Osteochondrosis
is a concept used to designate a group of diseases associated with degenerative and dystrophic changes in the structures of the spine.
First of all, the intervertebral discs suffer, and as the disease progresses, the vertebrae themselves. Degenerative
are changes associated with the processes of tissue wear, aging, loss of original properties, and
dystrophic
are changes caused by tissue nutritional disorders.
Thus, the term osteochondrosis unites most non-inflammatory spinal pathologies. Osteochondrosis of the spine
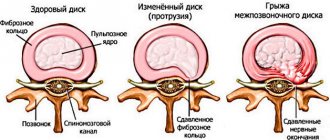
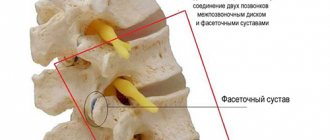
The spine forms the basis of the skeleton, connecting the various parts of the skeletal system. It supports the head, ribs and muscles are attached to it. The spinal cord passes through the spinal column, through which the brain is connected to various parts of our body. Man is the only upright creature in the world, and the spine is designed to ensure upright walking. Therefore, the spinal column has a curved shape, reminiscent of the letter S of the Latin alphabet and is not a rigid rod, but a complex structure consisting of elements fastened together - vertebrae. This structure of the spine allows us to perform various movements, be flexible and absorb shocks and shocks. The function of shock absorbers is performed by intervertebral discs - cartilaginous layers consisting of the nucleus pulposus and the fibrous ring surrounding it. The core takes on the load and absorbs it, and the fibrous ring prevents the core from flattening under pressure.
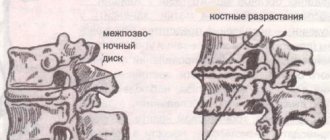
A decrease in the elasticity of the intervertebral discs can be the beginning of a wide range of problems. Unable to withstand the load, the intervertebral discs begin to deform and the spine loses its correct shape. The progression of the disease leads to further destruction of the intervertebral discs, the fibrous ring is torn, the vertebrae come into rigid contact with each other, and pinching of the nerves connecting the spinal cord with various parts of the body becomes possible. This is how osteochondrosis develops. Intervertebral hernias occur, and inflammation often develops. Deprived of shock absorption, the vertebrae can become flattened, and together their joints form scar and bone growths.
Osteochondrosis is one of the most common diseases. Only cardiovascular diseases are more common. According to some estimates, every second person on the planet suffers from osteochondrosis. Osteochondrosis is more common in women, but in men its manifestations are on average more painful.
What is osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis: parts of the spine
Osteochondrosis affects various parts of the spine. Depending on which department suffered the most, there are:
- lumbar osteochondrosis – most common;
- cervical – ranks second in “popularity”;
- sacral;
- chest;
- widespread osteochondrosis, which affects several parts of the spine at once;
- cross pathologies (lumbosacral or cervicothoracic).
Pain due to lumbar osteochondrosis
This species, according to statistics, accounts for half of the total diversity of the disease. And if with its thoracic variety the organs suffer less, since they are surrounded and held by the ribs, then the picture is completely different with the lower back. There are many nerve endings here, so the pain will be severe and sharp. Possible acute, subacute and chronic course. Acute pain syndrome in lumbar osteochondrosis is called lumbago or lumbago. At the same time, the person, as they say, cannot breathe or gasp, his lower back burns or goes numb. The duration can be up to a week, and from time to time, if a person is hypothermic, turns sharply, or physically works for a long time, it can come again and last a whole month. Irradiation is observed in the leg, buttock, and sacrum.
Causes of osteochondrosis
The causes of osteochondrosis are quite varied.
Firstly, with age, the elasticity of the intervertebral discs is gradually lost.
This means that our back requires special attention. Prolonged stay in a position that causes spinal misalignment can cause irreversible changes. You should avoid sitting in an asymmetrical position, fight the habit of lying on only one side, and carrying a load (for example, a bag) in only one hand.
A sedentary lifestyle has a detrimental effect on the health of the spine. It is necessary to move, but physical activity should be moderate. The spine should be given the opportunity to recover after stress, and it is also advisable to avoid injuries that also lead to the development of spinal pathologies.
The second group of reasons is associated with metabolic disorders
and
poor nutrition
. Food rich in carbohydrates and fats saturates the body with calories, which we, in our sedentary city life, often simply have nowhere to spend; As a result, energy is stored as fat tissue, creating excess weight. Obesity is an increased load on the spine, which leads to the development of osteochondrosis. In addition, such a diet usually contains insufficient amounts of microelements (calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese and others), which are so necessary to strengthen bone tissue. Endocrine diseases are often the cause of excess weight. At the same time, a violation of energy, water or mineral metabolism can also negatively affect the tissues involved in the structure of the spine.
Factors contributing to the development of osteochondrosis may be:
- flat feet;
- hormonal changes;
- infectious diseases;
- local circulation disorders,
as well as some other factors.
Medicines
The main goal during exacerbation of osteochondrosis is to relieve inflammation and accompanying pain and muscle spasm. To do this, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed in combination with muscle relaxants, which reduce the tone of skeletal muscles, reduce muscle spasms and compression of the nerve roots. Preparations of B vitamins help improve the condition of the nerve roots. Typically, the course of treatment lasts 7-10 days. Taking medications internally is supplemented with local treatment: ointments or gels containing NSAIDs or simply warming ones are applied to the affected area to increase blood supply, metabolism and quickly stop inflammation. External remedies quickly relieve pain, since the active substance penetrates the source of inflammation, bypassing the digestive system and general blood flow, but they are not enough for full treatment.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis - treatment at JSC Family Doctor
At the initial stage of osteochondrosis, there are no pronounced symptoms. The development of osteochondrosis can be assumed in the following cases:
- dull painful sensations in the back (in the affected area of the spine);
- feeling of heaviness in the back, constant tension in the spinal muscles;
- muscle numbness, the appearance of “goosebumps”. In such cases, they usually say that “the back is numb”;
- crunching when turning the body and neck;
- headache, dizziness, tinnitus (typical of cervical osteochondrosis);
- aching pain in the chest area (typical of thoracic osteochondrosis).
At the first appearance of such symptoms, it is advisable to undergo examination by a neurologist.
Further development of the disease manifests itself in symptoms that cause significant discomfort:
Back pain
There is severe pain in the back (along the spine). The pain may radiate to the limbs.
Numb fingers
A typical manifestation of osteochondrosis is numbness of the fingers and toes.
Limitation of physical activity
Even with minimal physical activity, the pain intensifies (for example, as a result of shaking and jolts when traveling in transport). Pain leads to significant limitations in mobility and physical activity.
Osteochondrosis of the lower extremities: what is it and how to treat it?
As a rule, the initial stage of the disease is difficult to recognize; there are practically no symptoms that would raise suspicions that something is happening to the joints. A person seeks the help of a specialist only when the cartilage tissue is already affected. This means that intense pain appears in the legs, and a crunching sound is heard when the patient bends or straightens the joint. There is a feeling of stiffness.
Medicines, massages, physiotherapy, and orthopedic products are often used to treat the disease. If this does not help, surgery will be performed.
Characteristic features of the disease
The main feature is that osteochondrosis of the lower extremities primarily affects cartilage. They do not receive enough nutrients, and they lose their elasticity, becoming rough, even cracked. Because of this, the joints cannot move smoothly when touching, which leads to even more damage to them. Over time, bone structures undergo deformation and osteophytes appear. They grow and shift, which leads to damage to soft tissues, pinching of nerve endings and blood vessels.
At risk are people who often experience intense physical activity, are overweight, lead a sedentary lifestyle, have joint injuries, or spinal diseases.
, flat feet.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the legs
At first, a person does not experience alarming symptoms, thinking that the feeling of discomfort in the legs is caused by fatigue. But since over time the cartilage lining is increasingly destroyed, severe pain occurs. And they can begin due to any sudden movements, heavy lifting, or a long fixed position of the body.
- Painful sensations. At first, mild pain gradually develops into severe and incessant pain. They appear not only as a result of activity, but also at night, which does not allow a person to get enough sleep and rest. During periods of exacerbation, pain is felt throughout the leg, even in the lower back.
- Inflammatory processes of the synovial membrane. Swelling appears in the places where the joint is located, the skin becomes hotter relative to other parts of the body. On palpation, a round-shaped compaction is felt, and fluid accumulates inside it. Children and weakened patients experience fever, chills, and gastrointestinal disorders due to synovitis.
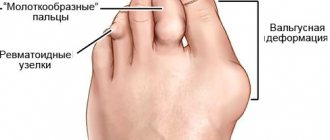
- Deformed joints. If the disease has reached a severe stage, then the patient’s lower limbs noticeably increase in size, which in turn can lead to their curvature, valgus deformity, etc. Because of this, a person’s gait becomes uncertain.
- The appearance of crunching and clicking sounds. When the disease occurs, cartilage, which is normally smooth and elastic, becomes rough, which prevents it from sliding. They seem to “cling” to each other, which leads to a characteristic sound in the form of a click or crunch.
- Limitation of mobility. The joint space becomes fused, muscle spasms and flexion/extension contractures occur, which is why the person can no longer move as before. Often the patient himself tries to move less so as not to experience pain. Sometimes the cause of limited joint mobility is swelling due to inflammation.
- The occurrence of paresis. Osteochondrosis becomes a consequence of a syndrome such as hepaesthesia, since the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted. Sensitivity decreases, and the person feels it as numbness. This provokes the occurrence of various disorders associated with limb mobility. The patient feels numbness in the legs, sometimes a burning sensation or even cramps at night. Often osteochondrosis of the lower extremities provokes paresis when the muscles become weak. In severe cases, the person cannot move their legs as if they were paralyzed.
How is osteochondrosis of the legs treated?
The principle of treatment for all osteochondrosis is the same: it is necessary to rid a person of muscle weakness, improve blood flow, eliminate pain, etc. It is recommended to take medications, massage, physiotherapy, etc. It is necessary to do everything in combination, in which case the treatment will have an effect. During periods of exacerbation, you should not move much. To stabilize the affected joint, it is sometimes necessary to wear special orthopedic devices. If, for example, there is minor damage to the cartilage, then the patient should wear an elastic bandage, and if the damage is serious, a semi-rigid or rigid orthosis.
- Application of ointments. Used in remissions or subacute conditions. Often these are ointments with analgesic, anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects. As well as products with local irritant properties to improve blood flow.
- Use of glucocorticosteroids, chondroprotectors.
- Dieting. Spices, salt, spices, baked goods, smoked meats, and semi-finished products are excluded from the diet.
- Manual therapy and acupuncture.
- Massage.
- Physiotherapy.
- Exercise therapy.
ethnoscience
During periods of remission, you can turn to traditional medicine.
- Chop young horseradish/cabbage leaves and mix with honey. Place on the joint, cover with cellophane and then with thick cloth. Wear for three hours.
- Collect horse chestnut flowers, dry and chop. Pour 1 tsp. flowers with a glass of hot water. Drink 30 ml three times a day after meals.
- Collect dandelion leaves, grind until smooth and apply to the joint. Wrap with film and warm cloth. Wear for two hours.
- You can prepare an ointment from 50 g of baby cream (good fat content) and wheat germ oil. Add dry mustard, turpentine, sea salt to them - only 1 tsp each. + two drops of thuja oil.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Methods for diagnosing osteochondrosis
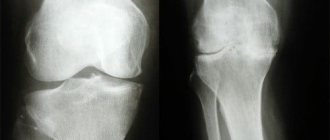
The main role in the diagnosis of osteochondrosis belongs to instrumental studies: radiography, computed tomography, MRI.
It may be necessary to confirm that the symptoms observed are not caused by other diseases. For the purpose of differential diagnosis, general and biochemical blood tests, general urinalysis, and ultrasound examinations of internal organs are performed.
X-ray of the spine
X-rays of problematic parts of the spine are taken. Which department needs to be examined is determined based on the patient’s complaints.
More information about the diagnostic method
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography (MSCT) makes it possible to obtain a more informative picture of pathological processes and determine the degree of their severity. In particular, MSCT can detect intervertebral hernia.
Computed tomography is performed in cases where radiographic data is insufficient.
More information about the diagnostic method
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI is the most informative method for diagnosing osteochondrosis. In some cases (for example, if osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is suspected), MRI cannot be avoided. Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to visualize cartilage and soft tissue, based on which you can localize the source of problems as accurately as possible and determine the cause of the disease.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.