In the stronger sex, dystrophic changes in the cervical area are less often diagnosed - a denser, more developed muscle corset takes some of the load off the discs. Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region in men, on the contrary, occurs more often due to heavy physical work, sports, and heavy lifting. They tolerate lumbar lesions better due to the less flexible transitions between the vertebrae.
Despite the difference in anatomy, osteochondrosis in men has the same symptoms as in women. Doctors develop a treatment plan personalized for the patient, taking into account his condition, not gender. Only the dosage of medications may vary depending on weight.
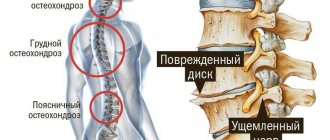
Cervical osteochondrosis in men: symptoms
- Pain in the head, neck (especially with sudden movements).
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Deterioration of hearing, smell, vision.
- Noise, ringing in the ears, feeling of a traffic jam.
- Episodic numbness of the tongue.
- Coordination failure.
- Hoarse voice, snoring.
- Poor neck mobility, crunching when turning.
- Deterioration of sensitivity of hands and fingers, their weakness.
- Sore throat.
- Panic attacks.
- Redness of the skin.
Reasons for appearance
Osteochondrosis occurs in a very large number of people, especially these days, when city dwellers massively lack adequate physical activity, proper nutrition and posture. Reasons that can provoke the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic regions include:
- age-related changes;
- genetic predisposition;
- sedentary lifestyle, physical inactivity;
- posture disorders;
- serious excess weight;
- injuries;
- overload;
- flat feet and other imperfections of the musculoskeletal system;
- stress and bad habits;
- hypothermia of the back and prolonged exposure to the cold.
Recently, osteochondrosis has increasingly begun to be observed in young people, which is associated primarily with an unhealthy lifestyle.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region in men
- High blood pressure.
- Tingling in the heart, liver.
- Increased heart rate.
- Chest pain, discomfort.
- Pain in the back radiating to the shoulder and arm.
- Muscle spasm in the spine at chest level, encircling compression.
- Loss of sensation in the upper extremities.
- The muscle corset in the sternum is in good shape, which makes it difficult to relax at night.
Symptoms are associated with impaired blood flow to internal organs, including the heart and lungs.
How to get rid of osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine?
Among the many diseases of the spine, osteochondrosis occupies a leading position. The cervicothoracic spine is especially often affected by this disease. The cause of the disease is a modification of cartilage tissue. Until recently, these changes were considered age-related, but recently the age of people suffering from osteochondrosis has decreased significantly. Neurologists' patients have become younger, and the nature of the disease has become more complex.
Osteochondrosis cannot be underestimated. This is a serious disease that is associated with metabolic disorders in the discs connecting the vertebrae. Discs experience enormous stress throughout their lives, this is due to the work of the human skeleton. The spine is one of its most mobile parts, so the cartilage that makes up the discs quickly wears out and provokes various diseases of the spine, including osteochondrosis. Intervertebral discs that have experienced deformation not only cause changes in the position of the vertebrae themselves, but also provoke inflammatory processes in adjacent tissues.
How to identify the signs, detect symptoms and begin timely treatment
Osteochondrosis of the spine, no matter in which part of it it began to develop, at first occurs hidden and unnoticed by a person. The reason for starting the process can be the most insignificant, at first glance, reason, for example, inactivity, excess weight, incorrect posture when sitting for long periods of time. All this can provoke stagnation of blood in the body, which can result in circulatory disorders in the spine. Chronic colds and weak immunity become causes of regular inflammatory processes in the body. Heredity also plays an important role in the development of osteochondrosis.
Doctors have identified a number of signs, when they appear, you should consult a doctor with suspected spinal disease. Let's look at them:
- Pain localized in the upper part of the body.
- Attacks of headaches, dizziness, problems with coordination.
- Sudden and unreasonable changes in blood pressure.
- Unpleasant sensations in the ears and difficulty with visual concentration.
- Feelings of anxiety, increased irritability, problems sleeping.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
If the symptoms are similar to other diseases (such as pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, hypertension, pneumonia, etc.), it is necessary to exclude them. There are several ways: medical examination, laboratory tests, X-ray and ultrasound examinations, and, if necessary, MRI and CT.
Treatment
Cervicothoracic osteochondrosis can be treated in different ways. The main thing is that therapy must be carried out in combination to achieve greater effect:
- Medications for pain relief and inflammation.
- Massage and special gymnastic exercises.
- Acupuncture.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Traction (based on spinal stretching) treatment.
An individual approach to each patient is also required.
Exercises to relieve the condition
Breathing exercises are great for pain relief. It can relax muscles, saturate the blood with oxygen, and cleanse the respiratory system. Gymnastics helps reduce pressure on nerve endings and blood vessels located in close proximity to the spine.
Special gymnastics for osteochondrosis is included in the treatment complex.
All exercises are designed specifically for patients with this diagnosis and are performed under the supervision of a doctor. Exercises should not cause difficulty in performing or discomfort. Physiotherapy exercises are prescribed only after the acute condition has resolved. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Clinical manifestations
First of all, the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are expressed in aching pain, localized in the neck and radiating to the upper limbs and shoulders. Their “faithful companions” are the following clinical manifestations:
- headache;
- increased pain when trying to turn or tilt your head;
- muscle spasms;
- restriction of physical activity.
If compression of the nerve roots is observed, the following symptoms can be added to the above:
- shooting, cutting pain in the neck;
- feeling of weakness in the arm or hands;
- numbness of the skin of the upper extremities;
- cervical scoliosis, curvature in the cervical spine;
- decreased reflexes.
With the development of vertebral artery syndrome, which can occur as a reaction to irritation of its sympathetic plexus, the following symptoms are observed:
- dizziness;
- throbbing, burning headache;
- floaters and colored spots before the eyes.
Thoracic osteochondrosis
Difficulty of diagnosis | Symptoms | Reasons | Complications | Treatment at Doctor Ost |
With age, the spine and joints wear out; unfortunately, we have not yet learned how to stop this destructive process, but it can be significantly slowed down if recognized in time!
In the diagnosis and treatment of osteochondrosis, “Doctor Ost” has no equal! Let's figure out together why thoracic osteochondrosis is insidious and how to cope with it.
Sign up
DIAGNOSTIC COMPLEXITY
The older a person gets, the more likely he is to develop signs of osteochondrosis in various parts of the spine. The cervical and lumbar regions are the first to succumb to the onslaught of the disease. Thoracic osteochondrosis develops less frequently. But is it?
There is an opinion that the thoracic region is stronger and more resilient. The vertebrae here are less mobile than others. In addition, the muscles in the chest area are well developed, which creates a kind of corset for the spine.
But according to another version, thoracic osteochondrosis is less often treated due to the complexity of diagnosis. Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are easily confused with other diseases.
Feeling pain in the chest, the patient listens to his feelings. What is it: heart, lungs or maybe stomach? Time is lost in going to offices. Subspecialists look for pathologies in their field, prescribe studies and even make prescriptions. The aggravation subsides. But the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, disappearing, return again.
“I’m still in the process of treatment, but I can already say that there is no trace left of the pain due to osteochondrosis!” Read full review
“Doctor Ost” specializes in pathologies of the musculoskeletal system of any degree of complexity, so our specialists can easily distinguish osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine from diseases of the internal organs. Timely diagnosis will help begin proper treatment. And the patented proprietary methods for treating thoracic osteochondrosis will not allow dangerous complications.
OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE THORACIC SPINE: SYMPTOMS
The first and most important symptom is, of course, pain in the thoracic region.
It can be localized both in the back and in the sternum, in the intercostal space. Or it can go under the shoulder blade, into the arm and back. Also, with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, breathing difficulties arise, and discomfort intensifies when inhaling. Moreover, the painful condition can quickly pass or, conversely, accompany a person for several days.
Other symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis include:
- numbness of the limbs, loss of sensitivity (this sign occurs when the spinal cord is compressed and indicates that the disease is in an advanced stage)
- pain in the abdomen.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is easily confused with diseases of the internal organs:
- heart pain, angina pectoris;
- cholecystitis, ulcer or gastritis;
- renal pathologies;
- lung diseases.
Against the background of thoracic osteochondrosis, the functioning of internal organs can actually be disrupted.
But such changes are already secondary and can be easily corrected when the underlying disease, osteochondrosis, is eliminated. Despite all the obviousness, it can be difficult to recognize the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, and treatment is delayed. As a result, patients spend years unsuccessfully treating non-existent diagnoses. To prevent this from happening, check yourself and learn to recognize the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis! Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis of the spine, by which it is easy to distinguish it from other diseases:
- acute reaction when pressing on the vertebrae;
- relief at rest, in a horizontal position;
- discomfort intensifies after a long stay without movement in an incorrect position.
REASONS FOR THE APPEARANCE
The reasons for the development of thoracic osteochondrosis are typical for other parts of the spine:
- regular overloads;
- age-related changes;
- prolonged stay of the body in a stationary, non-physiological position;
- posture disorders;
- injuries;
- excess weight;
- lack of vitamins and metabolic disorders.
Changing your lifestyle means getting better! But at some stage it is no longer possible to cope without professional medical help.
COMPLICATIONS OF THORACIC OSTEOCHONDROSIS
Without treatment, thoracic osteochondrosis develops into more severe forms: protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs, spondylosis. These are diseases in which pain becomes a constant companion. In addition, deformed vertebrae can compress the spinal cord canals. Internal organs (kidneys, liver, etc.) will no longer receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients, which will lead to disruption of the functioning of these organs. The cardiovascular and endocrine systems will be especially affected. At the initial stage, local pain syndrome bothers you from time to time and coping with it is not difficult. At the fourth stage, complete immobility of the segment and paralysis occurs, leading to disability. And in such severe cases, “Doctor Ost” is ready to come to the rescue, but urges not to let the disease progress to such an extent.
Ask a Question
TREATMENT OF OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE THORACIC AT MC "DOCTOR OST"
- The treatment program is prescribed depending on the complexity of the pathology with which the patient applied.
- If diagnostics are required, the necessary MRI examinations can be obtained at a discount.
- In any case, a comprehensive healing effect will be provided on the musculoskeletal system.
- Instead of drugs with their side effects, we use modern hardware techniques: high-intensity laser and a unique EPS painkiller system.
- We use modern technologies of regenerative medicine for the speedy restoration of damaged tissues of nerves, joints, vertebrae: catgut, alloplant, PRP, SVF.
- Posture correction and non-surgical treatment in severe stages (for protrusions, hernias) are performed using robotic systems DRX and ExtenTrak.
- Classes with rehabilitation medicine specialists on modern kinesiosimulators and manual therapy allow you to train the correct motor patterns, postures and a strong muscle corset for healthy posture and active longevity!
how much does it cost? Treatment of osteochondrosis at Doctor Ost is carried out by a therapist, neurologist, vertebrologist, and rheumatologist. Find the cost of a specialist consultation in the “Consultative Appointment” section of our price list. Follow the promotions, don't miss out on the best price!
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor begins to suspect the patient has osteochondrosis based on his complaints and the collected medical history. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the specialist prescribes diagnostic measures, the main of which is radiography of the spine in frontal and lateral projection. To obtain more detailed information, CT and MRI are performed: they help to track complications in a timely manner.
For osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine, complex treatment is prescribed. As a rule, it includes several main areas:
- drug therapy is primarily painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs that help reduce pain; in addition to them, muscle relaxants are often prescribed to relieve muscle spasms, chondroprotectors to strengthen cartilage tissue and B vitamins, which improve the condition of nervous tissue;
- physiotherapy includes massage and other procedures (ultrasound, magnetic therapy, etc.) aimed at improving the condition of the spine and removing mobility restrictions;
- physical therapy allows you to activate blood flow, strengthen muscles, thereby removing excess stress on the spine, tone the body and correct posture; it also helps relieve pressure on the nerve roots.
A spine stretching procedure is periodically applied to return it to its original shape.
A consultation with a doctor from the Health Workshop network of clinics will help you understand your body properly. At the reception we will tell you about everything that interests you.