What is post-traumatic contracture
The leg at the knee or the arm at the elbow cannot bend, it is difficult to move the fingers - all these are different manifestations of the same problem, called stiffness or contracture.
Read more The most common joint contractures are post-traumatic, resulting from various injuries.
Contractures caused by stress or trauma to the nervous system are called neurogenic.
Contractures that occur after a long forced position of the body are called immobilization.
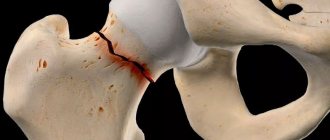
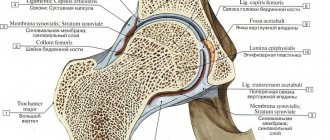
Contracture of the hip joint: what is it?
Contracture of the hip joint is detected somewhat less frequently than similar pathologies of other large joints - according to various sources, in 11-15% of all diseases of this joint.
In traumatology, it is believed that the more proximal (closer to the body) and larger the joint is, the more pronounced the consequences of its damage. This fully applies to the hip joint - due to its contracture, there is a high level of disability. Thus, from 20 to 25% of all patients who become partially or completely disabled due to damage to the hip joint have this diagnosis.
The described pathology is most often diagnosed in working age – from 25 to 45 years. Males get sick more often than females. This is explained not only by the fact that disorders that can lead to contracture of the hip joint are more common among them - men than women more often violate the recommended regimen for pathologies of this joint and more often ignore doctor’s prescriptions.
Causes
The role in the development of contracture of the hip joint is played by the same factors as in similar lesions of other joints. Most often this is:
- hip injuries;
- long-term immobilization;
- congenital developmental pathologies;
- pathologies of this joint of an inflammatory nature;
- diseases against which degenerative-dystrophic processes occur in the hip joint.
Please note
The most “popular” reason for the formation of contracture of the hip joint is traumatic injuries and degenerative-dystrophic disorders. In the latter case, the joint tissues are slowly but progressively destroyed - this disease is called coxarthrosis.
Injuries are the cause of contracture of the hip joint because they lead to the appearance of disorders such as:
- changing the shape of the joint;
- scar formation in soft tissues;
- damage to the muscle tendons that participate in the functioning of the hip joint;
- their shortening.
The terms for the development of contracture of the hip joint during immobilization (its forced immobilization - for example, using a plaster cast) are different and depend on the condition of the tissues. But on average, such contracture develops 20-25 days from the start of immobilization.
Scars that lead to the described pathology can develop in case of massive injuries and after burns, which also belong to the category of trauma. Such scars are located in the following locations:
- directly the area of the hip joint;
- anterior and posterior surface of the thigh;
- lateral wall of the abdomen in its lower sections.
The most common congenital malformations of the hip joint that cause its contracture are:
- his congenital dislocation;
- hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the femoral head;
- hypoplasia of the ligamentous apparatus of the hip joint.
Development of pathology
Contracture of the hip joint occurs:
- congenital – occurs due to hypoplasia (underdevelopment) or dysplasia (improper development) of the joint during the prenatal period of fetal development;
- acquired - appears at any period of life after birth, its cause is the previously described pathological factors.
Often a unique combined disorder occurs: changes in the structures of the hip joint occur during the prenatal period of development of the unborn child, but the contracture itself appears after birth.
Depending on the mechanism of development, contractures of the hip joint are divided into:
- neurogenic, or active;
- structural, or passive.
The neurogenic type of lesion develops due to the fact that the nerve supply to the muscles, which, in turn, ensure movement in the joint, suffers. Such neurogenic causes are:
- paresis – partial impairment of motor activity of muscles with impaired innervation;
- paralysis - complete lack of movement of such muscles;
- a number of mental illnesses.
Neurogenic contractures of the hip joint are:
central - they are caused by disorders of the brain or spinal cord;- peripheral - their cause is disorders of the peripheral nerves;
- psychogenic - can appear during an attack of hysteria (especially in persons who have already experienced disorders of the central nervous system).
Depending on the origin, neurogenic contractures of the hip joint are:
- traumatic - arise as a result of traumatic tear or complete rupture of nerve structures;
- pathological - appear in diseases of the central or peripheral nervous system.
By origin, peripheral neurogenic contractures of the hip joint are:
- pain;
- reflex;
- irritative-paretic (with metabolic disorders in the nervous tissue).
Structural contractures develop more often. They arise due to the fact that some physical obstacles do not allow movement in the hip joint. Such obstacles are:
- muscle shortening - due to injury, purulent diseases or technical errors during surgery;
- articular bodies (they are also called articular “mice”) are cartilaginous or bone fragments that arise due to degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the hip joint (for example, coxarthrosis) and are freely located in its cavity.
There is a uniform gradation of joint contractures based on the location of the lesion. It is also relevant for the described pathology of the hip joint. Contractures of this joint are divided into:
- arthrogenic – occur against the background of disorders that arise directly in the hip joint;
- myogenic - develop when the muscles that provide movement are damaged;
- desmogenic – formed due to the presence of scars, adhesions and ties;
- dermatogenous - occur due to scars on the skin covering the hip joint or structures near it (mainly the proximal part of the thigh);
- immobilization – formed during prolonged forced immobilization of the hip joint.
The last type of contracture is diagnosed most often and develops:
- with prolonged stay in a plaster cast;
- in the presence of prolonged skeletal tractions.
The limitation may affect different types of movement in the hip joint. Therefore, the following types of contracture have been identified:
- flexion – extension function is impaired;
- extensor – it is impossible to bend the joint;
- adductor – abduction function is impaired;
- abductor – it is not possible to perform adduction in the hip joint;
- rotational – it is impossible to perform rotational movements in the joint.
Symptoms of hip contracture
The main symptom based on the presence of which a diagnosis of contracture of the hip joint is made is the limitation of movements in it. The clinical picture may be complemented by other pathological signs:
- deformation (change in shape) of the joint;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- violation of support;
- pain;
- shortening of the leg on the affected side;
- her forced position.
note
Deformation in the area of the hip joint during its contracture is often insignificant, while the lower limb on the affected side of the joint may take an unnatural position.
Swelling of the soft tissues may be a symptom of a disease or injury that triggered the development of the described disease.
Impaired support means that it is impossible to lean on the lower limb on the affected side - it simply will not “hold”, and a person may fall.
Characteristics of joint pain:
- by localization - observed throughout the entire joint;
- by distribution - the presence of irradiation depends on the pathology that led to contracture of the hip joint;
- by nature – pulling, aching or twisting;
- in terms of severity - insignificant, and if the patient is at rest, they can disappear altogether, but with a careless attempt to make movement in the joint they can become quite intense;
- by occurrence - the appearance of pain depends on the pathology that led to the development of the described pathology.
Shortening of the lower limb on the affected side can be detected with flexion contracture - the leg seems to be pulled towards the waist of the lower limbs.
Symptoms of muscle contractures
Muscle contracture is caused by involuntary contraction of a muscle, which leads to damage. Muscle spasms are a rather painful condition. Moreover, a spasm can occur in any part of the body where the muscles are located: back, legs, arms, neck.
Muscle tension may go away in a few minutes, but muscle spasm can persist for a very long time, causing severe discomfort.
Immobility sets in, that is, the damaged joint does not start working until the muscle spasm is relieved.
In addition, in a state of spasm, muscles can compress blood vessels, disrupting the blood supply to internal organs. This can lead to serious complications and related illnesses.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of contracture of the hip joint is easy to make based on the patient’s complaints, anamnesis (medical history) and the results of a physical examination. Additional diagnostic methods (instrumental and laboratory) will be needed in order to establish the true cause of the development of this pathology.
In some cases, consultation with related specialists will be required - a vascular surgeon, neurologist, neurosurgeon, dermatologist, combustiologist (burn specialist). For the hysterical type of contracture, the patient must be examined by a psychiatrist. Since there are too many diagnostic methods, the examination of the patient must begin with a consultation with doctors of certain specialties - they will make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe specialized examination methods.
When studying anamnestic data, you need to find out the following nuances:
- whether there have been any injuries (fractures, dislocations, burns) or diseases of the hip joint in the past, can the patient associate the development of contracture with them;
- how long does contracture last?
- how it developed - progressed or regressed;
- whether treatment was carried out, and if so, whether there was an improvement;
- whether self-medication or treatment was carried out by people who are not authorized to treat - in particular, by the so-called “chiropractors”; did any changes occur in the functional capabilities of the hip joint after the manipulations; if so, what were they?
During a physical examination, the following is carried out:
- examination - the position of the lower limb, the condition of the skin in the area of the hip joint and muscles are assessed (visible muscle tension can be determined), visual shortening of the leg is detected (if any);
- palpation (palpation) – the presence or absence of pain, swelling, crepitus (crunching), deformation.
Functional testing is also performed to assess range of motion in the hip joint:
- passive - the patient lies on a horizontal surface, the doctor takes his lower limb in his hands and carefully performs movements in the hip joint, assessing their maximum amplitude. If the patient complains of pain or discomfort, testing should be stopped;
- active - while standing, sitting and lying down, the patient independently makes flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and rotational movements in the hip joint, the doctor assesses their volume.
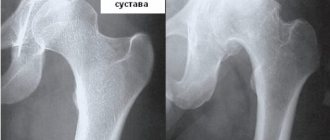
In the diagnosis of hip joint contracture, the following instrumental research methods are used:
X-ray of the hip joint in two projections - when studying X-ray images, the causes of contracture of this joint are determined. If necessary, X-ray examination is carried out in additional projections, with a special positioning of the patient;- computed tomography (CT) – using computer slices, you can obtain more detailed information about the condition of the structures that form the hip joint. Computed tomography is used in controversial cases or when it is impossible to determine the causes of contracture of the hip joint using x-ray examination;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - like CT, helps to assess in more detail the condition of the structures of the hip joint. But MRI is more informative when studying soft tissues;
- arthroscopy - through a small incision in the soft tissues, an arthroscope (this is an endoscope used in traumatology and orthopedics) is inserted into the cavity of the hip joint, the articular cavity and articular surfaces are examined, and the intra-articular cause of contracture is determined.
Laboratory research methods are auxiliary in the diagnosis of contracture of the hip joint. With their help, it is possible to carry out a differential diagnosis between pathologies that could lead to the development of this disease. Most often used:
general blood test - an increase in the number of leukocytes ESR indicates the inflammatory nature of the provoking disease, a sharp increase in ESR indicates a tumor;- rheumatic tests - confirm the development of inflammatory processes of rheumatic origin, which led to contracture of the hip joint;
- biochemical blood test - its implementation is necessary for neurological and muscle contractures. This determines the amount of microelements that are associated with nerve conduction and functional activity of the muscles involved in movements in the hip joint. These elements include sodium, potassium, calcium, and chlorine.
Treatment of post-traumatic contracture
“Prevention is easier than cure.” Prevention of contractures is important and effective.
- An effective measure is correct fixation of the injured limb (in a natural position without excessive compression of blood vessels and nerves). Some doctors have experience in providing conditions for rapid healing of fractures without applying a plaster cast.
- Promoting mobility of the joints of the injured limb as quickly as possible (passive and active gymnastics improves blood supply and nerve trophism, accelerates healing, and prevents the formation of scar tissue). If real movement is not possible, visualization of a variety of movements gives good results. Experiments have shown that people who did not stop training in their imagination recovered much faster and more fully, even after very serious injuries and a long period of complete immobility.
- Timely relief of pain and prevention of the development of edema and insufficient blood supply to tissues are the most important factors in the aggravation of contractures (pain relief, physiotherapy).
- If the injury does not require emergency hospitalization (and surgery), an osteopathy session (or sessions) provides an excellent effect. In this section of medicine there is the so-called. 72-hour rule: it is after this period that the injury is fixed in the tissues. Within three days from the moment of injury, there is a real opportunity to reconfigure the tissues to the “health matrix” and create conditions for the rapid and correct restoration of the integrity of the structures and their natural mobility.
Symptoms of hip contracture
Treatment of hip joint contracture is the treatment of diseases and pathological conditions that could lead to the development of the described pathology. It can be conservative and surgical. The patient is hospitalized in the trauma department - the conditions of the clinic will provide a more complete examination and adequate treatment.
Treatment regimens depend on the cause of the contracture. The following conservative prescriptions are common:
- bloodless correction of the position of the lower limb on the affected side;
- physiotherapeutic methods;
- exercise therapy;
- repeated massage courses.
Bloodless correction of the position of the limb consists in bringing the hip joint step by step to a physiological position. This is done gradually, using plaster casts, with the help of which the lower limb is in a certain position for some time.
Indications for surgery to eliminate contracture of the hip joint are:
- unsatisfactory results of conservative treatment or complete absence of its effect;
- progression of contracture;
- increased pain syndrome;
- complications in the form of atrophy.
Surgical intervention is performed:
- using an arthroscope - this method allows to reduce the trauma of the operation, reduces the length of the patient’s stay in the clinic and the terms of his rehabilitation;
- open classical access - in difficult cases or in the absence of endoscopic equipment.
The main objectives of surgical intervention, regardless of the technique performed, are:
- removal of scar tissue and articular bodies;
- restoration of the normal shape of the articular surfaces;
- lengthening of the muscles involved in the movements of the hip joint.
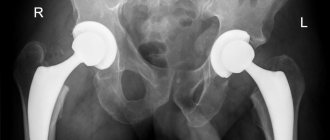
In case of severe violations of the articular surfaces, which have led to irreversible contracture, the affected joint has to be replaced with an artificial one - for this purpose endoprosthetics is performed. If such an operation is not possible, then arthrodesis of the hip joint is performed - the affected structures that form it are removed, fragments of the lower limb and pelvic bones are fastened together into a single whole, while giving the lower limb a functionally advantageous position.
After surgery, rehabilitation measures are carried out - they are based on physical therapy, massage and physiotherapeutic methods.
Treatment of joint contracture
Conservative treatment of joint contracture consists of the use of therapeutic exercises, therapeutic massage, and physiotherapeutic procedures, which allow you to restore the full range of motion in the joint, completely remove the restriction in the joint, relieve pain symptoms when moving the joint, improve nutrition in the joint and increase the tone of weakened muscles.
Depending on the degree and type of damage to the joint during contracture, the following therapeutic actions are possible:
- drug therapy (NSAIDs, analgesics, hormones)
- therapeutic blockades - injection of drugs into the joint cavity
- manual therapy (muscle and joint techniques)
- physiotherapy (UHF, electrophoresis)
- shock wave therapy (Ekaterinburg Medical Center on Botanika)
- physiotherapy
- surgical treatment
There are contraindications. Read the instructions or consult a specialist.
Prevention
The prevention of contracture of the hip joint is based on the following measures and actions:
avoiding situations that would lead to injury to the hip joint and, as a result, its immobilization, which can lead to contracture;- if it is impossible to avoid such situations, take a responsible approach to safety principles and use personal protective equipment;
- a rational approach to immobilization - it should not be delayed (for example, to “guarantee” fracture healing). The problem of long-term immobilization can be successfully solved with the help of surgical treatment of traumatological disorders;
- if it is impossible to avoid long-term immobilization, early prescription of exercise therapy and massage;
- prevention of diseases and pathological conditions that can provoke the development of contracture of the hip joint, and if they have already developed, their timely identification and adequate treatment.
What is the risk of complications?
The difficulty in treating the pathology is that scarring may reappear after surgical removal. Therefore, it is very important to remove the main cause of contracture formation. There is also a possibility that even after eliminating the problem, the functional activity of the joint will not return, since the muscles will be significantly atrophied. Scar contracture causes the development of osteoporosis of the femur and increases the risk of pathological fractures, and can also lead to ankylosis of the joint.
Contracture of the right hip joint develops more often than the left.
Forecast
The prognosis for contracture of the hip joint is ambiguous. With a rational approach and competent prescriptions, the condition of the joint can be improved, but 100% results are often not achieved - some limitation of movement in the hip joint remains.
As with other joints, fresh immobilization contractures can be completely eliminated if treatment is started early. With chronic contractures, the health prognosis worsens - scars often form both in the tissues involved in the pathological process and in healthy ones, so surgery cannot be avoided. Severe long-standing contractures can lead to disability of the patient - he is forced to walk with a cane, on crutches or move in a wheelchair.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
12, total, today
( 62 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5)
Arthrosis of the ankle joint: causes, symptoms, treatment
Blown back: how to treat it at home?