One of the most common diseases that affects the joints of the hands is osteoarthritis. This chronic degenerative disease mainly affects women over the age of 45. In young people, problems with the joints of the upper extremities occur less frequently. The Yusupov Hospital has created the necessary conditions for the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the hands:
- Comfortable rooms;
- Diagnostic equipment from leading manufacturers in the USA and European countries;
- Use of modern medicines and non-drug methods of therapy;
- Attentive attitude of medical staff to the wishes of patients and their relatives.
Experienced rheumatologists, orthopedists, and rehabilitation specialists treat patients with osteoarthritis of the hands. A multidisciplinary approach allows you to quickly stop inflammation and prevent further destruction of the hand joints.
Arthrosis of the hands: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment methods
The manifestations of the disease are directly related to the stage at which it is located. There are three of them in total. The longer you ignore the joints, the more destructive the symptoms will be.
- At the first stage, the cartilage gradually dries out, the joints crunch, and shock absorption gradually deteriorates.
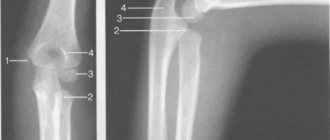
- The second stage is characterized by the formation of specific growths called osteophytes. They are clearly visible on x-rays. At night, my hands “twist” and they hurt, my fingers bend poorly
- At the last stage, ankylosis (immobility) develops, from time to time the muscles spasm, the pain does not leave the person, and the growths become visible to the naked eye.
If the cause is injury
Most often, dystrophic changes in the joints of the upper extremities occur after injury and microtrauma.
- Shoulder.
Shoulder fractures account for 9-12% of the total number of fractures. Much more often, this joint suffers from dislocations (50-60% of the total number for all joints), since it is characterized by weakness of the ligamentous apparatus. Even after professional reduction, there remains a possibility of relapse, and if the problem recurs, a nerve or vessel is pinched, and the blood supply to the cartilage suffers. Favorable conditions are created for the development of arthrosis of the shoulder joint.
- Elbow.
The elbow joint suffers from monotonous activities. If a person performs the same type of hand movements while the body is in a static position, epicondylitis, or “tennis elbow,” develops. The epicondyles become inflamed, causing pain and stiffness. Other injuries to this joint are less common. However, elbow bruises are very painful because the radial nerve passes through it.
Elbows suffer not from injuries, but from the same type of activity
- Wrist.
Wrist injuries are also more likely to be caused by repetitive movements, such as working at a computer for long periods of time. We are not talking about bruises, fractures or dislocations, although they also happen when falling or playing active sports. “Tunnel syndrome” occurs much more often. Due to constant flexion and extension of the wrist, swelling is formed, which compresses the nerves, blood vessels and tendons, interfering with normal blood circulation.
- Brush.
Fingers are actively involved in daily manipulations, so they are also susceptible to fractures and dislocations. After such an injury, arthrosis of the wrist joint can develop several years later, so you should carefully monitor the condition of the hand and listen to the slightest symptoms.
Extreme hobbies automatically put you at risk for wrist and hand injuries
Forms of the disease
Doctors consider two forms of arthrosis. These include:
- nodular - characterized by the presence of two types of nodules - Bouchard and Heberden, there are seals near the joints;
- rhizarthrosis is diagnosed near the base of the thumb and wrist joints.
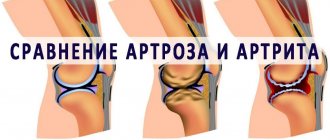
What is arthrosis-arthritis of the hand? If earlier it was possible to clearly state: arthritis is inflammation of the joints, arthrosis is their deformation, then in recent decades patients have suffered from arthrosis-arthritis, in which there is both inflammation of the joint and its deformation. Age distinctions between diseases have also become blurred.
What are the forecasts
Unfortunately, neither arthrosis of the knee joint, nor of the elbow or shoulder is completely cured. However, this does not mean that you should despair and refuse any therapy. There are many diseases with which a person peacefully coexists, and arthrosis is one of them. Of course, it is necessary to adhere to many rules, monitor the condition of the joints and monitor the course of the disease.
You should not refuse injections of synovial fluid prosthesis if the orthopedist-rheumatologist insists on it. With the help of the drug, the doctor will restore the deficiency of the lubricant - the friction of the cartilage will stop. In the case of Noltrex, such courses need to be repeated infrequently - once every one and a half to two years. If this condition is met, you can rest assured: your joints will continue to serve you faithfully!
Causes of the disease
Although the disease still presents many mysteries to scientists that require solutions, today several main factors have been identified that push destructive processes in the joint. These include:
- many years of hard manual labor;
- frequent hypothermia;
- hereditary factors;
- hormonal imbalances;
- injuries.
In order not to bring the disease to critical manifestations, when a person loses the ability to care for himself, it is necessary to contact specialists in the initial stages of arthrosis.
To make a correct diagnosis, the patient is first examined, questioned, and then diagnostics and laboratory tests are prescribed.
Since the joints are small and visible, radiography is usually sufficient to confirm the initial diagnosis. Ultrasound and MRI provide informative results. The main thing is not to waste time and not allow the cartilage to collapse. Arthrosis of the hand of 1st and 2nd degree, as well as deforming processes of the hands, is amenable to conservative treatment methods. Well-proven treatment methods have now been developed:
- medicinal;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- unconventional ways.
Diagnostics
Determination of the pathology that causes deformation of the fingers is carried out by orthopedic traumatologists. According to indications, patients are referred to rheumatologists, surgeons, neurologists, and other specialists. The most commonly performed diagnostic procedures are:
- Questioning, inspection
. During the conversation, the doctor establishes the time and circumstances of the occurrence of the symptom, and identifies other disorders. Explores the dynamics of disease development. Determines the nature and severity of external changes, the presence of edema, skin color and temperature, joint mobility. - Radiography
. Pictures of the fingers or hand are taken in two projections. Radiographs visualize dislocations, fractures, disturbances in the configuration of the phalanges, neoplasms, signs of inflammation and degeneration, and areas of bone melting. - , MRI
. Recommended when X-ray examination is insufficiently informative. They allow you to detail the identified changes, accurately determine their location, nature and volume, choose the optimal tactics of conservative therapy, and plan surgical intervention. - Lab tests
. Required to confirm hereditary diseases, oncological and inflammatory processes, rheumatic diseases.
The examination plan for secondary osteoarthropathy depends on the characteristics of the underlying pathology. During the diagnostic process, chest X-ray, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, echocardiography, and other techniques may be prescribed.
Surgical correction of finger deformities
How to treat arthrosis of the hands at the initial stage
It is immediately worth noting that medicine is not yet able to completely cure the disease. However, if the patient asked for help at the initial stages of the development of the disease, then slowing down destructive processes, restoring cartilage tissue, improving a person’s quality of life and changing the way he or she eats is a feasible task. Comprehensive treatment aimed at strengthening the immune system, changing diet, losing weight, and healing cartilage and joints produces results.
The doctor prescribes non-steroidal (i.e. non-hormonal) drugs in various forms. These can be tablets, gels, ointments, and in difficult cases, injections. The stomach does not like them and cannot be taken for a long time, but they relieve inflammation, pain and swelling well. Relatively “young” medications are chondroprotectors. They help slow down the degeneration of cartilage tissue. Vasodilators improve metabolism, muscle relaxants reduce muscle spasms. Antibiotics may be needed. Most often this happens if a person has suffered serious infectious diseases that have come back to life through the joints. In severe cases, it is necessary to inject hyaluronic acid directly into the joint.
Polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers
Other names for this disease are multiple arthrosis of the joints of the fingers, “knotty fingers.”
Polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers (multiple arthrosis of the joints of the fingers, “knotty fingers”) is a predominantly female disease. And although men also sometimes get it, this fate befalls them about 10 times less often than women.
As a rule, in women, the onset of the disease is directly related to hormonal changes in the body - polyosteoarthrosis usually begins during menopause, at the age of over 40-45 years (people under 40 years old suffer from this disease in extremely rare cases). The heyday of the disease most often occurs at the age of 50-60 years.
Causes of polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers
To date, scientists have not been able to identify any single cause for the development of polyosteoarthrosis. It is assumed that there is a hereditary predisposition - there are families in which several generations of women suffer from polyosteoarthritis of the fingers. Apparently, in these families some unfavorable features of metabolism and the structure of the cartilage tissue of the joints are inherited. And due to the congenital weakness of cartilage tissue in people with a burdened heredity during menopause, the cartilage of the joints begins to degrade, that is, they become inferior.
The degradation of cartilage is that it gradually loses its natural “lubrication” and becomes dry and cracked. From the friction of “dried up” articular cartilage, inflammation develops in the joints and abnormal “inflammatory joint fluid” is produced. It expands the joints from the inside, sometimes causing quite strong pain, while the joints themselves become deformed.
Although the risk of getting arthrosis of the fingers is somewhat higher in those people whose parents or close relatives were (suffer) from polyosteoarthrosis, there are other circumstances (in addition to hereditary predisposition) that contribute to the appearance of this disease. It is quite obvious that polyosteoarthrosis is more common in those people who suffer from metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus or diseases of the endocrine glands (thyroid, parathyroid glands, etc.).
Symptoms of polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers
With polyosteoarthrosis, special nodules appear on the fingers - the so-called Heberden's nodes and Bouchard's nodes .
Heberden's nodes form on the dorsal or lateral surface of those finger joints that are located closer to the nails (on the distal interphalangeal joints). Most often they develop symmetrically, that is, on the right and left hands at the same time and in the same places. Moreover, they can form on any fingers: from thumbs to little fingers. The size of Heberden's nodes can vary from the size of a grain of rice to the size of a small pea.
During the formation of Heberden's nodes, the joints underneath them often become swollen and red. Burning and pain may occur in the joints (but in a third of patients, the formation of Heberden's nodes occurs asymptomatically, without pain or burning).
Approximately half of the patients experience exacerbations at the onset of the disease, and then greasy, throbbing pains appear in the places where nodules form, which decrease after the skin over the vesicle bursts and its contents leak out. If the vesicle does not break through, then the exacerbation continues from several weeks to several months, after which the swelling, redness and pain disappear, and the nodules become dense and almost painless.
Subsequently, as polyosteoarthrosis progresses , the deformation of the finger joints and their stiffness increase. At times, without any apparent reason, exacerbations may occur again with the development of phenomena characteristic of the initial period of the disease - pain or burning appears in the nodules again. Then these exacerbations just as unexpectedly, sometimes even without treatment, subside.
Bouchard's nodules are distinguished by another feature - they most often develop gradually, slowly, without exacerbations. They are formed on the joints of the fingers located a little further from the nails (that is, in the area of the joints located approximately in the middle of the distance between the nails and the base of the fingers).
These nodules cover mainly the lateral surfaces of the joints, causing the fingers to acquire a spindle-shaped shape. Although Bouchard's nodes form more slowly than Heberden's nodes and are less painful, they also aggravate joint stiffness.
Over time, Heberden's and Bouchard's nodes increasingly deform the hand, changing its appearance and leading to what is called "knobby-fingered hands." But for all that, the disease, fortunately, does not change the general condition of the body; The activity of internal organs in polyosteoarthrosis, unlike arthritis, is not affected.
Arthrosis of the joints of the thumb (rhizarthrosis) is often combined with Heberden's and Bouchard's nodes. Rhizarthrosis affects the joint located at the base of the thumb and connecting the metacarpal bone of the thumb to the wrist joint.
Most often, rhizarthrosis develops in people whose profession involves increased stress on the thumb. But it can also develop in those who once injured their thumb or simply overloaded it greatly. For example, I have repeatedly seen rhizarthrosis that arose after summer exercise and even after banal rolling up jars of sauerkraut, mushrooms or jam, especially when the jars were rolled up for several days in a row.
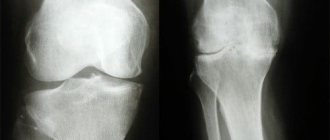
The disease manifests itself as pain at the base of the thumb when moving, as well as stiffness of the joint and a crunching sound in it when moving. In addition, when examining the hand, we can almost always see a deformation of the bones of the diseased joint (in the place where the thumb articulates with the wrist joint), which is clearly visible on an x-ray.
Attention! When faced with pain in the thumb, we must remember that the thumb is the “favorite place” for inflammation in gout and psoriatic arthritis. Therefore, if redness, swelling and severe pain develop in the thumbs, you should immediately consult a doctor who will conduct a differential diagnosis, determining what caused the inflammation - arthrosis or another disease.
Diagnosis of polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers
Diagnosis of polyosteoarthrosis usually does not require any extra effort. As a rule, the diagnosis becomes clear immediately, you just have to look at the patient’s hands. But still, in a number of cases, doctors, in order to prevent a diagnostic error, refer the patient for x-rays of the hands and blood tests - clinical (from a finger) and analysis for rheumatic tests (from a vein ).
With polyosteoarthrosis, the characteristic signs of the disease are clearly visible on x-rays - narrowing of the joint spaces of the affected joints and characteristic deformations of the bones of the affected fingers. In blood tests for polyosteoarthrosis, we usually do not detect any abnormalities; all indicators remain normal.
Attention! If in a patient with arthrosis we find in blood tests taken from a finger or from a vein, some “inflammatory” abnormalities, for example, an increase in ROE, C-reactive protein, seromucoid, etc., we should be wary - after all, arthrosis does not cause any changes in the tests. And if inflammation indicators are elevated, there is a high probability that we are dealing not with arthrosis, but with arthritis. And this is a completely different disease, more serious and complex. Then we need to continue examining the patient until the diagnosis of arthrosis or arthritis is finally confirmed or refuted.
Consequences of polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers
Polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers is not a dangerous disease. Even without proper treatment, polyosteoarthrosis does not produce any consequences other than “knottyness” of the fingers, and timely treatment can minimize this nuisance.
Article by Dr. Evdokimenko© for the book “Pain and Numbness in the Hands”, published in 2004. Edited in 2011 All rights reserved.
READ MORE:
- Treatment of polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers
- You can read the first chapters from the book “The Secret Formula of Health” here
- Where to buy books by Dr. Evdokimenko
What else is used to treat arthrosis of the hands?
Since the best results come from an integrated approach, in addition to taking medications, a person is prescribed physical therapy. Specific exercises are selected individually. They are designed to improve blood circulation and increase joint mobility. Physiotherapy gives good results, for example:
- paraffin hand wraps;
- mud therapy;
- massages and self-massages;
- penetrating compresses;
- hirudotherapy (application of leeches);
- acupuncture;
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
Patients with joint diseases have to reconsider their culinary preferences. Alcohol and smoking must be excluded, and the consumption of animal protein must be minimized. It is good for joints to eat foods and dishes that contain a lot of calcium and collagen. Accordingly, the diet should include various jellied meats and jellies. Gelatin, which helps these dishes harden, is an excellent tool for improving cartilage tissue. Food of plant origin, vegetable oils, and polyunsaturated omega-3 acids should predominate. A responsible attitude towards your health will allow you to keep your joints mobile for a long time.
We specialize in the treatment of the musculoskeletal system, even in severe stages of disease. We have been helping thousands of patients avoid surgery for 10 years!
Our doctors
This is the strongest team of experts who teach at the RUDN Department. We are the clinical base of leading universities, where the best doctors in Moscow, unique specialists from Russia and abroad are trained.
Folk remedies for arthrosis
Arthrosis is a deformation of the joints that occurs in older people. Unlike arthritis (inflammation of the joints associated with infectious diseases of the body), with which this disease is often confused due to the similarity of names, arthrosis affects only the joints. Check out folk remedies for arthrosis.
Folk remedies for arthrosis
Let us immediately note that the proposed folk methods for treating arthrosis require patience and time. Do not forget that the joints did not deform in one day, and salt deposits were also added to them, due to which they lost their elasticity.
For years, people passed on recipes to each other that helped patients with similar problems get back on their feet. Let's hope that the traditional methods of treating arthrosis presented in the article will also help our readers.
Horseradish.
For arthrosis, the roots of the plant are used. In the summer - fresh roots, and for the winter they can be dried. After pre-washing, the horseradish roots are grated. Then, in a small amount of water, steam it over fire. There is no need to bring to a boil, the horseradish should just soften. A piece of soft cloth or gauze is soaked in the resulting composition and applied warm to the affected area. You need to wrap it up and keep it warm for no more than two hours to avoid burns. It is best to do the procedure in the evening, before bed, as the compress is much more effective.
Tips for using horseradish.
It is better to grate horseradish in the air or in a ventilated area, as it greatly irritates the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose.
It should be applied to the skin no more than once a day to prevent burns. If you notice slight redness, then there is no need to worry, it will soon go away.
Do not use horseradish if you are allergic to the plant.
Compress based on medical bile.
To defeat arthrosis, traditional treatment suggests using medical bile, which is obtained from the gallbladders of animals. It can be purchased at a pharmacy.
The compress contains the following ingredients:
- alcohol solution of iodine;
All elements are taken in equal proportions, mixed and stored in a dark and cool place for ten days. Before applying a compress, the mixture should be heated in a water bath, soaked in gauze or a suitable linen cloth and immediately applied to the sore spot. The top should be covered with wax paper (never cellophane), cotton wool and secured with a bandage.
This compress improves blood circulation, restores cartilage, and relieves stiffness in movement. Contraindications include the presence of open wounds or cuts, pus, various skin diseases and individual intolerance to one of the components included in the composition.
Cabbage leaf.
Cabbage helps relieve pain, and in combination with honey, it relaxes joint movements.
For a compress, you need to choose fresh, juicy cabbage leaves, lubricate the concave part with honey and apply to the sore joint. Secure the top with film (cling film works great) and wrap it in woolen cloth. The procedure should be done before bedtime and the compress should be kept overnight. In the morning, rinse off the remaining honey with warm water. For visible results, the compress should be applied for 30 days.
Kefir with eggshells.
Affected joints are calcium deficient. You can try using this recipe to help them deliver this substance.
Grind thoroughly washed and dried eggshells in a coffee grinder to obtain a powder. Mix with kefir or matsoni until mushy. Transfer the resulting mass to a piece of soft cotton cloth and apply to the sore joint. Secure with film and tie with a scarf. Apply the compress in the evening, two hours before going to bed.
Chalk.
As in the previous recipe, but instead of eggshells, you can use regular chalk as a source of calcium. It should be crushed to form a powder. Mix with sour cream or yogurt, and, transferring it to a cloth, make a compress similar to that described in the previous recipe. It is important that the slurry does not drain.
Traditional methods of treating arthrosis of the hip joint require special attention. For the treatment of the hip joint, recipes for tinctures and rubbing ointments are more suitable.
Elecampane.
An alcohol tincture is prepared from dried elecampane, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. For 50 grams of plant, 125 ml of alcohol is consumed. The container with the infusion should be kept for two weeks, in a place protected from light. This product is convenient because it is prepared only once. Every evening before going to bed, you should rub the hip joint with alcohol tincture and it is advisable to wrap this part of the body with a shawl made of pure wool. This tincture can be applied to any sore joints.
Dandelion.
Tincture of dandelion flowers, prepared in May. Fresh inflorescences are thoroughly washed and doused with boiling water. Place in a jar (to the top) and fill with vodka. Infuse in a dark and cool place for one month. After this, the tincture is filtered and used as a rubbing agent. A similar tincture can be made from white lilac.
Celandine.
Celandine oil, prepared at home, can also relieve pain from cox arthrosis. To prepare it you need fresh leaves and stems of the plant. To one liter of olive oil you need to add 8 tablespoons of celandine minced through a meat grinder. Keep the oil in a warm place for fourteen days, after which it can be used. You need to massage the oil into painful areas. Can be applied three times a day.
To help worn-out cartilage recover and gain elasticity, in the old days rich broths (without salt) and gelatin were introduced into the diet. Broth made from chicken feet is especially useful. It contains a lot of collagen, which is necessary for the restoration of cartilage tissue. The only caveat to using broths is their high cholesterol content. Therefore, you should drink them in moderation.
With frequent consumption of various gelatin dishes (jelly, jelly, etc.), connective tissue can be restored. Contraindication is a tendency to thrombosis.
Bay leaf.
Bay leaf is a very effective remedy for cleansing joints of salts.
Wash exactly 12 healthy laurel leaves and place in an enamel pan. Pour 400 ml of cold water and put on fire. From the moment it boils, wait exactly 5 minutes and turn off the heat. Transfer all contents to a thermos and leave overnight. In the morning, strain and drink the entire broth throughout the day, sipping in small sips. The broth is prepared fresh the next day. You should drink the product for 7 days, after which you should rest for 5 days. Improvements occur after two months. Repeated cleaning with bay leaves can be done after 4-5 years. Contraindications to this method are pregnancy, liver and kidney disease. In case of side effects, stop taking the decoction.