A reflex is an uncontrolled action that is the body’s response to external irritation. They can be acquired or congenital.
The knee reflex belongs to the group of stretch reactions or unconditioned reflexes. It can be tested by asking the patient to place one knee on top of the other and lightly but sharply hit the area under the patella (the fossa). Normally, the limb will undergo extension. The physiology of the process is based on the fact that when the muscle tendon (quadriceps femoris) is acted upon, it stretches and acts on the leg extensor muscle. This provokes spontaneous straightening of the leg. The importance of the knee reflex in ensuring the function of maintaining posture and balance.
Research methods
Test options
The knee reflex is examined using several methods. If emergency medical care is needed due to injury or an attack of unknown etiology, the form of testing differs from traditional techniques.
There are three research methods:
- Deviations
- Knee reflex: reflex arc diagram, description
- Reasons for development
- At the doctor's appointment: what the patient should know
- Knee reflex and its absence in a child: reasons that indicate a blow to the knees with a hammer
- Anatomical features
- Reflex arc
- How to check?
- How to check?
- Pathological disorders of the reaction of the knee tendon
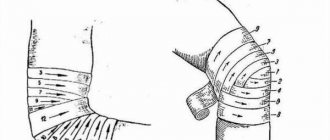
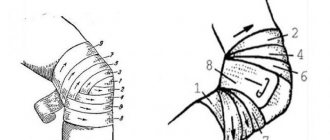
The patient is in a horizontal position, legs bent at an obtuse angle. One hand of the doctor is located under the knee, with the other he holds a special hammer and makes small amplitude blows on the femur in the area of \u200b\u200bthe connection with the patella. The patient sits on a chair, the feet of both limbs are pressed firmly to the floor, the limbs themselves are slightly extended forward
The doctor moves the patella down a little, after which he carefully hits the hammer from top to bottom above the knee. The patient sits on a chair, one leg is crossed over the other, after which the doctor hits under the patella. In the absence of pathology, the knee will straighten and bend.
The third method has variations. For example, the patient lies on a horizontal surface, one bent limb rests on the other, or a high chair is used from which the legs hang freely.
Sometimes during a visit to the doctor the patient is very tense. This makes diagnosis difficult and does not give reliable results. To achieve psychological relaxation, neurologists resort to the technique of Jendrassik and Shvetsov:
- deep and even breathing;
- simple mathematical calculations are performed loudly;
- directing a strong beam of light into the eyes.
How to test the knee reflex and why does it fall out? The structure and significance of the nervous system
A reflex is the body's response to an external factor. The response is regulated by the nervous system, and the path along which the nerve impulse travels is called a reflex arc. It includes the perceptive nerve ending, sensory, motor, intercalary and executive neurons.
The static element of the reflex works while the muscle is in a stretched state. The dynamic element functions for several moments, manifesting itself as a response to a sharp transformation in the length of the muscle. The basis of the two-component reflex lies in the presence of two types of intrafusal muscle fibers:
- Responsible for the static moment , called chain and capable of stretching evenly. When stretched, they allow the frequency of signals to increase.
- Responsible for the component of movement , marsupial fibers, have a convexity in the center, due to which they are more elastic. When exposed to rapid stretching, the middle is stretched first, then the side parts, the expansion of which may be accompanied by compression of the central part. As a result, the impulse from the nerve ending first indicates stretching and then compression, that is, an fluctuation in the length of the muscle.
Reflex monosynaptic arc of the knee reflex schematically
The presence of reflex impulses ensures human safety and a normal reaction to changes in the environment.
In addition to this arc, there is a connection between the tendon reflex and other neural processes that ensure the intersegmental movement of impulses along the ascending and descending pathways.
The spinal cord in the lower back sends signals to the brain, helping to consciously respond to key transformations occurring in the body. The person feels that his leg has straightened.
These are rising currents.
Return pathways take part in the creation of conscious movements, providing voluntary contraction of some muscles and relaxation of others. Accordingly, reflexes have a close relationship with the centers of the brain, which are located in the cortex and other areas.
Purposes of the neurological examination
What a neurologist checks and evaluates:
- examination and general assessment of the functioning of all organs and systems in the human body;
- the skin is examined;
- body type is determined;
- when communicating, the specialist pays attention to the shape, symmetry and size of the head;
- then the neck is diagnosed and the stiffness of the neck muscles is checked;
- chest examination;
- the peritoneal organs are palpated;
- the spine is examined.
Specifically, the neurological examination includes the following parameters:
- assessment of the state of consciousness and the presence of its disorders;
- how the patient can navigate space, his own personality and time;
- assessment of cerebral symptoms;
- checking the function of the cranial nerves;
- study of the motor sphere;
- reflexes are checked.
The nervous system performs many functions in the body and controls the functioning of all organs and systems. Therefore, examination of a neurological patient, depending on the patient’s condition and the necessary diagnostic methods, can last from 15 minutes to several hours.
The qualifications of a specialist are very important when undergoing an examination and making a diagnosis.
Pathological disorders of the reaction of the knee tendon
There are three types of knee reflex disorders:
- Hyperreflexia – the excitation reaction prevails over the inhibition reaction.
- Hyporeflexia - the inhibition reaction predominates over excitation.
- Areflexia is the absence of any reaction.
Indications for MRI of the knee joint and research methodology
Each type of knee reflex pathology indicates a number of diseases.
Causes of lack of response of the quadriceps femoris muscle
Factors leading to a decrease in knee reflexion or its complete disappearance may be the following diseases and conditions:
- infectious diseases, including those affecting the brain and spinal cord;
- intoxication of various etiologies, in particular medication, alcohol, drugs;
- mental disorders;
- incorrect and too long application of a medical bandage;
- postoperative condition;
- individual characteristic of a person.
One of the factors of central nervous system disorder may be large weight loss. Dystrophy leads not only to diseases of the internal organs and glands, it also affects unconditioned reflexes.
Fact! If the knee reflex is absent in both legs, then it is quite possible that you have a spinal cord disease called tabes dorsalis. This is the third stage of neurosyphilis, which affects the ganglia of the spinal cord.
Causes of hyperreflexia
The state of predominance of excitation reactions over inhibition is a sign of the following disorders of human central nervous activity:
- neurosis;
- neuritis;
- radiculitis;
- plexitis;
- reaction to intoxication.
Also, such a reaction can be a consequence of a person’s mental stress before visiting a doctor, and can also be an individual characteristic of a patient with a neurotic type of nervous system.
Important! If the pathology is not treated, a complication is observed, expressed by constant contraction of the muscles around the kneecap. This disorder is called clonus.
Types of reflex arcs with examples
There are somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
The first begins with the stimulation of pain sensitivity receptors, from which the impulse travels along the spinal nerve to the sensitive node located on the dorsal root.
Then - to the interneuron, where, as part of the anterior horn of the gray matter, the impulse is sent down the motor fibers to the corresponding muscles.
With autonomic innervation, irritation comes from the internal organs, is directed to the sympathetic node, spinal sensory node, dorsal horn, then to the lateral (as opposed to somatic) horn.
There it becomes efferent, reaches the prevertebral node, then the executive organ.
It is important to know: what is the difference between the autonomic reflex arc and the somatic one? Autonomic reactions are carried out only from internal organs and are peripheral (closed outside the central nervous system), taking place in the lateral horn of the spinal cord.
Simple
In physiology, they are understood as reflexes of a two-neuron reflex arc.
The simplest spinal reflex is carried out by this mechanism, without additional switching of nerve fibers. So, if a stimulus acts on the mechanoreceptors of the tongue and structures nearby, the swallowing reflex mechanism is triggered.
Irritation from the receptors is transmitted to the branches of the trigeminal, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves, then to the swallowing center of the brain. Further, along the motor fibers, excitation is transmitted to the muscles of the upper digestive tract.
Complex
They are represented by three-neuron arches due to the inclusion of interneurons. The number of the latter can vary, reaching three and four.
These include the following reflexes:
- The salivation reflex develops when food comes into direct contact with the receptors of the oral cavity, as well as the smell of food or the memory of it. After this, irritation is transmitted to sensory fibers running as part of the branches of the facial, glossopharyngeal, trigeminal, and vagus nerves. Information processing occurs in the medulla oblongata, which leads to activation of the fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system and the sympathetic part of the upper third of the spinal cord.
- The corneal or blink reflex occurs when the cornea is touched. This leads to activation of the afferent receptors of the fifth cranial nerve (trigeminal nerve), the impulse is transmitted to the reticular formation. Further along the efferent pathway of the facial nerve it reaches the motor neuron of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The eyelids close, and a tear is secreted in parallel (due to the anatomical proximity of the passing tracts).
- When the illumination changes, you can trace the arc of the pupillary reflex. Light irritates the retinal receptors, the impulse from them is transmitted to the ascending fibers of the optic nerve. Next, the impulse is split: part goes to the thalamus, part to the midbrain, after which the impulse along the descending fibers of the cranial nerves reaches the ciliary muscle and ends on it, the pupil changes its diameter. Bright light leads to contraction, low light leads to expansion.
This group will also include reactions that coordinate the work of internal organs, for example, the urination reflex.
Monosynaptic two-neuron
This group is represented by a single connection of neurons in the center of the arc. Representatives of this group are the flexion-elbow and knee reflexes.
The first is manifested by irritation of the receptors of the biceps brachii muscle, the second is more often examined during a neurological examination, assessing the contraction of the quadriceps femoris (which ends under the kneecap). These are deep reflexes of the muscle-tendon sense.
The hammer is the main tool of the neurologist
The neurological hammer is intended to test the patient’s reflexes during the initial examination by a neurologist.
This is the most important and indispensable tool for neurologists.
It is a source of pride for specialists who work in the field of development and research of the central nervous system, developing methods for diagnosing, treating and preventing diseases.
What are the types of tendon reflex disorders?
Reflexes may be impaired. This is manifested by their strengthening (hyperreflexia), weakening (hyporeflexia) or complete absence (areflexia).
Increased tendon reflexes are observed when the inhibitory influence of the cerebral cortex is lost. Thus, the reflexogenic zone expands and, consequently, the tone of the muscles that respond to the stimulus.
Deviations
Normally, the knee joint reflex is characterized by an average degree of tendon reactions, which is called normoreflexia. When the functions of the nervous system are impaired, signal transmission is disrupted, which leads to the development of the following conditions:
Hyperreflexia
The test records the maximum extension of the lower leg. This phenomenon is often the result of deviations accompanied by irritation of motor fibers:
- Intoxication.
- Polyneuritis.
- Radiculitis.
Hyperreflexia is also observed in healthy people of a neurotic type.
Cruciate ligament of the knee joint and its pathologies
Hyporeflexia
It is characterized by a weak reaction of the knee to a stimulus due to a failure in the conductivity of the reflex arc. A sharp decrease in a person’s weight and infectious diseases provoke depletion of neurons and failure of cell functions. The reason for the disappearance of the reaction is also the previous anesthesia.
Brain pathologies can lead to the absence of a reflex
Areflexia
Most often found in pathologies of the central nervous system. With areflexia, the reaction to the stimulus does not appear. The reason for its absence is often paralysis. Temporary areflexia appears if the femoral artery is compressed, during anesthesia, during an attack of epilepsy. A change in the strength of the knee reflex is evidence of pathology of the nervous system.
Sources
- https://VashNevrolog.ru/fiziologiya/axillov-refleks-postoyannyj-myshechnyj-refleks-cheloveka.html
- https://moisustav.ru/anatomiya/kolennyiy-refleks-shema-reflektornoy-dugi.html
- https://ProKoleni.ru/simptomatika/kolennyiy-refleks
- https://sustavs.com/diagnostika/shema-kolennogo-refleksa
- https://fb.ru/article/227655/kolennyiy-refleks-cheloveka-i-ego-znachenie-duga-kolennogo-refleksa
- https://NeuroDoc.ru/diagnostika/simptomy/kolennyj-refleks.html
- https://moyaspina.ru/raznoe/kolennyy-refleks
- https://prospinu.com/anatomija/kolennyj-refleks.html
- https://MedOtvet.com/stroenie-sustavov/kolennyi-refleks-fiziologiya-i-patologiya.html
Do deviations need to be treated?
Hyperreflexia and hyporeflexia are not independent diseases; they only signal damage to the central nervous system. It is possible to eliminate dysfunction of each part of the knee reflex in the following ways:
- If the brain is infected, it is treated with antibiotics.
- If mental disorders occur, mental blockers are used.
- When diagnosing radiculitis, treat with anti-inflammatory steroids.
- For paralysis of the legs caused by hemorrhage, post-stroke therapy is carried out.
- In the presence of intoxication, cleansing of the body is indicated.
Establishing the cause of the knee reflex disorder is important to match the sequence of treatment of the disease that caused the pathology. The study of the causes after the designation of knee reflex disorders includes hardware studies and laboratory diagnostics.
When nerve fibers are torn, resulting in paralysis, surgical suturing is performed
A special method of treating knee reflex disorders is massage, as well as therapeutic exercises. Exercises in the pool are useful. If knee sensitivity fails, constant monitoring is required, as the risk of hidden pathologies is increased. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and eliminating stressful situations contribute to obtaining a positive result in the treatment of knee joint disorders, which lasts for life.
Knee reflex: reflex arc diagram, description
A reflex is an uncontrolled action that is the body’s response to external irritation. They can be acquired or congenital.
The knee reflex belongs to the group of stretch reactions or unconditioned reflexes. It can be tested by asking the patient to place one knee on top of the other and lightly but sharply hit the area under the patella (the fossa). Normally, the limb will undergo extension.
The physiology of the process is based on the fact that when the muscle tendon (quadriceps femoris) is acted upon, it stretches and acts on the leg extensor muscle. This provokes spontaneous straightening of the leg.
The importance of the knee reflex in ensuring the function of maintaining posture and balance.
The arc of the knee reflex
A reflex arc is the path through which a nerve impulse travels from a receptor to a muscle or organ.
The transmission scheme is based on the fact that the impulse received during an impact is transmitted from receptors (neuromuscular spindles) along axons to the bodies of sensory neurons (cells located in nodes near the spinal cord). Next, the excitation is transmitted to alpha motor neurons (in the gray matter of the spinal cord), after which the motor cells cause the quadriceps muscle to contract (the leg will “bounce”).
There is also a pathway through which the agonist muscle (flexor muscle) relaxes. The physiology is similar, the path starts from similar sensitive cells, but the signal passes through collaterals to neurons that inhibit the impulse; they are located in the lateral horns of the gray matter. From these formations the inhibitory signal goes to the motor neurons of the flexor muscle.
How to test the reflex?
The work of the neurons responsible for the occurrence of the reaction is assessed in several patient positions. You can check the reflex in the following ways:
- The patient sits on a chair, the leg being examined is crossed over the other. There is a modification when the feet are on the floor. This method is described above.
- The patient is examined in a supine position, the doctor with one hand raises his leg to the level of an obtuse angle, resting on the popliteal fossa, strikes the quadriceps muscle, causing it to contract.
- The patient sits on the couch so that both legs hang from it and do not touch the floor, then the doctor acts according to the same scheme.
- The patient lies on the couch and places the knee of one leg on the knee of the other.
When carrying out this procedure, it is necessary to explain to the patient how to properly relax his legs, often inducing a knee-jerk reflex. The examination may be difficult precisely because the patient has not relaxed the muscles of the limb.
Doctors often resort to tricks by forcing the patient to solve simple problems in his head. They help distract the patient from the manipulation.
Reflex changes
There are pathological changes in the nervous system, manifested in changes in the knee reflex. Deviations may be of the following nature:
- Hyporeflexia.
- Areflexia.
- Hyperreflexia.
A neurologist, having noted such phenomena, will conduct a comprehensive examination to make a diagnosis.
Perverted reactions
A special type of knee reflex pathology is perverted or pathological reactions. They occur only when there is a serious pathology of the nervous system.
The physiology of unconditioned reactions to the influence of a stimulus is of great clinical importance for a neurologist. The knee reflex is a mandatory element of a comprehensive examination, the condition of which indicates various diseases of the nervous system.
Neurological examination reflexes
The human knee-jerk reflex and its meaning. The arc of the knee reflex
Improper functioning of the knee reflex indicates serious disturbances in the functioning of the body.
To diagnose the disease in the early stages, you should know what your reaction to a hammer blow under your knee indicates. Let's look at this in the article. The reception of information from the outside and its transmission throughout the body: through the muscles, organs, spinal cord and brain is ensured by the stable functioning of the nerves. The brain has a standard scheme for transmitting impulses along the path.
In cases where an immediate response is required, the reflex passes through the spinal cord. This reaction occurs, for example, if you step on a needle, then your leg jerks back sharply.
If the reflex went through the brain, there would definitely be a delay in the process, which can be dangerous for the life of the body.
So, a reflex is an instant response to an external stimulus; it is coordinated by the nervous system. And its path is called a reflex arc.
The irritation signal is transmitted via afferent nerves to efferent centers in the spinal cord.
It is then transmitted to the muscles, which contract. The absence of reflexes is a symptom of a disease of the muscles, nervous system, brain, or a special emotional state.
Vital body processes also operate reflexively, such as the production of saliva when food is consumed.
How to trigger the knee reflex?
The occurrence of the knee reflex is due to the fact that when a medical hammer hits the quadriceps tendon, it contracts. This contraction causes the leg to straighten.
The blow must be delivered directly under the kneecap, because the quadriceps extensor tendon is attached to the beginning of the tibia. It is not necessary to hit with force, the main thing is that the muscles are as relaxed as possible.
You can cross one leg over the other, then when the patellar reflex occurs, it will jerk upward.
What if you need other methods?
If the traditional method does not work, there are several other methods for demonstrating the knee reflex:
- The person should be seated on a chair with their toes touching the floor and their legs bent at an angle slightly greater than 90 degrees. The blow must be applied from top to bottom over the retracted patella. As a result, the patella rises;
- the knee of the required leg must be placed on top of the second knee;
- you can use a high seat so that your legs hang in a relaxed state;
- There is also a method when the patient is lowered onto his back with his knees stacked one on top of the other.
There are times when the patient is physically unable to sufficiently relax the limb being examined. Then specialists use methods of disinhibition of the knee reflex, for example, the techniques of Jendrassik and Shvetsov. The patient should also breathe deeply or solve simple mathematical problems out loud.
What do disturbances in the knee reflex indicate?
Muscles contract in a similar way on the upper pair of limbs and elsewhere in the body. But the significance of the knee reflex is that its violation is considered an important symptom of abnormalities in the functioning of the brain and spinal cord. The arc of the knee reflex is constant.
Only in rare cases can a healthy person not have a knee reflex; in this case, most likely, a childhood illness damaged his work. In the presence of diseases, it may be absent or, on the contrary, excessively intensified.
This is explained by the fact that the center of the knee reflex is located in the lumbar spinal cord, or more precisely in the II-IV segment. For some diseases there are specific deviations in the manifestation of the knee reflex. For example, cerebral lesions cause a pendulum-like knee reflex.
An enhanced reflex may indicate a form of neurosis. On the contrary, a reduced form of the reflex is a sign of infection or intoxication of the body. The complete absence of the knee reflex indicates significant damage to the nervous system.
Also, the reflex may disappear in epileptics after a seizure, after using a tourniquet, during deep anesthesia or after heavy muscle strain. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
What is a reflex arc?
The knee reflex occurs due to its reflex arc. Just as there is significant disruption to the overall functioning of a machine due to the presence of a damaged part, the human body is similarly unable to function when something is not working correctly.
A reflex arc is the path of a signal from the receptor that receives it to the organ that responds to it. It is also called the neural arch. This name is explained by the fact that the knee reflex occurs due to impulses in the nerves that travel a certain path.
The reflex arc consists of chains of neurons that are formed from intercalary, receptor and effector neurons. They themselves and their processes create a path for the transmission of irritation.
What are the types of reflex arcs?
The peripheral nervous system has two types of reflex arcs:
- those that supply internal organs with signals;
- those related to skeletal muscles.
How does the knee jerk reflex arc work?
The arc of the knee reflex involves three sections of the back, from the second to the fourth. In this case, the fourth department is the most important in the process.
The reflex arc of the knee reflex has five components:
- Receptors. They receive the stimulus signal and become excited in response. These are the ends of axons or bodies located in epithelial cells. Receptors are found everywhere in the human body, in organs, in the skin, they make up the sense organs;
- The nerve fiber is sensitive, afferent or centripetal. It transmits the signal to the center. Neuronal bodies are located outside the central nervous system, namely near the brain and in the nerve ganglia near the spinal cord.
- The nerve center is the place where the signal is transmitted from afferent neurons to efferent ones. The centers of efferent neurons are located in the spinal cord.
- The nerve fiber is motor, centrifugal or efferent. As the name suggests, excitation along it goes from the central nervous system to a specific organ. The efferent fiber is an axon (or a long process) of a centrifugal neuron.
- Effector. An organ that responds to stimulation of a specific receptor. This is a muscle that contracts after processing a signal from the center, a gland that exudes juice due to nervous excitement, and more.
How does the impulse move during the knee reflex?
To study the knee reflex in detail, its stages should be studied. The passage of nerve impulses during the knee reflex occurs as follows:
- hitting the tendon under the knee with a hammer causes this tendon to stretch, therefore, a receptor potential arises in the corresponding receptors;
- An action potential arises in the neuronal long process. In the spinal cord it is chemically transmitted to the motor neuron;
- the axon of the efferent neuron serves as a signal path to the gastrocnemius muscle;
- due to muscle contraction, the leg twitches.
Now you know how the reflex works and for what purposes it is diagnosed.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/227655/kolennyiy-refleks-cheloveka-i-ego-znachenie-duga-kolennogo-refleksa
Reasons for development
Hyperreflexia occurs when the inhibitory effects of the brain on the segmental reflex apparatus are weakened.
Increased reflex activity of the spinal cord and brain stem can occur when:
- Viral transverse myelitis, which develops when the anterior and posterior parts of the spinal cord are damaged over a sufficient length. Caused by herpes simplex virus type 2, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr and varicella-zoster viruses.
- St. Louis encephalitis virus, which is transmitted by Culex mosquitoes. Distributed on the American continent. Accompanied by general intoxication and damage to the central nervous system.
- Spinal cord lesions accompanied by autonomic disorders. A break in the spinal cord due to a spinal fracture causes areflexia at the initial stage, which is then replaced by hyperreflexia.
- Spinal cord infarction (areflexia that occurs during spinal shock is eventually replaced by spasticity and hyperreflexia).
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, which is a prion disease. Increased reflexes and spasticity are detected in more than half of the patients.
- Machado-Joseph disease (spinocerebellar degeneration type 3), which is a genetic disorder. Most often observed in residents of Japan and the American continent.
- Eclampsia (severe form of late toxicosis of pregnancy). Increased reflexes are combined with eclampsia and epileptic seizures.
- Preeclampsia (late toxicosis of pregnancy). The presence of hyperreflexia in this condition is a sign of damage to the nervous system.
- Fatal familial insomnia is a rare genetic disease that is accompanied by bilateral degeneration of the anterior nuclei of the thalamus and its mediodorsal nucleus.
- Multiple sclerosis (hyperreflexia of the bladder of spinal or central origin is observed).
- AIDS dementia syndrome, which is caused by HIV infection. Increased reflexes and other pyramidal symptoms are observed in half of the patients.
- Hepatic encephalopathy.
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever (increased reflexes are observed in 25% of patients). The disease, prevalent primarily in the United States, is caused by the intracellular parasite Rickettsia.
MORE ABOUT: Nutrition for sore joints Hyperreflexia is observed during intoxication, which develops as a result of:
- Bite from a Latrodectus (black widow) spider.
- Poisoning with psychostimulants (amphetamines, alpha and beta adrenergic stimulants). Increased reflexes often accompany nausea and other symptoms of poisoning.
- Tetanus as a result of the influence of tetanotoxin, a potent neurotoxin produced by vegetative cells of Clostridium tetani. Under the influence of tetanotoxin, the inhibitory effects on motor neurons are eliminated, which sharply increases muscle tone and causes hyperreflexia (accompanied by tonic convulsions in response to the slightest stimuli).
Violations
In normal conditions, reflexes, including the knee reflexes, are of average vivacity. That is, there is an average degree of severity of tendon reactions. In medical practice this is called normoreflexion. But with various pathologies of the nervous system, signal transmission is disrupted at one or several levels. In this case, the severity of the reflex changes, and the following conditions appear:
- Hyperreflexia (increase).
- Hyporeflexia (decreased).
- Areflexia (absent).
The medical significance of the knee reflex is precisely determined by the possibility of diagnosing various neurological pathologies based on violations of its severity.
Each of the listed options is a deviation from the norm and requires an adequate response and appropriate correction.
Hyperreflexia
When the intensity of the knee reflex increases during its testing, maximum extension of the lower leg occurs. This is observed when the inhibitory influences exerted by the brain through the pyramidal tracts are slowed down, and is manifested in an increase in spinal motor reactions. Often included in the symptom complex of spastic (central) paresis. However, such a sign may be a consequence of disorders in which motor fibers are irritated:
- Polyneuritis.
- Plexitov.
- Radiculitis.
- Intoxication.
In addition, symmetrical hyperreflexia occurs in practically healthy neurotic individuals in the absence of pathological symptoms. Sometimes increased involuntary movements lead to rapid contractions of isolated muscle groups - clonus. Most often this occurs in the kneecap area.
Hyporeflexia
A decrease in the strength of tendon reflexes appears when the passage of an impulse in the area of a peripheral motor neuron is disrupted, when its body or processes are affected. Thus, the source of pathology should be sought in the anterior horns of the spinal cord in the lumbar region, roots, plexuses and nerves. In addition, the integrity of the arc may also be compromised at the level of the sensitive link. Hyporeflexia is one of the symptoms of flaccid paresis of the lower extremities.
If the knee reflex is weakly evoked, then you need to understand at what level the damage to the neural arch occurred. Researching other symptoms will help with this.
Areflexia
The complete absence of a tendon reflex most often indicates an extreme degree of peripheral paresis - paralysis. But there may be other options: previous infectious diseases, muscle damage, exhaustion (cachexia). In addition, temporary loss of motor reactions is observed in the following cases:
- General anesthesia (anesthesia).
- Epileptic attack.
- Compression of the femoral artery.
In any case, it is necessary to comprehensively assess the condition of the patient’s body, taking into account all the symptoms and examination results. This is the only way to determine the cause and location of the lesion.
The quadriceps (patella) tendon reflex has important biological and diagnostic significance. Any change in its strength, as a rule, indicates pathological changes in the nervous system and requires appropriate treatment.
It can be useful:
- Kyphosis of the thoracic spine
- Anatomy of the leg above and below the knee joint
- What joints does a person have? Anatomy
- How are ligaments different from tendons?
- Anatomy of the spine, structural features of the vertebrae
At the doctor's appointment: what the patient should know
An experienced doctor can already assess the patient’s condition just by gait and movements. But a careful examination is necessary: visual, tactile and with the help of instruments to make a diagnosis. To assess some reflexes, the condition of the muscles will need to remove some clothing.
So, how does an appointment with a neurologist go:
- The specialist examines the patient’s appearance for the presence of asymmetry of the face and body.
- To study the functioning of the optic nerve, you will need to follow the movements of the hammer without turning your head.
- The doctor can check your reflexes using your facial expressions. The neurologist will ask you to wrinkle your forehead, stick out your tongue, or say “Ah.”
- You can check the sensitivity of your face using a needle. Don’t be scared; you will need to concentrate as much as possible and answer the neurologist’s questions about whether you experience the same sensations when receiving injections in symmetrical zones.
- To determine the condition of the muscles, their tone and reflexes, the doctor will be asked to shake his hand and resist when trying to bend the elbow. Evaluation occurs by assigning points from 1 to 5.
- Deep reflexes of the arms and legs are tested by striking the tendons with a hammer.
- Superficial reflexes are tested by irritating the skin of the abdominal wall with a needle.
- A deep examination of muscles and joints is carried out when the patient's eyes are closed, and the doctor moves his finger in different directions and asks him to name exactly in which direction he is doing it.
- Drawing various figures, letters and numbers on the skin of the patient’s back helps determine the condition of the spinal nerves and paravertebral pain points.
- Coordination of movements is tested by the Romberg pose. The patient stands with his feet together, arms extended forward, eyes closed. The neurologist will ask you to slowly move your index finger to your nose (with each hand). In this study, a person should ideally not stagger to the sides.
- You may need to answer specific questions about counting or dates to assess memory.
Tasks: what does a neurologist do?
Due to the fact that diseases of the nervous system are one of the most extensive and complex areas of medicine, it depends on the neurologist:
- How complete and reliable will the anamnesis be collected and the initial examination performed?
- Diseases associated with nervous system are often accompanied by pain; the doctor must correctly determine the cause.
- To make a final diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes the patient the entire necessary range of studies and tests, consultations (if necessary) with a cardiologist, ophthalmologist and endocrinologist, etc.
Sources
- https://proartrit.ru/vrach-nevrolog-kakie-bolezni-lechit/
- https://fb.ru/article/227655/kolennyiy-refleks-cheloveka-i-ego-znachenie-duga-kolennogo-refleksa
- https://VashNevrolog.ru/fiziologiya/chem-grozit-narushenie-kolennogo-refleksa-zhiznedeyatelnosti.html
- https://nevrologi.su/article/s-kakimi-simptomami-obrashhatsya-k-nevrologu
What are the consequences of a violation of the knee reflex of vital functions?
The knee reflex has acquired great importance in neurological practice. This happened due to the fact that it is relatively easy to cause, since it is located in an easily accessible place, and also because it is constant. The latter means that this reflex response of the body to a stimulus cannot disappear in a person with a healthy nervous system.
What is the knee reflex
The knee reflex is part of the group of unconditioned reactions, that is, such responses of the body that can appear immediately after birth.
A reflex response occurs after irritation of the quadriceps femoris muscle. The irritant may be a small blow, however, it must fall precisely on the tendon, which is located below the patella. This description of the knee reflex suggests that it is also included in the group of stretch reflexes.
The tendon that needs to be hit with the hammer is attached anteriorly to the surface of the tibia. It, in turn, is located under the kneecap. This means that when an irritant hits the tendon, it contracts and pulls or straightens the entire lower leg.
How does he work
After the stimulus acts on the tendon under the kneecap, the impulse travels along the sensory nerve endings to the spinal cord, namely to its dorsal horns. After this, the so-called interneuron is activated, whose task is to redirect the impulse to the anterior horns, which are responsible for movement.
As a result of the closure of the reflex arc, the lower leg straightens after the impact of a neurological hammer on the tendon.
How to test your knee reflex
The appearance of a reflex response depends not only on the place where the stimulus should arrive, but also takes into account the force with which it will be applied. For the knee reflex, a moderate stimulus strength is sufficient. It is much more important that the muscles are relaxed at this moment.
As a rule, patients who seek help from a specialist are always anxious and nervous. A good doctor must not only win the patient’s trust at the first meeting, but also distract him from unpleasant thoughts about his health. Therefore, while testing the knee reflex, a specialist can start a conversation on an abstract topic or turn on music or TV.
It should also be taken into account that the reflex response may differ slightly in the strength of its manifestation. This feature is not always associated with disorders of the nervous system. For example, an increased knee reflex can be observed in completely healthy (from a somatic point of view) people who have a hysterical or neurotic type of character.
To test the reflex response after tapping the knee, the patient should sit in a chair with his legs crossed. The blow is delivered to the knee of the crossed leg. This is the simplest pose to evoke the reflex. In addition, a reflex response to a stimulus can also be evoked in a supine position.
If a person is lying down, then it is necessary to bring his legs into a half-bent position so that the feet are firmly on the bed. One of the doctor's hands should be placed under the patient's knees to achieve maximum muscle relaxation. Next, the specialist strikes the tendon with a neurological hammer.
When the knee reflex may be impaired
From the point of view of the functioning of the body, the presence or loss of the knee reflex does not play a significant role. This means that the body will still function normally without fear of death.
In cases where the knee reflex is absent, this may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. In addition, this pathology can occur with the so-called syndrome of the third and fourth lumbar roots. These syndromes are also known as femoral neuritis.
There are several options for the manifestation of a pathological knee reflex. Depending on how the lower leg moves, it can be determined at what level of the spinal cord the injury occurred.
With cerebral lesions, the lower leg makes a pendulum-like movement after exposure to a stimulus. When the pyramidal tracts are damaged, exposure to the stimulus leads to the appearance of a pathologically enhanced reflex response, which is often accompanied by clonus.
Also, complete loss of the knee reflex often signals an organic lesion of the central nervous system. Most often this means a violation of the integrity of the reflex arc. In addition, the absence or decrease in the reflex response can be observed during intoxication, infectious diseases, as well as cachexia, which often appears with malignant tumors.
The reasons that can cause various disorders in the nervous system can be very different: from bruises and injuries to vitamin deficiencies, poisoning and radiation exposure.
The knee jerk reflex may disappear for some time after an epileptic seizure. Cases have been described when it may not appear after the patient has recovered from deep anesthesia. Due to strong muscle tension, it will be impossible to evoke such a reflex response during a narcoleptic seizure.
Source: https://VashNevrolog.ru/fiziologiya/chem-grozit-narushenie-kolennogo-refleksa-zhiznedeyatelnosti.html
Knee reflex and its absence in a child: reasons that indicate a blow to the knees with a hammer
The functioning of the human body is subject to certain patterns and processes. Reflexes play a significant role in this. Many people are probably familiar with this concept. It means unconscious (involuntary) actions that are the body’s response to external stimulation.
The functioning of the musculoskeletal system is impossible without tendon reflexes. These reactions are unconditional, i.e., innate and present in every person. And one of the most recognizable and accessible for research is the knee reflex. It is also the most important motor reaction in the lower extremities.
The value of the unconditioned reaction of the patellar tendon
The unconditioned knee reflex is a motor tendon reflex, with the help of which a person maintains an upright body position. An unconditioned response occurs with a short-term impact on the tendon, which leads to contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle.
The reaction includes the concept of a reflex arc - the path of an impulse from the nerve to the brain and back, which, under normal conditions, does not take more than a second.
Reflex testing: physiology and pathology
When a stimulus is applied, the impulse is perceived by sensory endings, then transmitted through afferent nerves to the efferent centers of the spinal cord, where the information is instantly processed and a return signal is sent, when it reaches the muscles, they contract, and a part of the body begins to move.
The absence of a knee reflex indicates that the patient suffers from a disease of the muscle tissue, brain and other parts of the nervous system, or is in a serious emotional state.
During the knee reflex test, the neurologist hits the base of the quadriceps tendon with a special hammer, awakening a nerve impulse in it, the response to which should be compression of the muscle fiber and movement of the leg
The force of the blow does not matter, what is important is the correct impact of the hammer and the relaxation of the leg
The normal knee reflex reaction occurs through several stages:
- as a result of hitting the tendon with a hammer, it is stretched, resulting in the formation of a receptor potential;
- an action potential is provoked in the axon, it enters the spinal cord and is transferred to the motor neuron;
- along the long process of the nerve cell the message moves to the calf muscle;
- it contracts and the leg twitches.
If the method used to assess the knee reflex did not work, you can assess its manifestation in other ways:
- the subject is seated on a chair so that his toes are on the floor, and his legs are at an angle slightly greater than straight, and the blow falls from top to bottom on the retracted patella, which must rise in the process;
- place the required leg above the knee of the second and strike;
- use a high seat on which the patient’s legs will hang, which means they will be in a state of relaxation;
- The subject is placed on his back, and his knees are placed one on top of the other.
There are situations when the patient is not able to completely relax the limb; in such a situation, specialists resort to methods of disinhibiting the reflex.
Why does the knee reflex disappear?
For medicine, the knee reflex serves as one of the most important and simple means of checking the effectiveness of the largest nerve of the thigh and the work of the spinal segments of the lumbar spine from 2 to 4.
Components of stretch reflexes
Characteristics of stretch reflexes are dynamic and static components. The statistical component takes effect during muscle stretching. The duration of the dynamic component is short-term and occurs as a result of changes in muscle length.
Types of muscle fibers
Muscle fibers involved in the knee reflex:
What to do if your knee joint pops out?
- Nuclear chain fibers. Due to their structure, they provide a static component. Thin long fibers are characterized by uniform stretching. When they are stretched, the endings of the arc neurons significantly increase the frequency of signals, which is the mechanism of the static component.
- Nuclear marsupial fibers. In the middle they have a bulge around which the endings of nerves are twisted, carrying a signal about the onset of stretching. The middle of the fiber can quickly elongate when stretched. The sides of the fiber resist rapid stretching, but stretching does occur when the fiber is stretched for a short time.
It follows from this that if the fibers are subjected to rapid stretching, the middle will take the lion's share of the stretching; when the side parts are stretched, the middle will contract. The nerve ending initially sends intense signals, then the frequency flow of impulses decreases due to stretching of the side parts, and the middle again becomes shorter.
Tendon stretching as a prerequisite for the manifestation of the knee reflex
An experiment can be conducted to reveal the features of spinal cord reflexes. It is known that tendon stretching leads to extension of the lower limb at the knee. During the demonstration, the reflex will weaken if the leg is pinched by the subject. To distract him, he is asked to clasp his hands.
During the experiment, the tendon is struck with a medical hammer. If the blow does not stretch the tendon, there will be no reaction. From this we can draw conclusions: the knee reflex occurs only if there is tendon stretching, when impulses enter the spinal cord, after which they travel through motor neurons to the spinal cord.
Anatomical features
The knee reflex is a response of the body that occurs when the femoral muscle is slightly stretched. Muscle contraction occurs as a result of a gentle blow to the patella, under which the tendon is located. Under the external factor, the tendons stretch and activate the extensor muscle. This reflex is very important for diagnosing many diseases. But it is impossible to perform this procedure without a reflex arc.
The body's activity depends on the response to irritating receptors that come from the central nervous system. It is precisely this structural basis of the reflex that is the reflex arc. A reflex arc is the path of passage of an incoming signal from a receptor to the corresponding organ that reacted to it. It is also called the neural arch. This name is explained by the fact that the knee reflex occurs due to nerve impulses that enter through a certain path.
The arch is located in the cells of the spinal cord, which, after excitation, are able to transmit impulses to the muscles. The diagram with the symbols of the reflex arc is not complicated, and it is possible to understand the functioning of the process with the help of a photo. The neural arch consists of the following components:
- Links (central, efferent, afferent);
- Receptors;
- Effector (organ that can change during the reflex).
There are two types of reflex arcs: simple and complex. Simple or monosynaptic reflex arcs consist of 2 neurons (efferent and afferent) and a synapse. Have the following features:
- Short reflex duration;
- Very close effector and receptor;
- The arc is two-neuron;
- Muscles have single muscle contraction;
- Neuron fibers of group A.
Complex or polysynaptic arcs contain three neurons (effector, receptor, or a pair of intercalary ones). Features of a complex neural arch:
- The arc is three-neuron;
- Nerve fibers of groups B and C;
- The receptor and effector are not close;
- Muscle contraction according to the type of tetanus.
Role and functions in the body
In simple words, a neural arch is the path along which an impulse passes from a receptor to an organ or muscle. According to this factor, the reflex arc is designed to transmit nerve impulses. The impulse transmission scheme is based on the fact that a signal is transmitted from the receptor to sensitive neurons. Next, the excitatory reaction is transmitted to the cells of the gray matter of the spinal cord. As a result, the motor cells contract, and the leg may jerk or rise.
The shock acts as an external irritant on the nervous system. Thanks to the connection between the spinal cord, the sensory system, and motor neurons, the process occurs. A drawing showing a neural arch will help you visually describe the description and understand the path of a nerve impulse.
Arc receptors receive signals from the stimulus and, as a result of feedback, are excited at them. The links carry out the transmission of impulses to a specific organ. They are: central, efferent and afferent. An effector is an organ that responds to the action of a receptor.
According to these components of the arc, it will perform the following functions:
- Transmits a signal to the calf muscle;
- From neurons it supplies impulses to motor muscles;
- Depending on the stimulus, it generates a neural impulse that transmits to the effector (organ);
- Affects the movement of the limb, muscle contraction of the leg.
content
We have much more animal essence than we imagine.
In our every movement, every action there is an animal, whether we want it or not.
For everything we do is done through reflexes.
- Reflex
- Implementation of the reflex
- Reflex arc. Receptor, conductor and efferent neuron
- Divisions of the reflex arc
- Reflex. Reflex arc. Types of reflexes
- Types of reflexes
- Reflex arc
- Types of reflexes
We even think with reflexes.
Because thought - in the brain - is a series of electrical impulses.
And this is a reflex mechanism.
Therefore, reader, in order to understand himself,
you must first know the animal that is within you.
Imagine, reader, that you are controlling some kind of biorobot. You control it through a powerful, magnificent computer. This computer contains one single computer program. And it's called "reflex". The “programmer” has been working on it for millions of years. Therefore, this program is the height of perfection.
The program contains only a few dozen ready-made, programmed actions. Information about these pre-programmed actions is embedded in exactly the same number of microchips. These microchips are called "effector nerves" and have a "keyboard" consisting of six blocks. Information is entered through them. They are called "sense organs". All these blocks operate independently of each other. And through each of them, only certain information is entered into the biorobot.
- Through the first block, information is entered in the form of light radiation. Or reflected light from objects.
- The second block can only perceive the effects of sound wave vibrations in the air.
- The third block perceives only the pressure of the environment (gas, liquid, solid).
- and 5. The fourth and fifth blocks perceive only chemical influences. One of them is the chemical effects of gases. The second is the chemical effects of solids and liquids.
Information from these “keyboard” blocks is also sent to five very powerful chips, compared to which the coolest and most sophisticated “Pentium” is just a child’s toy. These super-powerful “chips” are called “sensory nerve centers (NC) of the sense organs.” It is these “chips” that are the “heart” of our computer. Because they are the ones who perceive and store the entire wealth of information continuously coming from the “keyboard” blocks—the sense organs. It is they who determine which microchip of the “effector center” to send the electrical command impulse to.
And, it is to the “microchips of effector nerve centers” that ready-made, filtered information from the super-powerful chips of “sensory nerve centers” is sent.
We made such a figurative comparison to imagine how complex and perfect the animal essence of man is. We cannot even imagine the vast array of reactions that occur in our body with any of our actions, with any of our thoughts.
The reader can read about all this in detail, in the language of the physiology of higher nervous activity, in this and subsequent articles.
Reflex arc
The activity of the nervous system is based on reflexes (Latin reflexus - reflected). Reflex is the body's response to a stimulus.
Any reflex exists on the basis of a reflex arc - a set of nerve elements connected to each other, through which a nerve impulse is sequentially transmitted during the implementation of the reflex. The simplest example is the knee reflex, which is often checked by a neurologist, which allows one to quickly draw a conclusion about the safety of the elements of the reflex arc.
Neurons connect to each other using processes: axons and dendrites, at the end of which there are special contacts - synapses, which we studied in detail in the article about nerve tissue.
Reflex arc device
Reflex arcs can be very simple: consist of two neurons, like the reflex arc of the knee reflex (there is no interneuron), or they can include dozens of different neurons.
The reflex arc can be divided into 3 parts:
- Sensitive (afferent, centripetal)
It consists of a receptor (can be located in the skin, internal organs, blood vessels) of a sensory neuron and a sensory fiber coming from this neuron, which penetrates the spinal cord through the dorsal horns.
The body of the sensory neuron is located in the dorsal roots (!) of the spinal cord. Introduced? Now imagine a dendrite running from the tip of your index finger all the way to your spinal cord. That is why it is incorrect to assume that a dendrite is always a “short” process, and an axon is always a “long” one. We discussed this issue in the article about nerve tissue.
Intercalary (associative, intermediate)
Consists of an interneuron and its processes. The interneuron communicates between the sensory and motor parts of the reflex arc. Interneurons can communicate with other parts of the central nervous system.
The bodies of interneurons are located in the dorsal horns of the spinal cord.
Motor (efferent, centrifugal)
Represented by a motor neuron (efferent, executive, motor neuron), from which nerve fibers go to the working organ (effector, executive organ).
Depending on what the effector is - a muscle, a gland - when nerve impulses arrive to it, its work is activated: the muscle begins to contract, the gland begins to secrete.
Motor neurons lie in the anterior horns of the spinal cord, from where their processes emerge.
This may seem obvious, but it must be emphasized that afferent nerve fibers enter the spinal cord through the dorsal roots. Efferent nerve fibers exit the spinal cord through the ventral roots.
Nervous regulation
The reflex arc is the foundation on which the reflex is carried out. In the nervous system, not only processes of excitation occur, but also inhibition, which we will talk about in more detail in the topic devoted to higher nervous activity. Inhibition consists of weakening or delaying excitation that has already arisen.
Thus, coordination and regulation of the processes of excitation and inhibition is the basis for the coordinated work of organs and organ systems that make up a single organism.
Diseases
Paresis (Greek πάρεσις - weakening) is a neurological syndrome caused by damage to the motor (efferent) pathway and weakness in the limb or in another organ that innervated this nerve pathway. Paresis is manifested by a decrease in muscle strength, movements are preserved in an incomplete volume.
Paralysis (Greek παράλυσις - relaxation) is the complete absence of voluntary movements, due to the same reasons as paresis.
Hypothermia may cause paresis of the facial nerve. The reason for this is tissue inflammation, as a result of which the nerve in a narrow bone canal is compressed by inflamed tissue. Nerve impulses partially or completely stop reaching the facial muscles, making it impossible for the patient to move them.
Reflex
A reflex is the body’s response to a stimulus carried out by the nervous system. They are manifested by the beginning or cessation of any activity: muscle movement, gland secretion, changes in vascular tone. This allows you to quickly adapt to changes in the external environment. The importance of reflexes in a person’s life is so great that even their partial exclusion (removal during surgery, trauma, stroke, epilepsy) leads to permanent disability.
I.P. studied the central and peripheral nervous systems. Pavlov and I.M. Sechenov. They left behind a lot of information for future generations of doctors. Previously, psychiatry and neurology were not separated, but after their work, neurologists began to practice separately, accumulate experience and analyze it.
Important Brain pons
How to check?
To find out whether the knee reflex is normal, a simple test is performed. The patient sits on a chair or couch and crosses one leg over the other. The main condition is the free position of the leg that is participating in the test: it should not rest on the floor.
The doctor applies a gentle blow with a neurological hammer to the area just below the knee, where the kneecap ends. The conclusion that the reflex is preserved follows from the immediate contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle and the simultaneous raising of the lower leg.
The impact force may be small, but the leg muscles must be relaxed. If for some reason it is not possible to achieve relaxation and the patient tries to control his reactions, then disinhibiting techniques are used. For example, the subject is asked to mentally perform some kind of computational operation by adding or multiplying certain numbers.
It is worth noting that there are several positions in which the leg relaxes as much as possible. Depending on your health or other specific conditions, the patient may lie down during the test or sit without their feet touching the floor.
In the supine position, the test leg is either held suspended by the doctor, or the patient places one leg on the knee of the other. The knee reflex is assessed based on the angle of deviation of the tibia.
Types of reflexes
Globally, reflexes are divided into conditioned and unconditioned. The first arise in a person in the process of life and are associated, for the most part, with what he does. Some of the acquired skills disappear over time, and their place is taken by new ones that are more necessary in the given conditions. These include cycling, dancing, playing musical instruments, crafting, driving and much more. Such reflexes are sometimes called “dynamic stereotype”.
Unconscious reflexes are inherent in all people equally and are present to us from the moment of birth. They persist throughout life, since they are the ones that support our existence. People don’t think about the fact that they need to breathe, contract the heart muscle, hold their body in space in a certain position, blink, sneeze, etc. This happens automatically because nature has taken care of us.
How to check?
To find out whether the knee reflex is normal, a simple test is performed. The patient sits on a chair or couch and crosses one leg over the other. The main condition is the free position of the leg that is participating in the test: it should not rest on the floor.
The doctor applies a gentle blow with a neurological hammer to the area just below the knee, where the kneecap ends. The conclusion that the reflex is preserved follows from the immediate contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle and the simultaneous raising of the lower leg.
The impact force may be small, but the leg muscles must be relaxed. If for some reason it is not possible to achieve relaxation and the patient tries to control his reactions, then disinhibiting techniques are used. For example, the subject is asked to mentally perform some kind of computational operation by adding or multiplying certain numbers.
It is worth noting that there are several positions in which the leg relaxes as much as possible. Depending on your health or other specific conditions, the patient may lie down during the test or sit without their feet touching the floor.
In the supine position, the test leg is either held suspended by the doctor, or the patient places one leg on the knee of the other. The knee reflex is assessed based on the angle of deviation of the tibia.
Types of reflexes
Globally, reflexes are divided into conditioned and unconditioned. The first arise in a person in the process of life and are associated, for the most part, with what he does. Some of the acquired skills disappear over time, and their place is taken by new ones that are more necessary in the given conditions. These include cycling, dancing, playing musical instruments, crafting, driving and much more. Such reflexes are sometimes called “dynamic stereotype”.
Unconscious reflexes are inherent in all people equally and are present to us from the moment of birth. They persist throughout life, since they are the ones that support our existence. People don’t think about the fact that they need to breathe, contract the heart muscle, hold their body in space in a certain position, blink, sneeze, etc. This happens automatically because nature has taken care of us.
How to trigger the knee reflex?
The occurrence of the knee reflex is due to the fact that when a medical hammer hits the quadriceps tendon, it contracts. This contraction causes the leg to straighten. The blow must be delivered directly under the kneecap, because the quadriceps extensor tendon is attached to the beginning of the tibia. It is not necessary to hit with force, the main thing is that the muscles are as relaxed as possible. You can cross one leg over the other, then when the patellar reflex occurs, it will jerk upward.