Back pain - how to get rid of it?
This question sooner or later arises before almost every person, because back problems often happen to us. Back pain can be caused by various reasons - sprains, hypothermia, pinching, injuries or more serious diseases (osteoporosis, osteochondrosis, sciatica, etc.). Such pain seriously constrains the spine and a person’s quality of life sharply decreases. To establish the true cause of pain for the purpose of subsequent treatment, it is necessary to visit a doctor - a specialist in this field of medicine. This is explained by the fact that you can, of course, get rid of pain for a while on your own, but without understanding its causes, it is simply impossible to recover completely.
Methods for diagnosing back pain
Diagnosis of back pain begins with an examination of the patient by a therapist or general practitioner. The specialist must find out what diseases the patient and his relatives have had or currently have, assess their health status, and perform functional tests. Based on the information collected, the doctor can guess what pathologies caused the pain and write a referral for studies that are required to confirm the diagnosis. Also, a therapist or general practitioner, having suspected a patient of a particular disease, can refer him for a consultation to a specialist.
It is important! At the diagnostic stage, people who first complained of back pain are conditionally divided into three groups: patients with suspected serious pathologies, patients with radiculopathy (radicular pain), patients with nonspecific pain. The tactics of providing medical care in each of these cases are different.
When diagnosing the causes of back pain, the following laboratory tests are analyzed:
- general urinalysis (helps evaluate kidney function);
- general blood test (it is taken less frequently, mainly to identify inflammatory processes in the body or cancer);
- biochemical blood test (taken if there are suspicions of specific diseases: for example, a test for creatinine helps evaluate kidney function, myocardial infarction can be detected by the concentration of troponin, and the level of calcium in the blood helps diagnose osteoporosis).
We recommend
Stone massage: description, benefits, methods Read more
As for instrumental studies, the following is usually done to diagnose the cause of back pain:
- X-ray (thanks to an image in two projections, you can understand the condition of the vertebrae and detect calcifications in the intervertebral discs and ligaments);
- ECG (to rule out myocardial infarction);
- computed tomography (helps to understand complex pathologies of the spine, providing transverse images (sections) of the area under study);
- magnetic resonance imaging (this is used to obtain images of the spinal cord and assess the condition of soft tissues);
- fibrogastroscopy (helps identify gastric pathologies);
- Ultrasound examination (used mainly to identify somatic diseases, to assess the condition of the heart, blood vessels and kidneys).
Back pain – main risk groups
People who fall into one of the risk groups listed below are at greater risk than anyone else of developing certain back conditions.
Firstly, these are people who are severely overweight. In this case, excess weight puts increased stress on the spine and joints, significantly accelerating the appearance and development of back diseases.
Secondly, these are people who have spinal curvatures and problems associated with the musculoskeletal system (this could be flat feet, for example).
Thirdly, these are people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. Their characteristic features are a lack of physical activity coupled with a constant significant static load on the spine.
Fourthly, these are people who, due to their professional activities, live in conditions of increased, even sometimes excessive, physical activity. Paradoxically, too much physical activity, as well as a lack of it, is a serious problem that accelerates the rate of wear of intervertebral discs.
If you have any questions, ask our specialist! Ask a Question
All the categories described above are similar in that they have a rapid development of osteochondrosis and a high rate of loss of their properties in the intervertebral discs. As a result, it is not uncommon for them to have disc herniations or even the appearance of osteophytes, that is, bone growths. Both options are equally unpleasant and painful.
However, even those people who do not belong to any of the listed groups need to be attentive and careful, because proper nutrition and moderate exercise cannot completely eliminate the possibility that one day there will be no stretching or hypothermia of the back muscles, which sometimes occurs in absolutely healthy people.
Treatment of lower back pain
Modern medicine provides a huge number of ways to treat lower back pain, both in hospitals, with the help of medications, and without medication on the affected areas.
Relieving lower back pain with medications
In most cases, with back diseases, there is no obvious threat to life. Discomfort is caused only by pain that limits physical activity.
To alleviate the condition, the following are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - they will reduce swelling and reduce pain;
- Chondroprotectors – to improve the condition of intervertebral cartilage;
- Hormonal drugs - used for blockades. They relieve pain faster and retain the effect longer;
In addition to injections and tablets, local therapy - gels and ointments - can be used. But, with severe pain, they are ineffective.
Important!
Nerve endings responsible for the basic functions of our body pass through the spine. Damage to them can lead to irreparable consequences. Therefore, the qualifications of the doctor who carries out the treatment should not be in doubt. This is the key to your health!
Back treatment can be different, including self-treatment
In some cases, when the causes of back pain are not long-standing problems with it, ordinary painkillers and warming ointments, as well as warming compresses, baths using special medicinal herbs, etc. can help quickly. The purpose of their use is to warm up the sore area of the back, which significantly improves blood circulation in it and reduces pain. Medicinal methods can also help, which any qualified pharmacist from any more or less decent pharmacy can happily tell you about.
In addition, we can mention all kinds of folk remedies for treating the back, for example, a belt made of dog hair or a woolen scarf, which can be tied to the damaged area. This method is very comfortable, convenient and does not require any additional effort. Various rubbings are often used (for example, tincture of hot pepper and fir oil).
You can also warm your back with wax or propolis. It would also not be amiss to mention home acupuncture, which refers to all kinds of applicators (Lyapko, Kuznetsova, etc.). Their regular use improves blood circulation in damaged areas and relieves pain.
These are not all traditional methods of treating a sore back. You can also mention tinctures taken orally, or special store-bought massagers, but all of them - these methods - only temporarily relieve pain from the damaged area of the back, but do not cure the disease itself. Therefore, in order to get to the bottom of the cause of back pain and completely get rid of the disease, you need to seek help from an experienced neurologist. You can always find such a specialist in a medical office.
At the MART clinic on Vasilyevsky Island
- Experienced doctors (including those practicing in the USA and Europe)
- Prices affordable for everyone
- Expert level diagnostics (MRI, ultrasound, tests)
- Daily 8:00 — 22:00
Make an appointment
Common back diseases
To know which non-surgical method of treating back pain to use, you need to find out what disease led to it.
1. Diseases associated with joints and the spinal column. The following pathologies can manifest themselves as pain in the vertebral region of the back:
- Ankylosing spondylitis. The spine loses flexibility and mobility due to constant inflammation of the vertebrae, which over time even become stiff and grow together in a position uncharacteristic for the normal state - when a person constantly tilts the body forward. This is a forced reaction to spasms of the paravertebral muscles that occur with this disease.
- Spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis. The diseases are characterized by displacement of the lumbar vertebrae forward or backward, as a result of which compression of the nerve endings occurs - the person experiences pain in the lower back.
- Osteochondrosis. A disease in which the depreciation of the spinal column is reduced, cracks appear on the discs between the vertebrae, the fibrous ring ruptures, and the core of the disc is pinched, emerging through the resulting cracks.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. First, the disease affects the joints (knees, hips, shoulders), then spreads to the cervical spine. The affected vertebrae put pressure on the nerves, causing lumbago, and the person feels stiffness in the body, especially after a night's sleep.
- Osteomyelitis. With this disease, a purulent-infectious process develops in the bone tissue of the spine, inflammation is accompanied by acute pain in the muscles.
- Reiter's disease . This rheumatic disease causes pain as the small supporting muscles of the back become inflamed.
- Intervertebral hernia . Painful sensations appear during movement, because nerve endings are pinched due to protrusion of the nucleus.
2. Muscle-related diseases. Diagnosis of diseases that cause back pain often shows that the muscular corset that supports the spinal column has compactions and is subject to spasms. The causes of mobility impairment are:
- Fibromyalgia. It is characterized by pain in the area from the neck to the lower back with neuralgic symptoms - in some points of the back, pressure causes an acute reaction.
- Dermatomyositis. Soreness in this case is a consequence of inflammation of the skin located close to the striated and smooth muscles of the back.
- Polymyositis. This is inflammation of the back muscles as a result of overexertion or hypothermia. Turning the body causes severe pain, and weakness in the muscles is felt.
- Charcot's disease. Due to inflammation of the peripheral nerves along the spine, sensitivity decreases, muscles lose such strength that gait changes noticeably.
- Polymyalgia rheumatica. With this illness, which is recognized by the characteristic asymmetry of the back, a person can stand on his feet or raise his arms only if someone helps him with this.
Recommended articles on the topic:
- Thermal detoxification: lightness of the body and clear skin
- Lipolytic therapy: indications, contraindications, stages of the procedure
- Weight correction: everything you need to know about the procedure
3. Spinal cord pathologies. Often the cause of pain is infringement of the spinal cord, which, as is known, acts as a connecting link between the brain and the body. This organ of the central nervous system is located in the spinal canal. It runs between the vertebrae from the head to the coccyx and has 31 branches - each is responsible for supplying nerves to organs and tissues in a specific area of the body. If any areas of the spinal cord become inflamed or pinched, a person experiences back pain. This happens when:
- the spinal membranes are compressed as a result of spinal injuries, hematoma or abscess;
- cerebral circulation is carried out incorrectly;
- there is a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- hemorrhage occurs;
- the muscles located next to the spinal canal become inflamed;
- syphilis or HIV cause complications;
- multiple sclerosis occurs;
- Benign or malignant tumors appear in the back area.
4. Back pain due to psychosomatics. Back pain is not always caused by physical ailments or autoimmune diseases. It happens that an examination carried out in order to select non-surgical treatment methods shows that there are no pathologies. What does it mean? Most likely, the cause of pain is psychosomatic factors. Depression, nervous strain, prolonged stress, sexual experiences - all this can cause discomfort in the back to such an extent that a person’s gait will become different, and lumbago will torment him more often, and sensitivity will change.
We can handle it ourselves
There are two main directions of treatment: drug and non-drug. As a rule, they are used comprehensively.
Medicines used include:
Conventional analgesics (eg paracetamol). But they are usually ineffective for musculoskeletal pain.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They must be accepted first. But they should not be used for a long time and in large doses - due to side effects (on the gastrointestinal tract, heart and blood vessels). For those who have an ulcer or hypertension, NSAIDs are not prescribed or are given in minimal doses and under the cover of coating medications.
Central muscle relaxants. They must be taken along with NSAIDs. They relieve muscle spasms and provide additional pain relief. The duration of treatment is determined individually, the average course is 14–20 days.
What medications should be used to treat which pain? Advantages and disadvantages of analgesics Read more
Exercises to strengthen your back at home
We offer a simple set of exercises for the back that can be performed at home without special training or exercise equipment.
Forward bends
. A simple back stretching exercise. Stand up straight, straighten your arms above your head, lean back slightly, and then stretch down and forward. Try to touch your toes with your hands without bending your knees. If it doesn't work out right away, it's okay. The exercise must be repeated several times, each time you should strive to bend a little lower and feel the back muscles stretch slightly. There is no need to rush, it is better to do more approaches.
Lifting the knees in a lying position
. Grab a fitness mat, yoga mat, or just lie down on the floor. Bend your arms at the elbows and place them under your head, and bend your legs at the knees. Slowly raise your bent legs to your stomach and lower them back. Try to do everything smoothly.
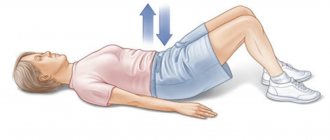
Lifting your hips while lying down
. Extend your arms along your body, bend your legs at the knees. Raise your hips so that your body from head to knees is off the floor. Hold the position for a few seconds, then slowly lower to the floor.
Twisting knees while lying down
. Stay on your back, arms out to the sides, legs bent at the knees. Slowly lift and twist your bent legs to the right and left. Try not to take your hands off the floor. If desired, you can place a small pillow between your knees.
Stretching while lying down
. Lie on your back, you can put a pillow under your head. Bend your knees, then take turns grabbing your knee with your hand and slowly, without excessive effort, begin to pull it towards the opposite shoulder. When your knee touches the opposite shoulder or reaches the maximum point physically possible for you, fix it in this position for a few seconds and then return it to the starting point. Repeat the exercise for both legs in turn, try not to lift your shoulders too much from the floor.
Rising from a lying position
. Roll over onto your stomach, place your arms bent at the elbows along your body and begin to lift yourself up on your arms, gradually straightening them. You should aim to raise your upper body with your arms outstretched, but if at first you find the exercise too difficult, you can start lifting yourself up on your elbows. At the same time, your hips should be pressed to the floor and your legs should be relaxed. If during the exercise you feel pain descending to the buttocks, then you need to stop the exercise.
Stretch on all fours
. Get on all fours, try to keep your neck and back straight, and do not bend your arms at the elbows. Inhale and as you exhale, lower your body onto your heels, then inhale and return to the starting position. Stretching should not cause discomfort, otherwise, stop the exercise.
Exercise “Cat”
. Stay on all fours and begin to bend and straighten your back. Do the exercise slowly, try to bend and unbend as deeply as possible.
It is important that the exercises are not painful. If during any exercise you feel dizzy or sharp pain, then stop and move on to another exercise or postpone the warm-up. It might be worth seeing a doctor.
New possibilities for ultrasound diagnostics.
In , “Losiny Ostrov”, “Maryino”, ultrasound diagnostics of all parts of the human vascular system is currently being carried out, starting from large main arterial and venous vessels and ending with the microvascular network of internal organs and surface tissues.
The main advantages of vascular ultrasound examination include: non-invasiveness and absolute patient safety, both during a single and subsequent dynamic examination; high information content of the received data; determining the assessment of intraluminal formations (atherosclerotic, thrombotic in nature), as well as studying the condition of the vascular wall.
Functional changes in blood flow are also assessed. This technique is an ultrasound scan of the brachiocephalic arteries, arteries of the base of the brain, peripheral arteries, peripheral arteries and veins of the upper and lower extremities, arteries and veins of the abdominal cavity.
The center performs echocardiography, which makes it possible to determine with absolute accuracy the dilation of the atria and ventricles and to clarify the thickening of their muscle walls. The method provides the opportunity to conduct a detailed study of the leaflets of all heart valves and determine the degree of their insufficient divergence or closure, determine myocardial contractility and ejection fraction. Consultation is also provided and treatment is prescribed. m>
The more expensive the better?
Before visiting a doctor, you do not need to do any research - neither expensive nor cheap. Because only a specialist after examination can decide what causes the symptoms. And the choice of research method is determined by what exactly the doctor expects to find in the patient.
When there is only pain, it is most likely a local muscle spasm and it is necessary to check for fractures or displacements of the vertebrae, scoliosis and lordosis. In this case, x-rays are more informative.
Article on the topic
Reveal the hidden. Who needs an MRI
But if the pain syndrome is combined with sensory disorders or, for example, with a headache, or if it hurts in a certain area, an MRI or CT scan may be required.
To exclude or confirm an intervertebral hernia, an MRI must be done.