences, paresis or paralysis, manifested due to neurological pathologies or abnormal brain activity. These deviations occur due to a negative effect on nerve endings.
With passive contractures, structural interference interferes with the function of the joint. The factor preventing normal joint activity may be the joint itself or the periarticular tissues. represented by tendons, muscles and fascia. Formed scar tissue, shortening of muscle length, joint deformation, inflammatory process - all this can give rise to the development of the disease. Also, the cause of impaired shoulder mobility can be injury caused by physical activity or prolonged immobilization of the joint in one position.
Contractures after injuries
After receiving even
After an insignificant injury, the body subconsciously begins to limit the movement of the affected area, providing the damaged tissue with rest. This method of self-medication may lead to complete recovery of the injured joint.
For more serious injuries, immobilization of the injured shoulder is required.
Contracture of the elbow joint
Contracture of the elbow joint refers to pathological conditions characterized by difficulty in flexion, extension, and turning the forearm inward and outward. The most common flexion and extension contractures of the elbow joint. The reasons for this violation are:
- developmental anomaly;
- injury;
- degenerative-dystrophic process in the elbow joint;
- long-term immobilization;
- connecting scar.
Disability due to contracture of the elbow joint rarely develops, unlike contractures that affect the joints of the legs and often lead to disability.
Contracture of the elbow joint after a fracture
There are contractures with limitation of movements: flexion, extension, supination and pronation. The elbow joint is most often affected by flexion contractures. The cause of the development of contracture of the elbow joint is periarticular fractures and dislocations, incorrect alignment of bone fragments after a fracture. The cause of contracture can be hemarthrosis, the formation of adhesions and the inflammatory process in the periarticular tissues.
Symptoms
Inadequate activity of the shoulder joint is the main symptom of shoulder contracture.
Often the pathology is accompanied by swelling, the affected joint is difficult to straighten and bend. Scar ties stretch the affected limb, fixing it in an incorrect position. An arm may be shorter than the other due to congenital contracture of the shoulder joint.
How does joint stiffness occur?
The elasticity of articular elements is provided by collagen. This is a protein compound produced by fibroblasts - special connective tissue cells. Insufficient collagen synthesis leads to loss of physiological sliding of the articular head in the joint capsule.
The most common causes of joint stiffness are:
- active growth of bones, ligaments, tendons in childhood and adolescence;
- dehydration of the cartilage covering the articular heads of bones;
- muscle spasms that appear against the background of a sedentary lifestyle;
- diseases affecting the joints;
- inflammation of bone and cartilage tissue;
- physical exercise.
We must not forget that any stressful situations or psycho-emotional stress can cause pain and affect joint mobility. If the pathological condition is based on nervous symptoms, painkillers do not affect the patient. The problem should be solved by adjusting the regimen and taking sedatives.
Treatment
To achieve results
The patient will have to undergo a complex of long-term and persistent therapy. The course of treatment is selected individually, depending on the reasons that provoked the disease.
Kinesiotherapy
The therapy is aimed at developing the shoulder joint. The technique includes two types of movement:
- Passive movements are performed only by a doctor and are aimed at smoothly and carefully stretching the muscles and tendons around the joint.
- Active exercises can be done independently. The patient performs movements with the maximum possible amplitude with a gradual increase in load. It is good to do similar gymnastics in a warm bath with the addition of aromatic oils, sea salt or relaxing herbs.
Massage
Before kinesiotherapy, experts recommend a massage session that will relax the muscles, relieve pain and warm up the shoulder joint. When treating contracture, there are several methods of influencing zones: the massage therapist actively presses on weakened muscles, kneading and rubbing the shoulder, while relaxing smooth movements are applied to the area of antagonists. During the massage, manual therapy techniques can be used.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy exercises for contracture of the shoulder joint are prescribed after reducing pain symptoms and relieving the inflammatory process. Exercise therapy exercises are aimed at developing muscles and strengthening antagonists. When an extensor spasm occurs, it is necessary to stretch the flexors and, accordingly, vice versa.
Types of disease
In addition to the classification into active, passive and combined contractures, there are many other divisions:
- by restriction of movements - extension, flexion, rotation (limitation in turning and when making circular movements), as well as adduction and abduction;
- by the time of onset of the pathology (acquired and congenital);
- in terms of functionality - functionally disadvantageous (the performance of the limb is not preserved) and beneficial (the mobility of the joint is limited, but the performance is preserved).
Active contractures are represented by the following types:
- central neurogenic (cerebral and spinal), cerebral occur with brain damage, spinal - with damage to the spinal cord;
- peripheral neurogenic - appear when peripheral nerves are damaged, most often accompanied by pain;
- psychogenic - appear during a hysterical attack, disappear at the end of the attack.
Passive contractures consist of the following types:
- myogenic (appear as a result of muscle shortening during reflex contraction or an inflammatory process);
- arthrogenic (due to changes in the ligamentous-capsular apparatus of the joint or articular ends);
- dermatogenic (after the formation of scars on the skin as a result of burns or inflammatory diseases);
- tendogenic (due to shortening of tendons as a result of the formation of adhesions);
- immobilization (caused by prolonged restriction of movements of the arms and legs);
- ischemic (appears after fractures due to limited blood supply to the extremities);
- desmogenic (as a result of wrinkling of fascia and ligaments during deep injuries or chronic inflammatory processes. One of the most common types of desmogenic contractures is Dupuytren's contracture , which we will talk about in more detail).
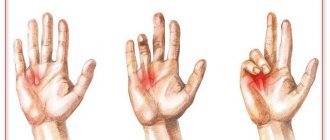
Dupuytren's contracture
Dupuytren's contracture (or palmar fibromatosis) is a fibrous degeneration of the palmar aponeurosis, which, according to doctors, occurs due to a genetic predisposition. This pathology occurs 6-10 times more often in men than in women.
In most cases, the ring finger or little finger on one hand is affected; less often, the pathological process affects all fingers on both hands and feet.
A small compaction appears on the surface of the palm, similar to a nodule, which begins to gradually increase in size, cords appear, and the tendon shortens. This leads to the fact that the affected fingers become increasingly difficult to bend and straighten, and over time, immobility of the interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints develops. The hand loses its functions, which causes loss of ability to work and self-care skills.
Classification of Dupuytren's contracture
1st degree of disease . The node reaches a size of about 1 cm, and some pain appears when touched. Fingers bend and straighten. Mobility in the joints is preserved.
2nd degree of the disease . The node begins to degenerate into a scar, which extends to the phalanx of the affected finger. Mobility in the affected joint is impaired. The finger with contracture is at an angle to the inner side of the palm of 30-90 degrees. The extension of the joint is impaired.
3rd degree contracture . The fibrous cord extends to the entire finger, the skin forms folds. Movement in the joints sharply worsens. Contracture appears in the metacarpophalangeal joints, which leads to complete ankylosis.
4th degree of the disease . It is possible for several fingers to fuse into a large scar. The fingers are gathered into a fist, which is completely impossible to straighten. The activity of the hand is completely impaired, which leads to disability of the patient.
1 MRI of joints
2 Treatment of contracture
3 Treatment of contracture
Prevention
To prevent the development of contracture of the shoulder joint, it is necessary to promptly and fully treat any injury, using the entire complex of rehabilitation therapy.
Correct fixation of the joint
at the required angle will help avoid rupture or stretching of the joint capsule, as well as the progression of edema and possible ischemia of the tissue around the joint. The injured arm can be fixed in an abducted position at a certain angle to prevent contractures.
Passivity of muscle tissue can lead to irreversible consequences.
To avoid such pathologies, the patient should strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations regarding the development and treatment of the affected joint, preparing himself for difficult work. The recovery period may be long, but a persistent patient will be able to overcome all difficulties and return to a full life.
Combined contracture of the hip joints
Contracture in the hip joint is most often observed in the position of adduction and flexion, and in most cases develops in older people. The main reason for the development of contracture is a fracture of the femoral neck, deforming coxarthrosis. In young people, contracture of the hip joints occurs due to innervation in the lower spine. Extensor contracture of the hip joints develops with damage to the spinal cord; it manifests itself in the form of a tonic extension position of the lower extremities (hips, legs). The most common is combined contracture of the hip joints.
The Yusupov Hospital diagnoses and treats fractures, injuries, and complications that develop subsequently. Diagnosis of contracture can be done in a diagnostic center using modern medical equipment from leading manufacturers in the world. The hospital provides inpatient services and a rehabilitation center. In the rehabilitation center, the patient will be able to undergo recovery from illness according to an individual program developed by a rehabilitation specialist. Classes at the center are conducted with an instructor, patients perform physical therapy exercises, and exercise on simulators. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Diagnostics.
A detailed narrative from the patient, specifying the location of pain and the situations when it occurs, is important in diagnosing impingement syndrome. Next, the doctor conducts an examination and special functional tests. A technique is also used in which an anesthetic is injected locally to clarify the diagnosis (Nir's test).
In some cases, auxiliary imaging diagnostic methods are prescribed to clarify the extent of the disease, namely:
- X-ray.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Ultrasound examination (infrequently).
- Arthroscopy (as the most accurate diagnostic method, allowing clear visualization of pathologically altered structures).
Ankle stiffness
About 50% of all patients with joint contractures turn to traumatologists for ankle joint stiffness. Changes in the functions of the ankle joints lead not only to limitation of motor activity. Against the background of contracture, destruction of the spine, changes in the shape of a healthy limb, flat feet, and atrophy of the lower leg muscles develop.
The most common causes of ankle stiffness are:
- physical exercise;
- sprains;
- tendon injuries;
- wearing a plaster cast;
- damage to nerve fibers;
- deforming arthritis;
- degenerative diseases.
It is important to remember that independent physical impact on the damaged ankle joint is unacceptable. Only a doctor should provide assistance to a patient.
Symptoms of muscle contractures
You need to be careful and not miss the first “alarm bells” that may indicate the development of pathology:
- At the initial stage of the disease, the symptoms appear vaguely, and the patient may not pay attention to them. However, an alarming signal should be a feeling of fatigue and aching pain even after minimal physical activity, numbness and stiffness, especially in the morning after waking up, dry skin in the affected area.
- As the disease progresses, difficulty and pain arise when trying to fully bend or straighten a limb subject to contracture.
- In later stages, there is an inability to fully bend or straighten the limb.