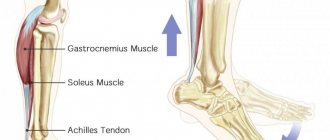
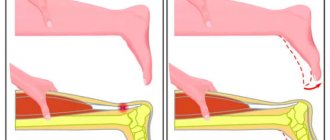
A muscle rupture is an injury that occurs when it is sharply contracted (falling) or subjected to excessive load (heavy lifting) in the area of the muscle belly or at the junction of the muscle and tendon.
As a rule, the muscles most often susceptible to rupture are the thigh muscles. Another common injury is a rupture of the rectus abdominis muscle. It occurs when falling backwards. A careless running jump can cause a torn calf muscle. Situations are also possible when ruptures of muscle tissue lead to bone fractures, in which significant displacement of fragments is observed.
You can undergo a course of treatment for a ruptured calf muscle at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. We have experienced specialists who will help you quickly recover from injury.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedic specialist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Clinical manifestations
Most often, ruptures of the calf muscles and other parts of the body occur in professional athletes: gymnasts, wrestlers, volleyball players, weightlifters, rowers, etc.
Symptoms of a muscle rupture, first of all, consist of intense pain that is localized in the damaged muscle. In addition, the following is observed:
- muscle dysfunction;
- the presence of a muscle defect that can be detected by examination and palpation;
- bulging of the muscle in the opposite direction from its separation in the form of a roller (with a complete rupture);
- the appearance of hematoma and edema at the site of injury.
Rehabilitation goals
A rehabilitation course after operations and injuries allows you to achieve the following results:
- regenerate muscle tissue, restore the previous level of strength and tone;
- restore motor activity of joints impaired after injuries, fractures, surgical interventions, immobilization;
- improve tissue regeneration, incl. cartilaginous;
- increase mobility with adhesions and scars;
- improve the trophism of muscle and bone tissues of the body;
- eliminate swelling and pain;
- improve blood circulation in damaged joints or limbs.
In addition, rehabilitation helps strengthen the patient’s overall tone and improve his emotional and psychological state. The absence of a timely rehabilitation course can lead to complications, re-development of the disease and threatens incomplete restoration of muscle strength.
Causes
Muscle rupture occurs when a cut wound or blow is received. But in more than 50% of cases, the injury occurs due to severe spraining and overexertion. This happens for 3 reasons:
- Muscle atrophy in old age.
- Changes in muscle structure due to disease.
- Pathological muscle weakness.
Often rupture occurs in weightlifters who work with critical weights. The likelihood of injury increases if you do not spend enough time warming up and warming up before physical exercise.
Early mobilization phase
Walking without an orthosis usually begins in this phase. It is extremely important to recognize both the importance of putting sufficient stress on the tendon and the fact that the risk of re-rupture is greatest at this stage. Stretching the tendon at this stage is not recommended to prevent it from lengthening. However, you can begin to perform active (without weight bearing) dorsiflexion of the foot. Below is a general rehabilitation protocol for this phase.
Friends, on April 24-25 in St. Petersburg, within the framework of the RehabTeam project, Georgy Temichev’s seminar “Ankle and foot (Block 3)” will take place. Find out more...
Early mobilization phase (sessions with a physical therapist 3 times a week, homework)
Exercise program
- Exercise on an exercise bike.
- Exercises to restore the range of motion of the ankle joint.
- Strengthening the calf muscles using an elastic band.
- Heel raises with a load of 25-50% of body weight.
- Lifting on toes (first on two legs, then on one).
- Walking training.
- Balance exercises.
- Leg press.
- Flexion/extension of the legs.
- Exercises for the foot.
If the patient meets the criteria of 5 calf raises on one leg at 90% of the height, then you can begin
- Bilateral jumping in place.
- Jog carefully in place.
In addition, during this phase it is useful to use compression stockings to prevent swelling of the lower leg.
Diagnostics
In case of partial muscle rupture, doctors at the CELT clinic apply a plaster cast, thus fixing the damaged limb in a certain position, which ensures maximum approximation of the edges of the injured muscle.
Complete muscle rupture requires surgery, in which a surgical suture is placed on the muscle itself. Sutures are also applied if a tendon tear occurs.
Professional medical care is decisive in terms of a favorable prognosis. During the recovery process, complete restoration of muscle tissue functions is observed. If you do not consult a doctor, there is a danger of the formation of rough scars that will limit the mobility of the muscle.
How to treat a complete or partial tear of the calf muscle
If we are talking about a partial variety, then it can be cured without surgery.
The patient is prescribed rest with maximum limitation of physical activity, limb immobilization, and therapy. In the acute period, characterized by severe pain, various analgesics, non-steroidal and anti-inflammatory drugs are used (cooling compresses also play an important role). Our doctors can accurately diagnose an ankle muscle tear using a step-by-step approach. They work in the following sequence:
- Conducts a survey regarding the nuances of what happened and chronic diseases that were present previously.
- Examines and palpates the painful area.
- Applies instrumental examination methods.
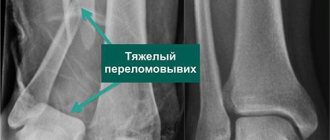
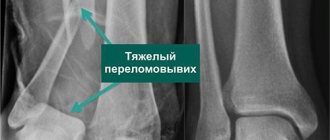
- Uses x-ray examination. It is used if, during the initial examination, signs of a fracture after a rupture of the calf muscles were detected (cracks, fragments, as well as individual parts will be visible in the image).
- Uses ultrasound. It is an effective way to determine damage to joints and joint capsules.
Our employees are able to select appropriate types of diagnostics or combinations thereof, based on the overall clinical picture.
Physiotherapist-rehabilitologist Irina Viktorovna Skrypova comments:
When the inflammation comes to an end, physiotherapy is prescribed, and UHF, ultrasound, and magnetic therapy can reduce discomfort and accelerate tissue regeneration. A partial tear of the calf muscle ligament can be treated at home if approved by the traumatologist. This type of therapy differs little from inpatient therapy, but the advantage is played by a familiar environment that relaxes the victim and speeds up recovery.
Surgical intervention is a must if the integrity of the muscle tissue has been completely compromised. This method consists of a set of small operations. For example, with a hematoma, it requires complete relaxation of the fibers and suturing them. Dissection is carried out, pus is removed, and the wound is drained. Antibacterial treatment is carried out, which plays the role of preventing infectious diseases.
Treatment
In case of local separation, treatment begins with immobilization and fixation of the affected area. The traumatologist applies a plaster cast to bring the torn edges closer together (this will speed up recovery). If the rupture is complete, then surgery is required, after which fixation and immobilization are performed.
Surgical sutures are required. Recovery takes one and a half or two months, depending on the severity of the pathology. During rehabilitation, you need to visit a specialist to perform physical procedures, as well as independently perform therapeutic massage.
Rehabilitation after surgery after a biceps muscle tear
A torn biceps muscle (biceps brachii) is most often associated with a sports injury, but this injury can also be caused by strong direct impacts, road accidents, etc. This injury leads to dysfunction of the elbow and shoulder joints and difficulty in free movements in the upper limb.
A biceps tendon rupture can be complete or partial. The difference lies not only in clinical data, but also in the amount of damage.
Patients with complete ruptures complain of intense, persistent pain in the shoulder area; they cannot bend their arm at the elbow joint. Externally, there is a deformation in the forearm area, which is often confused with a fracture. A few hours after the injury, swelling develops.
A ruptured biceps muscle requires surgical treatment to fully restore strength, which is especially necessary for athletes or people whose activities involve physical labor.
The operation is also advisable for people with partial tendon ruptures, if symptoms persist after conservative therapy.
Various surgical techniques are currently used that require minimal incisions and allow the tendon to be repaired. During surgery, the tendon is reattached to the bone. The doctor chooses the option for a specific surgical intervention. This operation is rarely accompanied by the development of complications. Repeated ruptures of the operated biceps muscle occur sporadically.
Rehabilitation after surgery after a biceps muscle tear primarily involves performing therapeutic exercises. To correct the range of motion in the shoulder joint, therapeutic exercises that strengthen the shoulder are prescribed.
Thanks to a successfully performed operation and a well-chosen set of rehabilitation measures, the deformation of the biceps muscle is corrected, its strength and function are restored.
Timely rehabilitation after surgery after a biceps muscle rupture helps prevent the development of serious complications: tendonitis, myositis, which tend to become chronic with debilitating pain during an exacerbation.
Physiotherapy and exercise therapy are highly effective during the rehabilitation period. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital rehabilitation clinic select an individual program for each patient; the duration of rehabilitation treatment is usually about three months.
Prevention
The main way to avoid injury is to use warming ointments and warm up thoroughly before physical activity. It is necessary to correctly time under load to avoid significant damage. Additionally, you need to carry out therapeutic massage and get plenty of rest to ensure 100% recovery of the body. It is also imperative to consume a sufficient amount of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, and during intense physical activity, take a vitamin-mineral complex.
Our clinic employs experienced traumatologists who are able to make a diagnosis based on palpation, determining the presence of a gap between the ends of the affected muscle.
If the gap is partial or closed, instrumental diagnostic studies are performed, including ultrasound. Do not self-medicate - contact traumatologists at the CELT clinic, and your full recovery is guaranteed!
Material and methods
In the period from 2005 to 2021, 37 patients with chronic rupture of the Achilles tendon were treated in the traumatology and orthopedic department No. 1 of the Samara State Medical University Clinic. The diastasis between the ends of the Achilles tendon in the neutral position of the ankle joint exceeded 10 cm. Due to the retraction of the triceps muscle, it is not possible to sew the tendon end to end; it is necessary to resort to plastic surgery of the diastasis formed between its distal and proximal ends.
In group 1 (control), we included 21 patients who underwent autoplasty with reversal flaps (according to Chernavsky, Krasnov), V-Y-plasty. The 2nd group consisted of 16 patients who underwent a new method of surgical treatment proposed by us [4]. In all subjects of the main and control groups, there was a significant difference (more than 4 cm) in the circumference of the symmetrical areas of the upper third of the legs, which indicated severe hypotrophy of the triceps muscle. Both groups were comparable in age, gender, mechanism of injury, time of visit to the traumatology and orthopedic department No. 1 of the Samara State Medical University Clinic, where their surgical treatment was carried out.
Before the operation, the patients were examined in the biomechanics laboratory of the Samara State Medical University Clinic (electromyography, podometry, measurements of the strength of the “flexors” of the feet), and an ultrasound diagnosis of the injury area was performed.
A team of authors from the Department of Traumatology, Orthopedics and Extreme Surgery named after. acad. RAS A.F. Krasnov received RF patent No. 2537888 dated November 13, 2014 for the invention of a new method of surgical treatment of patients with chronic rupture of the Achilles tendon with pronounced diastasis of its ends (more than 10 cm), which consists of transposition of the tendons of the peroneus brevis and tibialis posterior muscles to the distal end of the Achilles tendon in the optimal tension [4].
The proposed method is illustrated with graphic material. In Fig. 1 shown
Rice. 1. Isolation of the peroneus brevis and tibialis posterior muscles. 1 - proximal end of the Achilles tendon; 2 - distal end of the Achilles tendon; 3 - tendons of the peroneus brevis muscle; 4 - peroneus muscle; 5 - tendons of the tibialis posterior muscle; 6 - tibialis posterior muscle. proximal end (1) and distal end (2) of the Achilles tendon. The tendon (3) of the peroneus brevis muscle (4) was isolated and held. The tendon (5) of the tibialis posterior muscle (6) was isolated and held.
In Fig. 2:
Rice. 2. Relocation and plastic surgery of the Achilles tendon defect. 1 - proximal end of the Achilles tendon; 2 - distal end of the Achilles tendon; 3 - tendons of the peroneus brevis muscle; 4 - peroneus muscle; 5 - tendons of the tibialis posterior muscle; 6 - tibialis posterior muscle; 7 - sutures fixing the ends of the Achilles tendon. the peroneus brevis tendon (3) and the tibialis posterior tendon (5) are passed through the triceps muscle, covering the defect between the proximal end (1) and the distal end (2) of the Achilles tendon, stretched to optimal tension and fixed with sutures (7) parallel to each other to the distal end (2) of the Achilles tendon.
Clinical example
Patient P
., 53 years old, was admitted for surgical treatment to the traumatology and orthopedic department No. 1 of the SamSMU Clinic.
Life history: originally from the village of Sernovodsk. Works as a truck driver. Medical history: injured 20 years ago as a result of playing football. After visiting the clinic at the place of residence, a diagnosis was made: “bruise of the left ankle joint.” After the injury, he walked with crutches for 3 weeks due to pain. There is a decrease in the strength of plantar flexion of the foot over time. I applied for a consultation at SamSMU Clinics due to my inability to drive freight transport.
During local examination, wasting of the muscles of the posterior surface of the left leg was visually noted. Positive left calf compression test (Thompson sign). Circumference in the upper third of the legs: on the right 35 cm, on the left 30 cm. Strength of the plantar flexor muscles of the feet (according to the Lovvet scale) [2]: on the right 5 points, on the left 2 points.
Additional examination methods
According to the results of electromyography, there is a sharp decrease in the amplitude and frequency of contractions of the triceps muscle of the left leg in comparison with the healthy side (contraction frequency on the left 15 per 1 s, on the right 150 per 1 s; contraction amplitude on the left 25 mV, on the right 135 mV).
Podometry results revealed a pronounced asymmetry of gait.
Ultrasound conclusion: old injury of the Achilles tendon on the left with the presence of connective tissue in the area of the rupture, diastasis between the ends is 11 cm.
Surgical treatment is recommended.
Due to the severe hypotrophy of the triceps muscle of the left leg and the long history of the injury, it was decided to transpose the tendons of the peroneus brevis and tibialis posterior muscles to the distal end of the Achilles tendon in order to restore one of the most important functions of the ankle joint - plantar flexion [5, 6] .
Operation stages
Access to the Achilles tendon defect and its distal end was made. The distal end is isolated from scars. The Achilles tendon defect is visualized (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Isolation of the distal end of the Achilles tendon.
A linear skin incision 3 cm long was made along the outer surface in the middle third of the leg to isolate the tendon of the peroneus brevis muscle (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Isolation of the tendons of the peroneus brevis muscle.
Next, a 3 cm long incision was made along the inner surface in the middle third of the leg to isolate the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Isolation of the posterior tibial tendon.
After isolation, the peroneus brevis tendon and the tibialis posterior tendon are passed subcutaneously and brought into the defect area. Next, with optimal tension, the tendons are sutured to the distal end of the Achilles tendon (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Transposition of the peroneus brevis and tibialis posterior tendons to the distal end of the Achilles tendon.
After the operation, the patient was placed in a plaster cast along the anterior surface of the left shin from the upper third to the fingertips with a plantar flexion angle at the ankle joint of 20°. Recommended: walking without support on the left leg for up to 5 weeks. Then he underwent a course of rehabilitation treatment.
As a result, after 3 months the patient was able to lift his body weight on two feet, and after 6 months - to lift his body weight on one foot.
According to the results of podometry 6 months after surgery, no gait asymmetry was detected. Strength of the plantar flexor muscles of the feet (according to the Lovvet scale): on the right - 5 points, on the left - 5 points. The result of surgical treatment in patient P
. rated good.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| Ultrasound of soft tissues, lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 2 300 |
| MRI of soft tissues (one anatomical region) | 6 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Cruciate ligaments
When the “crosses” rupture, in the vast majority of cases it is not possible to do without surgical treatment. Ligaments do not heal on their own. And under no circumstances should you walk with torn ones: this leads to joint dystrophy, a decrease in muscle volume, and can result in chronic pain.
There are only two situations when surgery is not performed:
- partial rupture of the cruciate ligament (that is, only part of the fibers was damaged; this type of injury is also called a sprain);
- medical contraindications to surgery.
In the early period after injury, the joint is swollen and the pain is severe. Therefore, it is clinically impossible to determine whether the ligaments are completely torn. Adequate research is possible only after hemarthrosis has been eliminated and the knee has been anesthetized. To do this, a puncture is performed. The joint cavity is washed. After removing blood and clots from it, anesthesia is performed with a solution of local anesthetics. A solution of procaine with a concentration of 0.5% or 1% can be used, which is administered in an amount of 25-30 ml.
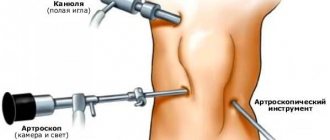
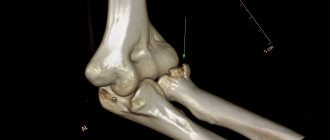
An instrumental study is required. It is likely that more than just the ligaments are damaged. At a minimum, the doctor does an x-ray. With its help, avulsion fractures (when a bone fragment is torn off at the site of attachment of the ligament) and damage to the condyles of the femur and tibia are excluded.
After carrying out the necessary therapeutic and diagnostic manipulations, the limb is immobilized. A plaster cast is applied for 2 months. As a rule, swelling is severe in the first week. It increases the volume of the limb. At the time of applying the plaster, it is always swollen, so after the swelling subsides, the bandage weakens. It needs to be changed after 5-7 days.
Next, the recovery process begins. Painkillers, exercise therapy, and physiotherapy are used. The patient is recommended to perform static loads on the thigh muscles. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid and platelet-rich plasma can be used to accelerate regenerative processes and prevent degenerative changes in the knee cartilage.