- General recommendations
If a person has a numb heel, the reasons can be both physiological and pathological. Numbness often occurs when a person hits their foot. However, if numbness in the heel and other parts of the leg occurs frequently and for no apparent reason, this may indicate a particular disease. In this case, you should seek medical help and begin treatment.
Heel numbness is often caused by wearing shoes that are too tight.
It is impossible to determine the disease by the symptoms alone. To make a diagnosis, a collection of complaints and anamnesis, an objective examination, instrumental and laboratory examination are carried out. The results obtained are assessed by a doctor. Consultations with a surgeon, orthopedist, neurologist, oncologist, and rheumatologist may be required.
Numb heel: reasons
Pathological
The main cause is foot injuries (often due to impact, the heel can also become numb when a splinter gets into the leg, if a person steps on a small object, etc.), while numbness can occur at the time of injury or after some time.
In addition, numbness of the heel (as well as the foot and toes) is most often observed with the following pathologies:
- osteocondritis of the spine;
- inflammatory processes in the joints;
- fasciitis;
- lumbar intervertebral hernia;
- gout;
- spinal tuberculosis;
- inflammation of the sciatic nerve;
- diabetic neuropathy.
Numbness is often caused by poor circulation:
- thrombosis;
- atherosclerotic vascular lesions;
- phlebeurysm;
- compression of blood vessels and nerve endings, as well as temperature effects on them (for example, frostbite of the lower extremities);
- stroke - in this case, the patient has numbness in the heel of his right or left foot, as well as other parts of the body on one side opposite to the one on which the area of the brain was affected.
Numbness combined with pain occurs when:
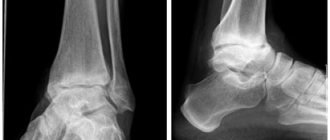
- fracture of the talus or calcaneus;
- foot paresis;
- brain tumors;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- migraine;
- encephalitis;
- mental disorders;
- multiple sclerosis;
- Morton's neuroma.
Physiological
Foot numbness is often caused by wearing tight shoes that do not fit the length and/or width of the foot. Such shoes compress nerve endings and blood vessels, which leads to unpleasant sensations. Risk factors include the presence of flat feet, constant stress on the feet (including when playing sports, especially cycling, having a job where you have to stand or sit for a long time, etc.).
The list of reasons why heel numbness and swelling in women may occur includes pregnancy. In this case, only one leg may be affected. Depending on which blood vessels are pinched by the growing uterus, the patient’s left or right heel goes numb. Pregnant women with reduced immunity, anemia, and fatigue often come to the doctor with complaints of numbness in their heels.
Risk factors
The following can contribute to the development of the pathological condition:
- emotional stress, frequent stressful situations;
- excessive physical activity;
- bad habits (abuse of alcohol and smoking lead to the development of changes in the blood vessels, which can also cause numbness);
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- overweight;
- poor nutrition.
Symptomatic manifestations
The initial symptoms of the formation of pathology are:
- There is a tingling sensation in the foot. Discomfort occurs both during physical activity on the limb and at rest.
- The heel feels cold and often freezes.
- In the case of sports activities (running, jumping, cycling), a painful sensation develops in the back of the foot. In case of significant manifestation, the woman is forced to put aside high-heeled shoes, since this gives her a lot of discomfort.
- Periodic appearance of a convulsive state in the foot and lower third of the lower limb.
The described symptoms may appear simultaneously or independently of each other. Clinical manifestations correspond to the causative factor in the development of the pathological process. At the initial stage, the painful feeling is insignificant and is almost not noticed by the patient. But it gradually intensifies and interferes with the patient’s normal life activities.
Signs and associated symptoms
Numbness can develop while walking, when a person is sitting or in a horizontal position. The patient may also experience a feeling of itching, burning, crawling, discomfort, aching pain, swelling, coldness of the extremities, cramps, and the heel area may become less sensitive.
With the development of numbness in the leg against the background of a particular disease with the progression of the pathological process and in the absence of adequate treatment, the symptoms usually become more pronounced. It may become difficult for a person to walk in high-heeled shoes, run, or ride a bicycle.
| Cause | Associated symptoms |
| Stroke | There may be disturbances in speech, vision, movements, consciousness, sharp and intense headache, paralysis on one side of the body. |
| Metabolic disorders caused by vitamin and/or mineral deficiency | In addition to numbness in various parts of the body, convulsions may occur. |
| Diabetic neuropathy | There may be numbness not only in the heel, but also in other parts of the leg, as well as in the upper extremities. |
| Morton's neuroma | It is a thickening of the lower limb (the growth of fibrous tissue in the area of the plantar nerve of the foot), which is often observed in the area of the third intermetatarsal space (the base area between the third and fourth fingers of the lower limb). Most often, a unilateral form of pathology develops; bilateral nerve damage is much less common. |
Symptoms
Heel numbness develops in the first stages of dangerous chronic diseases, but in some cases it does not pose a danger. To quickly establish its cause, it is important to describe in detail the sensations that appear in the foot:
- loss of skin sensitivity, decreased response to pain;
- goosebumps or even cramps - they can begin at night and cause insomnia;
- pain and numbness during walking or running, which spread to the lower leg area;
- burning, tingling, increased local temperature or, conversely, cold and bluish skin;
- the foot becomes cottony.
Additional signs may include inflammation and hardening of the vascular walls, the formation of nodules and neoplasms. It is important to indicate not only their locations, but also the growth rate and time of their appearance.
What to do and how to treat heel numbness
If the unpleasant sensations are short-term, then in most cases no special treatment is required; understanding the cause and eliminating the negative impact on the body is sufficient.
In other cases, therapy is selected by the doctor depending on the pathology that caused the symptom:
- For intervertebral hernia - drug therapy (corticosteroids, muscle relaxants, etc.), physical therapy.
- In diabetes mellitus , the patient’s condition improves when blood glucose levels normalize.
- In case of circulatory problems , phlebotonic drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, and vitamin-mineral complexes can be prescribed. Foot massage is effective; acupressure, acupuncture, and physiotherapeutic procedures (laser, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, hydrotherapy, the use of therapeutic mud or paraffin) can also be used.
You should be aware that the lack of timely treatment for serious pathology, for example, diabetic neuropathy (diabetic foot), can lead to the need for surgical intervention, to the point where amputation of the affected limb is sometimes required.
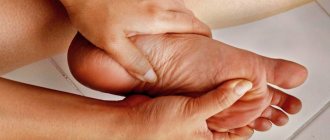
Foot massage can help with numb heels
General recommendations
To prevent the development of pathology and improve the patient's condition in the presence of numbness, self-massage can be performed using a hard sponge while taking a shower or bath. When the skin of the heel becomes rough, scrubs are recommended that stimulate blood circulation and have an exfoliating effect.
If the sensitivity disorder is associated with metabolic disorders, it may be necessary to limit the use of table salt. It is recommended to include foods rich in potassium, calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus in your diet.
The table shows some foods that may be helpful for numbness in a person's heels.
| Minerals | Food |
| Potassium | Carrots, potatoes, garlic, pumpkin, grapes, bananas, apricots, apples, melon, prunes, nuts, legumes, cocoa, meat |
| Calcium | Milk and dairy products, spinach, fish |
| Magnesium | Nuts, legumes, seafood, rose hips, poppy seeds |
| Phosphorus | Sunflower and pumpkin seeds, cashews, peanuts, almonds, yolk, fish, caviar |
ethnoscience
In some cases (if we are not talking about a serious illness), traditional medicine methods can help:
- Foot baths with solutions of medicinal herbs, milk, honey.
- Rubbing with products containing garlic, onion, black or hot pepper.
- Boiled pumpkin compresses Mash the boiled pumpkin into a puree and apply to the feet in the heel area. The pumpkin should be warm, the compress should be kept for 30 minutes.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
To understand what to do with heel numbness, it is necessary to conduct a more detailed diagnosis. To exclude the possibility of injury, x-rays are prescribed. Ultrasound is also informative, including with a contrast agent to assess the condition of the blood vessels. Additionally, general and biochemical blood tests are performed.
Treatment for numbness involves eliminating its causes and symptoms. The scheme may consist of several stages:
- anti-inflammatory creams, ointments and tablets;
- massage and physical therapy (walking on toes and heels, rolling objects with your toes, warming up joints);
- physiotherapy (laser exposure, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, low temperature treatment);
- if necessary - antibiotics;
- treatment of the underlying disease that caused a decrease in sensitivity.
If the heel is numb once, and additional symptoms do not appear, the symptom does not need attention. You should consult a doctor if numbness bothers you frequently, causes pain and discomfort.
Numbness in the heel area is an unpleasant symptom that affects the patient’s activity in everyday life. To avoid it, it is important to exercise, give up bad habits and unhealthy foods, and also monitor the condition of your blood vessels. At the first signs of serious disorders, which are accompanied by pain, numbness and discomfort, treatment should begin according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor.
Preventive actions
Any person should definitely take care of their own health. Yes, and preventive measures in this case are not very complicated, they can be easily implemented:
- A healthy and active lifestyle, performing sports exercises, eliminating bad habits.
- It is recommended to avoid stressful situations. Excessively intense neurostrain negatively affects the state of the cardiovascular system and metabolic phenomena.
- Fill your diet with foods rich in essential vitamins and microelements.
- Regular visits to the massage room and a course of foot massage. You are allowed to do it yourself.
- Timely treatment of various open wound surfaces on the foot with antiseptic solutions.
- Wearing comfortable shoes (proportional, wide-toed, etc.).
Restorative manipulations
Until a thorough medical diagnosis is performed and a reliable provoking factor for the development of paresthesia in the heel is determined, therapy makes little sense. In case of initial manifestation of discomfort, you should try to adjust your own lifestyle. To do this, it is recommended to give up smoking and drinking alcohol, take walks in the fresh air, and eat exclusively healthy foods.
The most common methods for restoring sensitivity in the heel area are:
- Drug therapy using drugs aimed at eliminating inflammation.
- Physiotherapeutic sessions.
- Treatment of the damaged part of the foot using a laser or special cryogenic beam.
- Exercise therapy and dietary nutrition.
- Vitamin therapy.
In order to achieve effective therapy, it is necessary to promptly identify the problem and the factor that provokes it. In case of prolonged discomfort and to avoid aggravation of the situation, it is recommended to immediately consult an appropriate doctor for advice and diagnosis.