Today, almost every second person is diagnosed with osteochondrosis, but few people take this disease seriously. But it would be worth it, because osteochondrosis is chronic, which means it is completely impossible to cure it. Many doctors even call osteochondrosis the “disease of the century” due to its increased prevalence. Moreover, from year to year this disease is getting younger. A sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, bad habits and other factors lead to the fact that already at the age of 25-30, many people suffer from back and cervical pain. Over time, everything only gets worse: the spine loses flexibility and mobility, and the intervertebral discs lose strength and elasticity. If you leave everything to chance, the consequences can be disastrous - even surgical intervention. But you shouldn’t despair, because you can live with osteochondrosis. And it’s even easier to prevent it. MIR 24 learned from doctors about what needs to be done to maintain a healthy spine, what is indicated by back pain, how to properly treat osteochondrosis and what will happen if it is neglected.
What is osteochondrosis?
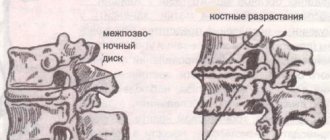
First, let's understand the terms. Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which degenerative changes occur in the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. Subsequently, changes occur in the vertebral body, ligamentous apparatus and, finally, in the joints. In modern medical literature, osteochondrosis is most often found under the name “degenerative-dystrophic disc disease.”
“Osteochondrosis is a disease that contributes to changes in the structure of the spine,” explains leading doctor - orthopedic traumatologist, chief podiatrist of the ORTEKA network of orthopedic salons Sergei Aleksutov
. – Each of the 33-34 (depending on individual characteristics) vertebrae that form the vertical axis of the human skeleton is subjected to daily stress. Along with the vertebrae, the ligaments and intervertebral discs that support the spine also experience stress. One of the main structural elements of the spine is the intervertebral discs, which soften the pressure on the vertebrae and absorb the load, like the springs of a car. When a person does not pay attention to his posture while working at the computer, sleeps incorrectly, or exposes his body to excessive physical stress, the intervertebral discs gradually wear out and perform their shock absorption function worse.”
It was not for nothing that teachers at school hit us on the back with a ruler and said: “Straighten your back!” After all, stoop and scoliosis are only the first “bells” of much more serious problems.
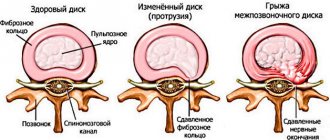
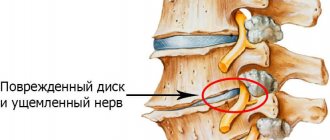
“After some time, due to improper distribution of the load on the surface of the intervertebral disc, herniated protrusions can form, which put pressure on the blood vessels and roots of the spinal cord. At the same time, pain bothers me and my back muscles become very tense. These are manifestations of osteochondrosis, which can lead to pain in the lower back, neck and head, thoracic region, breathing problems, changes in motor functions, curvature of the spine and improper functioning of internal organs. The presence of such a pathology significantly reduces the quality of life and harms not only the musculoskeletal system, but also the entire body as a whole,” says Sergei Aleksutov.
There are four stages of osteochondrosis, and the treatment strategy, as well as its success, will largely depend on how quickly the patient consulted a doctor.
“At the first stage, which is difficult to notice, the firmness and elasticity of the intervertebral discs is lost and their height decreases. At the second stage, protrusions appear, more pronounced changes in the vertebra and protrusions into the spinal cord with an initial impact on it. At the third stage, protrusions grow into hernias, which means, in addition to pain, inflammation, swelling, and severe limitation of movements occur. At the fourth stage, the intervertebral disc is almost completely destroyed, the vertebrae are injured, motor activity is significantly limited, and daily activities such as bending and normal walking are difficult,” Aleksutov lists.
Shutterstock/FOTODOM
“Payback for upright walking”: causes of the disease
Osteochondrosis can develop for a number of reasons, ranging from a sedentary lifestyle to injuries and overload.
“There is an opinion that spinal osteochondrosis is a person’s retribution for walking upright,” notes neurosurgeon of the highest category at SM-Clinic, Ph.D. Sergey Alexandrovich Kuznetsov
. – Currently, the cause of osteochondrosis is considered to be a combination of factors affecting the spine during a person’s life. An additional risk of developing the disease comes from spinal injuries and poor posture. A sedentary lifestyle and lack of proper physical activity also play an important role. This leads to insufficient functioning of the natural muscle “corset” that holds the spine in an anatomically correct position. As a result of this, and also in the presence of excess body weight, the intervertebral discs are overloaded with the development of a degenerative process in them.”
As noted by the senior medical consultant of the Teledoctor24 service, Neya Georgieva
, to one degree or another, osteochondrosis develops in all people with age. “Roughly speaking, this is one of the processes of aging of the body,” she says. “However, injuries and overloads of the spine contribute to the earlier onset of this disease. The main point in the occurrence of osteochondrosis is the constant overload of the spinal motion segment: poor posture, individual sitting style (wrong posture), walking with an uneven spinal column cause additional stress on the discs, ligaments and muscles of the spine. The occurrence of osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is often associated with its overload when bending and lifting heavy objects.”
It is necessary to monitor your posture from early childhood. But, unfortunately, our lifestyle does little to contribute to this: first we slouch at our desks at school, then in an office chair - and so on until old age. Many of us no longer even remember what a straight back should look like.
“When sitting, the head, shoulders and pelvis should remain at the same level. The back must be kept straight even when walking, when additional dangers may await, for example, due to shoes with heels, since when wearing such shoes the center of gravity shifts. But that's not all. Shoes with flat soles also harm the health of the musculoskeletal system, because they lack shock absorption - the spine suffers from impacts on the surface during normal walking or running. Few people know, but the center of gravity can be shifted due to flat feet, because unnatural foot placement leads to a change in gait and a twisted body position,” says Sergei Aleksutov.
What stage of the disease allows you to go jogging?
We will tell you at what stages of the development of the disease you can run and how this will influence the course of the pathology in the future.
If the first stage of the disease is diagnosed and there is no pain, light jogging will not cause any harm to the body. If there is a more advanced form, only walking is allowed. Osteochondrosis can cause the development of other diseases. Among them are infertility and dysfunction of the genitourinary system.
Osteochondrosis and sports activities are quite compatible. But before you start exercising, you need to consult your doctor. Only he will give the right advice regarding the type of sport and intensity of exercise. Even at the first stage of the disease, you need to be extremely careful.
At first, it is recommended to replace running with walking. This will allow the body to gradually get used to the loads received.
If you have a second or more complex stage of osteochondrosis, it is better to give up running altogether. It can provoke injury to the vertebrae, which will further aggravate the situation and contribute to the progression of the pathology. In addition, exercise also has a harmful effect during periods of significant exacerbation of the disease.
People who decide to start treatment for osteochondrosis by running should definitely consult a specialist.
From hernia to spinal cord infarctions
With advanced osteochondrosis, a person experiences pain even from minimal exertion, for example, getting out of bed in the morning. But even in such cases, many manage to turn a blind eye to the problem: at most, they drown out the pain with pills and, perhaps, buy an orthopedic pillow. But doctors shout with one voice: osteochondrosis must be treated!
“If osteochondrosis starts, you may encounter a complication such as a herniated disc. It, in turn, will compress the spinal cord (a person experiences numbness, weakness of the muscles of the limbs), which can subsequently lead to the appearance of paresis, muscle atrophy, even impaired urination and defecation (osteochondrosis of the lumbar region). An intervertebral hernia in the cervical or thoracic region can compress the arteries supplying the spinal cord and lead to infarction of parts of the spinal cord with the death of nerve cells (impaired movement, loss of sensitivity in the limbs in humans). In such cases, surgical intervention is indicated, which consists of removing the hernia and replacing the disc with an implant,” says Neya Georgieva.
The question often arises: which doctor should I go to with osteochondrosis? Several scenarios are possible here. In a public clinic, you will most likely be referred to a neurologist or orthopedist, but sometimes an ordinary therapist will take care of the treatment. Is it correct? We decided to ask our experts.
“Most often, patients with osteochondrosis, especially in the initial stages (stages one and two), turn to neurologists, chiropractors, reflexologists, and osteopaths. They are prescribed a variety of drug therapy regimens, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, B vitamins, muscle relaxants, and vascular drugs. Among non-drug methods, it is necessary to note: manual therapy, reflexology, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, kinesiotherapy,” says Sergey Kuznetsov.
Sergey Aleksutov, in turn, suggests immediately contacting an orthopedic traumatologist, since it is this specialist who deals with problems of the musculoskeletal system.
“If you have pain in your back, neck or chest, you should contact him first. The doctor will assess the condition of the spine, check your posture, if necessary, prescribe an X-ray, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. The doctor may also refer you to a neurologist based on the results of the examination. As treatment, the orthopedist uses orthopedic bandages and correctors to support posture, and medication to relieve pain. Physiotherapy, physical therapy, and wearing orthopedic insoles are also prescribed,” the doctor lists.
Neya Georgieva names another specialist who will help cope with osteochondrosis - a vertebrologist. This specialist is engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. “The research is instrumental: radiography of the spine in two projections. MRI is performed to diagnose intervertebral hernia, assess the condition of the spinal cord and identify complications of osteochondrosis, for the differential diagnosis of osteochondrosis with other diseases (ankylosing spondylitis, osteomyelitis, tuberculous spondylitis). They may prescribe discography - a targeted study of the affected intervertebral disc. Electroneurography will allow us to determine the degree and localization of damage to the nerve pathways,” says Neya Georgieva.
Vision, hearing and even bite can be affected
Osteochondrosis can be treated in different ways, and, depending on the examination results, the doctor will select the appropriate therapy. According to Sergey Aleksutov, the “gold standard” for the treatment of osteochondrosis is primarily conservative therapy. “Based on the data of each individual person, doctors prescribe posture correctors, orthoses, reclinators, Shantsy collar, orthopedic insoles, orthopedic pillows and mattresses - all possible weapons in the fight against osteochondrosis,” explains the doctor.
But in some cases, when all these measures no longer work, only surgery can help. “In the presence of prolonged pain (more than three to four weeks) caused by osteochondrosis, when the use of conservative methods is ineffective, a consultation with a neurosurgeon is indicated to decide on a minimally invasive percutaneous operation - radiofrequency denervation of intervertebral joints,” explains Sergey Kuznetsov.
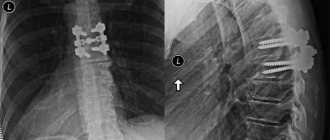
If a patient has a disc protrusion, the size of which reaches 5 millimeters, as well as symptoms of irritation of the spinal root, the doctor may prescribe puncture ablation (analogous to surgery) of the intervertebral disc or nucleoplasty, the specialist added. If an MRI confirms the presence of a hernia, then, of course, surgical treatment is also necessary - the hernia is removed, and the damaged segment of the spine is stabilized with an implant. “If surgical treatment is not undertaken promptly in this case, there is a high risk of progression of radiculopathy and the formation of irreversible changes in the spinal root, as well as persistent neurological deficit,” Kuznetsov emphasized.
Thus, the operation is used in cases where severe degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs can harm the structures of the central nervous system, primarily the spinal cord, nerve plexuses - vascular trunks. However, you should not immediately prepare for the worst. “Surgery is performed in no more than 10-15% of cases of osteochondrosis,” reassures Sergei Aleksutov.
And yet, doctors do not recommend relaxing. The fact is that osteochondrosis is dangerous not only in itself - it can have a very negative impact on the functioning of all organs.
“There are cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral osteochondrosis,” lists Sergei Aleksutov. – For example, such a pathology in the neck can affect the organs of vision, hearing, brain function and bite. Thoracic osteochondrosis often negatively affects the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, as well as the gastrointestinal tract. Lumbar osteochondrosis can cause disruption of the pelvic organs and lower extremities.”
Untreated osteochondrosis of the cervical spine also increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes, notes Sergey Kuznetsov. “The thoracic spine affects the internal organs - the stomach, intestines, liver, kidneys. Lumbar osteochondrosis can cause consequences such as inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs,” the neurosurgeon added.
“The great danger of back pain is that it can hide the clinical picture of diseases of internal organs, such as the kidneys. Therefore, you should not put off going to the doctor if you have pain. If you start to feel nagging pain in your back, it makes sense to reconsider your lifestyle and add moderate physical activity to it,” recalls the neurologist at the hospital. V.V. Vinogradova Petr Sokov.
The benefits of running when you are sick
In most cases, running with joint deformation is dangerous, but this type of physical activity helps to cope with some symptoms of the pathology. For training to be beneficial, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s condition and follow the running technique. Of course, before starting training you need to visit a doctor and consult with him.
We advise you to study: Pain under the left shoulder blade from the back
How to run with osteochondrosis:
- Jogging is allowed only in the initial stages of the disease;
- There is no need to set records, you need to train for fun, don’t rush, jogging is enough;
- Before training, you need to warm up thoroughly - bend over, squat, twist your torso, warm up your feet and calf muscles well;
- For osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, you should also warm up the neck muscles;
- For jogging, choose a soft, springy surface - grass, a rubber-surfaced track, but training on asphalt is prohibited.
The technique of rolling from toe to heel allows you to distribute the load during running as evenly as possible over the entire area of the foot, thereby softening the force of the impact when landing.
The back remains straight during training. You also need to choose the right sports shoes - with maximum shock absorption capacity. Sneakers should be slightly larger than your foot size - one finger width. If pain occurs while running, you need to immediately stop, relax your leg muscles and take a pain reliever.
If you can’t imagine life without jogging, consult your doctor and develop an optimal training regimen. It is strictly forbidden to train contrary to the specialist’s prohibition; this will only worsen your health and accelerate the development of pathological processes in the joints and spine. It is best to treat the pain with medication, wait for a period of remission and, after the doctor’s approval, begin training.
Start jogging - this technique and speed are safe for the spine and joints, and at the same time, your muscles become more resilient.
Cervical osteochondrosis is a contraindication to this type of activity at any stage.
There are no contraindications for healthy people. With regular jogging, muscle tissue, heart, immunity are strengthened, and the psycho-emotional state is stabilized. The lungs are perfectly ventilated due to the rapid heartbeat, more oxygen enters the blood, and all body cells receive more nutrients.
Intestinal peristalsis is stabilized if you run all the time. Active blood circulation is considered an excellent prevention of congestion. Let's consider the main arguments in favor of running for osteochondrosis:
- The blood supply to muscle tissue and joints is enhanced, cartilage receives more micronutrients and fluid, and degenerative processes are inhibited.
- Running during osteochondrosis due to muscle relaxation after the procedure eliminates tension in the back, blood circulates better, and nerve fibers are freed from pressure.
Although upon landing the main load falls on the lower legs, the remaining load is quite sufficient for microtrauma of the tissues.
In normal health, the benefits of running are obvious. During training, blood circulation improves, a sufficient amount of nutrients and oxygen reaches the cells, muscles, ligaments, and tendons are strengthened. All this happens during running with osteochondrosis. But the rate of regeneration of damaged tissues is significantly lower than the rate of their destruction.