Elevated temperature with osteochondrosis is a rare clinical phenomenon and much more often in this condition the doctor begins to exclude other pathologies of the internal organs. In most cases, with spinal osteochondrosis, body temperature remains within the physiological norm. Low-grade fever can occur during inflammatory local processes as a result of radicular compression syndromes.
In this regard, any increase in temperature during osteochondrosis requires a series of diagnostic studies to exclude somatic diseases of internal organs. You should not engage in self-diagnosis, much less treatment. This can lead to negative consequences.
It is important to understand that elevated temperature during osteochondrosis may indicate an infectious and inflammatory process in the spinal cord or in the soft tissues around the spinal column. if during osteochondrosis the body temperature rises to subfebrile levels, then this may indicate sciatica or internal hematomas due to soft tissue injury.
An elevated temperature during exacerbation of osteochondrosis is a reason to prescribe a comprehensive clinical blood test. If its parameters reveal pronounced leukocytosis with an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the doctor will prescribe a more in-depth examination to find the location of the inflammation.
In this material, we will consider all the main aspects that you should pay attention to when detecting hyperthermia against the background of exacerbation of osteochondrosis.
Can the temperature rise with cervical osteochondrosis of the spine?
In most cases, the temperature does not increase with cervical osteochondrosis. A change in this parameter can be observed when:
- damage to the radicular nerve;
- spinal cord injury, including the dural sac;
- tuberculosis, myelitis, tick-borne encephalitis and a number of other infectious processes;
- tumors in the area of intervertebral discs, vertebral bodies or spinal cord;
- myositis and internal hematomas in the stage of decay and aseptic inflammation;
- thyrotoxicosis (the development of a thyroid goiter can give a clinical picture reminiscent of cervical osteochondrosis in the early stages);
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract and salivary glands (mumps).
Low-grade fever with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine may be a signal that the destruction of the fibrous ring has occurred and the process of developing a hernia has begun. At the initial appearance of a hernial protrusion of the nucleus pulposus, the body triggers a compensatory inflammatory reaction. Factors of the inflammatory reaction are drawn into the lesion. They cause increased blood microcirculation. This provokes swelling of the soft tissues. Against the background of such changes, the immune system can increase body temperature to subfebrile parameters (37 - 37.8 degrees Celsius).
A high temperature during osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, reaching parameters of 38.5 - 39.5 degrees Celsius, is always a reason for urgently seeking medical help. In this way, meningitis, encephalitis, acute hemorrhagic cerebrovascular accident and many other dangerous diseases can manifest themselves. Tension of the neck muscles gives the same pain as with osteochondrosis, the patient experiences difficulty turning and tilting the head. If, with such signs, a sharp increase in body temperature is recorded, then it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance team.
As you can see, the answer to the question of whether the temperature can increase with cervical osteochondrosis is not unambiguous. If you are in doubt about what disease you are developing, we recommend that you immediately make an appointment with an experienced doctor. You can do this right now. Our manual therapy clinic offers a free consultation with a neurologist, orthopedist or neurologist for each patient. During the examination, the doctor will rule out dangerous diseases, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment for cervical osteochondrosis.
Herniated discs
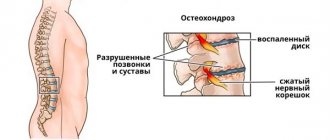
An IVD herniation is a rupture of the annulus fibrosus of the disc with subsequent displacement of the nucleus pulposus. The cause may be heavy lifting, sudden clumsy movement or heavy physical work. The formation of a hernia is usually accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process. Sometimes the spinal root is pinched, which also leads to the appearance of neurological symptoms.
Signs of a lumbosacral hernia:
- sharp sudden pain in the lower back, often radiating to the lower limb;
- difficulties in flexion and extension of the spine;
- weakness in the legs;
- inability to perform daily work or lead a normal lifestyle.
Lumbar hernia.
Characteristic signs of IVD herniation of the cervical spine:
- neck pain spreading to the back of the head and upper limb;
- feeling of stiffness, numbness in the cervical region;
- dizziness and headache;
- slight increase in blood pressure;
- numbness of the fingers, weakness in the upper extremities.
Hernias of the thoracic region are manifested by painful sensations and limited mobility of the spine. Because of this, it becomes difficult for the patient to sit in the same position for a long time. Such hernias appear in people with scoliosis, kyphosis or kyphoscoliosis. The reason for their formation is excessive load on the IVD due to spinal curvature.
A sudden increase in temperature during osteochondrosis of the cervical and lumbar spine often indicates the presence of complications. If this symptom appears, you need to go to the doctor and get examined.
Can there be a temperature with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine?
Only a doctor can accurately answer the question of whether there can be a temperature with osteochondrosis when examining the patient. There are many factors that provoke temperature in thoracic osteochondrosis.
To begin with, a little information about the pathogenesis of osteochondrosis and hyperthermia. Osteochondrosis is a chronic degenerative disease of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs. Pathogenesis consists in the gradual loss of cartilage fibers of their physiological properties, which provide them with the ability to absorb and release fluid.
Chronic course implies the presence of periods of remission and exacerbation. During the remission period, the patient does not experience any discomfort. Exacerbation of osteochondrosis is always expressed in the fact that due to a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc, compression pinching of the radicular nerve or its branch occurs.
Why does this process increase the temperature during osteochondrosis of the thoracic region? First of all, this is a compensatory reaction of the body to compression of the nerve fiber. In order to restore the normal position of the adjacent vertebral bodies, the following occurs:
- an inflammatory response is triggered (the body’s immune system is responsible for this);
- muscle tension begins at the site of injury;
- due to increased blood circulation, soft tissue swelling occurs;
- at the height of the pain syndrome, body temperature can rise to 37 - 37.5 degrees Celsius.
Thus, to the question of whether there can be a temperature with thoracic osteochondrosis, the answer is positive. Yes, such a symptom may be present. But, if the temperature lasts longer than 3 days in a row, you need to consult a doctor and have fluorography done.
Elevated temperature with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine may be a consequence of thermoneurosis. This is a pathology of the autonomic nervous system and the cause of its development is often osteochondrosis of the cervical or cervicothoracic spine.
Causes of a slight increase in body temperature
Sometimes with osteochondrosis the temperature rises sharply to 37-38 degrees. Along with this, difficulties appear in flexing and extending the spine, a feeling of stiffness, severe back pain, radiating to different parts of the body. Such symptoms usually indicate the development of nonspecific complications of osteochondrosis. Let's see what they are like.
Table 1. Nonspecific diseases of the spine, accompanied by a temporary increase in body temperature
| Disease | Features | Reason for the rise in temperature |
| IVD hernia | Sharp pain in the neck or lower back that occurs after lifting heavy objects | Inflammatory process in the IVD due to its damage. Compression by a herniated spinal root |
| Narrowing of the spinal canal | Low back pain, intermittent claudication, sensory and motor disturbances in the lower extremities | Pinching of the nerve roots before they exit the spinal cord canal |
| Radiculitis | Sharp pain in the back, radiating to the upper or lower limb. Symptoms appear after hypothermia or heavy physical work | Inflammatory process in the spinal roots. An increase in temperature can also trigger a concomitant cold. |
| Inflammation of muscles and/or ligaments | Aching back pain that is constant. Feeling stiff and numb | Development of the inflammatory process in spasmodic muscles or damaged ligaments |
Does temperature occur with uncomplicated cervical or lumbar osteochondrosis? Yes, this happens with a long course of the disease, accompanied by pronounced destructive processes in the spinal column. There are cases where people with osteochondrosis maintained a temperature of 37.5 degrees for many months.
Is temperature possible with osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine?
Let’s continue to figure out whether fever is possible with osteochondrosis and what pathologies should be excluded when such a symptom appears. So, the temperature with osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine rises very rarely. But with the appearance of even slight hyperthermia, irritation of the dural membrane of the spinal cord can be suspected. This condition occurs when there is intracanal protrusion of a herniated disc. It is necessary to exclude spinal canal stenosis, retrolisthesis and a number of other pathologies of the spinal column.
In most cases, temperature with lumbar osteochondrosis is a reason to conduct a thorough diagnosis of the condition of the kidneys, abdominal organs and pelvis. Only an experienced doctor will be able to exclude gynecological inflammatory processes, pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis, pancreatic necrosis and a number of other dangerous pathologies during the initial examination.
With lumbar osteochondrosis, short-term hyperthermia can occur during the following processes:
- disc herniation and radicular nerve compression;
- sprains of the ligamentous apparatus and internal hemorrhages in the thickness of overstrained muscle fibers;
- inflammation of the nerve fiber due to pinching;
- sequestration of a hernia into the cavity of the spinal canal;
- inflammation of the dural membrane of the spinal cord due to displacement of the vertebral bodies.
If symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis or lumbosacral osteochondrosis appear, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. We invite you to schedule a free consultation with a vertebrologist at our manual therapy clinic. During the examination, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and give the necessary recommendations for treatment.
Nerve root damage
Radiculitis can develop due to pinching of the spinal roots by IVD hernias. It can also be caused by hypothermia, acute intoxication, or compression of nerves by spasmed muscles of the back or neck.
With radiculitis, the temperature can rise to 37-37.2 degrees. If it rises above these numbers, a more serious pathology should be suspected. Under the mask of radiculitis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, tumors or tuberculosis of the spine, rheumatic diseases, etc. can be hidden.
Do not confuse elevated temperature due to cervical osteochondrosis with occipital neuralgia caused by hypothermia. The latter is manifested by severe pain in the back of the head and is often accompanied by headache, runny nose, cough and other colds.
High and low-grade fever with osteochondrosis: what to do?
If during the first two or three days a low-grade fever persists due to osteochondrosis, then you just need to continue the treatment prescribed by the doctor. If the symptom persists after 72 hours, then you need to visit a therapist and ask to prescribe a general blood test, ultrasound of internal organs, biochemical blood test and, if necessary, a blood test for rheumatic tests.
High temperature with osteochondrosis is a consequence of compression of the radicular nerve or spinal cord membranes. Therefore, to relieve such a clinical sign, it is enough to eliminate the pressure. This can be done using traction traction of the spinal column.
In our manual therapy clinic, a similar procedure is performed under the constant supervision of the attending physician. Before performing traction traction, we give the patient a massage; it allows us to prepare all the soft tissues for the procedure. After completing the traction, the osteopath conducts a session to consolidate the achieved result.
Subsequently, standard treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out. In addition, we are ready to provide assistance with hyperthermia using reflexology and pharmacopuncture.
What to do when the temperature rises
If you have a fever and back pain, you should see a doctor anyway. He will examine you and prescribe the necessary tests. This will help determine the cause of the fever and make sure there are no serious illnesses.
The diagnostic program should include general clinical examinations. With their help, you can detect kidney diseases, tuberculosis, rheumatological diseases, inflammatory processes in the body, etc.
Pathological changes in the spine can be detected using radiography or magnetic resonance imaging. The first method is more accessible and cheaper, but less informative. With its help, only advanced osteochondrosis complicated by spondylosis is detected. The disease can be diagnosed in the early stages only thanks to MRI, which allows one to see almost any changes in the IVD and intervertebral joints.
If there is a slight increase in body temperature, there is no point in taking antipyretics. Drugs from the NSAID group can be used to relieve vertebrogenic pain caused by complications of osteochondrosis. It is better to use them after consulting a doctor.