Detailed description of the study
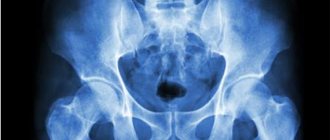
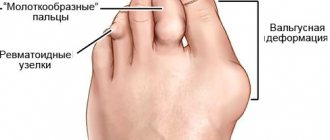
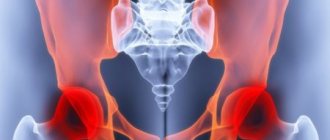
There are a large number of different joint diseases. Among them are often found: rheumatoid arthritis, gout, post-infectious joint damage. Inflammation in the joints is manifested by swelling, tenderness, redness and a local increase in temperature in the affected area. Patients often experience pain and impaired joint mobility. In the future, their deformation, destruction of cartilage tissue, and narrowing of the joint space may occur. Some diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, also have systemic manifestations: a person notices pathological weakness, fatigue, weight loss, and fever.
It can be difficult to make a differential diagnosis of joint diseases due to similar symptoms. Laboratory tests help establish the correct diagnosis.
This study contains two tests necessary to identify the cause of joint inflammation:
- C-reactive protein;
- Uric acid.
C-reactive protein (CRP) is one of many molecules involved in immune responses. CRP is detected in the blood of patients during various inflammatory processes and is considered a marker of the acute phase of their course. An increase in CRP levels is observed within the first four hours after tissue damage and reaches a peak after 24–72 hours.
The content of CRP during inflammation can be increased by 20 times or more. The most common joint diseases that are accompanied by increased CRP are:
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Gout;
- Reactive arthritis.
CRP is also a marker of disease activity.
It should be noted that determining the level of CRP plays an important role in assessing joint inflammation, but is not a specific marker for this group of diseases. The indicator may reflect inflammation of another localization, including against the background of acute infections, injuries, and others.
Uric acid is one of the main products of protein metabolism in the human body. This substance is mainly excreted in the urine. When there is an excessive level of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia), deposition of its salts (urates) is observed with the formation of crystals. The latter are deposited in joints, subcutaneous tissue, and kidneys (where urates can form stones).
Gout is a systemic pathology, which is characterized by the accumulation of monosodium urate crystals in the joints, as well as other organs and tissues. An increase in uric acid levels suggests that joint inflammation is associated with the development of this disease.
Thus, this comprehensive study will help the doctor in differential diagnosis of the causes of joint damage and selection of therapy.
It is necessary to donate venous blood for analysis. Often the complex is prescribed in conjunction with other studies, such as general analysis and blood biochemistry, to check other organs and systems.
A detailed description of the studies and reference values are presented on the pages with descriptions of individual studies.
Radiography
Radiography
One of the most common methods of visualizing the structures of the knee, which is used for the primary diagnosis of injuries to the knee joint, is radiography. The essence of the technique is that X-rays are able to penetrate the tissues of the body. In this case, on X-ray film or a special screen, the doctor can see dense structures (bones, ligaments), through which X-rays pass less well.
To obtain a better result, radiography is performed in frontal and lateral projections. This imaging method cannot detect small changes, so other methods are often used in addition. X-rays are used to diagnose damage to the meniscus of the knee joint, fractures or dislocations.
CT scan
An X-ray research method that has high resolution and makes it possible to visualize even minor pathological changes in the knee is called computed tomography. Using special equipment, layer-by-layer scanning of tissues is carried out, after which digital processing of the resulting images is performed on a computer with 3D modeling of the structures.
Computed tomography is used to diagnose pain in the knee joint, the development of which has an unclear origin. Also, using CT, visualization of the ligamentous apparatus is performed. This diagnosis of the knee joint ligaments makes it possible to identify small tears in individual connective tissue fibers without violating the anatomical integrity.
Diagnosis of the meniscus of the knee joint is performed if a traumatic or pathological injury is suspected.
Magnetic resonance imaging
The magnetic resonance imaging method is based on layer-by-layer imaging of tissues, based on the physical principle of resonance of the nuclei of atoms of organic compounds arising in a magnetic field. This type of study allows you to visualize even minimal changes in tissue.
For example, diagnosing osteoarthritis of the knee joint (a degenerative disease accompanied by the destruction of cartilage) using magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to identify the pathological process even before the development of irreversible changes in the cartilage tissue.
The main disadvantage of this research method is the impossibility of carrying it out if there are metal implants in the patient’s body.
References
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical recommendations. Association of Rheumatologists of Russia, 2021. - 102 p.
- Rheumatology: National Guide / ed. E.L. Nasonova, V.A. Nasonova. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. - 720 p.
- Kishkun, A.A. Guide to laboratory diagnostic methods. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - 800 p.
- Internal diseases in 2 volumes: textbook / ed. ON THE. Mukhina, V.S. Moiseeva, A.I. Martynova, 2010. - 1264 p.
- Kasper, D., Fauci, A., Hauseret, S. Harrison`s Principles of Internal Medicine 19/E (Vol.1). McGraw-Hill Education, 2015.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound diagnostics of the knee joints allows you to determine the condition of tissues that cannot be visualized using x-ray examination techniques. These include the connective tissue capsule and ligamentous apparatus. In particular, with the help of this study, a qualitative diagnosis of knee ligament rupture is carried out.
This technique also allows you to determine the amount of synovial fluid in the cavity, which can increase with various inflammatory pathologies.
Under ultrasound control, additional medicinal substances (hyaluronic acid, anti-inflammatory drugs) can be injected into the cavity using a special needle. Diagnosis of arthrosis of the knee joint makes it possible to administer drugs using ultrasound control.
Arthroscopy
If there is damage to the knee joint, diagnosis using arthroscopy directly assesses the condition of the internal structures and capsule.
How the research is carried out
Upon entering the office, the patient needs to take off his shoes, pants and socks and lie down on the couch. A special gel is applied to the skin of the area under study to facilitate contact of the sensor with the tissue. Next, you should be careful and follow all the specialist’s requests. To obtain a complete clinical picture, a change in body position may be required. The doctor examines the condition of the joint in various projections:
- Anterior projection - visualizes the joints of the tibialis muscle, extensor pollicis longus, the muscles of the anterior surface of the leg themselves, as well as the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus.
- Medial location - makes it possible to examine the posterior tibial muscle, deltoid ligament and tibial nerve, diseases of which are often accompanied by discomfort.
- Lateral approach—provides access to the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis tendons and most surrounding tissues.
- Posterior localization - allows you to evaluate the structure and general condition of the Achilles tendon, calcaneus and plantar aponeurosis.
On average, the examination is completed in 15-20 minutes, after which the patient is given a research protocol and referred to a doctor for deciphering and prescribing therapy if abnormalities are found during the ultrasound examination.
TREATMENT
There is no cure for arthritis. But, there are a number of procedures that help relieve pain. No surgery
Lifestyle changes: Reducing the load that worsens the condition. For example, climbing stairs. Switching from one sport to another, in which the intense load is less. For example, replace jogging with swimming or cycling. Losing weight helps reduce the load on the knee joint. As a result, pain is reduced and the functioning of the joint improves.
These tips can help reduce stress on the knee joint and slow the progression of arthritis.
X-ray method
The easiest and most accurate way to diagnose arthrosis is with an X-ray. It will show signs characteristic of one or another stage of the disease:
- Stage 1. The image does not yet show bone growths, but the surface of the joint is uneven, sometimes with slightly ossified areas. The joint space is slightly narrowed, so external symptoms are not yet pronounced.
- Stage 2. Bone growths are already clearly visible, the gap is approximately 2-3 times narrower than normal. The specialist notes subchondral sclerosis - one of the signs of arthrosis, hardening and proliferation of bone tissue.
- Stage 3. The picture does not show the joint space at all. Most of the articular surface has ossified and increased due to marginal growths. One of the signs is a “joint mouse,” the movement of a fragment of the meniscus, cartilage or bone, which radically limits motor activity.
Only x-rays can accurately determine the degree of arthrosis
In what cases is an ultrasound scan prescribed?
Pain, an unpleasant nagging pain or limited joint mobility are very alarming signs that can signal various diseases. In order for the doctor to determine further treatment tactics, he needs complete information about the condition of the joints, their structure, size and integrity. For this purpose, it is recommended to undergo ultrasound diagnostics.
As a rule, examination is recommended in the following situations:
- Trauma, blow or damage to the ankle joint;
- Suspicion of degenerative diseases of cartilage tissue (arthritis, arthrosis);
- Severe pain or limitation when moving the joint;
Also, an ultrasound examination of the ankle joint is often prescribed before and after surgery in order to determine the dynamics of treatment.
What can be detected on an ultrasound examination of the ankle joint?
- Joint rupture. Usually, when the integrity of the ankle joint is damaged, it is difficult for the patient to move his leg - the movement is accompanied by severe pain. The ligament and adjacent tissues become thicker, and motor activity is impaired. Fatty tissue has echogenicity within normal limits, and against this background the affected areas are clearly visible.
- With a partial rupture of the ligament, you can see an area with impaired echogenicity, usually reduced - in this case we are talking about internal hemorrhage and swelling of the tissue.
- When a tendon ruptures, a hypoechoic area (an area of reduced echogenicity) is visible. You may notice the presence of an abnormally large amount of fluid. There is a significant disturbance in the course of the fibers and their intermittency. Effusion accumulates in the synovial area.
- With tendonitis, there is an accumulation of effusion, but without disruption of the structure of the tendon itself, the tendon itself has no structural changes. Most often in such situations, a diagnosis of tenosynovitis is made.
- With rheumatism, an ultrasound examination clearly shows a change in size, the contours become blurry, and the joints narrow significantly.
- Hygromas are often detected during ultrasound examination: they are limited in length, the edges are rounded, and the contours are unclear.
- After joint surgery, ligatures with impaired echogenicity are noted during diagnosis. The transition from the acute stage of the pathological process to the chronic one has some features: the structure of the tendon is heterogeneous, sometimes granular.
Remember that early contact with a specialist significantly increases the chance of full recovery without the risk of relapse. When serious diagnoses are made, the patient may be referred for repeated diagnostic procedures, for example, CT or MRI.
Where to go?
Do you want to get tested at the clinic on Nakhimovsky Prospekt? Contact ENEL-CLINIC. We see experienced specialists who develop an individual diagnostic and treatment program for each patient. You will be able to undergo various tests and get consultations with doctors at a convenient time, without queues or waiting.
We are located in the Nagornaya metro area. It is more convenient to travel by car from Sevastopolsky Avenue. You will find the exact address and telephone number in the “Contacts” section.