Forms
Depending on changes in temperature indicators, low-grade fever is classified as follows.
Intermittent fever - the temperature first drops slightly and then rises again, and this alternation lasts for several days.
- Remitting - the temperature fluctuates more than 1°C during the day.
- Undulating fever - the patient has an alternation of normal temperature with a constant and remitting state.
- Constant fever - they talk about it when the temperature is constantly elevated and practically does not change during the day.
There is also a fever of unknown origin (genesis), the causes of which doctors cannot find out. In this case, there is an increase in temperature to 38°C over a period of three weeks or more for unknown reasons.
Fever of unknown origin (genesis) is divided into the following types:
- so-called “classical” fever of unknown origin - this includes all cases of infectious diseases that are difficult to diagnose, completely unusual for the area in which the patient lives, or have atypical forms;
- a sharp decrease in the blood of special elements that are responsible for human immunity can also lead to fever of unknown origin;
- hospital fever - it occurs in a patient after hospitalization for 24 hours;
- cytomegalovirus infection, histoplasmosis, mycobacteriosis are classified as HIV-associated fever.
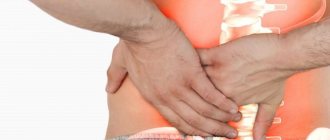
Stitching pain under the right shoulder blade
Pains of a stabbing nature usually pass quickly and are caused in most cases by prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, sudden movement or overstrain of the back muscles. In such situations, they go away on their own and do not require special treatment.
Less commonly, stabbing pain under the scapula is a consequence of spasm of the walls of the bile ducts, for example, during an attack of acute cholecystitis. Therefore, if their intensity does not decrease within 2 hours or more, you should contact a gastroenterologist or call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Causes
There are many reasons for the occurrence of low-grade fever. First of all, these are, of course, infectious processes occurring in the human body. Any infection, be it viral, chlamydial, bacterial or intestinal, can cause low-grade fever. When a person is infected with intracellular or protozoan parasites, low-grade fever is also observed. Constantly elevated temperature is also characteristic of cancer of various etiologies in men and women. The cause of low-grade fever can be sarcoidosis. Chronic fatigue syndrome, which occurs due to constant stress, lack of sleep, and overwork, also refers to the causes of low-grade fever. If we talk about newborns and infants, then due to imperfect heat exchange, any infection can cause a persistent fever. In pregnant women, low-grade fever occurs without any special manifestations, but it is necessary to find out the cause of the fever as quickly as possible. Since many infectious diseases are fraught with serious consequences for the fetus and unborn child.
Dull pain under the right shoulder blade
Dull, aching pain under the right shoulder blade is usually a sign of indolent changes in the kidneys and liver. This may result in:
- Chronic pyelonephritis of the right kidney is a common urological disease, accompanied by an inflammatory process in the renal pelvis, and sometimes in the renal parenchyma. Pain under the scapula on the right usually appears with the onset of sclerotic changes in the kidneys.
- Chronic cholecystitis is a disease in which a chronic inflammatory process develops in the gallbladder, in 95% of cases caused by the formation of stones. During its course, periods of remission are replaced by exacerbations, during which dull pain may occur under the scapula on the right.
- Tumors of the liver, pancreas, right kidney, lung are neoplasms of different nature. They can be benign or malignant, and their growth can provoke the appearance of dull pain under the right shoulder blade.
- Liver cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease in which irreversible changes occur in its tissues and the parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue. This certainly leads to a deterioration in the performance of the organ.
Chronic pyelonephritis
Chronic pyelonephritis is a constant, sluggish inflammatory process in the kidneys, which tends to worsen with decreased immunity or other diseases. It usually results from untreated or incompletely cured acute pyelonephritis.
Chronic pyelonephritis is diagnosed 8 times more often in women than in men, which is due to the structural features of the genitourinary system.
This disease, as a rule, is accompanied not only by nagging, dull pain that radiates to the lower back or under the shoulder blade (if the right kidney is affected, the pain is felt under the right shoulder blade), but also painful urination, as well as a rise in body temperature or chills against the background maintaining normal temperature. Sometimes with pyelonephritis, nausea and arterial hypertension are observed.
If such signs occur, you should contact a nephrologist, and if such a specialist is not available, contact a urologist.
Chronic cholecystitis
With chronic cholecystitis, dull pain occurs in the right hypochondrium and radiates under the scapula. They are paroxysmal in nature and do not cause significant discomfort to the patient. But against the background of this, the gallbladder shrinks, decreases or completely loses functionality, which necessarily affects the quality of digestion.
Chronic cholecystitis is not characterized by fever, but reflex muscle tension may be detected in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. In this case, the disease tends to regularly worsen and cause new attacks of not only dull, but also acute pain in the right side of the body. Therefore, often when stones are detected and pronounced calcification of fibrous altered bladder walls (porcelain gallbladder) and the tendency of stones to provoke biliary colic, the question of removing the organ is raised. Moreover, chronic cholecystitis sharply increases the risk of developing carcinoma.
Tumors
The formation and growth of tumors in the internal organs located on the right can provoke the occurrence of dull, aching pain, felt or radiating under the right shoulder blade. Often they are not present all the time. And if they are detected, it is recommended to contact an oncologist or surgeon. But the number of cases of detection of tumors of various internal organs as the cause of back pain is negligible compared to other diseases accompanied by such manifestations.
Cirrhosis of the liver
In the initial stages of development of liver cirrhosis, pain in the right hypochondrium may also be present, radiating under the right shoulder blade. This may be accompanied by:
- weakness;
- abdominal discomfort;
- decreased performance;
- indigestion;
- increased body temperature;
- flatulence;
- losing weight.
If symptoms characteristic of liver cirrhosis occur, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
Diagnostics
Low-grade fever does not occur out of nowhere, and is often a harbinger of a fairly serious illness. To find out the causes of a constantly elevated temperature, you must consult a doctor. Diagnosis of low-grade fever begins with collecting anamnesis and complaints about the state of health. The doctor will examine the patient’s medical history and ask about previous and current diseases. The presence of diseases such as tuberculosis, diabetes, HIV, various types of blood and liver diseases, as well as previous operations is one of the reasons for a persistent increase in temperature. When diagnosing low-grade fever, it is necessary to identify the possibility of infection with bacterial endocarditis and hepatitis during medical procedures, visits to the dentist, blood transfusions, and unprotected sexual intercourse. An epidemiological survey is also being conducted - the doctor will ask questions about which countries the person has visited recently, and whether he has traveled to areas characterized by certain infectious and parasitic diseases.
This is followed by a visual examination of the patient. The doctor examines the skin, mucous membrane, joints, lymph nodes, palpates the abdominal cavity, mammary glands in women, auscultates the chest cavity, examines the ENT organs, urogenital organs and rectum. To find out all the causes of low-grade fever, laboratory tests are prescribed, which include a general analysis of urine and blood, serological and biochemical tests, studies of sputum and cerebrospinal fluid.
Instrumental diagnostics are also mandatory: ultrasound, radiography, CT, echocardiography. Consultations with various specialists are scheduled: a gynecologist (for women), a neurologist, an oncologist, a hematologist, an infectious disease specialist, a phthisiatrician - all patients, men, women, children, pregnant women with low-grade fever, must be tested for tuberculosis.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia
The main symptom of the disease is excruciating pain in the chest, spreading along the nerve. Unpleasant sensations last for hours or even days, not leaving the person day or night. The pain can be acute, shooting or burning, the intensity is high or medium. It gets worse with coughing, sneezing and movement.
Sometimes the pain may resemble damage to the heart, stomach or spine. However, unlike intercostal neuralgia, cardiac pain goes away after taking nitroglycerin, and gastric pain goes away after antispasmodics.
Other signs of the disease:
- muscle tension;
- numbness of the affected area;
- tingling, sensation of goosebumps;
- sensitivity disorder;
- sleep disturbance;
- tearfulness;
- increased sweating.
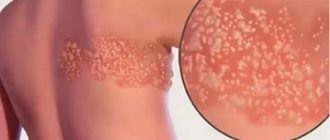
The temperature with intercostal neuralgia may also rise. The skin in the outbreak turns red or white. If the cause of the disease is herpes zoster, characteristic rashes appear along the nerve.
Treatment of low-grade fever
Having found out the exact cause of low-grade fever, a treatment plan is drawn up, which depends on the underlying disease. Drug therapy is prescribed to treat the disease that causes an increase in temperature, as well as taking antipyretic medications at temperatures above 38.5 ° C. If the temperature rises for a long time, the patient is hospitalized.
In order to prevent low-grade fever and its relapse, it is recommended to observe the following precautions: avoid harmful working conditions, hypothermia, overheating, ensure a complete and correct sleep and rest regime, observe personal hygiene rules, diet, and monitor the quality of nutrition. And, of course, regular examination by a doctor.
Primary appointment with a neurologist: 1850 RUR.
Sign up Online 5% discount when registering from the site
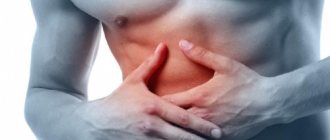
Constant pain under the right shoulder blade
In the vast majority of cases, the constant discomfort felt in the area of the right shoulder blade is caused by biliary dyskinesia (BDH) of the hypotonic type. This is a common pathology that is often considered a functional disorder and is not taken seriously.
JVP is characterized by impaired motility of the bile ducts, as a result of which bile enters the duodenum untimely. This negatively affects digestion and can provoke the appearance of constant pain under the scapula on the right, which is especially often observed with hypotonic type bile ducts, i.e., with it, the motility of the biliary tract is reduced. In this case, loss of appetite, nausea, bitterness in the mouth, flatulence, constipation, and belching of air are also often observed. Treatment of GIVP is the task of a gastroenterologist.
Another reason for the appearance of constant aching pain under the right shoulder blade may be muscle hypertonicity, i.e., their constant tension. It can be triggered by prolonged sitting, carrying heavy objects, and overexertion of the back and shoulder muscles. Over time, the pain goes away on its own if you create conditions for the muscles to recover and do not overstrain them. You can quickly cope with the problem with the help of massage or manual therapy.
Recovery forecasts
Timely detection and treatment of back neuralgia shortens the duration of the disease and provides a favorable prognosis. The period of temporary disability varies from 5 days to 14 days.
The disease is highly treatable. Ignoring qualified medical care leads to the development of a chronic form of pathology, characterized by prolonged pain that will bother the patient for weeks and months.
Self-diagnosis leads to the loss of precious time and the lack of taking measures to eliminate serious diseases with similar symptoms.