There are a number of diseases united by the collective concept of lumbar ischialgia, with painful attacks of a shooting nature and localization in the lumbar region of the spine, the cause of which is inflammation of the sciatic nerve. The pain can spread to the pelvic region, thigh, lower leg, foot.
The disease, as a rule, progresses against the background of pathological changes in the hip joints, spine, fascia and muscles and in the presence of chronic diseases of the internal organs.
When making a diagnosis, the disease must be differentiated from diseases that have a similar clinical picture.
The development of lumboischialgia occurs in cases where there are pain symptoms in the back of various origins. The disease most often affects people at the peak of physical activity, whose professions and activities involve a heavy load on the spine.
What it is?
Back pain, called dorsalgia , occurs in many diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The combination of sciatica and lumbago complicates diagnosis and sometimes leads to inadequate treatment.
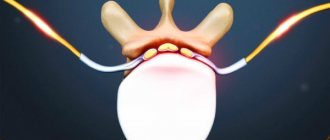
With sciatica, the sciatic nerve or nerve endings located near the sacral region are affected. The pain is localized in the thigh and moves to the ankle.
Over time, if sciatica progresses, then lumbago joins it . The disease is characterized by acute pain (lumbago), which begins even with mild nerve irritation. This condition can be caused by various pathologies. Therefore, accurate diagnosis is required.
Severe pain syndrome is vertebrogenic lumboischialgia . It can appear on one or both sides. The pain varies in intensity and nature. It is caused both by visible factors and spontaneously, without reason.
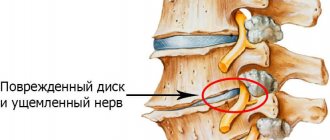
Lumboischialgia occurs due to compression of nerve endings in the lumbar spine
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), it is assigned code M 54.4. In the diagnosis, the doctor indicates not only the code, but also the clinical manifestations of the pathology, as well as information about the degree of development of the disease .
There are certain types of vertebrogenic lumboischialgia:
- Musculoskeletal . Caused by diseases of the musculoskeletal system in the lumbar region and lower extremities.
- Angiopathic . Pain occurs due to damage to the arteries or veins, which causes a deterioration in the supply of nutrients to the lumbar region.
- Neuropathic . Pinched nerve endings in the lower back cause pain that spreads throughout the sciatic nerve.
- Mixed . This form is common. It is characterized by the presence of several factors simultaneously.
Vertebrogenic lumboischialgia is characterized by pain of varying localization and severity.
Therefore, this pathology is divided into certain forms of pain.:
- Neurodystrophic . Severe burning pain, but of low intensity. This form is quite common and is often accompanied by significant changes in the tissues of the affected area (the skin becomes thinner).
- Vegetative-vascular . Numbness of the feet appears. Pain also appears when the patient stands up.
- Muscular-tonic . Combat syndrome with muscle spasm in the lumbar region. In the sacral region, loss of mobility is possible, which causes curvature of the spine.
This pathology often occurs in middle-aged people, but most often in men over 40. Treatment begins after identifying the cause of the pathology. Only by eliminating the symptoms, complete recovery will not occur.
Diagnostic measures
If the symptoms described above appear or you suspect the formation of an abnormal process, you must urgently visit a specialized clinical institution where you can receive qualified assistance. An expert in the field of neurology will conduct a consultation with the patient, during which he will be able to conduct static and dynamic tests, assess the severity of symptoms of sciatic nerve tension, and also collect an anamnesis (to exclude the presence of infectious agents or oncology). In addition, the patient will need to undergo a standard examination, where the doctor can examine the organs of the pelvis and abdomen. In addition, the doctor prescribes the following medical procedures:
- X-ray examination - to detect decreased disc height, hypertrophy, osteophytes, etc. The main objective of this examination is to exclude the presence of a malignant neoplasm, injuries and fractures of a pathological nature, congenital abnormalities, etc.
- CT or MR scanning of the spine is carried out based on the recommendations of a specialist and existing contraindications.
- Myelographic testing - done when it is impossible to conduct a computed tomogram or magnetic resonance analysis.
- Lumbar puncture - shows an increased number of protein particles.
- Ultrasound and excretory urography are performed based on indications.
Risk factors and causes
The pathogenesis of the disease is irritation of the nerves due to their pinching and inflammation. The pain intensifies if the nutrition of the affected tissue is disrupted, it becomes tense and nodes appear.
The main causes of this pathology are:
- Osteochondrosis is in the progressing stage, when dysfunction of spinal segments appears, protrusions and hernias occur, and bone osteophytes are formed.
Familiarize yourself with the main causes of lumbar sciatica; Osteoporosis of the pelvic bones and spine.- Disc arthrosis.
- The vertebrae have congenital defects.
- Scoliosis.
- Tumors of internal organs.
- Abscesses in the lumbar region.
- Damage to the hip joint.
- Diseases that impair blood circulation in the lower back.
- Failed injections and postoperative complications.
- Nerve damage due to infectious diseases.
- Lumboischialgia without an unclear cause.
It is necessary to prevent factors that provoke the development of the disease:
- Obesity.
- Hypothermia.
- Depression and frequent stress.
- Incorrect posture.
- Hard physical labor.
Other causes include pregnancy and age-related changes in the spine.
Mechanisms of formation of lumboischialgia
Lyubmoischialgia is formed as a result of irritation of the nerve roots. The cause of this irritation can be deformation of bone structures, compression of the nerve by muscles, injury and inflammation. As a result of irritation, a painful sensation appears, which can lead to lumpiness and muscle tension, the formation of nodules in the muscles and problems with the nutrition of the skin.
The nerve, under the influence of certain factors, ceases to function normally, which may cause chills or fever in the limbs, increased pallor of the skin and a sharp change in its color. These changes already indicate the presence of the disease, and also ensure its development, increasing pain.
Consequences
The danger of lumboischialgia, which is vertebrogenic in nature, largely depends on the area where the nerve fiber is pinched. If a “horse tail” has formed, then failure of the intestines and urethra may occur .
Lumbago with sciatica often leads to emergency surgery if there is a large intervertebral hernia.
To prevent this, timely comprehensive treatment of lumbar diseases is necessary. Periodic pain syndrome in the lower back is the reason for a thorough diagnosis and the prescription of certain methods of therapy.
Vertebral lumboischialgia with neurodystrophic development is characterized by pathological lesions of nerve roots that have been pinched. Some tissues die and cannot be restored. There is a threat of paralysis and paresis . In the advanced stage, as well as in the absence of therapy, trophic changes in the skin of the leg develop, which leads to persistent lameness.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
The first signs of the disease occur if osteochondrosis begins to progress.
Main symptoms:
- Acute throbbing attacks of acute pain in the lower back.
- Painful sensations spread to the buttocks and legs to the feet.
- The pain is usually localized inside the muscles and much less often near the surface of the skin.
- Former mobility is lost, any movement is difficult.
- The skin becomes pale and cold.
- When changing body position, the pain intensifies.
- If the disease is advanced, then the processes of defecation and urination are not controlled.
In addition to shooting pain in the lower back, lumboischialgia is accompanied by pain in the leg and buttock
The duration of attacks varies from several minutes to a day or more. Sometimes the pain disappears spontaneously.
In order not to confuse vertebral lumboischialgia with renal failure, it is necessary to carry out a competent diagnosis.
Proven methods are used for this.:
- X-ray of the lumbar spine.
- Laboratory tests to find out the cause of the pathology.
- and MRI. These studies make it possible to determine the condition of blood vessels and nearby tissues.
- Ultrasound.
- Densitometry.
Only after diagnostic examinations, a final diagnosis is made and an individual course of treatment is prescribed.
Video: “What is lumbar sciatica?”
You can learn more about pain syndromes in the spine in the following articles:
- More information about dorsalgia of all parts of the spine is described on the page
- Treatment of thoracic spinal dorsopathy
- Find out about the symptoms of dorsopathy in the cervical spine by going here
Treatment
Did you know that...
Next fact
Treatment of the disease is aimed at relieving pain and eliminating the underlying pathology.
Drugs
The patient is usually recommended bed rest (up to two weeks) and taking medications of various groups:
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
|
| Non-narcotic analgesics |
|
| Muscle relaxants. Prescribed to relieve muscle spasms |
|
| Diuretics. Used when nerve trunks swell |
|
| Sedatives |
|
| Blockades with novocaine, and in case of severe pain with glucocorticosteroids |
|
| Medicines that stimulate blood circulation |
|
| For local anesthesia, ointments and creams with anti-inflammatory components are used |
|
When the pathology becomes chronic, treatment methods must be selected individually. In this case, the main goal of therapy is to exclude causes of pain, such as tumors, osteoporosis or infection. Then you need to regain mobility. Usually, this is possible without the use of drugs.
We should not forget that getting rid of pain does not mean recovery. It is necessary to treat the disease that caused the pain syndrome.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is usually not required. Almost 90% of patients recover after conservative treatment . Surgery is necessary only in extreme cases. For example, if pain cannot be neutralized with conservative therapy. Surgery is also indispensable when there is a “cauda equina” (pinching of a bundle of nerve endings), which causes serious disruption to the functioning of the pelvic organs.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Electrophoresis can be used to treat lumbago and sciatica. Physiotherapy procedures are also quite effective. The following are usually prescribed :
- Electrophoresis with drugs.
- Magnetotherapy
- UHF.
- Application of microcurrents.
- Massage.
- Acupuncture.
- Paraffin compresses.
Physiotherapy
As soon as the pain attack is relieved and the patient can move, you can begin performing special exercises.
Approximate complex (all exercises are performed lying down):
- Inhaling deeply, raise your hand up and stretch well. As you exhale, return to the starting position. Performed 5 times with each hand.
- Flexion and extension of the feet. First, both at the same time, and then in turn. Repeat 5 times.
- Pull your knees towards your chest. Spread them apart, then bring them together. Perform the exercise at least 10 times.
- Legs extended. Bend each leg at the knee without lifting the heel from the surface 5 times with each leg.
Over time, exercises are added that are performed standing and sitting. You should not rush into gymnastics, otherwise you can cause an exacerbation again.
Treatment at home
Traditional medicine methods can also help eliminate the discomfort associated with this disease. They rarely cause adverse reactions and are effective.
Some healing recipes:
. If the pain worsens, then a compress is applied to the sore spot on the lower back. It lasts for several hours. It is not recommended to leave it on for a long time, as skin irritation is possible.
To eliminate back pain, you can use a turpentine compress. Alcohol tincture of valerian- Turpentine . You need to roll out 100 g of rye flour dough and add a spoonful of turpentine. Then rub the painful area with turpentine oil and apply the prepared cake. The compress is left for one hour, and this treatment is carried out for no more than 3 days.
- Red clay . Add hot water to it and stir until it reaches a consistency similar to thick sour cream. The mixture is distributed over the entire lower back and kept for 30 minutes. Therapy continues for several weeks.
Before using folk remedies, you should definitely consult a doctor. Alternative medicine recipes cannot be used for independent treatment; they are used in combination with the main treatment to enhance the effect.
Prevention
To prevent the disease or not cause its recurrence, you must follow basic advice:
- Try to normalize your weight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Forget about bad habits.
- Reduce the load on the lower limbs as much as possible (it is better to sit than stand).
- During inactive work, periodically stretch your muscles.
These simple rules will help mitigate or even avoid this disease.
Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of spinal ailments and to detect them in a timely manner, do not forget about the following::
Familiarize yourself with the rules for preventing lumbar sciatica; if you suffer from sciatica, you should ignore the annual medical examination;- Hypothermia and back injury should not be allowed;
- you should watch your posture;
- do not wear high heels on a regular basis;
- avoid lifting heavy objects alone;
- if you still have to work with a heavy object yourself, follow safety precautions: when lifting a massive object from the floor, you should not bend over, but sit down; when carrying, hold the item not on outstretched arms, but closer to you; push a large weight (for example, a cabinet) no longer with your hands, but with your back;
- take useful gymnastic breaks during work, if possible, make stops to warm up during a long car ride;
- give up bad habits: they increase the body’s susceptibility to infections;
- monitor your weight and nutrition;
- don’t forget about rest: it is recommended to take a preventive sanatorium-resort vacation at least once a year
Forecast
If this pathology is detected at the first stage of development, then the prognosis for recovery is very positive . If the disease becomes chronic, you should not rely on medications. Only therapeutic exercises that will maintain the mobility of the spine will help improve the situation.
The main thing is to endure the acute pain, and then immediately begin treatment of the underlying pathology (osteochondrosis, hernia). With adequate therapy, pain may disappear completely.
Gymnastics
To reduce pain and prevent possible relapses, patients are advised to undergo a course of therapeutic exercises. This course of exercises is aimed at strengthening the muscles that surround the spinal column, thereby reducing the risk of vertebral displacement and making them more resistant to stress. Patients should perform exercises in specialized institutions under the supervision of specialists. However, over time, after completing a course of physical therapy, they will be able to continue their activities at home on their own.
The complex of therapeutic gymnastics necessarily includes exercises that help stretch the muscles (turning the body, bending, bending the back). Exercises aimed at restoring the mobility of the hip joints and spine (squats, leg swings, lifting the body from a lying position) are also considered effective. Patients are also recommended to engage in exercise equipment and yoga.