Our license
Our doctors
Prices
Ultrasound of joints is a common, informative and safe method for diagnosing disorders in articular structures. The absence of ionizing radiation allows it to be used even in childhood. Using ultrasound, it is easy to monitor the progress of treatment and its effectiveness.
One of the advantages of the method is the ability to study the soft tissues of joints, most connective tissue structures, the vascular network and nerve formations.
Why is ultrasound of joints necessary?
The hip and knee joints are the most vulnerable in the human body. During movement, they are subject to enormous impact. Lifting weights, sports, jumping and falling - all this often leads to injuries and the development of inflammatory, degenerative changes in cartilage tissue.
Ultrasound of joints allows you to assess the degree of damage to structures, make prognoses for recovery and choose a treatment method. The study allows us to study the properties of the interarticular fluid, which is beyond the power of other diagnostic methods.
Unlike radiography, ultrasound can be used many times without fear for the patient's health. It provides comprehensive information about the nature of the injury or inflammatory disease.
Young children often have abnormalities in the development of the hip joint. Ultrasound of the hip joints is performed mainly during the neonatal period. The main indication is dysplasia . The prerequisites for them may arise during intrauterine development, but deviations often appear after birth injuries.
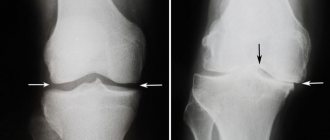
Ultrasound of the knee joints is the main method for diagnosing injuries in athletes. Meniscus tears are a common injury for all people actively involved in outdoor sports.
What does ultrasound equipment look like?
Ultrasound scanners consist of a console containing a computer and electronics, a video display screen, and a transducer that is used to scan. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone, attached to the scanner by a cord. Some exams may use different transducers (with different capabilities) during the same exam. The transducer sends high-frequency sound waves (which the human ear cannot hear) into the body and then listens for return echoes from the body's tissues. The principles are similar to sonar used by ships and submarines.
The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video image screen that looks like a computer or television monitor. The image is created based on the amplitude (loudness), frequency (pitch) and time it takes for the ultrasound signal to return from the area in the patient's body that is being examined. The information then goes to a transducer (a device placed on the patient's skin to send and receive the returns). sound waves). The type of body structure and the composition of the body tissue through which sound passes are immediately obtained. A small amount of gel is applied to the skin to allow sound waves to travel from the transducer to the area of interest inside the body and then back again. Ultrasound is an excellent modality for some areas of the body, while other areas, especially the air-filled lungs, are not well suited to ultrasound.
Indications for ultrasound examination of joints
Indications for ultrasound examination of joints are:
- trauma (fresh injury or history of injury);
- systemic diseases;
- autoimmune diseases;
- inflammatory, acute and chronic diseases;
- obesity;
- endocrine pathology;
- osteochondropathy (if suspected based on clinical manifestations or confirmed x-ray);
- pain in the joint(s);
- restriction of movements in the area of the joint (joints);
- increase in the volume of the joint (joints), swelling;
- screening study of hip joints in newborns at risk;
- suspected hip dysplasia in newborns;
- suspicion of dislocation (subluxation) of the hip joint in newborns and children up to the first year of life;
- dynamic observation during therapy for dysplasia, dislocation, subluxation of the hip joint in children under the first year of life;
- muscle pain;
- palpable mass formations in the soft tissue area;
- dynamic observation during treatment for inflammatory diseases of joints and tendons (arthritis, tendinitis, tenosynovitis);
- dynamic observation during therapy of traumatic damage to muscles, tendons, ligaments (partial and complete ruptures, sprains);
- suspicion of Becker's cyst;
- suspected rupture of a Becker cyst;
- dynamic observation of bursitis (bursitis).
How is the procedure performed?
For some musculoskeletal ultrasound examinations, the patient may sit on an examination table or swivel chair. For other ultrasound examinations, the patient is positioned face up or face down on a couch. The radiologist or sonographer may ask you to move or guide the limb being examined to evaluate the anatomy and function of the joint, muscle, ligament, or tendon.
Most ultrasounds of infants and children are performed with the child lying on his or her back on a couch, but a different position may be required.
Once you are on the examination table, a radiologist (a doctor specially trained to observe and interpret x-rays) or sonographer will apply a warm, water-based gel to the area of the body being examined. The gel will help the sensor make safe contact with your body and eliminate air pockets between the sensor and your skin that could block sound waves from entering your body. The transducer is placed on the housing and moved back and forth across the area of interest until the desired images are captured.
As a rule, there is no discomfort from pressure when pressing the sensor on the area being examined. However, if the scan is performed in an area that is too sensitive, you may feel pressure or slight pain from the transducer.
Once the image is acquired, clear ultrasound gel will be wiped off your skin. Any parts that are not washed dry quickly. Ultrasonic gel does not typically stain or discolor clothing.
What diagnoses can be made based on the results of the study?
Depending on what the ultrasound shows, the doctor can diagnose diseases such as:
- Osteoarthritis.
- Knee arthrosis.
- Arthritis, synovitis, tendinitis.
- Disease associated with the meniscus.
- Various ligament injuries, such as sprains.
- Fracture, both open and closed.
- Congenital disorders of the knee joint. Various neoplasms.
The advantage of ultrasound examination is that the patient can receive the examination results five minutes after the procedure. Based on the results of the ultrasound, the doctor who gave the referral for this procedure can confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
How does this procedure work?
Ultrasonic imaging is based on the same principles as sonar used by bats, ships and fishermen. When a sound wave hits an object, it bounces back or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, one can determine how far away an object is, as well as the size, shape, and consistency of the object (whether the object is solid or filled with liquid).
In medicine, ultrasound is used to detect changes in the appearance, size or contour of organs, tissues and blood vessels, or to detect abnormal masses such as tumors.
In an ultrasound scan, a transducer sends sound waves into the body and receives echo waves. When the sensor is pressed against the skin, it sends small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As sound waves bounce off internal organs, fluids and tissue, a sensitive receiver in the transducer records tiny changes in sound and sound direction. These signal waves are instantly measured and displayed by a computer, which in turn produces a real-time image on a monitor. One or more frames of moving images are usually captured as still images. Short videos (image streams) can also be saved.
Preparing for the examination
During the consultation, SM-Clinic doctors always give detailed recommendations on preparing the child for the examination. Ultrasound is a quick and painless procedure that does not require special preparatory measures and has virtually no contraindications.
The child should be brought to the procedure in loose clothing, which can be quickly removed if necessary to give the doctor access to the knees. It is also recommended to feed the baby about an hour before the visit so that he is full, and immediately before the procedure, take him to the toilet. Thanks to this, the little patient will feel as comfortable as possible and will not become capricious.
A child over three years old should be explained why he is going to the doctor and how the procedure will be carried out. You should tell him in detail about the manipulations and convince him that the procedure will be quick and painless.
Reasons for formation
Factors influencing the formation of an anechoic formation largely depend on its location. Causal factors vary significantly from case to case. It depends on the organ in which the process developed. A cyst that has an anechoic property often appears at an age considered reproductive. After menopause, it occurs much less frequently. Ovarian tumors in this case are rare due to decreased estrogen levels. In this case, the formations are more often benign in nature.
It is not always possible to pinpoint the exact cause of tumor growth.
The most common factor is considered to be hormone imbalance. It has a bad effect on the performance of the ovaries. After menopause, a cyst in the ovaries is possible due to inflammation, postoperative adhesions, or injury.
Urologists also cannot explain the reason for the appearance of a renal cyst. But some nephrologists argue that the culprit for the appearance of cystic elements is the improper development of the fetus in the mother’s womb. In addition, these formations can occur due to inflammation of the renal pelvis, stones formed in the kidneys, as well as due to infection of the organ.
Cysts on the ovaries most often form during reproductive age.
Anechoic formation that appears during pregnancy
During pregnancy, this formation is often detected at short notice:
- Before the sixth week of gestation, the baby is found at the top of the uterus. This is a fertilized egg. When performing an ultrasound, a hyperechoic rim is visible at the edges of the formation.
- In the ovary, a dark spot indicates the presence of a luteal or sometimes a follicular cyst. These formations subsequently resolve on their own.
- Ultrasound shows the same picture with the formation of a paraovarian cyst - a cavitary single-chamber neoplasm. It grows from the ligaments connecting the ovaries to the uterus.
During an ultrasound, the corpus luteum is also identified as a black spot. Thus, when identifying formations in the uterus, you should not panic. A dark spot may indicate the development of a normal pregnancy, indicate a corpus luteum or the appearance of a cyst that will disappear without intensive treatment.
Luteal and follicular cysts do not require treatment and resolve on their own
Complications and prognosis
If the visit to the doctor occurred at an early stage of development of the anechoic area, then the patient can get rid of it quite quickly. Only a doctor, after conducting research, will be able to say whether this structure is pathological or not.
If the formation is not treated, some complications may develop, including:
- in the uterus there may be bleeding, death of tissue of the myomatous node;
- hydronephrosis or uremia, peritonitis or renal failure, as well as cancer may develop in the kidneys;
- in the liver - hepatomegaly, suppuration and even rupture of the formation;
- In the thyroid gland, the manifestation of cystic goiter, hypo- or hyperthyroidism, and osteoporosis is possible.
A detected benign neoplasm in the mammary gland rarely becomes malignant. If it is small in size, it does not pose a danger. Usually complications arise only in the presence of inflammation and suppuration of the cyst.
Who interprets the results and how to obtain them?
The radiologist, a doctor specially trained to monitor and interpret x-ray studies, will analyze the images and send a signed report to your primary care physician or other health care provider who requested the analysis. Typically, the referring doctor or health care provider will share the results with you. In some cases, the radiologist may discuss the results with you at the end of your examination.
Follow-up inspections may be required. Your doctor will explain the exact reason for requesting another test. Sometimes follow-up testing is done because the potential abnormality needs further evaluation with additional views or special imaging techniques. In addition, follow-up testing may be required so that any change in the known abnormality can be monitored over time. Follow-up examinations are sometimes the best way to see whether treatment is working or whether the result is stable or changes over time.
You can sign up for a consultation and find out more from the administrator by calling +7 (495) 356-30-03.
Treatment methods
The type of treatment chosen by the doctor depends on the stage of development of the tumor. Sometimes, when a cyst is detected, for example, in the ovaries, therapeutic intervention is not required. The types of therapy used in medicine are summarized in the table.
| Type of treatment | Methods used |
| Waiting tactics | This method is used only when identifying the functional type of formation. Most often, it disappears on its own after a period of several months. Therefore, the doctor is monitoring. If it does not go away, then medications are required. |
| Conservative therapy | Hormonal treatment is used. It is necessary to reduce the production of sex hormones. Oral contraceptives are used. The menstrual cycle and ovarian function are restored. |
| Surgical intervention | The method is used in the absence of the expected result or when the cyst degenerates into a cancerous tumor. |
| Aspiration method of therapy | It is used when the cyst has no signs of cancer. Using a nozzle used for puncture, its contents are removed from the formation. After which ethyl alcohol is poured into the growth, which destroys it. It is possible to use a special solution. |
The first stage of treatment is eliminating symptoms. In addition, doctors prescribe hormonal medications and iodine preparations. Medications must be prescribed by the attending physician. For these diseases, self-medication is prohibited, as it can cause negative consequences. Drug therapy is carried out only in cases where the cyst is small in size and does not grow. If it enlarges or becomes infected, doctors prescribe surgery.
To treat ovarian cysts, your doctor may prescribe oral contraceptives.
If the cyst measures about 7 centimeters, then the surgeon performs a puncture. To do this, a needle is inserted into the formation, after which the contents are pumped out. The collected liquid is sent for testing. This procedure is carried out under ultrasound. The next stage of puncture involves the use of the aspiration method. A special solution helps to destroy the walls of the formation, due to which they are replaced by normal tissue. This method is performed under local anesthesia.
Therapy of echo-negative structures in the ovarian area is most often carried out with the help of medications. The gynecologist prescribes hormonal drugs, for example Duphaston, Anteovin or Marvelon.
If necessary, additional anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics are prescribed.
From the video you will learn in detail about anechoic formations in the uterus, urinary and gall bladder: