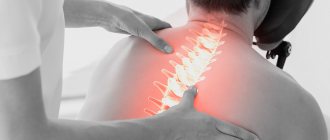
Headache is one of the most common types of neurological disorders according to the World Health Organization. WHO statistics state that half of the world's adult population experiences an episode of headache at least once a year.
Despite its widespread prevalence, the pathology is often not treated properly: many patients prefer not to seek medical help, but to take available painkillers to temporarily numb the pain. But such a decision is dangerous because of its consequences: a headache may not be an independent disease, but a symptom of a serious neurological disorder. What types of headaches exist and which specialist should I contact for treatment?
Why does my head hurt?
Any discomfort that occurs in the body indicates the occurrence of pathological processes, and headaches are no exception. There are many reasons why discomfort occurs. Among the most common:
- violation of the tone of blood vessels supplying the brain;
- poisoning;
- infections;
- fever;
- traumatic brain injury (TBI);
- diseases of the spine.
A headache attack can be triggered by a disturbance in sleep patterns, a change in climate zone, or prolonged physical or intellectual overload. Even a single case of headache indicates some kind of disorder in the body, but if attacks occur regularly, it is recommended to make an appointment with a neurologist.
Headaches can be concomitant symptoms of other diseases: meningitis, sinusitis, sinusitis. If discomfort persists for a long time or is constantly repeated, the patient may have cardiovascular pathologies, kidney disease, or parasitic infestations. Sharp pain in the orbital area can be caused by glaucoma and eye abnormalities.
Only a specialist can determine the exact cause of headaches after examination and additional tests.
Lung diseases.
Pneumothorax (collapsed lung), high pressure in the blood vessels supplying the lungs (pulmonary hypertension), and severe asthma may also cause chest pain. Muscle diseases.
Pain caused by muscle diseases usually begins to bother you when you turn your body or raise your arms. Chronic pain syndrome such as fibromyalgia. May cause persistent chest pain.
Damage to ribs and pinched nerves. Bruises and fractures of the ribs, as well as pinched nerve roots, can cause pain, sometimes very severe. With intercostal neuralgia, pain is localized along the intercostal spaces and intensifies with palpation.
Shingles. This infection, caused by the herpes virus and affecting the nerve endings, can cause severe chest pain. The pain can be localized in the left half of the chest or be of a girdling nature. This disease can leave behind a complication - postherpetic neuralgia - the cause of prolonged pain and increased skin sensitivity.
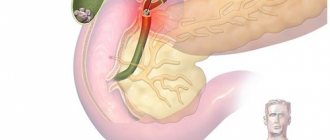
Diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas. Gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) and pancreas (pancreatitis) can cause pain in the upper abdomen, radiating to the heart and much more.
Since chest pain can be the result of many different reasons, do not self-diagnose or self-medicate, and do not ignore severe and prolonged pain. The cause of your pain may not be so serious - but in order to establish it, you need to contact a specialist.
What types of headaches are there?
In neurology, the “International Classification of Headache Disorders” approved by WHO is used. According to the current classifier, there are 13 main groups of headaches, some of which are characterized as primary (that is, being an independent pathology), and some as secondary (occurring against the background of other diseases).
The cause of the primary headache can be:
- vascular in nature - caused by cerebral vascular dystonia and can be different: pulsating, aching, causing a feeling of squeezing and heaviness. Symptoms depend on the characteristics of the pathology: for example, if the venous outflow is impaired, the patient complains of a feeling of fullness, which intensifies when lying down;
- vertebrogenic – caused by spinal pathology, for example, cervical osteochondrosis. In this case, the curvature of the spinal column disrupts the normal nutrition of the brain, which becomes the cause of acute or aching pain;
- Tension headache is the most common type, which is described by patients as a feeling of pressure, a “hoop” or “helmet”. It can occur occasionally or regularly - in this case, neurologists talk about chronic pathology. Develops against the background of autonomic dysfunctions and constant stress;
- migraine - paroxysmal severe pain that appears on one side of the head. Often accompanied by sensitivity to light and smells, nausea, and vomiting. Usually occurs in young people under 35 years of age;
- trigeminal autonomic cephalgia, which includes, for example, cluster pain. It is characterized by sharp painful attacks that occur on one side of the head, alternating with periods of remission. As a rule, the attack is quite short and lasts a few seconds;
- cough - occurs against the background of coughing, sneezing or other physical stress associated with straining. It has a sharp cutting nature, lasts from several minutes to half an hour;
- developing after physical activity - appears exclusively after various exercises, training, running or heavy physical work
A separate classification exists for secondary headaches. According to it, pathology can develop against the background of infections (for example, meningitis), after traumatic brain injuries and neck injuries, with ENT diseases, mental disorders, and depression. A separate category includes headaches that appear from uncontrolled use of painkillers.
For effective treatment, it is necessary to establish the type and cause of the headache. This can be done during an examination by a qualified neurologist.
How is a migraine different from a headache?
Migraine is often called any headache, but this is a misconception. In fact, migraine is one of the types of headaches that has a number of distinctive features:
- pain is localized in one half of the head;
- has a sharp, often pulsating character;
- pain syndrome is accompanied by increased sensitivity to smells and light, as well as nausea, often vomiting;
- an attack rarely lasts longer than a day.
Often before a migraine, patients experience characteristic signs of developing pain: for example, short-term blurred vision, tingling in the fingertips. The disease is more often diagnosed in young people aged 18 to 35 years, women are more susceptible to migraines than men.
Despite the prevalence of migraine, neurologists have not fully established the cause of its occurrence. The main factors associated with the development of migraines:
- heredity;
- vascular pathologies of the brain;
- congenital abnormalities of brain tissue.
An attack can be triggered by stress, an unbalanced diet, lack of proper rest, or sudden intense physical activity. Migraine is one of the most severe headaches, temporarily depriving a person of his ability to work. To stop it, it is necessary to choose the right medications, as well as adhere to preventive measures developed by the observing neurologist.
Why is it dangerous and does it need to be treated?
Even if you are faced with a single attack of mild headache, this indicates the presence of hidden disorders that can develop in the future and lead to various pathologies: for example, vascular disorders. But there are markers indicating that you should contact a neurologist immediately:
- the pain is sudden, intense, and difficult to bear;
- pain appeared after physical labor or sports training;
- you recently had a head injury (severe bruise, blow from a fall);
- headache increases with changes in body position;
- painful sensations are accompanied by other symptoms: blurred vision, numbness of the limbs, goosebumps, nausea, unfocused attention, fever.
An attack can be caused by a stroke, acute poisoning, oxygen starvation of brain cells, or infections. Therefore, it is necessary to make an appointment with a neurologist as soon as possible. The specialist will conduct an initial examination and prescribe additional examinations:
- Doppler ultrasound – ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck and head. Allows the doctor to determine the volume of blood flow, detect fluid stagnation, assess the elasticity of the vascular walls, and so on. Vascular problems are one of the most common causes of frequent pain and dizziness;
- SCT (spiral computed tomography) is a non-invasive examination that allows you to assess the condition of the brain tissue and meninges, detect deviations from the norm, structural abnormalities, foci of inflammation, tumors, bleeding;
- MRI of the brain. Another non-invasive study, painless and safe for the patient. In the images, the neurologist can see pathologies, injuries, paroxysmal conditions, abnormal vasodilation and other abnormalities.
If the infectious nature of the disease is suspected, general tests may be prescribed: for example, urine and blood tests.
You should also consult a neurologist if you periodically suffer from headache attacks. The doctor will determine the causes of pain and select effective therapy to eliminate it.
What does the surgeon look for during the appointment? How is the reception going?
At the initial appointment, the doctor will listen to the patient’s complaints, study the medical history, and collect an anamnesis. If necessary, first aid can be provided or a referral to a hospital can be issued. At the consultation, the surgeon will ask about the presence of injuries, previous operations, then conduct a diagnosis, paying attention to:
- skin for the presence of purulent formations, inflammation, deformations, injuries, neoplasms;
- foot placement;
- position of the spine when bending over and in a sitting position;
- condition of the abdominal organs by palpation of the abdomen;
- how easily the limbs move;
- how the head turns from side to side and back and forth when bending;
- presence of vascular obstruction, varicose veins.
For women, the mammary glands will be examined for the presence of lumps; if there are problems, the doctor will give a referral to a mammologist. During a comprehensive diagnosis, the surgeon may recommend consultations with specialists, as well as laboratory and instrumental studies.
Which doctor should I consult for treatment of migraines and headaches?
If you have episodic or regular headaches, you should consult a neurologist. In order for the doctor to quickly determine the nature of the pathology and establish its cause, be prepared to answer a number of questions:
- in which area of the head the discomfort is localized: in the forehead, in the temples, on the back of the head;
- what is the nature of the pain: pulsating, dull, sharp, migrating, etc.;
- how long ago it appeared and how often it repeats;
- is it accompanied by additional symptoms: sensitivity to light, smells, nausea;
- whether other family members suffer from headaches;
- Do you have a history of birth, traumatic brain injury, neuralgia, or previous neurological infections?
Patients may be advised to keep a special diary in which to record recurring episodes, their triggering factors, duration, and course characteristics. The neurologist may also ask about the daily routine, the nature of work, and lifestyle. After examination and receiving test results, the doctor will accurately determine the type and cause of pain and select the appropriate medicine.
The treatment is complex and is aimed both at relieving attacks of pain (with the help of various analgesics) and at eliminating the root cause of its occurrence. Much attention is paid to lifestyle correction.
Changes in chronic diseases that should alert you and lead to a surgeon
Let's consider the most common reasons for contacting a surgeon and changes in chronic diseases.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum:
- the nature of the pain and/or the time of its onset, whether associated with food or not, has changed;
- the pain now radiates to the shoulder blade, back, shoulder, etc.;
- appetite has worsened or disappeared;
- there is nausea, vomiting;
- the pain no longer subsides after eating or drinking soda;
- body weight decreased;
- taste sensations have changed;
- there is general weakness;
- the stool turned black.
Cholecystitis:
- the nature of the pain has changed;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- pain radiates to the shoulder, back, etc.;
- nausea, vomiting;
- body temperature rises in the evenings;
- the skin became jaundiced.
Is it possible to get rid of headaches using traditional medicine?
Many patients faced with recurrent headaches are in no hurry to consult a neurologist and try to recover with the help of traditional medicine. However, this approach does not lead to a positive result: any self-medication is dangerous. This is due to a number of reasons:
- uncontrolled use of painkillers (even of herbal origin) can lead to serious side effects: disruption of the liver and kidneys, allergic reactions, problems with the gastrointestinal tract. This will not only not relieve neurological disorders, but will also lead to the development of new pathologies;
- The cause of the headache can only be determined after a series of medical examinations. Without this, any therapy comes down to masking the symptoms, while the pathology causing the headache continues to develop.
Therefore, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor and rely on traditional medicine. But patients can actually take some actions that will reduce the frequency of relapses and relieve headache attacks. We are talking about developing healthy lifestyle habits:
- regular physical activity. One of the common causes of headaches is physical inactivity, as a result of which the tone of muscles and blood vessels decreases, the blood supply to the brain tissue deteriorates, and degenerative processes begin. Sports and exercise help strengthen the body and reduce the risk of chronic headaches;
- balanced and varied diet. It is recommended to exclude fast food, fatty, smoked and salty foods from the diet, eat more vegetables and fruits, replace white bread with rye bread or baked goods with bran. A properly selected diet is a good prevention of vitamin deficiencies; it also prevents excess fluid from accumulating in the body, which can increase intracranial pressure and lead to migraines;
- full 8-hour sleep. During sleep, the body recovers and “gets rid” of psycho-emotional stress. Regular lack of sleep undermines a person’s immunity, increases stress levels, and leads to cerebral vascular spasms;
- correct drinking regime. Necessary for maintaining a healthy water-salt balance in the body. Doctors usually recommend drinking up to 2 liters of clean drinking water per day (not counting liquid obtained with other products). During hard physical work, intense physical activity, and in hot weather, the amount of water consumed should be increased;
- regular walks in the fresh air (from 1 hour a day). While walking in parks and forested areas, the body receives the missing physical activity, the blood is saturated with oxygen. This is also important for preventing headaches.
Treatment of chest pain by a neurologist
For various painful symptoms in the thoracic spine, a vertebrologist or neurologist can prescribe emergency, conservative or surgical therapy. Emergency treatment allows you to quickly relieve pain using various spinal blocks. The main goal of drug blockade is to relieve severe pain and enable the patient to either undergo further examination or begin conservative treatment.
Surgical intervention for thoracalgia is a last resort. It is required in rare cases when there are forms of large and advanced hernias that lead to paralysis of the limbs. In most cases, it is possible to treat chest pain using conservative methods:
- prescribing physical therapy to relieve peripheral symptoms and rehabilitate surrounding tissues;
- plasma therapy of the spine to relieve inflammation, restore damaged tissue and improve metabolism;
- acupuncture, which helps to successfully relieve painful processes of varying strength and cope with inflammation of various types;
- droppers with B vitamins;
- laser and vacuum reflexology.
Author: Shogenov Ramish Kurbanovich
Neurologist with 10 years of experience
Is it possible to get rid of headaches and migraines? It is expensive?
If you consult a neurologist in a timely manner, you can completely get rid of headaches. The doctor will select drug therapy and develop preventive recommendations to prevent relapse.
To fully recover, you will need:
- follow medical instructions;
- normalize work and rest schedules;
- get rid of the causes of headaches (concomitant diseases);
- lead an active and healthy lifestyle.
Your health is in your hands! There is no need to think that recovery is expensive. Much of your success depends on how willing you are to change your life for the better and follow your doctor's orders.
1
0
0
Article rating:
5 out of 5 based on 1 rating
Author: Atamanenko Alena Valerievna
General practitioner, endocrinologist, physiotherapist. Second category. Work experience more than 9 years.