What is fluid accumulation in a joint?
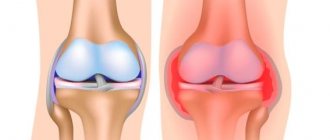
The accumulation of fluid in the joint is considered one of the symptoms of hydrarthrosis or dropsy - a peculiar syndrome in which the volume of the joint increases due to the formation of synovial fluid in its cavity.
Most often, this syndrome is observed in the knee joint, less often in the ankle, elbow and others. In this case, there may be a restriction in joint flexion; the intensity of pain depends on the amount of fluid and the degree of stretching of the joint capsule.
An increase in local temperature is not observed unless the inflammatory process has begun.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine can only be used in combination with drug therapy and other classical methods of treatment.
| Means | Components | Preparation | Method of use |
| Ointment | Fresh or dried comfrey - 250 g, lard - 250 g | Melt the lard and mix with chopped comfrey, place in the refrigerator for 7 days. | Apply to the damaged area morning and evening, secure with a tight elastic bandage. |
| Infusion | Bay leaves - 2 tablespoons, sunflower oil - 200 ml | Grind bay leaves and add sunflower oil. Leave for 7 days | Rub the strained infusion on the sore joint three times a day. |
| Tincture | Dry or fresh comfrey roots - 1 tablespoon, vodka - 5 tablespoons | Grind the comfrey roots and add vodka. Leave to infuse for 14 days in a cool place. | Take 30 drops of strained tincture three times a day |
Advertising:
Folk remedies are recommended to be used only if the damage to the knee joint is aseptic in nature - without the accumulation of pus, acute pain, a noticeable decrease in mobility and severe inflammation.
Causes
The accumulation of fluid in a joint can be a consequence of a disease, but the most common cause is injury. These include:
- Injury – sprain, ligament rupture. This can lead to a buildup of fluid that becomes infected after a viral illness.
- Various joint diseases, including gout or arthritis.
- Lupus erythematosus.
- Bursitis, which is common in dancers or athletes.
- Incoagulability of blood and others.
Important! These reasons must be mentioned when visiting a doctor, this will help to correctly establish a diagnosis and prescribe competent treatment.
Is the procedure dangerous?
Removal of exudate should be carried out under sterile conditions by an experienced specialist. Then complications will be minimized. Possible complications:
- intra-articular hemorrhage due to damage to soft tissues and blood vessels;
- damage to the branches of peripheral nerves - a feeling of numbness or tingling in the knee appears;
- damage to cartilage tissue;
- damage to intra-articular ligaments;
- introduction of infection.
All complications of this kind occur extremely rarely, and the practicing surgeon is excellent at dealing with them.
Classification
The fluid that accumulates in the joint cavity can be classified by its nature into exudate and transudate. Accordingly, exudate is associated with the occurrence of inflammatory processes and comes in several types:
- Serous.
- Purulent.
- Hemorrhagic.
- Frail.
Transudate is formed for other reasons that are not related to inflammation, but are associated with circulatory disorders and other abnormalities.
Lateral and medial lateral inversions
The lateral inversions of the knee joint are pockets that provide stability to the position of the tibial and femoral condyles. They reach the upper or lower surface of the menisci.
The medial inversion of the knee joint, located at the top, is covered by the lateral ligaments and muscle tendons. The lateral inversion of the knee joint is located symmetrically on the other side. The lower ones duplicate the upper ones. The lateral one covers the head of the fibula. The medial connects to the tibial condyle.
Pathologies
The accumulation of fluid in the joints is a health hazard and can lead to the development of the following pathologies:
- Hemarthrosis is formed due to damage and blood flow into the joint.
- Arthrosis is the most common pathology and occurs as a result of mechanical damage or age-related changes.
- Arthritis can occur for a variety of reasons, including infections or allergic reactions.
- Synovitis is an inflammatory disease.
- Bursitis can develop due to injury or after an infectious disease.
Possible complications
Occasionally, puncture of the knee joint may be complicated by infection. The development of this kind of negative consequences occurs due to non-compliance with asepsis rules. There may be swelling at the area where the needle enters. Often the temperature may be elevated for several hours after surgery.
If there are problems with blood clotting, severe bleeding may develop and hemarthrosis occurs. In this case, you need to visit the doctor again.
Puncture of the knee joint is performed even on a child, since he will not be hurt during the procedure.
If various kinds of complications arise, the knee joint can be punctured again to eliminate the existing problems. This method of surgical intervention can be performed several times.
Diagnosis of the causes of fluid accumulation in the joint
Diagnosis of this pathology consists of an initial examination of the patient by a specialist, for example, an orthopedist or traumatologist. After an external examination, palpation and questioning of the patient, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis and refers the patient for additional examination for clarification:
- x-ray,
- Ultrasound of the joint,
- MRI of the joint
- joint puncture and others.
Reference! To identify hidden infections, a general or extended blood test, ECG and blood type identification may be needed.
After carefully studying the examination data, the specialist will prescribe comprehensive treatment depending on the cause of the disease.
Risk factors
First of all, those people who have already been diagnosed with arthritis or arthrosis of the joints, especially the knees, are at risk of encountering such a disease. The same risk category includes patients who chronically experience knee problems - athletes, cyclists, lovers of an active lifestyle. To prevent the development of pathology or successful treatment at an early stage, experts recommend regularly undergoing medical examinations and protecting your joints from unnecessary stress. And also seek medical help if you discover any deviations from the norm.
Which doctor treats fluid accumulation in a joint?
The accumulation of fluid in the joint is considered a fairly common problem, which, even in the absence of pronounced symptoms, requires immediate seeking qualified medical help. Like treatment of the spine, fluid removal from the joint cavity should be done immediately after the problem is discovered. You need to contact an orthopedic traumatologist who specializes in diseases of the musculoskeletal system and rehabilitation after surgical interventions.
In our Kuntsevo treatment and rehabilitation center, you will not only receive qualified assistance from experienced orthopedic traumatologists if fluid is detected in the joints, but you will also be able to undergo a full examination using the latest diagnostic equipment and, if necessary, recover in our rehabilitation center after injuries according to a specially developed comprehensive program .
The accumulation of fluid in the joint significantly reduces the patient’s quality of life. As a rule, a person cannot fully perform movements and complains of pain and discomfort in the joint area.
Important! This symptom cannot be ignored, because the progression of the pathology can lead to the development of chronic inflammatory joint diseases.
At the first signs of pathology, make an appointment with a qualified doctor - orthopedic traumatologist at the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center, who will be able to fully examine the joint, find the source of the pathology and prescribe the correct treatment, in particular at the rehabilitation stage.
Sign up
How is it carried out?
The technique of performing such a surgical intervention as puncture of the knee joint is very simple, which is explained by the anatomical structure and topographic location of the knee. The topography of the joint makes the procedure easier. According to anatomy, the patella is displaced slightly forward. During surgery, the patient assumes a supine position, and a soft cushion is placed under his knees.
The step-by-step operation includes the following manipulations:
- The puncture area is treated with an antiseptic solution of iodine and alcohol. To ensure that the patient does not feel pain during the operation, the site of the future puncture is anesthetized.
- If a puncture is performed to administer oxygen, a thin needle with a diameter of no more than a millimeter is used. If it is necessary to suction the pus, use a needle with a size of 2 millimeters.
- To prevent infection, the skin at the puncture site is moved to the side.
- The needle advances slowly and rather heavily until it reaches the joint capsule. After piercing the joint capsule, the needle is moved no more than 3 millimeters to prevent damage to the cartilage.
- To remove the liquid, use a special syringe. After completing the operation, the puncture point is disinfected, after which a sterile bandage is applied. The bandage is not removed until the joint is fully restored at home.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient's condition is monitored by the attending physician. If the operation is performed correctly and all restoration requirements are met, a repeat procedure will not be required, and the positive effect will not be long in coming. The main thing is not to deviate from the doctor’s recommendations, and then the puncture area will not even swell.
During rehabilitation, you need to regularly visit the doctor for routine examinations. After the operation there are no scars, so you don’t have to think about plastic surgery.
The average price of the procedure in Moscow is 1,600 rubles.
Types of treatment for fluid accumulation in a joint
The accumulation of fluid in the joint can be treated in different ways, depending on the degree of advanced disease. Among the various joint treatment methods offered by the Kuntsevo Center, the following can be listed:
- Drug treatment, which consists of prescribing and taking medications and vitamins.
- One of the ways to treat joint diseases and relieve pain is blockade - special injections into the joint or periarticular tissue. This method of therapy is also used during the rehabilitation period after completion of treatment.
- ACP SVF therapy is the latest unique method for treating degenerative joint diseases. To carry out this type of treatment, it is necessary to extract the stromal-vascular fraction from the patient, then prepare a special composition based on it and introduce it into the affected area of the joint by injection.
How much does the procedure cost?
Pumping out synovial discharge from the knee costs differently in Moscow clinics. Prices depend on the location of the clinic, the degree of its promotion and are:
- arthrocentesis – from 1500 to 5000 rubles;
- arthroscopy – from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles.
Pumping out exudate from the knee is a simple but very effective procedure. If carried out on time, you can significantly speed up recovery and prevent the development of numerous complications. The specialists at the Paramita Clinic have extensive experience in treating joints and performing such procedures. We'll get you back on your feet!
Literature:
- Kolesnikov, M.A. Treatment of gonarthrosis: modern principles and approaches // Practical medicine. No. 8 (47). pp. 97-99. Kolesnikov, MA Treatment of gonarthrosis: modern principles and approaches. Prakticheskaya medicina. 2010. No. 8 (47). pp. 97-99
- Neverov V.A., Lankin I.V. Experience in the treatment of gonarthrosis using arthroscopic joint sanitation // Bulletin of Surgery named after. I.I. Grekova. 2010. No. 4 (July). pp. 86-9. Neverov VA, Lankin IV Experience in the treatment of gonarthrosis by arthroscopic joint repair. Vestnik hirurgii im. II Grekova. No. 4. pp. 86-9
- Strobel M. Guide to arthroscopic surgery, vol. 1 (edited by A.V. Korolev). Bean, 2012 -658 p. Strobel, Michael J. Manual on arthroscopic surgery, vol.1 (edited by AV Korolev). binom. 2012. p. 658
- Figueroa D. Clinical Outcomes after Arthroscopic Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery. 2011. 27, 5. P. 45-46. DOI: 10.1016/j. knee.2012.09.014
- Wang Y. and all. Osteoarthritis year in review 2015: imaging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021. Vol. 24, No. 1, p. 49-57 DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.07.027
Themes
Joints, Pain, Treatment methods Date of publication: 02/02/2020 Date of update: 02/02/2020
Reader rating
Rating: 2.8 / 5 (5)