Degenerative and dystrophic changes in the tissues of the spinal column very often affect several discs and even departments at the same time. Medical statistics inexorably show that polysegmental osteochondrosis is being diagnosed in an increasing number of patients. More than 10% of such pathologies lead to inevitable disability and loss of the ability to move independently. More than 40% of patients undergo surgery. Polysegmental osteochondrosis of the spine is a very serious disease. Immediate initiation of effective treatment is required.
Unfortunately, official medicine currently does not have effective methods of treating these pathologies. Therefore, patients are offered symptomatic treatment methods. This leads to temporary pain relief. But at the same time, the pharmacological drugs used lead to an acceleration of the process of destruction of the cartilage tissue of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc.
Please note that polysegmental osteochondrosis can produce clinical symptoms similar to some somatic diseases for a long time. Patients complain of pain in the stomach, liver, heart, pancreas, and kidneys. But at the same time, these organs, when carrying out differential instrumental diagnostics, turn out to be actually healthy, but with truly impaired function due to the lack of innervation.
In such cases, it is necessary to urgently examine the corresponding part of the spinal column. Polysegmental osteochondrosis can be successfully treated in the early stages. Manual therapy allows you to completely restore the health of the intervertebral discs. Unlike official medicine, a chiropractor conducts a course of treatment aimed at eliminating the causes of pain, and not at stopping the inflammatory process while maintaining the tendency of destruction of the intervertebral disc.
What is polysegmental osteochondrosis?
In order to understand what polysegmental osteochondrosis of the spine is, you need to delve a little deeper into issues of anatomy and physiology. So, the spinal column is part of the musculoskeletal system of the human body. It performs a supporting and innervation function, provides flexibility and the ability to perform certain movements.
It is formed by 24 vertebral bodies, separated by cartilaginous discs. Flexibility and mobility are provided by the facet joints. The vertebrae are surrounded by a ligamentous apparatus and a muscular frame. Muscle fibers provide diffuse nutrition to cartilage tissue, since the discs do not have their own capillary network. To ensure shock-absorbing function, the vertebral discs require a sufficient amount of fluid. If it is not supplied enough, the fibrous ring becomes dehydrated and undergoes destruction. This is the beginning of polysegmental osteochondrosis in one or another part of the spine.
The spine also has a safety function for the spinal cord inside it. This substance is responsible for the innervation of the entire human body and the performance of all internal organs. The radicular nerves depart from the spinal cord and exit through the foraminal openings of the vertebral bodies.
Polysegmental osteochondrosis is a degenerative process during which several radicular nerves are constantly injured and compressed simultaneously. In this regard, the neurological picture is not typical for osteochondrosis, but resembles a somatic or endocrine disease. This significantly complicates the primary differential diagnosis.
The reasons for the development of this disease are as follows:
- sedentary lifestyle and lack of regular and adequate physical activity on different parts of the back;
- overweight and obesity with significant fluid retention in the cells of the human body;
- disruption of the capillary blood supply to the muscle fibers in the back frame;
- various hormonal disorders;
- improper placement of feet and diseases of the hip joints;
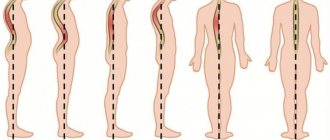
- poor posture and curvature of the spine;
- inflammatory and traumatic effects;
- violation of the work and rest schedule;
- poor nutrition and lack of sufficient amounts of water consumed during the day;
- improper organization of work and sleeping space.
For successful treatment, it is necessary to exclude all of the above causes of polysegmental osteochondrosis - this is the key to a successful recovery.
Causes of the disease
Osteochondrosis develops as a result of a decrease in cartilage tissue, which serves as a source of nutrition for bones and provides flexibility to the spine.
Types of osteochondrosis:
- cervical;
- lumbar;
- chest
Degenerative changes that affect several parts of the spine at once are provoked by both internal and external factors.
Internal causes of polysegmental osteochondrosis:
- Genetic predisposition - the more family members suffer from osteochondrosis, the higher the risk that this unpleasant disease will manifest itself in you.
- Age-related changes in the structure of the vertebrae - the likelihood of developing pathology increases over the years.
- Congenital anomalies.
There are an order of magnitude more external provoking factors:
- Disturbance of metabolic processes in the body.
- Spinal deformities (scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis), constant stoop.
- Serious injuries to joints and spine.
- Deficiency of important vitamins and minerals in the body.
- Infectious diseases.
- Regular increased loads on the spinal column.
- Physical inactivity is insufficient physical activity, prolonged stay in one position.
The risk group for polysegmental osteochondrosis includes athletes and people whose activities involve regular intense exercise.
Symptoms of polysegmental osteochondrosis
The main symptoms of polysegmental osteochondrosis are pain, neurological disorders and limited mobility. The clinical picture may depend on those segments that are affected in the case of compression of the radicular nerves. So, the following manifestations may be signs of the disease:
- a feeling of numbness in the upper limbs and their fingers or lower limbs;
- swelling of the soft tissues of the hands and feet (especially the ankles and wrists);
- panic attacks, depression, dizziness, headaches, numbness of the scalp;
- chronic fatigue and emotional burnout syndrome;
- regular pain in the projection of internal organs, for the innervation of which the damaged segment of the radicular nerve is responsible;
- signs of pathologies of the cardiovascular system in the form of arrhythmia, increased or decreased blood pressure, changes in the tone of the coronary blood vessels;
- changes in the functioning of the intestines, bladder, postnatal gland in men;
- increased irritability;
- neuroses and sleep problems;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, you will need to take an x-ray, MRI or CT scan. It is also required to prescribe an ECG, ultrasound, general blood and urine test, biochemical blood test, etc. to exclude diseases of the internal organs.
Classification according to the degree of change in intervertebral discs
According to the degree of damage to the intervertebral discs, there are four stages of the disease, which are based on radiographic studies:
- Zero. With grade zero, there are no visible lesions in the spinal column.
- First. Internal disc ruptures without external changes.
- Second. The disc changes noticeably without external damage.
- Third. The intervertebral disc is severely affected. In this case, the cracks spread to the inner surface, and the disc itself is squeezed out of the vertebrae.
Polysegmental osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Polysegmental osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is considered a very dangerous disease. It can lead to disability due to the development of flaccid paresis and paralysis of the upper limbs, a significant decrease in mental performance, and the appearance of chronic depression. Polysegmental cervical osteochondrosis leads to constant headaches, dizziness, sleep disturbances, irritability, neuroses, nausea and other unfavorable symptoms. Patients develop arterial hypertension associated with heart rhythm disturbances. There is the following relationship: when the blood pressure level increases, an attack of tachycardia occurs. And as blood pressure levels drop, heart rate decreases.
Flashing of flies and artifacts before the eyes appears at an early stage of the disease. With the development of polysegmental osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, shooting pain occurs in the lower or upper jaw, bridge of the nose, along the trigeminal nerve, in the ear. Possible decrease in visual acuity and hearing.
In advanced cases, acute cerebrovascular accident may occur with the appearance of signs of cerebral stroke. The prerequisites for this are vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypertensive type in young people and arterial hypertension in patients over 40 years of age.
Treatment at the Yusupov Hospital
High-quality therapy for spinal osteochondrosis is carried out by neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital.
This is a multidisciplinary medical center that provides treatment for spinal diseases of various types and complexity. Treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out by the best neurologists in Russia, honored figures of medicine. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed by experienced specialists who know effective methods for eliminating osteochondrosis. The Yusupov Hospital employs qualified massage therapists, reflexologists, chiropractors, and exercise therapy instructors, who create a suitable complex for the patient for spinal osteochondrosis of any stage.
The Yusupov Hospital uses an individual approach to each patient. Doctors take into account all the intricacies of the situation and draw up the optimal safe treatment plan. Treatment of spinal osteochondrosis at the Yusupov Hospital allows you to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and slow down or completely stop the degenerative process. After treatment, patients note a significant improvement in their condition and can return to their usual activities.
At stages 3-4 of spinal osteochondrosis, in cases of intervertebral hernia development, neurosurgeons at partner clinics of the Yusupov Hospital perform surgical interventions. You can make an appointment with a neurologist, clarify information about the work of the diagnostic center and ask the contact center specialists another question of interest by calling the Yusupov Hospital phone number. Timely diagnosis and treatment of osteochondrosis allows you to avoid complications of the disease and the need for surgery.
Make an appointment
Polysegmental osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Polysegmental osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is quite rare. This is due to the fact that the vertebrae here lack mobility. Polysegmental thoracic osteochondrosis manifests itself in the form of symptoms inherent in the pathology of the cardiovascular system. There may be complaints of pain in the heart area, heart rhythm disturbances, and changes in blood pressure levels.
At a late stage, intercostal neuralgia begins with partial paralysis of the muscles. Patients complain of difficulties with the process of taking a deep breath. It is important to differentiate between angina pectoris and myocardial infarction.
Diagnostics
If you notice at least some of the symptoms, you need to contact the clinic for qualified advice. Due to the fact that some symptoms may resemble other diseases, examination by specialized specialists, for example, a cardiologist, may be required. Pinching of the vertebrae in the sacral part can cause problems with urination - then a visit to the urologist is necessary. You will also have to do an MRI and blood tests.
What is POSSIBLE for diseases of the spine
What NOT to do for spinal diseases
Polysegmental osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
It is very difficult to recognize polysegmental osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine at the initial stage, since pain similar to renal and hepatic colic occurs. In fact, it is with suspicion of these attacks that the patient first enters a medical facility. But after an ultrasound and excretory urography, it turns out that everything is in order with these organs. The patient is discharged with an unspecified diagnosis. And here it is important not to waste time and undergo a full examination of the vertebral spine.
Lumbar polysegmental osteochondrosis occurs very often, since this department bears the maximum physical, static and mechanical load. But here intervertebral hernias and protrusions very often occur, which further complicates the course of this pathology.
Polysegmental osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is manifested by the following symptoms:
- acute pain in the lumbar region;
- irradiation of pain to the lower extremities;
- disruption of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and pelvis (constipation followed by diarrhea and urinary retention);
- decreased skin sensitivity in the lower back, gluteal region and upper thighs;
- striped pain on the outer or inner side of the thigh and lower leg;
- limited mobility;
- muscle tension syndrome.
If symptoms of polysegmental osteochondrosis appear in the lumbar spine, you should immediately seek medical help. We invite you to schedule a free initial consultation at our manual therapy clinic. Experienced doctors will conduct an examination, make an accurate diagnosis and, at your request, relieve acute pain without the use of pharmacological drugs.
How to treat grade 2 osteochondrosis
Treatment of second-degree osteochondrosis is usually carried out using conservative methods and requires the complex use of pharmaceuticals, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, diet and orthopedic regimen. In later stages and when standard treatments are ineffective, grade 2 osteochondrosis is treated surgically.
Conservative rehabilitation is aimed at eliminating pain, resuming the conduction of nerve impulses and restoring healthy metabolic processes in the spine. Rehabilitation of patients with osteochondrosis requires from 1 month to 1 year, and preventive treatment is carried out for life. Therefore, it is important that it becomes a habit.
Self-medication for grade 2 osteochondrosis risks the disease progressing to advanced stage 3, when hormonal medications or even radical surgery are required to eliminate pain. Therefore, you should not take simple analgesics that mask pain and symptoms without the knowledge of a doctor - they remove discomfort, but not the cause of the disease.
Treatment of second-degree osteochondrosis requires an integrated approach and precise execution of all doctor’s instructions.
Physiotherapeutic techniques
Physiotherapy is carried out as prescribed by a doctor in courses of 10-12 sessions. The most effective methods for grade 2 osteochondrosis include:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- shock wave therapy;
- UHF therapy;
- detensor therapy;
- hydromassage;
- balneotherapy and mud therapy;
- manual therapy.
Massage for osteochondrosis 2 degrees
Therapeutic massage for second-degree osteochondrosis should be performed only by a certified specialist. Due to the proximity of large arteries and the spinal cord, it is dangerous to trust it to a non-professional!
To relieve pain and maintain muscle tone, you can independently perform the following massage movements:
- stroking with fingertips (to stimulate nerve endings);
- rubbing with the palm of your hand (in circles, back and forth - for relaxation and better blood supply);
- squeezing (grasping the skin with the thumb and forefinger, performing movements that resemble twisting or squeezing).
Unskilled kneading with force (deep massage) is contraindicated!
In addition to regular massage, hydromassage is also effective - a safe physiotherapeutic technique that improves blood supply to the spinal column and the sensitivity of nerve fibers.
Exercise therapy for grade 2 osteochondrosis
Exercises for grade 2 osteochondrosis are performed daily. The most effective are demonstrated by the so-called. “physical education minutes.” During work, the spine is subjected to static load, which negatively affects metabolic processes and can accelerate degenerative processes. To prevent this from happening, it is advisable to pause for 5-10 minutes of charging every 1-1.5 hours.
To maintain the muscle corset and control the disease, a set of 7-10 exercises for grade 2 osteochondrosis, which are performed in the morning, evening and during working hours, is sufficient. For example:
- Bring your hands to your shoulders and rotate your elbows, first in one direction, then in the other. 10-16 times.
- Raise both arms up and stand on your toes, trying to stretch up as far as possible. 5-8 times.
- Sitting on a chair, press your right hand on your right knee and slowly count to 3. Repeat for the left hand and then for both hands at the same time.
- Pull your shoulder toward your ear, first on one side, then on the other, then both at the same time. 6-7 times.
- Rotate your shoulders first forward, then back. One by one and at the same time. 10-15 times.
- Get on your knees and place your hands on the floor. Raise your head while arching your back. Then lower your head and arch your back. 10 times.
- While sitting on a chair, smoothly turn your head 180°. 5-10 times.
- With your hands behind your back, knead the back of your head as intensely and deeply as possible with your fingertips until you feel a pleasant pulsation. Perform the exercise without pain.
- Do the “mill” exercise by rotating your arms. From 10 times.
- While sitting on a chair, move your chin back, trying to bring it behind your chest line. 7-10 times.
For osteochondrosis of the second degree, exercises on the horizontal bar or wall bars, aimed at stretching the spine, as well as swimming (especially on the back), are useful. It is also worth taking care of organizing a comfortable workplace and a place to sleep. The pillow should not be too high (it is better to give preference to special orthopedic ones), and the mattress should not be too soft. If you have poor posture or flat feet, it is recommended to wear orthopedic insoles.
Treatment of polysegmental osteochondrosis
As mentioned earlier, polysegmental osteochondrosis can only be treated with manual therapy. Official medicine is not able to offer any effective help to the patient other than surgical intervention.
In our manual therapy clinic, treatment of polysegmental osteochondrosis begins with pain relief. For this purpose, traction traction, osteopathy and pharmacopuncture are used. All these techniques are absolutely safe and allow you to quickly relieve pain.
Then an individual course of therapy is developed. It includes massage and therapeutic exercises, kinesitherapy and other methods of restoring the health of the spinal column.
Prevention
Polysegmental osteochondrosis is a disease that, with the right approach, can always be prevented. To do this, you should perform the following activities:
- Monitor your posture and, if necessary, correct it using special corsets.
- Exercise regularly, strengthen the muscle corset - physical activity should be chosen based on your age, general condition of the body, and the presence of contraindications.
- Eat right - for a healthy spine, protein and calcium must be on the menu.
Avoid excessive physical activity, especially when exercising on weight machines.