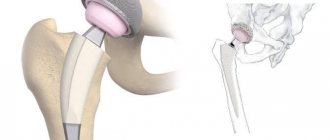
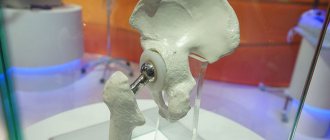
Total hip replacement is the only radical treatment method for deforming osteoarthritis. The operation allows you to restore the ability to support the lower limb, eliminate lameness, restore range of motion and, most importantly, relieve a person from chronic pain in the hip. After surgery and rehabilitation, the patient returns to an active lifestyle, which is the main goal of endoprosthetics.
Bilateral operation.
Often in the postoperative period, pain is a concern, which can neutralize the positive result of surgical intervention. After all, when agreeing to an operation, a person strives first of all to get rid of painful sensations. Nevertheless, the pain syndrome persists in 17-20% of those operated on, and in another 32-35% it occurs again within 10 years after surgery. But getting rid of it can be extremely difficult, and sometimes even impossible.
What are the causes of pain after endoprosthetics and how to avoid their occurrence - this will be discussed in this article.
Pain in the early postoperative period
Pain in the first 2-3 weeks after surgery is absolutely normal and should not cause concern. Doctors characterize it as a natural reaction of the body in response to extensive surgical intervention. During the operation, the soft tissues of the hip, ligaments and bones are damaged. Until their integrity is restored, and the bones and endoprosthesis fuse firmly enough, the person will experience discomfort and mild pain.
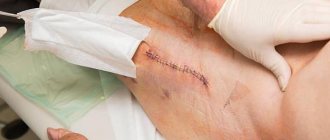
Fresh suture after a “classic” operation.
To make it easier for the patient to endure painful sensations, he is prescribed painkillers in the postoperative period. This allows him to move and exercise more freely, which is extremely important during post-operative rehabilitation.
Sometimes pain in the early postoperative period indicates the development of complications. In this case, they are of high intensity and are accompanied by other alarming symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of purulent discharge from the postoperative wound;
- local swelling and redness of the skin;
- limited mobility of the operated joint;
- a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the lower limb, etc.
The appearance of pathological symptoms may indicate the development of purulent-infectious, thromboembolic, orthopedic and other complications. In this case, the patient requires a thorough examination and, if necessary, treatment of the resulting pathology.
Minimally invasive endoprosthetics in the Czech Republic: doctors, rehabilitation, terms and prices.
Find out more
Treatment methods
If pain in the pelvic area develops, radiating into the pelvis, it is better to consult a rheumatologist, traumatologist or orthopedist. After diagnosing and establishing the causes of the pathology, the doctor makes a diagnosis and selects effective treatment methods.
Treatment
General principles of conservative therapy
Patients with joint problems must be prescribed:
- sleep only on the healthy side;
- complete peace;
- refusal of loads;
- frequent changes in body position;
- prevention of hypothermia;
- wearing loose and sufficiently warm underwear.
All possible manipulations and the selection of methods depend on the causes of the pathology, its clinical picture and the degree of complications.
Drug therapy involves taking NSAIDs, antirheumatic drugs, hormonal drugs, and chondroprotectors. Sometimes immunosuppressants are required as additional therapy, as well as drugs to normalize blood circulation.
If conservative treatment is not effective, surgery is required - joint replacement. Sometimes I use special orthopedic devices, and they may apply a plaster cast.
Treatment options
Features of treatment of specific diseases
If the doctor detects the presence of excess fluid or even blood in the joint, then drainage and rinsing with antibacterial agents are required.
In the most difficult situations, hip replacement is implemented, when the destroyed joint is replaced with a new one - an artificial analogue. When the operation is completed, rehabilitation is organized in order to restore mobility and function of the limb. The person can gradually return to normal life.
Modern operations are high-tech, precise. After a joint replacement, a person gets rid of constant pain and limitations in physical activity.
Folk remedies
Consultation with a doctor is necessary for any type of pain. The doctor will conduct a study and clarify the diagnosis. Only then can you consult about the use of traditional medicine recipes.
Sabelnik
Cinquefoil tincture effectively copes with discomfort due to joint pain. The recipe for oral use is as follows:
- chop the dry cinquefoil and compact it tightly into a previously prepared container - it should be one third full;
- fill with water to the top;
- leave for three weeks in a dark place.
You need to take 20 ml three times a day, regardless of meals. The full course is 2 weeks. Then after a two-week break the course can be repeated again.
Existing and newly emerging pain: what is the difference?
There are two types of pain syndrome in the postoperative period: persisting and newly emerging. The first is in no way connected with the operation, since it is observed in a person even before it is performed. And it doesn’t go away after surgery. It can be caused by pathologies of the spine, somatic diseases or concomitant diseases of the hip joint itself (but not osteoarthritis).
Possible causes of persistent pain:
- hernias - inguinal or intervertebral;
- diseases of the urinary system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- abdominal aortic aneurysm;
- arthritis or synovitis of the hip joint.
New pain syndrome is caused by the consequences of surgical interventions. It can occur at different times after surgery - either after a couple of weeks or after several years.
Gymnastics in the pool.
Types of new pain after hip replacement:
- Positional. Caused by incorrect spatial arrangement of the components of the endoprosthesis.
- Adaptive. Usually caused by lengthening of the operated limb or other changes in anatomical parameters in the hip joint area.
- Neurogenic. They arise due to damage to the nerves of the lower limb: obturator, femoral, sciatic, lateral cutaneous.
- Neuropathic. Caused by pathological excitation of neurons in peripheral nerves in the absence of their structural damage. Most often localized in the area of the postoperative suture.
- Incongruent (or psychogenic). They have an unknown etiology, that is, the cause of their appearance usually cannot be determined.
- Contact paraarticular. Caused by excessive tension in the structures surrounding the hip joint, namely the muscles and fascia of the thigh.
- Caused by instability of the endoprosthesis or septic inflammation. Such pains are the most dangerous because they indicate severe complications. When they appear, a person requires serious treatment, and often repeated (revision) surgery.
The type of pain and its cause can only be determined after examination and analysis of clinical and radiological data. However, the localization of painful sensations and accompanying symptoms make it possible to suspect one or another cause even before conducting instrumental diagnostics.
Causes of pain
If during movement, at rest or when changing body position, pain in the pelvic area is felt and gradually intensifies - this is a signal that pathological changes are occurring in the body.
The source of discomfort may be:
- infections that cause inflammation (arthritis);
- changes in the anatomy of the joint that occurred as a result of injuries (bruises, fractures), as well as dislocations and subluxations (congenital or acquired);
- degenerative diseases (osteoarthritis, coxarthrosis);
- aseptic necrosis of the femoral head (accompanied by tissue necrosis);
- inflammation of the periarticular bursa (bursitis) or tendons (tendonitis);
- tuberculosis;
- inflammation associated with autoimmune diseases (occurs against the background of dysfunction of the immune system);
- inadequate blood supply to joint segments;
- diseases that are associated with neurological disorders (neuritis of the sciatic nerve, pathology of the piriformis muscle).
The pain that radiates to the groin can be different: from sudden sharp to constant and aching.
Don't delay visiting the doctor. Only a specialist will determine the true cause of the pathology and prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
The main causes of pain in the groin area
Pain in the groin after endoprosthetics most often has a positional or adaptive nature. This means that they are caused by lengthening of the leg after surgery or changes in anatomical parameters in the hip joint area.
However, other reasons cannot be ruled out:
- stenosis (pathological narrowing) of the superior and inferior gluteal arteries;
- excessive tension and injury to the psoas major muscle (m.iliopsoas);
- inguinal and femoral hernias, abdominal aortic aneurysm, damage to the spinal roots at the L2-L5 level (in the case of persistent pain).
Let's take a closer look at the main causes of postoperative groin pain.
Excessive lengthening of the lower limb
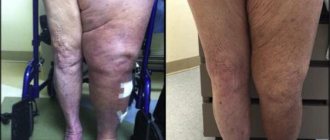
Pain in the groin area occurs in almost half of patients with lower limb lengthening. Moreover, the longer the leg after surgery, the more intense the pain. The problem is faced by those people whose lower limb after surgery has lengthened by 1-4 or more centimeters.
An example of significant lengthening of the operated limb.
It is curious that such pain is often combined with pain in the anterior thigh and lumbosacral spine. Those, in turn, are caused by a secondary distortion of the pelvis against the background of tension in the muscles and fascia of the thigh, as well as the psoas major muscle.
Pain due to unequal limb lengths can significantly worsen a person’s quality of life after endoprosthetics. And the stronger they are, the more limited the patient’s activity is. Patients with intense pain may find it difficult to move around and do normal daily activities.
Impingement of m.iliopsoas
Impingement is characterized by damage to the muscle fibers of the psoas major muscle. The pathology is manifested by pain in the groin area, which occurs when the leg is extended at the hip joint. This can cause a lot of discomfort to the patient.
Layout of m.iliopsoas.
Impingement can develop for two reasons:
- due to damage to the psoas major muscle with unequal length of the lower limbs;
- due to injury to the m.iliopsoas by the cup of the installed endoprosthesis (usually with cement installation).
For impingement syndrome, a person requires treatment, including pain medications and physical therapy.
Vertically installed acetabular component
In this case, the head of the endoprosthesis tends upward and outward during walking, injuring the periarticular tissues. This is what leads to the appearance of pain. Note that pain during vertical installation of the acetabular component appears soon after walking, as well as with active flexion and strong adduction of the hip. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a characteristic clinical picture, radiographic data and, if necessary, MRI.
Excessive anteversion of the acetabular component
Pain often occurs when the acetabular component is tilted too far forward. In this case, the person experiences pain when rotating the hip outward, both active and passive. To make a diagnosis in this case, X-ray examination and MRI are also required.
Definition of anteversion.
Pathologies causing pain in the hip joint
When, during movements, at rest, or in a sudden change in body position, pain is felt and increases in the pelvic area - this is a negative sign that pathological changes are progressing.
The main causes of discomfort are:
- infections that provoke inflammation of the joints - arthritis;
- disruption of the structure of joints under the influence of injuries, with dislocations - acquired or congenital;
- degenerative processes;
- inflammatory process in the periarticular bursa, tendons, muscles;
- aseptic necrosis of the femoral head – characterized by gradual tissue death;
- tuberculosis;
- disruption of blood flow in joint segments;
- inflammation due to autoimmune diseases;
- neurological diseases.
Traumatic injuries
The hip joint is the largest joint in the human body. Usually it is he who suffers from constant stress - from excess weight, overexertion, etc. Against this background, various damage may appear - trauma or microtrauma. They greatly weaken tissues and change their structure.
Arthritis
Arthritis causes aching pain, especially when walking. Movements become constrained, reflex restrictions arise, because negative symptoms affect not only the thigh, but also the groin and buttocks. Sometimes acute attacks of pain develop, which radiate and shoot up to the knee.
Arthritis affects all connective tissues, and discomfort is directly related to inflammation. The pathological process develops in the synovial membrane, which lines the joint cavity, that is, within the joint itself.
If you ignore the pathology and do not take measures to relieve the symptoms and causes of its development, arthritis will soon transform into osteoarthritis of the hip joint. In this case, the processes acquire a degenerative-destructive character - the functioning of the organ changes, physical activity suffers, and it is significantly limited. Often the disease leads to disability.
Symptoms of arthritis
Coxarthrosis
Pathology does not immediately announce itself. At first, the pain in the groin area is weak and aching. But over time, it radiates down the leg, affecting the front of the thigh and side, and less often the buttock.
Discomfort becomes noticeable when moving around or getting up from a chair. The pain appears already at the first step, then dulls, but with a long walk it also makes itself felt.
Relief occurs only in a state of rest and rest for the joint.
- Pain on the inner thigh radiating to the groin: causes, diagnosis and treatment
Coxarthrosis is the destruction of cartilage inside the joint. First, one joint suffers, and over time, others too. If the signs are ignored, the disease will definitely progress. The pain intensifies to such an extent that it is difficult to do even the simplest movements. This is due to compression of the ligaments and pinched nerves.
Joints with coxarthrosis are very crunchy, as the surfaces rub strongly against each other. As it progresses, severe exacerbations develop, lasting from a couple of days to several months.
Synovial chondromatosis
With chondromatosis, the condition of the synovial membrane changes. The shell begins to degenerate into cartilage tissue, like an articular element.
The main symptom is the formation of chondromic elements in the intra-articular cavity. They are round in shape and dense in consistency and can occupy a significant part of the cavity. Usually these are nodules or elevations.
Perthes disease
Perthes disease is diagnosed in children. This is a condition of impaired blood flow in the femoral neck. She does not receive enough nutrition, so bone tissue is destroyed. As a result, the pathology leads to avascular necrosis.
During the growth process, blood circulation in the femur improves and the structures are restored. One of the most negative consequences is deformation, problems in the functioning of the hip joint and chronic pain.
Perthes disease
Diabetic arthropathy
The disease affects bones and joints, leading to their gradual destruction. This is a complication of diabetes. As the disease develops, the joints often become inflamed and, as a result, become deformed and destroyed. The disease affects both young and old people.
Juvenile epiphysiolysis
Epiphysiolysis is a disease that develops in children and adolescents aged 8-15 years, that is, during a growth spurt. The pathology consists of slipping of the femoral head onto the neck due to too weak a growth plate.
The causes of the disease have not been precisely established. But more often epiphysiolysis develops in boys and with obesity, less often it is provoked by injuries or problems with the functions of the endocrine system.
- Remedies for pain in the hip joint - medicines and traditional medicine recipes
The pathology is stable. The child limps for a long time, but the limb remains supported. The pain is concentrated in the thigh, sometimes radiating down to the knee. Over time, the normal volume of motor activity of the hip joint is lost.
To carry out diagnostics, an MRI is performed and the characteristic clinical picture of the disease is taken into account. Treatment is required immediately, because continued slipping provokes severe arthrosis, arthritis and other dangerous complications.
Intermittent hydrarthrosis
This is a chronic disease that is mainly diagnosed in women. The etiology has not been established.
In most cases, hydrarthrosis damages only one joint, begins unexpectedly, and degenerative changes quickly occur in the joint. It increases in volume due to the accumulation of a large volume of synovial fluid. Because of this, the joint tissues are stretched, causing discomfort, stiffness, and weakness. But overall health does not change.
Pseudogout
This is a chronic disease characterized by infrequent but acute attacks of arthritis. The pain is often unbearable. The main reason is the deposits of calcium salts in the joints.
Tenosynovitis
Tenosynovitis is an inflammatory process affecting the tendons and nearby tissues. In contrast, tendonitis affects tendons with a soft tunnel of connective tissue.
Tenosynovitis occurs acutely or with periodic exacerbations, that is, chronically. It manifests itself as pain, which becomes stronger with movement, and may be accompanied by swelling, redness and an increase in local temperature.
With the infectious nature of the pathology, general intoxication develops. Non-infectious forms are not accompanied by disturbances in general well-being. Therapy depends on the form and type of the disease, and can be either conservative or surgical.
Infectious lesions of periarticular tissues
Infectious inflammation is indicated by redness of the skin over the joint and a local rise in temperature. At the same time, joint mobility deteriorates.
- Causes of pain in the hip joint at night while lying on your side, accompanying symptoms
In the case of the chronic form, there is a high probability of developing secondary arthrosis up to the complete loss of the ability to move.
Pain after surgery
After hip surgery, pain is not felt for several hours, as painkillers continue to work. But after the anesthesia wears off, acute pain develops, which also needs to be relieved with analgesics.
The pain may not go away for several days, but its intensity decreases and gradually it goes away completely. By the time of discharge from the hospital, the sensations almost always pass. But they may appear later, especially in unstable weather conditions. In old age, the pain is aching and quite strong, but young people experience discomfort as easily as possible.
Pain after surgery
Prospects for treatment
Pain due to improper installation of the endoprosthesis occurs after surgery and is chronic. They are characterized by low or medium intensity, and also appear under certain conditions (after walking, when bending the lower limb, turning it outward, etc.). These features make it possible to distinguish them from other pains: those that persist and those caused by postoperative complications.
The development of complications is signaled by high-intensity pain, accompanied by other alarming symptoms. They may indicate paraprosthetic infection, displacement of the endoprosthesis, periprosthetic fractures, neuropathy of the peroneal nerve, etc. The listed complications require quick diagnosis and immediate medical care. Therefore, if you suspect their development, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Causes of coxarthrosis
More often than others, the cause of pain is the progression of coxarthrosis. The cartilage surfaces break down and rub against each other, causing pain. It is very important to understand what caused the pathology:
- age-related changes in the joint;
- metabolic disease;
- congenital dislocations;
- injuries;
- rheumatoid arthritis or other causes.
If the original source cannot be found, idiopathic coxarthrosis is diagnosed. Typically, it affects both joints. Secondary – called post-traumatic arthrosis. It occurs due to major or minor damage to the hip joint and can only spread to one side.
Excess weight and lack of physical activity greatly accelerate the progression of coxarthrosis
Prevention of pain during hip replacement
Careful planning of the operation will help to avoid pain in the postoperative period. It will allow you to achieve the correct length of the lower limb, as well as avoid incorrect orientation of the components of the endoprosthesis. To prevent the onset of pain, surgery should be done in good clinics where experienced surgeons work. This way, the risk of postoperative complications will be minimized.
Let's summarize:
- Pain in the groin area in the late postoperative period is usually caused by lengthening of the lower limb or incorrect orientation of the prosthesis.
- The remaining pain syndrome is in no way related to the operation. Its cause may be inguinal and femoral hernias, abdominal aortic aneurysm, diseases of the genitourinary system, etc.
- High-intensity pain usually indicates the development of postoperative complications: infectious, orthopedic, etc. In this case, the patient is also worried about other symptoms: increased body temperature, impaired mobility of the lower limb, swelling of soft tissues, and the appearance of purulent discharge.
- To avoid pain and postoperative complications, the operation must be planned especially carefully - it must be done in a timely manner, by experienced doctors and undergo rehabilitation.
Diagnostics
The main methods for diagnosing hip joint pathologies are:
- X-ray, ultrasound – examination standards for joint pathologies.
- General blood analysis.
- Biochemistry of blood.
- Urine studies - its color, volume, density, transparency, glucose, protein and bilirubin content are taken into account.
- Computed tomography helps to study the joint in several projections and determine bone density.
- MRI.
The doctor must take into account the stiffness of the joint, pay attention to the increase in temperature, the presence of headaches, redness, and swelling.
Is it possible to cure coxarthrosis?
Unfortunately, a way to completely get rid of coxarthrosis has not yet been invented. Even joint replacement does not guarantee that degenerative changes in it will stop. Of course, the earlier the diagnosis is made, the easier it is to keep the disease under control and prevent relapses. It is quite possible to live with the disease at stages 1-2 and feel comfortable if you follow some rules and restrictions.
Treatment will be effective only after a comprehensive diagnosis. The goal of treating osteoarthritis in this case is to increase the joint space, restore the functionality of the joint and, if possible, regenerate cartilage tissue. Solving the last problem is very difficult and even impossible, since the cartilage surfaces are destroyed faster than they are restored with the help of chondroprotectors - chondroitin and glucosamine. Therefore, therapy for coxarthrosis is always comprehensive and includes:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief (short course);
- chondroprotectors (long-term);
- vasodilators;
- vitamin complexes to maintain the body;
- intra-articular injections.
Treatment of coxarthrosis depends on the stage of the disease. The video shows the most commonly used methods in the first, second and third stages:
One of the most effective and safest methods for eliminating joint pain is injection of Noltrex synovial fluid prosthesis. The drug is injected into the joint, where it is distributed over the damaged cartilage surfaces and acts as a lubricant. It is not capable of restoring damaged cartilage, but, nevertheless, after a course of 3-5 procedures, the pain syndrome subsides and does not appear for 12-18 months.
If you experience frequent or recurring hip pain, don't ignore it. Will it be possible to detect the disease at an early stage? You can stop the disease and prevent its development. If the doctor pleases you with the absence of a serious diagnosis, so much the better! Continue to lead a healthy lifestyle and do not forget to regularly visit the orthopedist - after all, the first alarm bell has already been heard.