If a child has heel pain, then this symptom should alert parents. This may be a sign of inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which require immediate treatment. Also, discomfort in the foot area can often occur after injury. With minor injuries, children may not experience pain in the first days. But trauma can affect the child’s well-being after some time. In this article we will look at the most common causes of pain and methods of treating pathologies.
Natural causes
Often, a child’s heels hurt due to increased physical activity on the feet. An exacerbation of such symptoms is most often observed in the fall. During this period, children resume attending sports activities after the summer. During long rests and vacations, the legs become unaccustomed to regular exercise. And resuming training can lead to pain. Usually, the discomfort goes away as the body adapts to the stress.
If a child's heels hurt after playing sports, this may indicate excessive physical activity. In this case, the intensity of training must be reduced and close attention to the diet should be paid. A deficiency of calcium and vitamin D in the body can provoke pain in the heel area. Also, unpleasant sensations in the legs after playing sports more often occur in children who are overweight and have flat feet.
Uncomfortable shoes can also be a cause of pain. In this case, you need to choose an insole with arch support. This will help reduce the stress on your feet when walking and running.
All according to plan
An orthopedic examination is required:
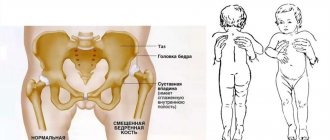
– immediately after birth, this is necessary to exclude congenital deformities and skeletal diseases, including congenital flat feet; also at this age it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the hip joints;
– at 3 and 6 months;
– at 1 year, when the child already sits, crawls, and walks independently;
– at 3 years of age to check posture, gait, condition of the feet and measure the length of the limbs.
Pathological causes
However, there are times when discomfort in the feet does not disappear even after reducing physical activity and choosing comfortable shoes. Parents should be concerned if their child’s heels hurt for a long time. The reason for this may be various pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Such diseases can be divided into several groups:
- Pathologies characteristic of childhood. These include osteochondropathy (Schinz disease), apophysitis, epiphysitis, inflammation of the Achilles tendon. These diseases often occur in children aged 7 to 12 years. During this period, the child’s musculoskeletal system continues to develop. At the same time, children usually lead a very active lifestyle. A large load on a fragile musculoskeletal system can provoke inflammatory diseases.
- Injuries. Often parents suddenly notice that their child’s heel hurts and it’s painful to step on. This can be caused by various types of damage. The heel bone is quite fragile, and its trauma is not always accompanied by severe pain. Therefore, discomfort in the foot area sometimes does not occur immediately after a fall or bruise.
- Diseases that are rare in childhood. These include bursitis and heel spurs. These pathologies are more typical for adults, but can also occur in children due to previous infections, metabolic disorders or excessive physical exertion. This group of diseases also includes plantar warts (thorns), which are rarely found in young children.
Next, we will consider in detail the symptoms and methods of treatment of the above pathologies.
Big problems for a little leg
It is only at first glance that it seems that a child’s leg is a smaller copy of an adult’s. In babies, the longitudinal arch of the foot is flat. This is due to the fact that the bone tissue is still soft, the muscular system is not developed enough. When children begin to walk independently, the function of a shock absorber is taken over by the “fat pad”, which is located on the foot. By the age of two or three, the ligaments and muscles become stronger, which allows the child to be “on his feet” longer. This is when flat feet can be diagnosed. By the way, in children under 9 years of age, longitudinal deformation is more common, since the transverse arch is just forming at this age.
There is an opinion that children under 3 years old do not have flat feet. This is not entirely true. There are children who are at risk. These are kids:
- whose parents have flat feet. The hereditary factor plays a significant role in this disease;
- early (before 8–9 months) those who began to get up and walk;
- with dysplastic syndrome (joint hypermobility);
- with endocrine diseases;
- with excess body weight;
- with post-strachitic deformity of the lower extremities;
- with an incorrectly healed fracture of the leg and foot bones.
Osteochondropathy
This pathology is otherwise called Schinz's disease. Osteochondropathy of the calcaneus most often occurs in girls 7–9 years old, and in boys 10–12 years old. The cause of the pathology is increased physical activity and calcium deficiency in the body.
With this disease, the absorption of nutrients by bone tissue deteriorates. Because of this, necrotic changes occur in the heel bone. This is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- heel pain, worsening during the day when walking;
- swelling of the heel area;
- lameness (the child avoids stepping on the sore leg);
- malaise, fever;
- difficulty flexing and extending the foot.
In the acute stage of osteochondropathy, the foot must be provided with complete rest. For fixation, use a plaster cast or a special splint with stirrups.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed:
- ultrasound;
- electrophoresis;
- applications with ozokerite.
To relieve pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the form of ointments and tablets.
Epiphysitis
Parents often notice that their child’s heels hurt after training. This may be a sign of microdamage to the heel cartilage - epiphysitis. This disease most often affects teenage boys who are intensely involved in sports. Vitamin D deficiency can provoke pathology. It has been established that children living in regions with cold climates are especially susceptible to this disease. Due to lack of exposure to ultraviolet radiation, the skin's production of vitamin D decreases. Therefore, this disease is also called Sever's disease.
With epiphysitis, the child’s heel hurts when running, jumping and fast walking. At rest, the unpleasant sensations weaken. The pain is localized at the back and side of the heel and intensifies with pressure. If the cartilage is severely damaged, swelling and redness may occur. In advanced cases, the child cannot bend the foot and begins to limp.
A sick child is recommended to wear orthopedic shoes with soft insoles, a cushion under the heel and an instep support. A course of treatment with vitamin D supplements and painkillers are prescribed. Physiotherapeutic procedures indicated:
- electrophoresis with novocaine and calcium;
- massage;
- baths with medicinal mud.
Epiphysitis has a favorable prognosis. The signs of this disease completely disappear in adulthood, as the cartilage tissue undergoes ossification.
Apophysitis
There are cases when pain is not observed at rest. There is practically no swelling in the foot area. However, the child's heel hurts when walking. The cause of this may be an inflammatory process in the heel cartilage - apophysitis.
This disease most often occurs in children under 14 years of age who are actively involved in sports. A child’s cartilage tissue is quite weak and easily becomes inflamed with increased stress on the legs. Most often, this pathology appears during puberty, when the teenager is growing rapidly.
Apophysitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the back and side of the heel;
- discomfort when walking;
- disappearance of pain at rest;
- absence of swelling (there may be only a slight swelling).
If there is an inflammatory process in the heel cartilage, it is recommended to temporarily stop sports activities. The little patient is prescribed a course of physical therapy and massage. It is recommended to wear special shoes with soft insoles. Drug therapy consists of prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, Ibuprofen) and complexes with vitamin D, ascorbic acid and calcium. The disease practically does not occur in adults, since with age the cartilage undergoes ossification.
Inflammation of the Achilles tendon (tenosynovitis)
The Achilles tendon runs along the back of the lower leg. This is the strongest ligament in the human body that can withstand heavy loads. However, in childhood, excessive sports activities often cause inflammation of the tendon. As a result, the ligament thickens and prevents normal extension of the leg. The disease is more common in adolescence.
With tenosynovitis, the child’s heel hurts and it hurts to step on the foot. Unpleasant sensations may radiate to the foot. The back of the lower leg appears swollen. The calf muscles are tense. In advanced cases, a creaking sound is heard when moving.
Treatment consists of fixing the affected limb with an orthosis or elastic bandage. To relieve pain, oral and local anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesil, Ibuprofen) are prescribed. The application of compresses with solutions of novocaine or analgin is also indicated.
After relief of acute pain, the child is prescribed a course of physiotherapy:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser treatment;
- electrophoresis;
- mud baths and applications;
- ultrasound.
After treatment is completed, it is recommended to reduce the load on the legs. The child is prescribed a course of restorative physical therapy.
What to do?
First of all, you need to find out the reason why your child’s foot hurts. Were there any skin lesions or injuries, what did you do in recent days, how did your activity change, did you wear new shoes? These questions will help you navigate. If the pain does not disappear within several days and prevents you from walking normally, be sure to consult a doctor.
This could be a pediatric surgeon, traumatologist, or orthopedist. Tell us all the symptoms, when the pain first appeared, whether there are difficulties when walking, where the child’s foot hurts (in the middle, in the heel or toes), what other complaints.
Be sure to see a doctor if, in addition to foot pain, your child has:
- temperature;
- redness;
- signs of infection, purulent discharge;
- tingling, numbness;
- changes in the normal position of the foot;
- loss of stability when supporting the leg.
child
Injuries
If a child has a sore heel and it hurts to step on his foot, then these symptoms may be a sign of injury:
- fractures;
- bone cracks;
- sprains.
Such injuries are the result of unsuccessful jumps and falls from heights. It is important to remember that pain from a heel bone fracture can be quite tolerable. Injuries are always accompanied by severe tissue swelling. In severe cases, the leg appears deformed. It is necessary to urgently take the child to the emergency room and take an x-ray.
If the calcaneus is fractured, a plaster cast is applied to the leg. If the injury is accompanied by displacement of fragments, the child must be admitted to a hospital. Under anesthesia, the bones are repositioned, and only after this the limb is fixed with a plaster. Healing of the fracture can take up to 6 - 7 weeks. During the rehabilitation period, the child is prescribed a course of physical therapy and physiotherapy.
Norms for the development of motor skills
| Norms for the development of motor skills | |
| Sitting without support | 6-8 months |
| Crawling on all fours | 9-11 months |
| Walk independently | 12-14 months |
| Climb the stairs on all fours | 15 months |
| Descending the steps | 20-24 months |
| Climbing stairs (alternating legs) | 3 years |
| Single leg jump, long jump | 4 years |
| Balance on one leg 20 seconds | 6-7 years |
Other diseases
These pathologies are more typical for adults. However, in rare cases they can also occur in children. Such diseases include:
- heel spur;
- achilles bursitis;
- plantar warts (spikes).
Heel spurs are otherwise called plantar fasciitis. The disease is accompanied by inflammation and degeneration of the ligament (fascia) of the foot. In advanced cases, pathological growths (osteophytes) appear on the heel bone, which look like spurs. In the initial stages, the child’s heel hurts only in the morning. When osteophytes appear, the pain becomes constant and difficult to relieve.
This pathology most often affects children with flat feet and excess weight. At an early stage, heel spurs are amenable to conservative treatment. The child is prescribed anti-inflammatory and hormonal ointments, as well as physical therapy sessions. In advanced cases, surgery is indicated.
Achilles bursitis most often occurs after an ankle sprain. This disease is accompanied by inflammation of the joint capsule located between the Achilles tendon and the heel bone. There is pain in the heel and limited joint mobility. The pathology very quickly becomes chronic. Patients are prescribed a course of antibiotics, painkillers and shock wave therapy. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections are given into the area of the joint capsule.
Why does a child’s heels hurt and growths appear on the foot? This may be caused by plantar warts (thorns). This type of papillomas is more often observed in adolescence, but it is possible that growths may appear in childhood.
The growth of warts is a consequence of infection with the HPV virus and decreased immunity. The child’s heels hurt when walking, as he constantly has to step on growths. For plantar warts, the patient is prescribed antiviral drugs and immunomodulators. If papillomas interfere with normal walking, then removal of the growths is indicated.
Plantar fasciitis
This is the name for inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick strip of connective tissue that runs along the bottom surface of the foot. It connects the heel bone to the bones of the forefoot and supports the longitudinal arch. Plantar fasciitis is caused by flat feet, a sharp increase in physical activity, running, jumping, and excess weight.
The child complains of pain in the foot in the heel area in the morning when he takes his first steps. With difficulty he steps on his foot after getting out of bed. After it disperses, the pain decreases or disappears, and the next morning it appears again.
Rest, cold, anti-inflammatory drugs, exercise therapy, massage, orthopedic shoes help. It is necessary to temporarily exclude running, jumping, and long walking. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor.
Diagnostics
We have found that there are many reasons why a child has heel pain. What to do if such a symptom appears? It is necessary to contact a pediatric surgeon or orthopedist. Pain in the heel bone can have different origins. Only a specialist can identify their etiology.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following examinations are prescribed:
- radiography of the calcaneus;
- MRI of the foot and ankle;
- clinical blood and urine tests (to detect inflammation);
- examination of synovial fluid (for diagnosing bursitis).
If you suspect plantar warts, you should consult a dermatologist and take a blood test for papillomavirus.
Help with severe heel pain
Let us note once again that there is no need to self-medicate. At the first complaint of pain, take your son or daughter to a specialist. The symptoms of many of the above diseases are very similar, and only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis. But what to do if there is no opportunity to contact a specialist, for example, the trouble occurred while on vacation outside the city? Try to reduce the patient’s physical activity to zero; in other words, provide him with bed rest and fix the foot in one position, for example, with an elastic bandage. The sore limb can be placed on a pillow so that it is at some elevation. Use painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications that are suitable for children.
First aid
How to properly provide help if a child has heel pain? Only a doctor can treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The choice of the necessary method of therapy will depend entirely on the type of pathology.
However, at the pre-medical stage, you can try to relieve discomfort. If a child has heel pain, it is necessary to interrupt sports activities and avoid putting stress on the legs. Before visiting your doctor, you can apply a cold compress to the affected area. If the pain occurs as a result of an unsuccessful jump or fall from a height, then it is necessary to apply a splint to the injured limb.
It is not advisable to give your child painkillers before visiting a doctor. This can blur the clinical picture of the disease, and it will be difficult for a specialist to make a correct diagnosis.
Flat feet
If the cause is flat feet, then the child’s feet often hurt after physical exertion, standing for a long time or walking for a long time. The pain can spread to the ankle joint, shins, and reach the knees.
Parents may not know for a long time that their child has flat feet, or may not attach much importance to it. But this is a mistake, since it affects the health of the entire musculoskeletal system, causes improper distribution of body weight, and increases the load on overlying joints and the spine.
Flat feet happen:
- flexible, when in a standing position the foot is flat, and when rising on the toes or raising the big toe upward, the arch (bend) becomes noticeable. This type of flatfoot does not cause any discomfort and goes away on its own after 3 years;
- hard, when the arch is not visible in any position of the foot. To correct the shape of the arch, special shoes or orthopedic insoles are prescribed, as well as gymnastics to strengthen the muscles.
Prevention
How to prevent pathologies of the heel bone and Achilles tendon? To prevent such diseases, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- A child's sports activities should be moderate. Grueling workouts with increased load on the legs are contraindicated in childhood.
- Children's diets should regularly include foods rich in calcium and vitamin D. These substances are necessary for the proper formation and strengthening of bone tissue.
- It is important to ensure that the child wears comfortable shoes with soft insoles and arch supports.
- If pain occurs after falls or bruises of the heel bone, it is necessary to promptly contact a traumatologist.
- It is very important to pay attention to the child's weight. Extra pounds create increased stress on cartilage tissue.
- You need to monitor the condition of the skin on your heels. If growths occur on the epidermis, you should immediately visit a dermatologist.
Following these steps will help reduce your risk of heel pain and limping.
Abnormal gait in children
Abnormal signs of disorders that require the attention of parents and doctors include the following:
- Antalgic gait (gait caused by pain).
- The time of possible load on one of the legs has been reduced.
- A young child may be reluctant to stand up.
- “Circular” gait, when the child seems to be spinning around one leg.
- Excessive abduction of the hip when turning the leg forward.
- Leg length discrepancy.
- Limited joint mobility.
- Spastic gait.
- Stiffness, foot dragging with inversion of the foot. This is often observed in neurological diseases.
- Ataxic (uncoordinated) gait.
- Unsteady walking (atactic gait) with alternating narrow and wide stance of the legs.
- Trendelenberg gait (sailor gait) with outward rotation of the hips, knees and feet.
- Constant gait on toes without contact of the support with the heel.
- Walking gait (the leg is raised high with each step).
- Clumsy gait (problems with coordination of movements, falls.