Heel pain when walking
- a frequent companion of a modern person, especially if, due to the nature of his work, he spends a lot of time on his feet. Heel pain can be caused not only by fatigue, but also by soft tissue bruises caused by an uncomfortable heel or direct injury. But most often, discomfort that lasts for weeks indicates the presence of a disease.
Most patients manage to ignore the onset of diseases localized in the sole area: pain in the heel when stepping is attributed to work loads, uncomfortable shoes, varicose veins and age-related changes. However, frequent, daily and, especially, acute pain that intensifies over time is a sure sign of a disease that can affect the tendons, articular cartilage and bones in the heel area.
You should be especially alert to severe pain in the heels, which begins in the morning, immediately after waking up and walking for a short time.
. If you didn’t conquer the mountains yesterday and spent a normal day, but your feet are “humming” - read the article to find out how to treat heel pain when you step.
Heel pain often bothers modern people who lead an active lifestyle.
Causes of heel pain
Although the exact cause of heel pain can only be determined after a diagnostic test by a podiatrist or rheumatologist, the nature of the pain can tell a lot.
Heel pain in the morning usually indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. If it does not stop after 2-3 weeks, it means that the process has become chronic.
— and therefore you shouldn’t put off going to the doctor, hoping for chance.
Some acute inflammatory diseases can lead to irreversible changes in the joints within a few days
.
Pain in the heel, which is accompanied by numbness, deterioration of sensitivity, change in skin color, and ankle cramps, indicates compression of the nerve and/or disruption of tissue trophism. They can occur due to varicose veins, muscle and ligament sprains, and traumatic injuries.
In summary, the causes of heel pain include:
- injuries
; - circulatory disorders in the legs
(often accompanied by roughening of the skin)
and hypovitaminosis
(its frequent symptom is cracking of the skin on the heels, dry calluses); - diseases of bones and tendons
(calcaneal epiphysitis, achillobursitis); - diseases of the spine
(in particular, the lumbosacral region); - metabolic disorders
(osteoporosis, gout, diabetes and other metabolic diseases); - fungal diseases
; - infectious diseases
(including tuberculosis).
Heel pain can also be caused by more harmless factors - for example, rapid weight loss, which sometimes thins out the fatty “cushion” of the heel.
Injuries
Due to its shock-absorbing role, the heel is exposed not only to high pressure, but also to frequent impacts, which leads to injury. Contrary to popular belief, injury can occur not only as a result of a strong blow or traction, but also as a result of a series of repeated microdamages (for example, due to vibration or uncomfortable shoes.
Any injury to the heel area - be it damage to the muscles, ligaments, tendons, heel bone, nerve fibers, or even severe bruising of the subcutaneous fat or blood vessel - disrupts the physiological position of the foot (for example, when the patient “saves” part of the sole due to pain ).
Traumatic heel pain when stepping usually occurs due to:
- tendon rupture or sprain;
- cracks in the spongy calcaneus, fracture;
- bruise of the soft tissues of the heel.
Treatment of traumatic heel pain should be carried out by a qualified traumatologist.
. Patients are prescribed rest for the affected limb (fixation with a bandage, plaster, splint), drugs to improve tissue trophism, chondroprotectors for better healing and prevention of changes in the joints.
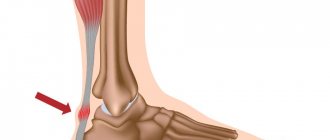
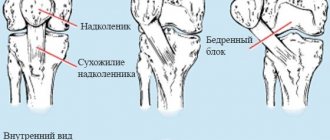
Heel spur
A striking example of a disease that is accompanied by inflammation and severe pain in the heel when stepping is a heel spur. The pathology often develops against the background of flat feet and other curvatures of the foot, uncomfortable shoes, or under the influence of other factors in which the load on the plantar part of the foot is unevenly distributed. This leads to an unnatural position and deformation of the tendon.
, due to which inflammation begins in the places where it is attached to the head of the bone. To compensate for the load, the body triggers ossification of the tendon tissue - as a result of which it takes on the shape of a spike (spur).
Heel spurs are characterized by a gradual increase in pain in the heel when walking and throbbing in the leg. The peak of pain occurs in the morning and evening, and in the middle of the day the pain usually becomes moderate and tolerable. Many patients complain of a feeling of “walking on glass” - the pain in the heel can be so intense when stepping on it.
If left untreated, patients may develop difficulty moving independently. ankle orthosis helps
(bandage), which helps distribute the load, reduce pain and inhibit
ossification
(ossification) of the tendon.
Also, for heel pain in the morning, doctors recommend taking anti-inflammatory drugs, correctors of cartilage and bone metabolism, physiotherapeutic procedures, and therapeutic massage. In advanced cases, surgical treatment is indicated
.
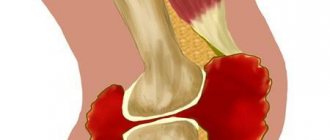
Bursitis
Often bursitis
affects the so-called
Achilles tendon
(Achilles bursitis). This disease, which is accompanied by heel pain, is most susceptible to athletes (especially runners), overweight people and lovers of high heels.
With bursitis, there is swelling, pain in the heel when stepping, and swelling of the foot due to the accumulation of synovial fluid. The skin over the ankle joint becomes red and hot. Patients are prescribed a strict rest regimen, a pressure bandage made from an elastic bandage, and adherence to clinical recommendations.
. If the disease does not recede, a puncture is performed (fluid drainage through a puncture), the patient receives glucocorticoids to relieve inflammation.
If conservative treatment of heel pain when walking does not have an effect, the affected fragment of the synovial bursa is removed through a microscopic puncture with a diameter of about 4 mm. After 2 days the patient can already walk.
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis
is a chronic disease that affects not only the joints of the foot, but also other joints of the body. As a rule, the disease begins in the spine and affects the intervertebral joints of the lumbar region.
Men are more susceptible to ankylosing spondylitis than women. Although its exact causes have not been established, an increased risk of development is observed in people with a hereditary predisposition, injuries, frequent colds and infectious diseases
(including foci of chronic infection in the body).
In addition to pain in the heels when walking, there is stiffness of movement, inflammation in the knees and lower back. Treatment, due to the incurability of the disease, is symptomatic and consists of taking painkillers and symptomatic medications. Since the “cartilaginous” type joints are primarily affected, the use of chondroprotectors is recommended.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis of the foot
often observed in female patients aged 30+.
This is a chronic autoimmune disease, which is accompanied by inflammatory erosive lesions of the articular surfaces
(in this case, the joint is destroyed by the body’s own immune cells, considering its cells hostile). In addition to heel pain in the morning, arthritis is indicated by swelling of the foot and hot, reddened skin over the joints, increased fatigue of the legs and other signs of inflammation. The onset of heel pain in rheumatoid arthritis is usually preceded by an infection, stress, or other shock to the immune system.
The disease is characterized by a high degree of disability
, so you need to seek help at the first symptoms of heel pain.
Treatment consists of the use of immunosuppressants
,
anti-inflammatory drugs
and
chondroprotectors
.
Gout
Gout
is a severe metabolic disease that often
affects the interphalangeal joints of the legs
and can cause severe heel pain.
Pain syndrome is caused by uric acid crystals, which are deposited in the joints and provoke chronic inflammation due to mechanical trauma to tissues. Gout is often a hereditary disease
and is observed in relatives of patients.
Heel pain when walking and heel pain in the morning, at night increases after consuming fatty meat foods and alcohol.
Treatment of heel pain due to gout involves following a diet, taking medications that reduce the level of uric acid in the blood, anti-inflammatory drugs and chondroprotectors.
There are many causes of heel pain
Achilles tendonitis
This disease is described as a pathological inflammation of tendon fibers. Most often it affects professional runners, tennis players, basketball and volleyball players who do not control the intensity and smoothness of sports training. The disease is accompanied by classic symptoms - redness, swelling, pain and stiffness of movement. Pain usually occurs during activity and subsides during rest.
During inflammatory processes, the following picture occurs: the removal of salts and metabolic products from the tissues is disrupted, causing the fibers to lose their strength and flexibility. If they continue to receive load, cracks and micro-fractures form. Over time, the tendons recover, but lose elasticity and acquire scars, therefore, in order to prevent chronic consequences, it is necessary to seek help in time.
Diagnosis of heel pain
Diagnosis and determination of the cause of heel pain is carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist or rheumatologist; consultation with other specialized specialists (neurologist, oncologist, infectious disease specialist) may also be required.
Diagnosis begins with an oral questioning of the patient about the specifics of heel pain, history taking, palpation, and motor tests. Based on preliminary observations, the doctor issues further directions.
To confirm or refute existing hypotheses regarding heel pain when stepping, the following is used:
- general and biochemical blood test, analysis for tumor markers and rheumatic factor;
- microbiological and bacterioscopic studies (synovial fluid, sputum, etc.);
- determination of blood glucose levels;
- X-ray of the affected limb;
- puncture biopsy (if bone tuberculosis is suspected);
- Ultrasound (to detect damage to bones, blood vessels, etc.);
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography;
- electroneuromyography.
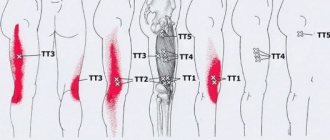
Symptoms of heel tendon diseases
Regardless of what caused the inflammation, you can always emphasize the same symptoms:
- redness in the area of the diseased ligament;
- increased sensitivity and pulsation;
- discomfort that increases when the patient leans on the foot;
- pronounced swelling of soft tissues;
- increased body temperature;
- sharp and burning pain stretching from the heel to the calf muscle;
- A crunching sound may be heard in the joint.
If the cause of pain is a tear of the Achilles tendon , other symptoms are added:
- sharp pain similar to a mechanical shock;
- the patient is unable to stand on his toes or extend his foot forward;
- palpation of the “notch” in the affected area;
- the swelling site turns blue.
Treatment for heel pain
The question of how to treat heel pain when stepping is decided after determining the cause of heel pain.
If heel pain is infectious in nature, antibiotics
. In case of injuries, as a rule, conservative treatment is carried out using bandages, blood microcirculation correctors, bone and cartilage metabolism correctors. For autoimmune causes of heel pain, basic therapy drugs, NSAIDs, and glucocorticoids are recommended. In case of metabolic diseases, therapy of the underlying disease is necessary.
Surgery
Surgery
heel pain is used for displaced fractures of the calcaneus, as well as in severe cases, in the later stages of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Indications for surgery are:
- tendon rupture
; - advanced heel spur
; - bursitis that cannot be treated with medication
.
Also, partial excision of synovial cartilage may be recommended in some cases of rheumatoid arthritis.
Modern medicine uses minimally invasive methods for treating heel pain when stepping - most operations are performed through small punctures, last no more than 30 minutes, and the recovery period takes only a few days. Surgery for heel pain when walking helps relieve pain and inflammation.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy in the treatment of heel pain helps relieve swelling and inflammation in the acute stages of the disease, normalize tissue nutrition and restore impaired metabolism. If you have severe heel pain, you should consult your doctor about the choice of technique: some types of physiotherapy can only be performed in a state of remission
.
For heel pain when stepping, the following may be prescribed:
- electrophoresis
(especially medicinal); - magnetotherapy
; - laser therapy
; - ultrasound therapy
; - phonophoresis
; - thermotherapy, cryotherapy
; - mud therapy and balneological procedures
; - taping
; - manual therapy
; - shock wave therapy
; - ultra high frequency therapy
; - therapeutic massage
(on the foot, lower leg, thigh); - physiotherapy
.
orthoses is also recommended for heel pain when walking.
or
tires
.
Drug treatment
In addition to specialized medications, if heel pain when walking is secondary (caused by a systemic disease), the following are used:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
. NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Meloxicam, Lornoxicam and others) are usually prescribed in courses of 10-12 days to relieve acute heel pain when walking. Longer use of drugs in this group can cause erosive lesions of the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines. - Analgesics and glucocorticoids
. If other methods for heel pain are ineffective, extra-articular drug blockades with novocaine, lidocaine and glucocorticoids (Hydrocortisone, Diprospan, Prednisolone and others) are used. - Chondroprotectors
. Correctors of bone and cartilage metabolism help relieve inflammation in bursitis, arthritis and other causes of heel pain when stepping. They improve the elasticity of connective tissue, promote the synthesis of collagen and proteoglycans, and prevent joint complications from developing. Taking this group of drugs promotes the healing of cracks and fractures of the heel bone, prevents the ossification of tendons and the progression of arthrosis and arthritis, normalizes the calcium-phosphorus balance and provides support to bones and joints in systemic metabolic diseases. One of the most effective and easy-to-use chondroprotectors is Artracam - glucosamine sulfate in sachet form. Artracam has maximum bioavailability for the body and begins to act after 2 weeks of administration. Also, for the treatment of heel pain when walking, doctors recommend Dona, Movex Active and others.
Chondroprotectors
have a cumulative effect, so they must be taken for at least 3-6 months. They help reduce pain, and with it the amount of medications taken for heel pain.
In case of mild disease, compresses with dimexide
,
novocaine
,
acetylsalicylic acid
.
Therapeutic massage is one of the ways to prevent heel pain
Operative methods
If conservative treatment does not help, Achilles tendon surgery . It is often resorted to if the patient has severe damage, in particular a rupture. Surgical intervention is performed in two ways - stitching or plastic surgery:
- Stitching. It is used if the rupture is fresh, received within the last 24 hours.
- Plastic. Usually it is resorted to if long-term conservative treatment has not helped. The operation is quite complex and is aimed at transferring a piece of tendon from one part of the lower leg to another. After the manipulations have been performed, the patient is given a plaster cast.
Preventing heel pain when walking
If your job requires prolonged standing or walking, the following guidelines should be followed:
- Give your legs a rest
. If you have to stand a lot, place a low stool or a rolled-up towel at your feet. Periodically place your foot on an elevation so that the muscles have time to relax and tissue nutrition can be restored. After a while, change your leg. - Wear comfortable shoes with low heels
. If necessary, use orthopedic insoles or shoes with orthopedic heels. Make sure your shoes don't put pressure on your feet or pinch blood vessels. - Watch your diet and try to lose excess weight
. To relieve heel pain in the morning, consume as many natural vitamins and minerals as possible and as little simple carbohydrates as possible (sweet fruits, baked goods, fast food, sugary drinks). - If an orthopedist or rheumatologist has ruled out the inflammatory or traumatic nature of heel pain, it is advisable to alternate loads on the foot or periods of long immobility with therapeutic exercises
. These include rotating the foot, stretching and pulling the toes (away from you and towards you), rolling a rolling pin or gymnastic stick with your foot, picking up pencils scattered on the floor with your toes and other warm-up methods. - Be sure to wear warm socks in cold and wet weather
- hypothermia is dangerous for your joints and can worsen heel pain in the morning. - Do not develop chronic or infectious diseases; have your injuries treated promptly by a doctor
.
Easy walking for you!
Images designed by Freepik
Achilles tendon bursitis
Achilles tendon bursitis is an inflammatory process affecting the tendon bursa. Its development is caused by injuries, tight and uncomfortable shoes, and gout. Depending on which side of the tendon its focus arose, posterior and anterior bursitis are distinguished:
- Posterior bursitis. Occurs mainly in women as a result of wearing high heels. The lift provokes so-called “bumps”, which lead to the disease. Early symptoms include pain, redness and hyperthermia, and late symptoms include a hard and tender growth known as Haglund's deformity.
- Anterior bursitis. A disease that is also known as Albert's disease. It can be caused by any condition accompanied by a load on the tendon area. Associated diseases are gout and rheumatoid arthritis. If the cause is a bruise or gout, the symptoms develop quickly, but if other disorders develop gradually. Symptoms include pain, swelling and red spots spreading on both sides of the heel.
Preventive measures
To never have troubles with your ankle, you just need to remember about preventive measures. These include exercises for the Achilles tendon , well-chosen shoes, and a balanced diet:
- Warm up the ankle before complex physical exercises.
- Properly pump the calf muscles, thereby strengthening the limb.
- Practice the “jumping” exercise - they will ensure the elasticity of the fibers.
- Practice exercises aimed at stretching the tendon.
- Eat enough protein, calcium and vitamin D.
- Minimize heels and stilettos in everyday life.
- Buy anatomically correct shoes, namely with a hard back.
If you experience pain and discomfort in the tendon area, self-medication can play a cruel joke on you - lead to lameness or chronic inflammation. The Center for Rehabilitation Medicine offers you consultation with competent orthopedic traumatologists, advanced treatment methods and individual rehabilitation.
Free, unrestricted movements are part of our full life, so any alarming signal is a reason to call us.
You can find out the prices of the clinic in the price list or by calling: +7 (8552) 78-09-35, +7 (953) 482-66-62.
Achilles tendon rehabilitation
After surgery, rehabilitation time is on average 1–3 months. Not only the strength of the sutures, but also the likelihood of re-injury depends on compliance with restorative measures. Measures include a state of complete rest, lack of physical activity and fixation of the foot in an elevated position. Traditionally, rehabilitation includes the following stages:
- The use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Wearing a plaster cast for the first week after surgery.
- After removing the plaster, careful development of the joint begins, but without putting stress on the sore foot. In this case, crutches are used.
- After one to two months, bandages and orthoses are applied.
The most important thing in rehabilitation is its gradualness, because any careless premature measures lead to rupture of the stitches.