Almost every person over 35 has experienced neck pain. This is not always a constant feeling. Pain in this area may appear and disappear, may be weak, may be strong.
The main cause of these unpleasant sensations is cervical osteochondrosis. The spine is made up of muscles, vertebrae and intervertebral discs. Dystrophic-degenerative damage to the discs is osteochondrosis. In non-scientific terms, this is wear and tear on these body parts.
Discs consist of a soft, elastic material, which during life gets damaged, stretched, torn, and deformed. The complex of these negative changes is called osteochondrosis.
Causes and mechanism of development of osteochondrosis
To understand why your back hurts, you need to understand how our spine is structured, how it works, what functions it performs and what factors can lead to its damage.
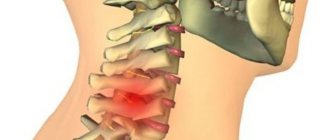
The human spine consists of 32-34 vertebrae (7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 3-5 coccygeal), between which there is an intervertebral disc consisting of cartilage tissue. In the middle of the intervertebral disc there is the nucleus pulposus - a semi-liquid formation in the form of a “ball”, which performs the function of shock absorption and is surrounded by dense cartilage tissue (fibrous ring). The spinal canal, which contains the spinal cord and the nerves extending from it, runs through the entire spine. This entire structure is surrounded by muscles and ligaments. The main functions of the spine are musculoskeletal, shock-absorbing, and protective.
Imagine the Ostankino TV tower, which is held in a vertical position thanks to a whole system of cables stretched from the base to the top. Likewise, our spine is held in the desired position by a group of stabilizer muscles, which normally evenly distribute the load on the spine and joints. Unlike the Ostankino TV tower, our spine is more complex; it can bend in different directions and even twist, all this is possible due to the presence of an intervertebral disc, muscles and ligaments.
Every day a person makes some monotonous, repetitive movements associated with work or leisure activities. If the same muscles work for a long time, they become overstrained and spasm, while other muscles at this time do not experience any stress at all and atrophy. This leads to a change in the “geometry” of the body, the load on the intervertebral disc is redistributed, spasmed muscles tighten the vertebrae, and nutrition deteriorates. With monotonous hard physical labor, the same processes occur. In addition, the intervertebral disc does not have blood vessels, and its nutrition is provided by the surrounding muscles, and during movement in the intervertebral joint, nutritious synovial fluid enters it.
Cartilage tissue consists of 80-85% water, so the drinking regime is of great importance. During the day, a person should drink at least 2 liters of clean water. If not enough water enters the body, then dehydration (drying out) of the intervertebral disc occurs, the cartilage cracks and collapses.
In my practice, I have long noted that stress, anxiety, and worries often contribute to the occurrence of back pain. Our body perceives any stressful situation as danger. At the same time, the sympathetic part of the nervous system is activated, the adrenal glands “inject” stress hormones into the blood, blood pressure rises, the heartbeat quickens, and muscles tense. In nature, if an animal is frightened of something, it runs or defends itself, accordingly, stress hormones burn and the muscles, after working, relax. Man is a social being; he begins to worry more often and move less, so there is no relaxation. As a result, pain in the spine, headache, motor tics and more occurs.
In the literature you can find different formulations of osteochondrosis, but their essence is the same. Osteochondrosis is a “breakdown” of the motor segment, destruction, degeneration of cartilage tissue. The reason is an incorrect motor stereotype and, as a consequence, a malnutrition of the cartilage.
The progression of osteochondrosis is promoted by: a sedentary lifestyle, heavy physical activity, heavy lifting, obesity, carrying a bag on one shoulder, high-heeled shoes, too soft a mattress for sleeping, frequent hypothermia, bad habits, hereditary predisposition, stressful situations, insufficient drinking regime and other.
Decoctions and fees
Of the existing folk remedies, the most popular for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis are decoctions. Properly prepared decoctions relieve pain, reduce swelling and inflammation, and normalize metabolism. Various types of plants are used to prepare decoctions. Below are the most popular recipes.
Decoctions and mixtures are very popular in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Sunflower
Sunflower rhizomes are used to prepare the decoction. Roots must be stored in the fall. After collection, rinse, dry, chop and store in a dry place. To make a decoction, pour 150 grams of roots with two liters of hot water, put on low heat, boil for half an hour, and cool. You need to consume the decoction 3 times a day, it is advisable to wait 20-30 minutes after finishing your meal. The course of treatment is a month.
A decoction is prepared from sunflower root
Needles
Fresh pine needles are collected directly from the trees, take 250 grams of it, pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes. Use twice a day, waiting 30 minutes after meals; it is advisable to maintain an interval of eight hours between doses. Treatment with decoction should be carried out for a month.
This is what fresh pine needles look like
Dandelion
Dandelion root for preparing a decoction
For a decoction of dandelions, the roots are prepared, dried, and crushed. 15 grams of roots are poured with 250 ml of hot water and placed in a steam bath for fifteen minutes. After settling the broth for half an hour, it must be filtered, then the original volume of 250 ml is restored using boiled water.
Drink before meals, 3 times a day, a third of a glass. It is important to remember that decoctions help remove salts from the body, but cannot affect damaged cartilage tissue. Therefore, it is important to combine this treatment method with others.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Manifestations of osteochondrosis will depend on the location and severity of the lesion in the spinal motion segment. At the initial stage, patients complain of dull, aching back pain, discomfort, slight limitation of movements in the spine, periodic numbness in the arms or legs, headache, and fatigue. By starting treatment and changing your lifestyle during this period, the result will not be long in coming and recovery will come quickly.
With severe damage to the intervertebral disc, severe pain, persistent numbness and/or weakness in the arm or leg occurs (depending on the level of damage). These signs may indicate destruction of the intervertebral disc and the presence of a hernia, and it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
In the most severe cases, the pain syndrome can be extremely severe, possible dysfunction of the pelvic organs, severe weakness and numbness in the arm or leg. If these signs are present, urgent hospitalization in a hospital is necessary to resolve the issue of surgical treatment.
With cervical osteochondrosis, pain occurs in the neck, can radiate to the shoulder, arm or head, numbness or weakness in the arm, headache, dizziness.
With osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, pain occurs in the chest, radiates to the sternum or scapula, intensifies with breathing and movement, and sometimes there is a feeling of lack of air. Patients often confuse this condition with heart pain.
When the lumbosacral spine is affected, the pain is localized in the lower back, intensifies with movement, radiates to the leg or perineum, and numbness or weakness in the leg may occur.
It is necessary to remember that our body is a single whole, and the division of osteochondrosis into cervical, thoracic, and lumbar is arbitrary. As a rule, the disease develops throughout the spine, but manifests itself in the part that experiences the greatest load.
Why does it happen?
The reason for the occurrence is relatively simple - intervertebral discs have a certain margin of safety. Our neck is not designed to be constantly tilted when we work or read. Therefore, in modern life, the neck is constantly exposed to overload, starting from school.
Previously, cervical osteochondrosis affected people by the age of 50-60, now this disease can appear as early as 30. All this is due to overload of the neck in the modern lifestyle.
Therapeutic baths
Herbal infusions are used for medicinal baths.
For the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine using traditional methods, medicinal baths are also used. Warm water with a medicinal decoction acts on the skin, and through it on the muscles, warming them, increasing blood flow to them, relieving swelling and relaxing them. Herbal mixtures sold in pharmacies and self-assembled combinations are used.
It is necessary to pour boiling water into an enamel bowl, place the herb there (300-400 grams) and let it brew. The temperature of the water in the bath should be kept as close to body temperature as possible. Bath time is 25-30 minutes. It is not recommended to stay in water that has already cooled for a long time. Patients with high blood pressure should take a bath with caution. After taking a bath, you need to rub yourself well with a towel and rub the sore spot with warming ointment. A similar procedure must be performed every day in the evening for two weeks.
The following plants are recommended for bathing:
- May birch leaves;
- pine, cedar, fir needles;
- chamomile flowers;
- calamus root;
- motherwort.
Risk factors for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
While virtually all people will eventually develop involutional degenerative changes in the cervical spine, there are some factors that can make it more likely that osteochondrosis will develop early or become symptomatic. These risk factors may include:
- Genetics. Some studies of twins show that genetics plays a larger role than lifestyle in the early development of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine and the rapid onset of symptoms.
- Obesity. Weight is associated with the risk of developing degenerative disc disease (osteochondrosis).
- Smoking. This habit can prevent nutrients from reaching the discs and speed up their hydration.
- In addition, spinal trauma can sometimes initiate or accelerate the process of degeneration in the cervical spine.
Less common symptoms
The more the cervical spine degenerates, the more likely it is that the spinal canal will narrow and increase the risk of spinal cord compression. If compression of the spinal cord occurs, myelopathy will develop and symptoms such as:
- Difficulty moving arms and/or legs
- Problems with coordination and/or balance
- Loss of bowel and/or bladder control
- Weakness and/or numbness anywhere below the neck
- Shooting pain in the limbs, which may worsen when bending forward
Cervical myelopathy is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. This condition usually occurs in people over 50 years of age.
What complications does untreated osteochondrosis lead to?
If you allow the disease to develop and do not begin correction in the initial stages, unpleasant consequences may arise:
- vertebral artery syndrome (fainting, decreased vision and hearing);
- severe neurological disorders (muscle atrophy, paralysis, sensitivity disorders, potency problems);
- loss of ability to work (disability, inability to work and perform usual household chores).
In the most critical cases, surgery becomes the only option. In our clinic, operations are not encouraged; everything possible is done to avoid a scalpel. For this purpose, a complex of various correction methods is used.
Ointments
Ointments prepared from components available at home are also widely used as one of the methods of folk treatment for cervical osteochondrosis. These remedies are quite effective and have almost no side effects.
Butter and egg
To prepare this ointment you need to take:
- flour - 20 g;
- egg - 1 piece;
- sunflower oil – 100 ml;
- vinegar – 20 ml.
The ointment is considered ready after two days.
Mix all ingredients and place in a dark place. After two days the ointment can be used. The resulting ointment is rubbed into the affected area, wrapped with paper or polyethylene on top, tied with a warm scarf or handkerchief and sent to bed.
Ginger ointment
Using ginger for osteochondrosis can relieve severe pain and inflammation within an hour after use.
Ginger ointment will help relieve severe pain
To prepare ginger ointment you need:
- fresh cow butter – 30 g;
- garlic – 3 cloves;
- ginger root (unpeeled) – 50 g;
- essential oil – 2-3 drops.
Chop the garlic, grate the ginger. Soften the butter, mix with essential oil, add to the garlic and ginger. Mix everything well, apply to the inflamed area, insulate, and leave overnight for a warming effect.
Egg-mustard mixture
To obtain the mixture you need to take:
- egg white – 3 pcs.;
- mustard powder – 50 g;
- camphor alcohol – 50 ml;
- vodka – 60 ml.
Mustard-egg ointment
Mix the ingredients well with a mixer or in a shaker and put in a dark place for 12 hours. The mixture is used in the form of a compress, which is applied to the affected area and left until completely dry. Apply twice a day for 12 days.