The term “osteochondrosis” appeared in 1933, when the German orthopedist A. Hildebrandt proposed combining a number of pathological processes of the musculoskeletal system with one general term. Today, osteochondrosis is understood as a group of orthopedic diseases that occur in children and adults.
In childhood and adolescence, osteochondrosis of various joints develops as a result of abnormally rapid growth, which leads to disruption of the blood supply to the bone in the area of the epiphysis, followed by localized necrosis [1]. There are several nosologies of juvenile osteochondrosis. Among them are Perthes disease, manifested by pain in the hip joint, Osgood-Schlatter and Sinding-Larsen-Johanson syndromes, the main symptom of which is knee pain that worsens with physical activity, and other pathologies.
Various types of juvenile osteochondrosis have one thing in common - an optimistic prognosis [2].
Completely different prospects open up for adults suffering from spinal osteochondrosis. This process, unfortunately, has a chronic and progressive course. It is characterized by a decrease in hydrophilicity and destruction of intervertebral disc tissue, their protrusion towards the spinal canal, as well as reactive changes in the adjacent bone tissue of the vertebrae and the further development of arthrosis, which is accompanied by severe pain [3]. The pain syndrome that develops against the background of osteochondrosis reduces the quality of life and forces you to seek help from a doctor or pharmacist. What external medications alleviate the condition?
What is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
Cervical osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease of the spine, during the development of which the structure of the connective tissue changes.
The disease is often disguised as a disorder of another type, but timely contact with a specialist allows for timely diagnosis and immediate treatment.
Degenerative changes in the tissues of the cervical spine are most often found in the medical history of people of mature (45-59) and elderly (60-74) age.
Despite this, it is worth noting: in modern society there is a rejuvenation of the disease, which is confirmed by the periodic diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis in children and adolescents.
It is important that osteochondrosis can occur both in isolation and in combination with damage to other parts, in particular the thoracic, lumbar and sacral.
Consequences
Exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis requires immediate consultation with a doctor . If you ignore the symptoms of relapse over and over again, exacerbations will occur more and more often.
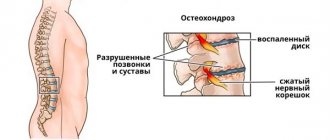
Complications of cervical osteochondrosis are dangerous and varied in their manifestations. The most insidious consequence is considered to be compression of the vertebral arteries , which supply 30% of the brain’s nutrition.
With osteochondrosis, compression of the vertebral artery occurs
Pinching of such arteries can lead to starvation of the brain and the appearance of characteristic symptoms in the form of surges in blood pressure, breathing problems, dizziness, partial numbness, etc. If things are left to chance, complications will spread to the entire spine, which will lead to paralysis of the limbs and disruption of the functioning of all systems and organs.
In severe cases, exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis can cause disability.
Causes of cervical osteochondrosis
Today it is impossible to name the exact causes of degenerative processes occurring in intervertebral discs. There is no confirmation that cervical osteochondrosis is an aging phenomenon.
Numerous studies conducted by scientists from different countries have found that osteochondrosis of the cervical spine has predominantly provoking factors.
Among the predisposing causes of the development of osteochondrosis of the neck are:
- low level of activity, inactivity and a predominantly sedentary lifestyle;
- types of work that involve a static load on the cervical spine;
- excess body weight, insufficient level of physical development;
- disruption of connective tissue development processes;
- old spinal injuries;
- spinal deformity, use of insufficiently comfortable pillows and mattresses for rest;
- genetic predisposition.
The vast majority of reasons are in one way or another related to the natural processes of aging of body systems, as well as the likely development of pathologies of bone and cartilage tissue.
What is the danger of cervical osteochondrosis?
A reduction in the level of mobility and limited flexibility of joints, loss of muscle elasticity and other signs of aging of the body are inevitable, natural processes that accompany a person in ontogenesis.
Annoying pain that occurs when moving much earlier than the natural period of aging often leads to loss of quality of life and even disability.
To determine how to treat cervical osteochondrosis, a professional consultation with your doctor is necessary. In the absence of professional, timely diagnosis and necessary treatment, the disease progresses, which can cause not just a deterioration in well-being, but also serious disruptions to the functioning of the nervous and vascular system.
Main signs and symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
The structure of the human skeleton, the ability to walk upright and the impressive size of the head have led to the fact that some parts of the spine are the most vulnerable, in particular the cervical one.
Among the striking features of the structure of the cervical spine, it is worth highlighting the presence of predominantly small vertebrae and a relatively small number of muscles, and therefore it is in this area that ailment such as osteochondrosis most often occurs.
Pain is the most characteristic syndrome of spinal column disease. Depending on the affected area, it can concentrate:
- in the collarbone and/or shoulder;
- along the entire cervical spine;
- not the anterior surface of the sternum.
It is quite difficult to independently determine the primary signs of the disease, because in the vast majority of cases they are insignificant and very nonspecific:
- pain in
the neck
, mainly in the evening; - heaviness,
pain in the back of the head;
- slight numbness,
tingling in the shoulder, hands;
- crunch,
clicking sound when turning the head.
The progression of the disease is accompanied by a number of already noticeable leading symptoms.
Vegetative-dystonic symptom
It is characterized by shooting pains in the neck, especially noticeable in the area just below the back of the head.
Pain often occurs when staying in the same position for a long time, for example, in the morning.
The neck muscles are tense, there are difficulties when moving the arm to the side, and stiffness in the movements of the fingers.
Due to compression of the vertebral arteries, neurological manifestations often occur:
- recurrent headaches;
- nausea;
- fainting.
Spinal symptom
Localization of the area is on the left behind the chest.
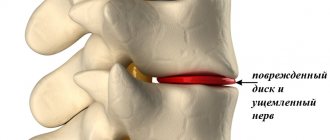
In the process of gradual disruption of the structure of the intervertebral discs, compression occurs and, as a result, pinching of the nerve roots occurs, which leads to narrowing of the arteries and veins, which in turn leads to the formation of radicular and ischemic syndrome.
Poor circulation causes:
- severe, migraine headaches;
- dizziness;
- visual impairment, tinnitus;
- disorders of autonomic functions.
In rare cases, a manifestation of cardinal syndrome can be observed, accompanied by compressive pain in the heart muscle, lack of air, and cardiac arrhythmia.
Stages of disease progression
The disease progresses rapidly in the absence of treatment and the factors and causes of its occurrence persist. The symptoms of osteochondrosis appear gradually; the disease goes through four main stages during its development:
- Preclinical. The symptoms of the disease are not clearly expressed. Patients experience pain during movement and turning the head, muscle tension and increased fatigue are observed. At the first stage of development of cervical osteochondrosis, symptoms and treatment can be passive. In most cases, it is enough to change your lifestyle and enrich your diet with healthy foods.
- Pain in the second stage intensifies and periodically manifests itself at rest due to progressive pinching of nerve endings. Unpleasant sensations in the muscles and spine are accompanied by migraines, limited mobility, decreased performance, general malaise and chronic fatigue.
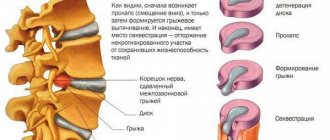
- The third stage is characterized by significant damage to the intervertebral discs with the possible appearance of protrusions and hernias. In this case, intense pain is accompanied by numbness of the skin in the affected areas, weakness of the muscles of the arms and back, and the manifestation of pain in the upper limbs and shoulders, in the periphery. Chronic fatigue, malaise and general weakness and painful condition persist.
- In most cases, the fourth stage progresses from one or more intervertebral hernias. Damaged soft and hard tissues are replaced by connective tissue, which is why there is a pronounced limitation of mobility. A pinched nerve leads to autonomic disorders, problems with coordination and perception, and tinnitus. Migraines become constant, accompanied by dizziness, characteristic of cervical osteochondrosis. Treatment at home and taking painkillers only bring temporary relief. Hospitalization followed by a hospital stay may be required.
The choice of treatment methods for cervicothoracic osteochondrosis directly depends on the stage of its progression. Before starting therapy, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out using hardware and laboratory methods.
Degrees of development of cervical osteochondrosis and their characteristic symptoms
The process of development of the disease proceeds quite slowly, but at the same time it has 4 clearly visible stages:
- 1st degree cervical osteochondrosis – discomfort and minor pain during prolonged walking or static position. The beginning of the formation of compactions in the intervertebral discs;
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, degree 2 – intense pain. In order to eliminate pain, manual therapy and appropriate medications are used;
- 3rd degree cervical osteochondrosis – the presence of severe lesions of the connective tissue of the affected area;
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, grade 4, is the final stage of the development of the disease, characterized by damage to almost all parts of the spine.
The last stage of development of the disease requires surgical intervention, which entails a long recovery.
Diagnosis of the disease
If there are characteristic symptoms, in order to diagnose and treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, you must consult an orthopedic doctor or neurologist.
As part of the diagnostic measures, the specialist will determine mobility and pain in the neck area, as well as assess the degree of sensitivity, and identify other functional disorders.
Among the most effective diagnostic methods are:
- X-ray of the cervical spine, performed in various projections;
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), if a hernia/protrusion is suspected.
In case of circulatory disorders, rheoencephalography and fundus examination may additionally be used.
Traditional medicine recipes
Traditional medicine can be used in treatment only as an effective addition to the main treatment. The use of folk methods as an alternative to traditional ones is not allowed. The most effective and safe recipes are:
- Ointment made from natural honey. In equal proportions (a tablespoon) you need to mix liquid honey, aloe juice and lanolin. Add a few drops of turpentine and eucalyptus essential oil to the mixture, mix well until smooth. Add 100 grams of medical Vaseline. Rub the prepared ointment into painful areas as the pain syndrome manifests itself.
- Rubbing. Mix alcohol and camphor in equal quantities, add a few drops of iodine. Rub the painful areas as discomfort appears.
- Mustard plasters. You can use ready-made mustard plasters or prepare them at home. The product is fixed on the painful area of the neck for 20 minutes, then the area is washed with clean water.
Possible complications
Lack of timely treatment can lead to serious complications, including:
- bulging intervertebral discs
(formation of hernia/protrusion);
- intervertebral disc rupture,
accompanied by pinching of nerves and blood vessels, which can cause death;
- radiculopathy
(damage to the nerve roots), the formation of osteophytes (spikes on the vertebral body) with the manifestation of numerous paresis and paralysis.
Risk factors and causes of exacerbation
There are several reasons why symptoms of exacerbation occur:
- direct change in the structure of the vertebrae, i.e. formation of osteophytes;
- change in the position of the vertebrae relative to each other, compression of the nerves and vessels passing in the lateral canals formed by the spinous processes;
- development of complications caused by the disc extending beyond the boundaries of the spine;
- pinched nerves in the cervical spine;
- chronic strain of the neck muscles.
The likelihood of an exacerbation increases with:
- sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work;
- the presence of acute diseases, disruptions in the hormonal system, exacerbations of existing pathologies;
- hypothermia of the neck, rearrangement of the body’s biological clock (for example, in the fall);
- making sudden movements of the head, for example, turning or bending (the so-called lumbago indicates serious structural changes in the cervical region);
- prolonged experiences, stress;
- improper treatment of osteochondrosis (non-professional massage, physiotherapeutic procedures and gymnastics in cases where they are contraindicated).
How to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is determined by a specialist and depends on the degree of development of the pathology, the form of its course and the characteristics of the clinical manifestation of the disease.
Today, the most effective methods of treating the disease are:
- treatment with conservative methods, including medicinal/non-medicinal;
- surgical intervention;
- complex combination of techniques.
Physiotherapy
Involves the impact of physical factors on the affected area. With an integrated approach and proper implementation of all procedures, improvements become clearly noticeable already in the second or third month of treatment.
Among the most popular areas of physiotherapy prescribed for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis are:
- electrotherapy;
- shock wave therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- ball therapy;
- laser therapy;
- vibration massage.
Neck massage for osteochondrosis
Massage should be performed carefully, without the use of force. Violation of massage technique can cause negative consequences.
The starting position for the massage is the “lying on your stomach” or “sitting with a straight back” position.
All existing massage techniques are based on techniques such as:
- stroking - influencing the surface layers of the skin. It is performed with the palms of the hands and fingertips downwards from the back of the head, to the level of the upper third of the back;
- squeezing - influencing the deep layers of skin in the upper third of the back. Performed with two fingers (thumb and index), carried across the neck;
- rubbing – the main goal is to warm up the skin and increase blood flow in the desired area;
- kneading – affects deep-lying tissues; it must be used with caution, as improper use can aggravate the situation.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis
There are certain exercises for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis. The most effective of them include:
Self-extension
Starting position: sitting/standing with a straight back.
Execution order: while maintaining the starting position, try to lower your shoulders as low as possible, while stretching your head up.
Intensity of execution: at least 10 times (2-5 seconds each), at least 3 times a day.
Self-massage
Equipment: terry towel.
Starting position: sitting/standing, wrap a towel around your neck, and grab its ends with your hands.
Procedure: pull the ends of the towel one by one, gently kneading the neck muscles.
Important! During the exercise, you must ensure that the towel does not slip and rub your neck.
Gymnastics (flexion/extension, turns, bends)
Starting position: sitting/standing with a straight back.
Execution order: from the starting position, perform smooth flexion/extension, rotation or tilt of the head, first in one direction, then in the other.
Intensity of execution: 5-7 movements in one direction.
Drug treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
It is especially important during an exacerbation, since it is through the cervical spine that important blood vessels pass through, providing nutrition to the brain.
Tablets, injections, ointments, as well as other topical agents prescribed by the attending physician can be used as treatment.
Important! Self-medication with drugs of various groups is unacceptable and can lead to disability and death.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
One of the most effective drugs, often used for osteochondrosis in the form of injections, but also available in the form of tablets, patches and ointments.
The key direction of action is to reduce pain, eliminate swelling and inflammatory processes.
Among the most effective drugs in this group it is worth noting Ortofen, Meloxicam, Artradol and Airtal.
Muscle relaxants
Provide effective reduction of muscle tension, which significantly reduces pain.
The recommended treatment period is from 2 to 4 weeks.
Among the most effective remedies, it is customary to highlight Sirdalud and Mydocalm.
Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and warming ointments for cervical osteochondrosis
In order to increase efficiency, anti-inflammatory and painkillers contain steroid substances.
Among the frequently prescribed ones are Fastum gel, Nise and Voltaren.
The effect of warming ointments is aimed at pain relief, as well as warming, which activates blood flow at the site of application of the drug. The most effective are considered to be: Nicoflex, Capsicam.
Chondroprotectors
They are used to slow down degenerative processes and accelerate the regeneration of connective tissue. Has a cumulative effect.
Recommended dosage: from 2 to 6 months.
Among the most popular drugs in this group are Chondroxyz, Artracam and Alflutop.
No pain!
What drugs, ointments and creams effectively help against osteochondrosis? First of all, drug therapy for this disease is aimed at relieving unpleasant, painful sensations that exhaust the patient. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have an analgesic effect, including when used externally.
NSAIDs for external use have local analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-exudative effects for various diseases of the musculoskeletal system, including osteochondrosis. They are absorbed into the blood in small quantities, practically do not accumulate in the body and have low bioavailability, which, of course, has a beneficial effect on safety. However, in case of erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, external NSAIDs should be used with caution [4], since they all non-selectively inhibit cyclooxygenase-1, which protects the gastric mucosa, and cyclooxygenase-2, which is associated with the inflammatory process.
If the patient has osteochondrosis and peptic ulcer disease without an exacerbation, it is necessary to scrupulously follow the recommended dosage of local NSAIDs and the course of treatment, and if pain or discomfort occurs in the epigastrium, discontinue the drug and consult a doctor. During exacerbation of peptic ulcer, any NSAIDs are contraindicated.
External NSAIDs are available in a wide range of dosage forms, which allows you to choose the most “convenient” drug depending on individual preferences and tolerability. You can use ointments, creams, gels and even patches; they all help well against osteochondrosis and provide an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, regardless of the etiology of the disease. By the way, the effect of external NSAIDs can manifest itself very quickly. For example, a combination of emulsion and gel begins to work within a few minutes after rubbing in and lasts for 6–8 hours.
Diclofenac, ketoprofen, ibuprofen, nimesulide, meloxicam, piroxicam, and indomethacin are used externally.
Features of nutrition in the treatment and prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
Proper nutrition is undoubtedly an important component of maintaining a healthy body.
In the context of the prevention or treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, diet is an auxiliary, but at the same time a very significant component.
The main goals of proper nutrition in the treatment or prevention of osteochondrosis are:
- eliminating the possibility of a deficiency of nutrients necessary for metabolic processes in the tissues of the intervertebral discs;
- maintaining optimal body weight;
- reducing the risk of developing vascular changes, preventing circulatory disorders.
Principles of diet
Nutrition for cervical osteochondrosis is based on the principles of rationality and functionality:
- Minimizing inhibitions - a healthy diet is varied, balanced and at the same time rich in all necessary substances.
- Compliance with the drinking regime is an important component in preventing tissue degradation of the intervertebral discs.
- Reducing salt consumption eliminates the possibility of increasing the load on blood vessels and ensures support of water and electrolyte balance.
- Limiting the consumption of starches and sugars in order to eliminate the possibility of metabolic disorders.
Prohibited and recommended foods
Nutrition in the treatment and prevention of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine requires the exclusion of products that clog the body, such as:
- alcohol, which disrupts the water-electrolyte balance and causes tissue dehydration;
- fatty meats and smoked meats that are difficult to digest;
- acidic, spicy dishes that increase inflammatory processes;
- semi-finished products that negatively affect digestion processes;
- sweets, sugar, which disrupt blood circulation.
The list of products recommended for consumption includes mainly easily digestible products of plant and animal origin, rich in protein, complex carbohydrates and fiber, including:
- chicken, rabbit, lean beef and pork;
- Fish and seafood;
- dairy products, eggs;
- cereals of various types;
- whole wheat bread;
- fruits, vegetables, berries and herbs.
Therapeutic methods
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis can be carried out on the basis of conservative (drug and non-drug) and radical (surgical) methods. The basis for using only conservative measures (usually both in combination) may be the first degree of progression of cervical osteochondrosis. Drug treatment in this case is aimed at relieving pain and inflammation, restoring bone and cartilage tissue, and establishing normal blood circulation and nutrition. All this is complemented by physiotherapy, physical therapy and proper rest.
At later stages of the disease, surgical intervention is required to remove growths (if any), restore posture and install prostheses. After the operation, patients are given a rehabilitation period.
Therapeutic methods are in most cases combined. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, symptoms and treatment require an integrated approach to achieve a sustainable result.
Use of drugs
The use of medications involves treatment in courses, since medications have a strong symptomatic effect, but do not completely eliminate the disease. In the course of therapy the following are used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They help reduce inflammation and swelling of soft tissues, as well as reduce the severity of pain caused by compression of the nerve roots by the vertebrae. In the first stages of the development of cervical osteochondrosis, NSAIDs are often used in the form of gels and ointments; severe pain is reduced by tablets. In severe situations, it is possible to administer injections of analgesics.
- Muscle relaxants. The main purpose of the products is to relieve muscle tension and spasms in the neck area. As a result, blood supply and oxygen supply are restored, the severity of pain is reduced and one of the causes of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is eliminated.
- Chondroprotectors. They are not direct drugs, but they help to significantly improve the condition of cartilage tissue. Promote the restoration processes of intervertebral discs and strengthen them. Used during therapy and the recovery period after surgery. The effect of chondroprotectors is felt six months after the start of use and remains constant with systematic use.
- Vasodilators. They improve blood circulation and blood supply, dilate blood vessels, improve overall well-being and help regulate blood pressure. Used in the form of injections.
- Sedatives. Help relieve stress as one of the risk factors. For severe persistent disorders, antidepressants may be used.
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used in short-term courses in cases where NSAIDs do not have the desired effect. Long-term use of glucocorticosteroids is not allowed due to side effects such as decreased immunity, deterioration of the condition of internal organs, bones, and joints.
- Paravertebral blockades. They are used in emergency situations to quickly relieve pain of increased intensity. Injections are placed directly into the affected area. The analgesic effect lasts for several hours.
- Vitamins. Help restore metabolic processes in nerve tissues. Vitamin-rich foods are also included in the restorative diet.
Drug therapy is almost never prescribed as the main and (or) only method of therapeutic intervention. Drug treatment is combined with exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and diet.
Surgical methods
The main indication for surgical intervention is narrowing of the lumen of the spinal column, which is usually a consequence of a protrusion or hernia. The phenomenon is often accompanied by stenosis, compression of nerve endings and blood vessels. In such situations, the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are pronounced, and surgical treatment becomes a necessary measure.
The choice of surgical intervention as a treatment method for cervical osteochondrosis is made on an individual basis. The patient may be indicated for surgery if there is no positive effect from conservative therapy carried out for six to eight months previously.
Surgical methods are used to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
- Dynamic stabilization of the spinal column. It involves installing a stabilizer made of high-strength silicone, which redistributes pressure on the spine. The implant is inserted between the spinous processes along the back.
- Spinal fusion. One of the most common and frequently used methods. It involves removing the damaged cartilage disc and then replacing it with an implant. The mobility of the back, neck and individual vertebrae is restored and preserved.
- Laser surgery. During the operation, the laser beam is directed directly to the core of the disc, after which the size of the protrusion is reduced. The advantages of the method are minimal time costs and low trauma. But laser treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is effective in cases where the size of the hernia is no more than six millimeters.
Surgical treatment is performed in a hospital setting and requires a recovery course that lasts for several months. During the rehabilitation period, the patient is shown:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- analgesics and anesthetics;
- antimicrobial medications;
- chondroprotectors;
- proper rest and sleep;
- corsets and other orthopedic devices (as indicated and prescribed by a doctor);
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- therapeutic diet.
Immediately after the operation, bed rest is required. Next, the intensity of physical activity increases gradually. This requires constant monitoring by a surgeon and neurologist.
Physiotherapy
It is one of the most important methods of treatment, but is rarely used separately from other methods of therapeutic intervention. Physiotherapeutic measures allow:
- reduce the severity of pain and completely eliminate it for a certain period of time;
- reduce inflammatory processes;
- relieve tension and spasms from muscles and blood vessels in the affected area;
- improve metabolic processes in tissues;
- improve blood supply and oxygen supply to tissues.
In practice, they most often use:
- Laser exposure. Helps relieve pain and speed up the process of restoration of soft and hard tissues of the neck.
- Electrotherapy. It involves the impact on osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with electrical impulses.
- Wave treatment. It involves the impact of acoustic waves on the affected areas to relieve spasms and tension.
- Detensor treatment. It is a process of stretching the spine under the influence of the patient’s own body weight.
- Balneotherapy. It is a water treatment and involves taking mineral and salt baths and mud therapy.
- Magnetotherapy. One of the most common methods. The treatment process uses magnetic waves on the affected area.
Physiotherapy is used in conjunction with medications to increase their effectiveness. In particular, anesthetics are used during the treatment to relieve pain.
Manual therapy and massage
Manual therapy is used for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in most cases. This method is indicated at almost all stages of development of cervical osteochondrosis. Symptoms and treatment at home to relieve them also involve manual therapy. The selection of a course of treatment is made individually and depends on the characteristics of the patient and the progression of his disease. The method allows you to reduce the intensity of pain, improve nutrition and blood supply to tissues, restore mobility of the spine and align it.
Contraindications and limitations to the manual treatment method:
- pregnancy;
- acute infectious lesions (as well as exacerbations of chronic ones);
- recent traumatic injuries;
- polyarthritis;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- damage to the circulatory system.
This type of treatment is not recommended for three to four months before scheduled surgery. Manual therapy is performed by a professional doctor.
Physiotherapy
As a rule, therapeutic physical education (PT) is a mandatory measure in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical and cervicothoracic spine. It is usually prescribed two to three weeks after the start of drug therapy and is systematically carried out further to maintain the tone of the back muscles and maintain the patient’s well-being. The set of exercises is selected by the attending physician on an individual basis. In this case, important implementation rules are taken into account:
- movements should be as smooth and slow as possible, sharp and fast movements are not allowed;
- the occurrence of pain indicates improper execution of the exercise or the presence of contraindications to it;
- exercises should be aimed primarily at strengthening and stretching the muscles of the neck and back.
Additionally, it is allowed to use yoga at home and swimming pools. Before using these methods, you should consult your doctor.