Joint diseases affect people at different ages, and in most cases the treatment regimen is approximately the same. However, sometimes a woman expecting a baby comes to see an orthopedist. In this situation, almost all medications and many manipulations are contraindicated. How to cope with the problem during pregnancy?
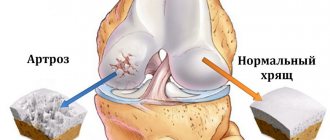
Osteoarthritis also occurs in pregnant women
Reasons for the development of osteoarthritis in pregnant women
Joint diseases during this period develop mainly against the background of concomitant diseases, such as pathologies of the endocrine system or metabolic disorders. While carrying a child, chronic illnesses worsen, the body cannot cope with the load, and therefore complications arise as a result.
Treatment of arthrosis and osteoarthritis during pregnancy is often required by former athletes. Previously obtained tendon sprains, soft tissue bruises and other microtraumas provoke a pathological process that worsens during these nine months.
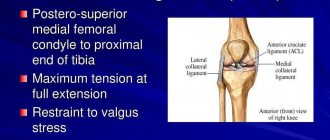
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
The pubic symphysis is located on the anterior side of the pelvis and is the anterior border of the perineum. The pubic bones form a cartilaginous joint in the midplane called the pubic symphysis. This joint holds the pubic bones together and provides stability during movement.
Together with the sacroiliac joints, the symphysis pubis forms a stable pelvic ring. There is very little mobility in this ring.
You can read more about the anatomy of the pelvic floor here.
The pubic symphysis is a cartilaginous connection of the pubic bones, between which there is a fibrocartilaginous interpubic disc. The pubic bones are connected to each other by four ligaments. The superior pubic ligament begins at the upper edge of the pubis and extends to the pubic tubercles. The arcuate ligaments of the pubis form the lower border of the pubic symphysis and are woven into the fibrocartilaginous interpubic disc. The stability of the joint is mainly provided by the strongest arcuate ligaments. Together, these four ligaments stabilize the joint and keep the articular surfaces from shifting and stretching.
The disc connects the articular surfaces of the two pubic bones. Each of these surfaces is covered with a thin layer of hyaline cartilage. The connection is not smooth; it contains papillary projections, depressions and protrusions.
In children, the disc is very small, the hyaline layer is very thick, but becomes thinner over time. In men, the disc is higher, smaller and narrower than in women. In its thickness, the disc has a slit-like cavity, which is normally 4-5 mm wide in women. In the last trimester of pregnancy, it increases by another 2-3 mm, which is necessary for the baby to pass through the birth canal. With dysfunction of the symphysis pubis, the joints become more relaxed, which leads to instability in the pelvic girdle. When the width of the cavity is equal to or exceeds 10 mm, diastasis of the pubic symphysis occurs.
Diagnostic features
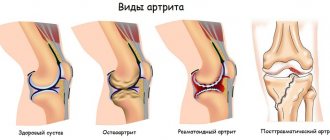
The first sign of osteoarthritis is pain when moving. If the disease has not yet entered the second or third stage, the pain subsides after rest. Some women also complain of pain after prolonged walking or other physical activity.
During pregnancy, manipulations and various instrumental research methods are prohibited, so pain becomes the main thing when making a diagnosis. If the period is still short enough and the woman is not yet aware of her “interesting” situation, she can be given an x-ray. In other cases, the diagnosis is made based on a survey, examination and general blood test.
X-rays and MRIs are contraindicated during pregnancy
Pain in the hip joint during pregnancy occurs much more often not due to arthrosis, but against the background of the woman’s “special” condition and hormonal changes, however, there are exceptions - thinning of the cartilage, which continues to manifest itself even after childbirth:
Epidemiology/Etiology
There are several theories about the origin of symphysis pubis dysfunction:
Aslan et al. They say that the etiology of the disease is unknown. During pregnancy, the load on the pelvis changes, ligaments and muscles weaken. This leads to spinopelvic instability, which manifests itself as DLS.
In early pregnancy, the corpus luteum produces large amounts of the hormone relaxin and progesterone. From the 12th week, this function is taken over by the placenta and the decidua of the uterus. Relaxin breaks down collagen in the sacroiliac joints, causing tissue softening. Progesterone has a similar effect. However, there is no correlation between relaxin levels and the degree of symphysis pubis dysfunction. A Norwegian study found that genetic predisposition to DLS may be caused by defects in relaxin secretion. It may seem that relaxation of the ligamentous apparatus directly indicates the presence of a hormonal basis for the disease. However, there is not enough data to support this theory.
The influence of stress and cortisol levels on pelvic pain.
Other factors leading to DLS include physically exhausting work during pregnancy, as well as pathological fatigue, poor posture and lack of exercise. Excess weight, multiple pregnancies, older pregnancies, a history of difficult labor, and shoulder dystocia may also play a role.
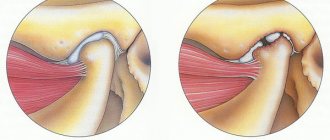
Effective adaptation of joints to a given load requires adequate joint compression and coordinated efforts of muscles and ligaments. This is the key to effective joint reactions to changing conditions. During pregnancy, ligaments and muscles become weaker and cannot perform their functions as they did before. As a result, the pelvic tilt changes, which leads to spinopelvic instability, most often manifested in dysfunction of the pubic symphysis.
In short, the causes of this instability are hormonal (influence of the hormone relaxin), metabolic (calcium metabolism), biomechanical (stress during pregnancy and exercise), underdeveloped muscles, body composition (weight), anatomical and genetic variations.
- The pelvic floor is made up of three layers of muscles. The superficial layer innervated by the pudendal nerve includes the bulbocavernosus muscle, the ischiocavernosus muscle, the superficial transverse perineal muscle, and the external rectal sphincter.
- The deep layer is the urogenital diaphragm, which is also innervated by the pudendal nerve. These include the urethral sphincter, constrictor bladder muscle, urethrovaginal sphincter and deep transverse perineal muscle.
- The pelvic diaphragm is made up of the following muscles: the levator ani muscle (pubococcygeus muscle, also known as pubo-prostatic, pubovaginal, pubo-anal, puborectal, iliococcygeus), coccygeus muscle, piriformis muscle and obturator internus muscle. These muscles are innervated by the sacral roots of the spinal cord (S3-S5).
The function of the pelvic floor muscles is to support the organs lying on it. The sphincters (anal and urinary) allow conscious control of the bowel and bladder. Thanks to this, we can consciously control the excretion of feces or fatus, as well as urine.
When contracted, the pelvic floor muscles are able to lift the internal organs and compress the openings of the sphincters of the vagina, anus and urethra. When the pelvic floor muscles relax, urine may leak and feces may be released uncontrollably. Pregnancy changes the functioning of these muscles, as well as their function.
Treatment tactics for pregnant women diagnosed with osteoarthritis
In advanced cases, osteoarthritis can seriously progress, bring discomfort into everyday life and even lead to disability. Therefore, the success of treatment largely depends on how quickly the woman seeks help. Today there are a number of therapeutic methods that are not capable of harming the fetus, but at the same time significantly alleviate the condition of the expectant mother.
At the initial stage of osteoarthritis the following is prescribed:
- gymnastics to strengthen joints;
- massage;
- mud baths;
- visiting specialized sanatoriums.
It is very important to reduce the load on the joint: for example, in the case of osteoarthritis of the knee, keep the limb completely at rest. Fixed postures and excessive physical activity are also contraindicated. If the disease has progressed, an orthopedic rheumatologist may prescribe heat treatments to reduce pain. It is prohibited to take pills on your own for pain relief: many of them can harm the fetus.
In the case of pregnant women, orthopedic doctors are very limited in the choice of medications and treatment methods
Physical therapy
The following devices can be used as part of DLS therapy:
- Crutches with elbow support.
- Pelvic support devices: Lumbopelvic brace (the brace should be positioned strictly cephalad to the greater trochanter of the femur. The study does not recommend the use of a lumbopelvic brace as monotherapy because lumbar stability must be achieved through proper motor control and coordination ).
- Prescription pain relievers (use NSAIDs during pregnancy with caution).
- Social services.
Birth planning
- Women with DLS should give birth in an upright position with their legs slightly apart.
- The gap between the pubic bones should never exceed the maximum, so patients are advised to wear special tapes on both legs.
- During childbirth, you should not rest your feet on the midwife's thighs, use footrests, or use surgical forceps, as they can further stretch the ligaments.
- During labor and childbirth, the legs should be minimally apart.
Prevention
- Informing the patient: about her illness, as well as about the connection of the disease with the required and permissible load;
- about the need for rest;
- to reduce fear;
- to motivate the patient to actively participate in the treatment process;
- tips for everyday life (do household chores while sitting if possible, sleep with a pillow between your legs, keep your legs bent to get in/out of bed).
- The patient should avoid activities that place excessive stress on the pelvis (squats, intense exercise, prolonged standing, lifting and carrying heavy objects, stepping over things, twisting movements, vacuuming, and stretching exercises).
Exercises for hips
Aerobic exercise
- Moderate-intensity vigorous walking, defined as 64 - 76% of maximum heart rate, or 3 times a week for 25 minutes.
- Stretching exercises for the following muscles: hamstrings, inner and lateral thighs, quadriceps and back muscles. We should do it 3 times a week, 2 times a day. The duration of each exercise is from 10 to 20 seconds.
Strengthening exercises
Read about lower back pain and pelvic floor muscle incompetence here.
- The patients performed the following exercises: bending the torso forward, “cat”, diagonal twists, bending the upper body, raising the legs from the knee-elbow position (with parallel performance of Kegel exercises and control of pelvic tilt).
- The exercises are performed 3 times a week (2 sets of 3-5 repetitions on each side).
- The duration of each exercise is from 3 to 10 seconds.
- Pelvic muscle exercises [evidence level 1a]. (Exercises for instability of the lumbar spine)
- In early pregnancy: to reduce the risk of developing symphysis pubis dysfunction:
- Deep Abdominal Exercises: To increase core stability and prevent women from developing pelvic or back pain during pregnancy.
- You should start with a small number of repetitions, gradually increasing the time of muscle contraction.
- Particular attention should be paid to the transverse abdominis muscle, an important muscle whose contraction synergistically activates the pelvic diaphragm.
Stabilization exercises
Intra-articular injections and surgeries during pregnancy
Only a doctor can recommend safe painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs during this period. Intra-articular injections of synovial fluid substitutes, for example, Noltrex or preparations based on hyaluronic acid, are usually not given to women during this period, since many of them are hormonal and are contraindicated for pregnant women.
In difficult cases, when joint replacement is recommended, it is postponed until after the birth of the child, and before that, adequate supportive therapy is prescribed.
Symptoms of restless legs syndrome
In modern medicine, the term “Willis-Ekbom syndrome” . It manifests itself primarily as problems with falling asleep - a person cannot fall asleep due to discomfort in the legs. This cannot be called pain, but rather a painful need for movements that help eliminate discomfort for 10-15 seconds. Every 5-30 seconds the patient experiences symptoms such as:
- tingling;
- aches;
- severe burning sensation;
- movements under the skin;
- twitching;
- goosebumps;
- seizures, etc.
With RLS, there are usually problems with sleep, namely with its deep phase. With a certain frequency, such patients experienced twitching of their limbs during sleep. The more such spasms there were, the worse the person felt the next morning: there was no feeling of refreshing sleep.
An important feature of this condition is that symptoms become more active in the evening or at night, and in pregnant women most often in the 2nd or 3rd trimester .
The syndrome is diagnosed if:
- The patient has the symptoms described above. Often women cannot describe exactly what they feel, but note that the symptoms are extremely unpleasant and are mostly localized in the feet, legs or thighs.
- The amplitude of unpleasant sensations increases at rest (in a lying or sitting position, when the woman is about to sleep).
- Movements help temporarily relieve discomfort. When stretching, straining the legs, walking or exercising, the discomfort disappears.
- Symptoms are cyclical. Signs of restless legs syndrome intensify in the evening and in the first half of the night - from 18.00 to 04.00. With the onset of morning, the discomfort most often goes away.
Among pregnant women, RLS is diagnosed in about a third of cases, which is often associated with changes in the electrolyte composition of the blood.
Features of the course and treatment of osteoarthritis during lactation
During breastfeeding, manipulations are already allowed for the purpose of accurately diagnosing arthrosis - x-rays, biopsy and analysis of synovial fluid, so it is possible to make a diagnosis much faster and more accurately. Treatment tactics depend on the stage of the disease. In addition to painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, glycosaminoglycans are shown to protect cartilage from destruction.
The doctor recommends the best physical treatments - magnetic therapy, exposure to electric currents, ultraviolet radiation. An excellent effect can be achieved with the help of thermal procedures, paraffin application and mud therapy. The massage is aimed at restoring the functions of the affected joint - reducing muscle spasms, increasing the tone of weakened muscles. Unfortunately, in severe cases it sometimes comes to endoprosthetics. The issue of intra-articular Noltrex injections is decided on an individual basis.
For osteoarthritis during lactation, exercise therapy is often prescribed
Does the syndrome need to be treated?
Since such a pathology significantly impairs the quality of sleep, it must be eliminated. Constant lack of sleep causes:
- overwork;
- depression;
- neurasthenia;
- decreased concentration;
- deterioration of cognitive functions;
- feeling of energy deficiency, etc.
In addition to the above, the presence of Willis-Ekbom syndrome is one of the predictors of the development of cardiovascular diseases. Patients are much more likely to suffer from arterial hypertension, arrhythmia, and in the presence of risk factors (overweight, diabetes, etc.), a heart attack or stroke cannot be ruled out (especially during childbirth). And restless legs during pregnancy are an additional danger, because constant discomfort associated with lack of sleep increases the risk of premature birth and placental hypoxia.
Prevention of osteoarthritis during pregnancy
The main rule when carrying a child is to avoid injury and behave with extreme caution. If trouble happens and affects a joint, you should not turn a blind eye to it and let damage to cartilage and tendons take its course.
If a woman feels normal, she is recommended to lead an active lifestyle, move, and walk a lot in the fresh air. It is very important to avoid excessive weight gain, since excess kilograms create a dangerous load on the joints - both during pregnancy and after birth.
Causes of pain in the shoulder joints
There are many reasons for the appearance of painful sensations. Pain in one or both shoulders can be a consequence of inflammation of the tendons, microtrauma of the articular cartilage, inflammatory-degenerative pathologies of the joints and cervicothoracic spine. The discomfort can be either minor or so intense that you cannot move your arm.
Among the causes that cause sharp or aching pain in the shoulder are:
- one-sided intense load for a long time;
- scoliosis, lordosis and other deviations in the normal position of the spine;
- physical inactivity.
In addition, pain can occur due to infections, inflammatory processes, hereditary predisposition, diseases of internal organs, and tumors.
In cases where the right shoulder hurts, the following pathologies may be present:
- Tendonitis is inflammation of tendons and soft tissues due to significant physical activity.
- Myositis - when the muscles of the shoulder joint are involved in the inflammatory process.
- Arthrosis is the destruction of articular cartilage.
- Arthritis is an inflammatory process in a joint due to infection, allergic reaction or autoimmune diseases.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Bursitis is an inflammation of the joint capsule.
- Capsulitis is a pathological change affecting the joint capsule and synovium.
- Brachial nerve neuritis.
- Tuberculous lesion of the joint on the right.
- Humeroscapular periarthritis.
- Metastasis from a nearby tumor.
- Chondrosarcoma.
- Right-sided pneumonia.
Pain in the left shoulder joint is much less common, especially if the person is right-handed. Still, the load on the left hand is significantly less compared to the right. When your left shoulder hurts, the reasons may be the following:
- sprain;
- biceps tendinitis;
- intervertebral hernia in the cervical spine;
- calcification in the tendon;
- angina pectoris or myocardial infarction.
There are cases when the shoulder hurts when raising your arm. Here we can talk about pathologies such as:
- joint injuries;
- rheumatic lesion;
- rotator cuff tendinitis;
- tenosynovitis;
- tendobursitis and bursitis;
- myositis;
- hernia of the cervical spine.
The appearance of pain in the shoulder when trying to move the arm back indicates the presence of bursitis, radiculitis, tendinitis, spinal overload, arthrosis-arthritic joint damage, myocardial infarction.
Solution
After the birth of a child, most women establish breastfeeding, during which a limited number of medications are allowed. Buying and taking medications on your own is strictly prohibited. The most natural and seemingly safe drugs can negatively affect the health of a newborn. Active and auxiliary components pass into breast milk and may harm the baby.
Usually the problem is solved comprehensively. First you need to undergo an examination to understand the exact cause of the pathology. If there is an urgent need, the doctor will prescribe medications approved during lactation. Therapy is supplemented with diet, therapeutic exercises or massage. A comprehensive approach gives a positive result and a long-lasting therapeutic effect.
Medications
Depending on the nature of the pain, several groups of drugs are prescribed:
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- corticosteroids;
- chondroprotectors;
- vitamins, mineral complexes, biological additives;
- products for external use (gels, ointments, creams).
When the problem is caused by a lack of calcium, magnesium or potassium, the woman is advised to take vitamin complexes (Calcium D3 nikomed, Pantovegir, etc.). The diagnosis must be made after laboratory tests.
Discomfort and pain are effectively eliminated by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. However, in this case, the therapy will be incompatible with breastfeeding.
Ointments for external use are relatively safe and are not absorbed into the general bloodstream. It should be understood that these remedies alone will not give a noticeable effect.
Diet and drinking regime
A proper diet can pursue 2 goals - reducing excess weight and replenishing missing vitamins and microelements. When losing weight, your diet should be balanced. Mom should not lose nutrients, especially when breastfeeding (the baby should receive all vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates).
Prohibited products:
- baked goods, sweets;
- canned or pickled foods, semi-finished products;
- sausages, sausages;
- carbonated drinks;
- too salty or spicy food;
- fried foods (foods need to be cooked by boiling, stewing or baking).
Allowed (useful) products:
- dairy and fermented milk products (natural, without preservatives, flavors, stabilizers, with a short shelf life);
- vegetables, fruits, berries;
- lean meat and fish;
- fatty fish rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids;
- porridge;
- nuts and dried fruits;
- vegetable oils.
It is necessary to drink clean water (tea, coffee or compotes do not count) in sufficient quantities. Water is essential for the normal functioning of the body and helps you lose weight. Proper drinking regimen will relieve swelling, which can also cause pain in the knees or arms.
Joint exercises and massage
Physical therapy exercises are selected depending on the location of pain. When a woman has severe knee pain after childbirth, she needs to alternately raise her legs bent at the knee joint and stay in this position. Over time, increase the number of repetitions.
For pain in the pelvic bones, you need to work out the hip joints. Gradually, squatting and standing up will not cause discomfort. It is useful to do health-improving exercises for all muscle groups. This will strengthen the body and improve your figure.
Therapeutic massage must be prescribed by a doctor and performed by a specialist. Otherwise, there is a risk of getting the opposite effect.
ethnoscience
Joint problems worry many, and traditional medicine has in its arsenal many means of combating them. Among them there are those that are suitable for nursing mothers. You can use the following recipes:
- Infusion of bay leaf. It removes excess salts. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over 25–30 leaves and keep on low heat for 15–20 minutes. Leave for a couple of hours and then drink several times throughout the day.
- Jellied meat and chicken cartilage. They contain a lot of collagen, which is necessary for joints.
- Warm baths for feet and knees. A decoction of chamomile, lemon balm, and lavender is suitable.
- Alcohol tinctures for compresses from propolis or horseradish. Soak gauze in the tincture, apply to the sore spot and wrap with cling film.
How to get rid of knee pain
Knee pain in the postpartum period can be a consequence of natural processes occurring in the body. In this case, the woman should not worry: the discomfort will gradually disappear within one or several months. However, some measures will help speed up this process.
Massage
A massage will ease the condition of a young mother: it will normalize blood flow in the lower extremities and reduce pain. You can do it at home, although, of course, the ideal option is to contact a professional.
When performing manipulations, a woman should use foot creams or special massage oils (if breastfeeding, you should choose hypoallergenic options). For best effect, they are preheated.
During knee joint massage, stroking, rubbing and kneading techniques are used. Each action is repeated three to six times.
- Sitting on the bed, the woman straightens one leg (it is massaged first), and lowers the other. One hand is placed just above the sore knee, and the other below. Then the problem area is stroked in opposite directions. After this, the actions are repeated on the other leg.
- The next technique is rubbing the lateral surfaces of the knee with forward and backward movements. This is done first with the fingers and then with the palms.
- Next, rubbing the side zones is done with the thumbs using circular movements.
- All areas of the knee are kneaded with deep but gentle pressure from the fingers (index, middle and ring), while the skin moves forward and backward.
- The massage ends with gentle stroking of the knees.
This procedure should be done, if possible, two to three times a day, its duration will be no more than 10 minutes. If the massage is performed once a day, then it should take about 25 minutes.
If the knee is clearly injured (for example, due to careless actions with a stroller), swelling is pronounced, then massage will be an addition to other therapeutic procedures. In this case, the duration of the course is determined by the doctor, and the manipulations themselves are carried out by a specialist. They will be more delicate. You should start with small loads, which gradually increase. To the standard techniques of stroking and rubbing will be added shaking the leg, vibration and kneading the joint with a rib and fists.
Special exercises
Special exercises help cope with pain. Provided there is a successful birth, you can start doing them a week or two after the baby is born (in the case of a cesarean section, this is done much later - no earlier than two months, and in agreement with the attending physician).
The exercises are aimed mainly at stretching and lengthening the muscles. You can perform them in the morning (even while lying in bed), during the day (while the baby is sleeping) or in the evening (to relax before bed). The number of repetitions is 5–7 times.
- Why joints hurt after childbirth: main causes, symptoms and treatment
- Bridge. The purpose of the exercise is to strengthen the hips to reduce tension in the knee joints. The woman lies on her back, her arms are located along her body. Your knees should be bent and your feet should be shoulder-width apart (with your toes straight). With a slow movement, the pelvis is raised from the floor, fixed in this position for a few seconds, and then lowered.
- Raising your legs from a side lying position. The woman extends her lower arm, puts her ear to her shoulder, bends slightly at the waist and brings her folded legs forward a couple of centimeters. Next, the upper leg needs to be raised as high as possible, without bending the body forward or backward. After 5–7 repetitions, you should change the upper leg. If it is difficult for mother to maintain balance, then when performing the exercise, she is allowed to lean her back against the wall.
- Squats with a fitball - a large gymnastic ball. This uses not only the leg muscles, but also the buttocks (which makes them more elastic). The ball is leaned against the wall using the lower back. The feet are shoulder-width apart and the toes are pointing straight forward. Pressing the projectile against the wall, the woman slowly squats down. To avoid pain in the knees, movements should be very careful and smooth.
Taking medications
If knee pain is caused by a lack of calcium in the body (this is confirmed by a blood test), then the doctor prescribes the appropriate medications to the mother: Calcium D3 Nycomed, Pantovegir, Kalcemin and others.
In some cases, knee pain can be relieved by taking calcium supplements.
To reduce pain, many women agree to take painkillers. However, if a mother is breastfeeding, then most of these medications are contraindicated for her. In this case, only the doctor selects analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs or chondoprotectors (agents for nutrition and regeneration of cartilage tissue), allowed during lactation. There are also special patches that have a local effect on the affected joint.
Diet for knee pain
To speed up the recovery of the knee joint, the body must be provided with all the necessary nutrients. A balanced diet will help with this. Thus, calcium can be obtained from dairy products, as well as vegetables (cabbage, parsley and dill, green onions, legumes) and some fruits (persimmons, grapes, oranges), berries (currants, strawberries, gooseberries). In addition, the formation of cartilage and bone tissue is promoted by vitamins E, C and B, which are also found in large quantities in certain foods (for example, there is a lot of vitamin E in vegetable oils and egg yolk). Omega-3 fatty acids also benefit joints, and nuts, seafood, and lentils are rich in them.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine offers its own ways to combat knee pain: warm foot baths (with immersion of the kneecap). For this, herbal infusions of chamomile, lemon balm, and lavender are used, which have anti-inflammatory properties, promote relaxation and relieve muscle tension.
As an option, you can try alcohol processes. Gauze is soaked in tincture of propolis, horseradish or comfrey root and applied to the joints. For the best effect, the problem area should be wrapped in cellophane and wrapped in a towel. The duration of the procedure is at least half an hour.
Before using an alcohol compress, you should consult a specialist. Alcohol is absorbed through the skin into the blood and passes into breast milk, so some doctors consider this method of treatment unsafe.
Compresses with medicinal herbs or alcohol will help cope with knee pain.
Organization of daily routine and rest
In order for a woman’s joints to recover faster after childbirth, she needs to rest more, because it’s not without reason that pain often makes itself felt in the evening after a busy day full of worries. The husband and other close people should, if possible, take on household responsibilities.
If all the above measures do not bring relief to the mother, then she needs to undergo a thorough medical examination. Perhaps knee pain is associated with more serious pathologies (for example, kidney disease). The sooner full treatment is started, the sooner the woman will return to a full life.