Why does the lower back hurt during pregnancy?
Lower back problems are one of the most common problems during pregnancy.
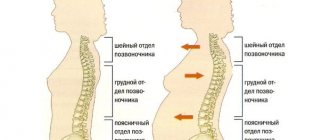
Due to the growing belly, the pelvis tilts forward and the lumbar deflection increases, becoming a violation of posture. This entails pain in the lower back, sacrum, discomfort in the pelvic joints, and increased fatigue. In pregnant women, the center of gravity naturally shifts and the tilt of the head increases, thoracic kyphosis increases, due to which the lumbar deflection (lordosis) increases, and all curves become more pronounced.
From the moment the sperm and egg meet, a mechanism is launched in a woman’s body aimed at carrying out colossal changes.
The internal organs and systems, appearance and emotional state of the expectant mother are rapidly changing under the influence of these processes. And although the stomach becomes the center of increased attention during this period, it is often the culprit for the appearance of many pain sensations in different parts of the body, including pain in the lower back and back.
Why do muscles cramp in pregnant women?
Carrying a child leads to significant changes in the body. In particular, metabolism is rebuilt. As a result, many expectant mothers are faced with magnesium deficiency, which is why cramps appear.
Pregnant women's legs are subject to greater stress due to weight gain. Hence the involuntary muscle contractions that occur in the evenings and at night. They can also be triggered by varicose veins, which often accompany hormonal changes.
Pregnant women often complain about back pain. The lumbar spine is under constant tension, forced to bend under the pressure of the uterus, so such sensations are normal. Therefore, expectant mothers are recommended to lie on their side to relieve the load on the spine.
Causes of back pain during pregnancy
1) Muscle overstretching and hormonal changes.
Under the influence of the hormone relaxin, the immobile pelvic joints and intervertebral ligaments begin to relax and expand. This is how the body prepares for the upcoming birth. In addition, as the fetus grows, the abdominal muscles also stretch and weaken. Therefore, the back muscles begin to work for two, which also causes back pain.
2) Balance imbalance.
As the pregnancy increases, the center of gravity of the pregnant woman’s body shifts forward, which causes tension in the back muscles that are not accustomed to this position.
3) Incorrect posture.
To compensate for the change in the center of gravity, the woman involuntarily begins to stick her stomach forward, while moving her shoulders back. In this position, the spine has to bend strongly.
4) Enlargement of the uterus.
The closer to childbirth, the larger the uterus becomes. It begins to put pressure on the nerve endings and blood vessels surrounding the spine, which is especially felt in the later stages when lying down.
5) Increase in body weight.
An increase of 8-15 kg puts significant pressure on the lower back and legs. Plus, standing or sitting for long periods of time puts a significant strain on the body, and it reacts to this with back pain.
6) Diastasis during pregnancy - separation/divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles
As the uterus expands, the two parallel bundles of muscles (rectus abdominis) that connect the rib cage and pubic bones may separate along the central suture. This separation/divergence can worsen back pain in pregnant women.
7) Stress during pregnancy
Emotional stress can lead to tension in the pelvic muscles, which can be felt as back pain or cramps. You may find that you experience an increase in back pain during stressful periods of pregnancy.
 Other reasons:
Other reasons:
High heels also increase stress on the spine. Problems with the musculoskeletal system in the past are likely to cause lumbar pain: curvature of the spine, hernia, radiculitis, osteochondrosis, poor development of the hip muscles.
Lower back pain during pregnancy can radiate to the leg, intensifying after physical activity, prolonged walking, prolonged standing, or sitting in an uncomfortable position. It can also be a consequence of false Braxton-Hicks contractions - in this case, tension in the uterus is felt and, accordingly, pain in the lower back. Such training contractions in late pregnancy prepare the body for childbirth.
Sources of pain in early pregnancy
Doctors deservedly call the initial months of gestation the most critical, because during this period of time there is a rapid change of events in the body. You need to be aware of the factors that cause back pain during pregnancy in the first trimester. You can’t take all unusual sensations as reasons for concern. To be calm about your health, you should understand what causes natural pain syndromes characteristic of pregnancy, and what feelings indicate defectiveness.
Back pain in early pregnancy can be caused by a number of factors:
- In the first 14 days, the fertilized egg attaches to the uterus. This event usually causes some discomfort in the lower abdominal region. Ladies who are unaware of their situation may mistake discomfort for premenstrual symptoms;
- By 3-4 weeks, you also cannot help but panic, because at this time the formation of tissues for the future placenta occurs. In the first month, villi are introduced into the wall of the uterus, and subsequently the blood supply system to the fetus develops;
- A week later, over 14 days, the muscle layer disappears, which can damage the embryo through spasms;
- The described sensations occur in a woman at 7-8 weeks, when an active hormone called relaxin is produced. This substance affects the joints, allowing tissues to relax;
- The muscle fibers of the uterus actively grow at 9-10 weeks, the mass of this organ increases several times, the shape changes for the qualitative development of the baby;
- Also, painful sensations occur at the end of the formation of all organ systems. This happens at 11-12 weeks, when the first trimester ends.
The presented points are positive for a woman, but there are also negative factors. Sometimes a frozen pregnancy occurs, during which the embryo stops developing. Various inflammatory changes occur in the fertilized egg. At this moment, the body temperature also rises.
Almost always, the back hurts during an ectopic pregnancy, when the fertilized egg begins to form not in the immediate uterus, but outside it. Often a woman with this type of interesting position complains that there is pain in the area of the right side of the abdomen. This condition must be examined by a doctor and given recommendations on further actions with this process.
Severe back pain during pregnancy can be determined by physiological transformations, but can also be a signal of a pathological process. The first semester is the most critical stage for the formation of an embryo, therefore, in case of discomfort, you should go to an experienced doctor who can make a differential diagnosis and answer the question of why your back hurts in the early stages of pregnancy.
How to relieve back pain during pregnancy
In general, “ordinary” lower back pain usually appears in the second or third trimester, and completely disappears only after childbirth. And although there is no special treatment for this condition (except for pain caused by specific diseases), and doctors advise simply to endure this period, you can still improve the situation by doing just a few exercises a day - here are a few of my recommendations for relieving lower back pain:
Yoga for pregnant women is a universal way to relax all areas of the body that, to one degree or another, are stressed during pregnancy. Almost all yoga exercises engage the back muscles, providing a gentle but effective workout to strengthen your back.
Choose back exercises that don't cause too much discomfort and are easy for you to do. It is important to remember that the better a woman’s physical fitness, the easier labor will be for her and the faster her previous form will be restored.
Causes of pain
If an ovarian cyst hurts, this most often indicates the occurrence of a number of problems or complications of the condition. If you ignore the gynecologist's recommendations, discomfort may appear during:
- Active sex.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Injuries and impacts to the pelvic area.
If a woman followed all the recommendations, then the appearance of pain may indicate:
- Changing capsule sizes.
- Cyst rupture.
- Twist the legs.
These conditions require emergency intervention and constant medical monitoring, so if discomfort occurs, you should immediately seek help.
Exercises for back pain during pregnancy
The second trimester is the best time to work on the muscles of the pelvic girdle.
Training the pelvic floor muscles allows the sacral bone to take the correct position, stretches the muscles of the groin area and gives a slight turn of the legs outward, which makes the legs straight and also improves the situation with flat feet.
Weak pelvic floor muscles cannot hold the pelvis in an upright position. Over time, the pelvic floor descends, along with it the pelvic organs descend and their blood circulation is disrupted.
Here are some example exercises:
1) Lie on your back, tense your pelvic floor muscles as you exhale, and relax as you inhale. Feel how the perineum retracts and returns.
2) Lying on your back, bend your knees, do not press your lower back to the floor, let it lie naturally. Tighten your pelvic floor muscles as you exhale, feel your lower back lower towards the floor.
In the last months of pregnancy, you need to be especially careful when performing exercises. During this period, the baby takes the correct position for childbirth; the “cat” exercise will help him in this.
Cat Pose:
While kneeling, lean on your forearms and sway smoothly from one side to the other. It is also good, when portraying a cat, in the same position, turn your head first to the left and look over your shoulder at the buttocks, then to the right, as if you were looking for a tail.
You can arch your back like a cat, while tensing the muscles of your abdomen and buttocks, and then relax, returning to the starting position. This exercise helps train the oblique abdominal muscles and relaxes the lower back.
Lateral Pulls:
We lie down on our right side. We rest our left foot on the right ankle. For convenience, surround yourself with pillows or a blanket and make yourself more comfortable. And stretch slightly, clinging to the floor with your right hand as far away from you as possible. Feel the right side of your body stretch and lengthen. If you feel so comfortable, then try to stretch your arm so that your elbow does not touch the floor and raise your legs above the floor. Then repeat on the other side.
Paschimottanasana.
During pregnancy, you should not bend forward deeply or lie on your stomach. Therefore, expectant mothers should perform a variation of Paschimottanasana. We sit in dandasana, exhale and clasp our big toes (if possible). We place our feet hip-width apart. We lower our shoulders down, try to connect our shoulder blades behind our backs, and keep our spine straight. This asana stretches the spine well and relieves back pain, which often occurs during pregnancy.
Urdhva paschimottanasana.
This pose perfectly stretches the spine, eliminates back pain and strengthens muscles. Lying on your back, bend your knees, place your palms on your feet and pull your straightened or semi-straightened legs behind your head. Do not try to place your feet on the floor behind your head; your pelvis should only slightly lift off the floor. Feel how your spine stretches. Hold for 15-30 seconds and slowly lower down.
Stretching:
It is important to remember about stretching during exercise. Stretching during pregnancy is needed, surprisingly, for relaxation. A muscle has two states: tense and relaxed. In an untrained person in a calm state, some muscles seem to tense by themselves. We don’t feel it, but in the evening there comes an inexplicable fatigue, heaviness throughout the body. A stretched muscle cannot be tense - therefore, by doing stretching exercises, we help the body “remember” how to relax.
Urgent medical care
When diagnosing a tumor, it is very important to visit your doctor regularly. Cyst rupture, leg torsion and malignancy require emergency medical care and hospitalization. When torsion or rupture occurs, the following symptoms occur:
- Ovarian cyst colitis.
- Painful sensations intensify and become more intense.
- The area where the formation is located increases in size and swells.
- After sudden movements or intimacy, the pain intensifies and is pulsating.
- Discomfort spreads from the lower abdomen to the lumbar region and sacrum.
- There is a feeling of weakness, vomiting is possible.
- Body temperature rises.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. As a rule, the specialist insists on hospitalization and performs diagnostic laparoscopy. If necessary, the complication can be removed immediately. The recovery period after laparoscopic intervention is 5 days.
If a woman arrives in serious condition, abdominal surgery with removal of the ovary may be required. In this case, the recovery period will be from 1 to 2 weeks, depending on the complexity and volume of the intervention.