Video on the topic:
all videos on the topic
Bone tuberculosis (osteoarticular tuberculosis) is a specific inflammatory disease that occurs in conditions of hematogenous dissemination of the tuberculous process. Tuberculous lesions of bone tissue are most often localized in areas rich in bone marrow (vertebral body, epiphyseal sections of long tubular bones, spongy bones) and are much less common in the diaphyseal sections of short and long tubular bones. When the tuberculosis bacillus penetrates the spongy parts of the bone, a primary lesion (ostitis) occurs, which subsequently spreads to the joints and surrounding tissues, causing their destruction.
The disease can affect various parts of the musculoskeletal system, but most often develops in the spine and large joints (knee, hip, elbow, shoulder and wrist). Complications of tuberculosis of bones and joints, in the absence of adequate treatment, are curvature of the back, the formation of a hump, complete immobility of the joints, muscle atrophy, shortening and paralysis of the limbs.
There are three phases of the disease:
- pre-arthritic phase – formation of a primary lesion (ostitis);
- arthritic phase - the beginning, height and subsidence of secondary arthritis,
- post-aging phase – consequences of tuberculous arthritis (exacerbations, prolonged course, relapses).
Causes of bone tuberculosis
Bone tuberculosis is always a consequence of hematogenous transfer of the tuberculosis bacillus from the primary source of infection (with late reactivation of the process - from old tuberculosis foci). A reactive inflammatory process begins around the pathogen, an infectious granuloma develops, with the growth of which the bone substance dissolves, abscesses, fistulas and sequesters are formed.
Osteoarticular tuberculosis occurs in all age groups, but due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of a growing organism, which is characterized by a richly developed vascular network of the epiphyses of bones and vertebral bodies, the disease poses the greatest threat to children. In old age, this form of tuberculosis develops relatively rarely.
The development of bone tuberculosis can be caused by the influence of various factors:
- poor social conditions,
- fasting or malnutrition,
- frequent infectious diseases,
- chronic stress,
- long-term treatment with glucocorticoids or immunosuppressants;
- HIV.
Causes and risk factors
Previously, spinal tuberculosis was considered a disease that affected people living in unfavorable conditions (immigrants, people without a fixed place of residence). However, diseases are increasingly being detected in people who are financially and socially successful. .
Various unfavorable factors can lead to the development of pathology, such as:
- Contact with a patient or use of his personal belongings;
- Diseases of a bacterial and viral nature, leading to disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- Unfavorable living conditions (unsanitary conditions);
- Lack of adequate nutrition, insufficient intake of vitamins and protein products;
- Heavy physical activity;
- Back injuries;
- Prolonged general or local hypothermia;
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol or drugs).
Complications and consequences
Did you know that...
Next fact
Bone tuberculosis leads to purulent inflammation and destruction of the vertebrae. If left untreated, spondylitis can lead to very adverse consequences. The presence of a chronic focus of inflammation in the body provokes the appearance of painful abscesses and fistulas , which often become the entry point for secondary infection.
The patient has significant deformation of the spine and impaired functionality. As a result, a person’s motor activity is significantly limited, which leads to permanent loss of ability to work and disability.
In addition, if the source of inflammation is localized in the lumbar or sacral regions, the functioning of the pelvic organs is disrupted , which contributes to problems with urination and reproductive function. Inflammation of the bone or cartilage tissue of the spine is also a common cause of the development of cancer in this area.
Video: “Tuberculosis”
Symptoms of bone tuberculosis
Clinical manifestations of bone tuberculosis are determined by the location and nature of the pathological process. The initial stages of the disease often occur without significant symptoms.
The first signs of tuberculosis, characteristic of the prearthritic phase of the disease:
- lethargy, drowsiness, general weakness;
- moderate increase in body temperature (up to 37 - 37.8 ° C);
- irritability;
- nagging muscle pain.
When the disease passes into the arthritic phase, an intensification of existing clinical symptoms is observed, which are accompanied by signs of local damage. The nature of the symptoms depends on the location and stage of development of tuberculous inflammation:
- increase in body temperature to 38 – 39 °C;
- severe, severe pain in the spine or joints;
- limitation of joint mobility;
- swelling, hyperemia, muscle contractions, soft tissue atrophy and accumulation of serous exudate in the area of the affected joint;
- shortening of limbs, lameness, sudden stoop;
- formation of abscesses.
The calming stage is characterized by a gradual improvement in general condition, a decrease in body temperature, a decrease in the inflammatory process and normalization of blood tests.
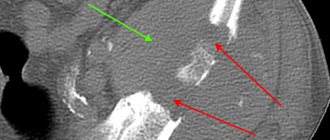
Dynamics of radiological changes in spinal tuberculosis
in the prearthritic phase, a focus of destruction with unclear contours containing a sequester is determined in the vertebral body. However, these changes during this period of the disease are not detected in all patients.
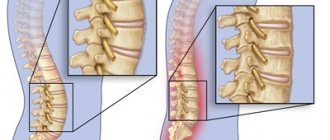
In the initial period of the spondylytic phase, the focus of destruction is clearly expressed, a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc and contact destruction in adjacent vertebrae are observed. In some patients, shadows of edema abscesses are identified at the level of the affected vertebrae.
In children, the increase in destruction is accompanied by increased osteoporosis, while in adults the density and structure of bone tissue may be little changed.
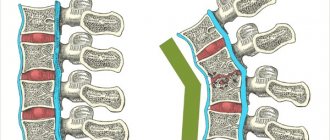
During the most active period of the disease, destruction of the bodies of 2-3 vertebrae with destruction of the intervertebral disc is visible. The contours of the vertebrae are unclear, blurred, and a mildly expressed deformity of the spine, predominantly kyphotic, is revealed.
In most patients, shadows of leaky abscesses are found, which in the thoracic spine are determined by the presence of compaction of the pre- and paravertebral soft tissues, which have a fusiform, triangular or spherical shape. Most often these changes are symmetrical.
In the lumbar spine, the presence of a leaky abscess is indicated by a change in the contours of the iliopsoas muscle, their expansion or disappearance on one side.
In the post-spondylytic phase, the contours of the affected vertebrae are clear and sclerotic; partial filling of defects in the vertebrae with newly formed bone trabeculae, spinal deformation, osteochondral growths, dystrophic and sclerotic changes in bone tissue are determined.
Diagnosis of bone tuberculosis
If tuberculosis is suspected, the patient is sent to a specialized dispensary for an in-depth examination and diagnosis.
Diagnostic research methods:
- physical examination,
- clinical blood test,
- bacteriological examination of exudate or bone tissue,
- Mantoux test,
- linked immunosorbent assay,
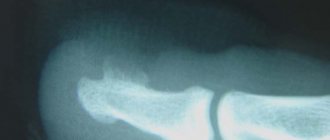
- x-ray of bones,
- MRI or CT,
- bone biopsy.
One of the main tasks of the differential diagnosis of bone tuberculosis is the exclusion of diseases such as epiphyseal osteomyelitis, joint syphilis, joint hydrops, osteochondropathy, arthritis of various etiologies and tumor processes.
Prevention
In order to protect yourself from a dangerous disease, you need to:
- Avoid contact with sick people, do not use their things;
- Strengthen immunity;
- Create acceptable living conditions, take care of the cleanliness of the house;
- Undergo routine medical examinations (in particular, once a year it is necessary to do fluorography);
- Receive timely vaccination against tuberculosis.
Pay attention to how you can strengthen your immune system
Treatment of bone tuberculosis
Osteoarticular tuberculosis is of a secondary nature, therefore general and local treatment is carried out, aimed at strengthening the body's resistance and limiting pathological changes. The recovery process is always long and can take from one and a half to three years of continuous comprehensive treatment, which includes:
- regular nutritious meals;
- prolonged exposure to fresh air;
- orthopedic treatment (in case of damage to the spine - bed rest in a plaster bed, wearing a plaster and removable corset; in case of damage to the joints of the limbs - application of a plaster cast);
- prescription of anti-tuberculosis drugs;
- surgical treatment (joint resection, endoprosthetics, alloplasty, intra-articular necrectomy, etc.).
Return to list
General information
TBS of bones and joints is a specific inflammatory disease of the musculoskeletal system, which leads to anatomical and functional changes in the skeleton.
According to statistics, bone localization accounts for 3.4% of all tuberculosis diseases. The most common TBS is:
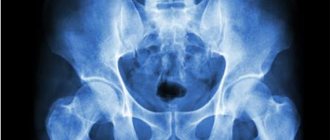
- spine – 40%;
- hip joint – 20%;
- knee joint – 20%;
- foot bones -3-5%.
In the photo - TBS of the spine
Note! Just a few decades ago, before the development of modern methods for the prevention and treatment of tuberculosis, the proportion of multiple osteoarticular lesions was more than 30%.
Today, bone tuberculosis in children practically does not lead to death. However, due to late diagnosis, in 50% of cases the disease can cause disability in a small patient.
What is the result?
Your body will receive additional strength to fight infection. Your pain will disappear or its intensity will significantly decrease. The nutrition of bone, muscle and cartilage tissue will improve. The load on the spine will be reduced. Foci of inflammation and necrosis of bone tissue are localized. Degenerative changes in bones will stop. Motor activity will be restored.
Powerful and effective treatment with the Neurodoctor device will quickly eliminate the clinical manifestations of the disease, localize the foci of pathology, and reduce the dose of medications. This will allow you to live a full life and forget about your illness forever.
The device will help localize foci of bone tissue destruction, restore musculoskeletal functions and shorten the time of treatment of the disease with other drugs. You will return to active life faster and restore your health.
What will happen if left untreated?
In most cases, the development of spinal tuberculosis leads to severe complications that pose a real threat to your health, ability to work and physical activity. Among these complications:
- Rarefaction and breakdown of bone matter
- Tuberculous osteitis
- Muscle contracture
- Spondylosis
- Spinal cord compression
- Paralysis of limbs
- Dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system
If you do not take urgent measures or use ineffective treatment, then powerful pathological processes will inevitably start in your body, which will lead to the destruction of bone tissue. The disease will cause destruction of the vertebrae, compression of the spinal cord and lead to partial or complete disruption of musculoskeletal function. Severe pain will aggravate the overall severe course of the disease.
Do you need effective treatment, but still have doubts?
“Neurodoctor” is today one of the most effective methods of treating diseases of various etiologies. It combines well with traditional treatments and allows the body to recover better. Today the Neurodoctor device is:
- A treatment method that won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
- The history of the device goes back more than 20 years.
- Neurodoctor takes part in medical exhibitions around the world.
- The press writes about the Neurodoctor device (publications such as KP and others).
- Neurodoctor is used by thousands of people in 26 countries around the world.
- Manufactured in Russia at enterprises of the military-industrial complex.
- Can be used effectively together with any medications, without any side effects.
- The device has no contraindications.