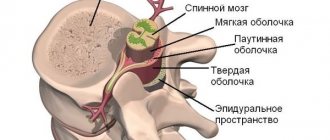
The spinal column is a rather susceptible structure. Inappropriate load on the back, sedentary work, lack of physical activity and other factors affect the health of the osteochondral system. Muscle tension, pain or pinched nerves appear.
We offer you 10 easy exercises to relax your back, which will help remove discomfort and optimize the condition of your spine.
Help with back pain - blocks and muscle spasms
The main cause of many spinal is associated with spasms of the deep short lateral and medial intertransverse lumbar muscles and interspinous muscles! Moreover, these muscles can remain in a state of spasm for years, causing muscle blockade of the intervertebral discs . Thus, muscular blockade of the disc does not develop as a result of degeneration and protrusion of the intervertebral disc and not as a result of bone growths of neighboring vertebrae .
The primary pathological process consists of excessive tension of these muscles (awkward rotation of the body, excessive flexion of the spine , hypothermia of the back, previous infectious disease, prolonged static muscle tension ,
arising - when a person sits incorrectly at a computer, when carrying a bag on one shoulder, etc.), exceeding their operating stress, which leads to long-term, reflexively fixed tension, a reflexive spasm of these muscles.
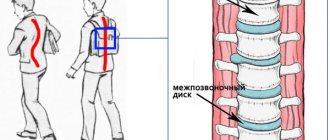
And all this time, the intervertebral discs can be in a compressed, compressed state, sometimes even protruding between the vertebrae , squeezing the nerve endings and causing pain of varying intensity. When excessive pressure is placed on the intervertebral discs, they flatten and expand in all directions. The expanding discs press in all directions.
The most vulnerable to this pressure are the roots of the spinal cord and the autonomic nerves; they become irritated. This irritation causes contraction of the intervertebral muscles (interspinous intertransverse and other short muscles), which increases pressure on the discs, which further irritate the roots of the spinal cord, i.e., a vicious vicious circle is formed and a blockage of the spinal segment is formed. As a result, pain occurs and the surrounding muscles tense to protect the injured area. A spasmed muscle compresses nerve fibers and blood vessels, as a result of which nutrition and energy-information exchange are disrupted both in the tissues of the muscle itself and in the internal organs, the nutrition and innervation of which is carried out by the compressed vessels and nerves. (Example: the vagus nerve is pinched in the neck , relaxation impulses do not pass through it to the liver, resulting in chronic spasm of the gallbladder.)
When muscles spasm, lactic acid accumulates in them, which is a product of glucose oxidation under conditions of lack of oxygen. A high concentration of lactic acid in the muscles causes pain. When the muscle relaxes, the lumen of the blood vessels is restored, the blood washes out lactic acid from the muscles and the pain goes away. Compression of the spinal nerves leads to loss of sensitivity of organs and tissues. Compression of blood vessels leads to swelling and pain.
When the spine is stretched, muscle tension is relieved, intervertebral spaces are increased, nerve compression is reduced, blood circulation is improved and metabolic processes are enhanced in the vertebrae and adjacent tissues, in the joint capsules and throughout the ligamentous apparatus of the joints. Thus, spinal , joint stiffness is eliminated, pain is relieved, which contributes to the rapid restoration of full movements after injuries, joint diseases, nervous strain and stress.
During a muscle spasm, a simultaneous contraction of the fibers located inside the muscles occurs. Such spasms often occur during sudden movements or when tense muscles are overextended. Bending quickly after sitting for a long time, for example, can cause strain in the back muscles and pain in this area. In response to this, an immediate contraction of muscle fibers occurs. Something like a protective shaft is formed, which protects the back from further irritation. Increasing pain provokes even greater muscle tension.
First of all, the muscles of the neck and back are susceptible to spasms. These areas of the body are often in a state of tension. They are more sensitive even to minor loads. A slight draft can be enough to cause stiffness in your neck , which are tense when working with a computer or playing tennis. Spasmodic pain in the back and neck combined with skin numbness, tingling or muscle weakness may indicate a ruptured intervertebral disc or nerve damage.
Osteochondrosis and muscle blockade of discs are different diseases that occur independently of each other! Thus, the main cause of severe pain in the spine is usually excessive contraction of the short deep muscles of the back, causing their reflex spasm and blocking of the intervertebral discs .
A small
disc herniation vertebral growths by themselves do not cause pain and often occur in parallel with muscle spasms . Therefore, the diagnoses “ osteochondrosis ” and “ radiculitis ” do not reflect the essence of pathological processes and are more correctly called fibromyalgia - pain in the back muscles.
If there are chronic muscle spasms that correspond to certain negative emotions, then they will bring these emotions to life. Physical pain, constantly maintained static tension in certain postures, emotional stress - can act both individually and together in various combinations; the blocks and spasms they generate Stretching , alternating with isometric tension, relieves spasms of individual muscle fibers well.
During muscle activity, most chemical energy is produced in powerful strength muscles during the anaerobic stage without the presence of oxygen. The aerobic stage is the main one for muscle fibers that provide rhythmic work that is not associated with heavy loads and is designed for greater endurance. That is why stretching a muscle ensures its energy saturation more effectively than compression, immediately causing chemical energy to transform into nervous energy.
An injury, trauma or stress can cause excessive tension in a muscle over a long period of time, programming the brain. As the healing process begins, the brain needs additional impulse input from the movement of the spasmed muscle to break the vicious cycle. Another phenomenon that is often encountered is muscle amnesia. When an injury occurs, the natural tendency is to limit use of the injured body part.
The problem is that the body (that is, the muscles or the brain that controls them) remembers a limited movement pattern, even after healing has occurred. The consequences of this are weakness in certain muscles. Bodily re-education - static and dynamic exercises that re-integrate these muscles into unified functioning with the rest of the body.
Do exercises, consistently tensing and relaxing all muscle groups in the body, starting with the legs and ending with the muscles of the face and head. As you exhale, the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for relaxation, is activated, so combining relaxation with exhalation enhances the effect.
Relaxation of a spasmodic muscle area
Relax the cramped muscle area in one of the following ways:
- using pulmonary breathing (inhale - tension, exhale - relaxation; then inhale without tension, while exhaling we reproduce the feeling of relaxation) on this specific part of the body;
- through extreme tension - the spasmodic area must be tensed as much as possible and this tension must be maintained for 20-30 seconds, as long as possible, then relaxed with an exhalation;
- passing through the tense area a feeling of good bodily well-being, bodily pleasure.
Massage of the spasmodic area in all types (kneading, deep pressure, vibration massage). Stretching a tense area can be alternated with isometric tension.
Try a light massage with ice . Rubbing the sore spot in a slow circular motion with a piece of ice somewhat dulls the pain. The effect is achieved within a few minutes. First, ice causes the blood vessels to constrict, then they suddenly dilate, promoting muscle relaxation. After applying ice, slow and gentle movements help restore normal blood circulation and return the muscles to their normal ability to contract and relax.
If the cramping does not stop after three days, you can try heat treatment . As soon as the acute pain and swelling go away, start using heat, which drives blood to the sore spot. To do this, you just need to take a towel soaked in hot water, wrap it around the sore spot, put a plastic bag and a dry towel on top to better retain heat. Repeat such warming procedures for 20 minutes five times a day.
Stretching is necessary to maintain flexibility. As we age, tendons begin to shorten, reducing flexibility. Your movements become slower and smoother, your stride becomes shorter, and your posture .
All patients with osteochondrosis benefit from massage, self-massage, exercises in water, swimming, especially breaststroke and backstroke. Exercises to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, which are included in the exercise sets, are useful. When muscles are tense, compression of the nerve roots increases and the blood supply to the intervertebral discs .
Therefore, it is so important to include relaxation exercises in your classes, which must be alternated with special exercises. First of all, you need to learn to relax the back muscles that bear the main load:
- slow, rhythmic movements that stretch the tonic muscle (repeat 6-15 times, 20 seconds break);
- under the influence of gravity, create a position for the tonic muscle that stretches it, the stretching phase lasts 20 seconds, 20 seconds break, repeat 15-20 times;
- tensing the tonic muscle against resistance for 10 seconds, then relaxing and stretching for 8 seconds, repeat 3-6 times;
- tensing the tonic muscle group against resistance on the opposite side for 10 seconds, relaxing for 8 seconds, stretching the muscle group, repeat 3-6 times.
The sauna has a great therapeutic effect for diseases of the musculoskeletal system: osteochondrosis, rheumatism, arthrosis of the joints and fights the root cause of these diseases. Heat has a pronounced therapeutic effect on the spine and joints by eliminating spasm and restoring muscle nutrition, improving blood supply to the cartilage and bone structures of the skeleton.
Inflammation of compressed spinal nerve roots decreases. As a result of this, bone growths on the vertebrae cease to put pressure on the nerve roots, back pain and so-called referred pain, simulating heart disease, stomach or intestines, disappear. When nerves are compressed, the functions of internal organs are disrupted. The sauna helps restore lost functions and restore lost health to organs. After which the mobility of the joints increases, their swelling decreases and the secretion of interarticular fluid increases, pain disappears.
Why does my back hurt?
Most adults experience back pain in one way or another, especially in the lumbar region. Discomfort may be accompanied by spasms of the muscles located along the spine, numbness, and tingling. There are several reasons for this condition.
- Muscle tension occurs due to muscle weakness or overuse.
- Sprains occur due to inaccurate and sudden movements, causing pain. Ligaments connect the vertebrae and provide stability to the spinal column.
- Poor posture leads to muscle fatigue, joint compression and intervertebral disc tension.
- Age-related changes lead to a decrease in the density, strength and elasticity of bones, muscles and ligaments.
If the pain arises as a result of injury (you fell, turned unsuccessfully or lifted something heavy), then you should first ensure yourself peace: if possible, do not move or do any exercises and be sure to consult with a specialist, he will prescribe an examination if necessary and draw up a treatment and rehabilitation plan .
You can apply ice (but not heat!) and take painkillers. After the pain has subsided (usually within a few days to several weeks), you can begin to perform rehabilitation physical exercises. If the condition does not improve, you should consult a medical specialist.
There are several simple causes of pain:
- If you feel pain in your back, but you definitely haven’t fallen or made sudden movements, this means that you are overloading your spine or incorrectly.
- If your occupation mostly involves sitting (at the wheel, at a computer, at a desk), then you need to do light exercises every hour.
- If your job involves heavy physical labor, you need to learn how to properly load your back.
- Don't forget to lie comfortably. If you are lying on your back, place pillows under your knees. If you like to lie on your stomach, place a pillow under your hips. If you choose the side position, hold a pillow or blanket between your knees.
- If you experience difficulty urinating or defecating after an injury, numbness in the genital area, severe weakness in the legs and unsteadiness, consult a doctor immediately!
Through regular physical activity, any person can maintain their musculoskeletal system in good shape and minimize the risk of back pain.
The Science of Relaxation
Muscles compressed in spasm bend the spine . The vertebrae shift and compress the neurons coming from the spinal cord. This can cause pain in any organs. It may “shoot” in your chest, you will think that there is a problem with your heart, but it’s all the same nerves.
Constant tension in the neck makes it difficult for the optic nerves to function normally, and vision may begin to deteriorate. The nerves that control the diameter of small blood vessels are also affected, limiting blood flow to the head. Chronic tension causes blockage of blood vessels and contamination of muscle fibers. The skin covering the muscles in this area becomes flaccid and dry.
The negative effects can go on for a long time. So know: behind most ailments there is one reason - the muscles of the back and neck have forgotten how to relax on their own. With their spasmodic tension they put pressure on the spine and bend it. But salvation is in your hands. You should regularly perform special gymnastics plus lifestyle recommendations, and your life will again become painless and joyful.
Preparing for gymnastics
Before you start exercising, you need to remove any discomfort in your muscles. Doing gymnastics through pain will only make it worse. If the muscles in your lower back are tense, sit on the edge of a bed or sofa, the surface of which (this is important!) does not sag too much. Now lean back and use your hands to pull your knees towards your chest. Catch a position in which the unpleasant sensations completely go away. Lie down like this for a couple of minutes and get up so as not to strain your muscles again. Do you feel them tightening up again? Then try to jump up quickly, rolling like a tumbler.
Lie down again, bringing your knees to your chest. Swing your legs left and right. Relax and place your feet on the bed. If tension has accumulated in your shoulders and upper back, sit loosely and lean back in your chair. Place your hands on the back of your head. Sit like this for a couple of minutes and carefully, so that your muscles don’t accidentally tense up again, lower your arms. Take the time to look for positions in which the muscles relax and the pain disappears. You need to turn back and forth, find a comfortable position, hold it for a couple of minutes, and then, trying not to tense up again, return to the normal position.
Exercises for neck pain
Do each of them 5 times twice a day. For the first couple of weeks, do only the first three exercises; the rest should be added later.
1) Slowly tilt your head forward as far as you can. Then tilt it back - also all the way.
2) Slowly turn your head from side to side, as far as possible.
3) Bend your head to your shoulder without moving towards them. Then to the other shoulder.
4) Place your hands on your forehead and tilt your head forward, overcoming resistance. Hold this for about five seconds. Move your hands to the back of your head and tilt your head with resistance. Tilt your head left and right in the same way.
5) Take a light (1.5-2 kg) weight in your hands and keep them straight down. Shrug your shoulders slowly.
Relaxing the back muscles
1) Stand up straight, place your hands on your waist. Raise your right shoulder , lower it. Do the same with your left shoulder .
2) Get down on all fours, resting your knees and palms on the floor. Press your chin to your chest. Now bend your back upward, rounding it.
3) The same, but in a standing position: put your hands on your belt, turn your elbows forward. Tuck your chin to your chest and round your back, arching it back.
4) Lie on your stomach, place your hands under your hips, straighten and bring your legs together. Lift your feet off the ground, trying to raise them as high as possible. Hold them in the maximum position until the count of two and slowly lower them.
5) Continue to lie on your stomach, but clasp your hands behind your back. Raise your head and lift your shoulders off the floor, extending your palms towards your feet. Hold the maximum position until the count of two and slowly lower.
6) Roll over onto your back. Using your hands, pull your knees towards your chest. Bend your head towards your knees. Stay in this position for a few seconds, then relax.
Complex for the lower back
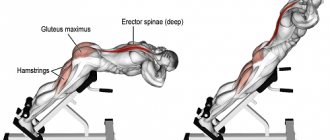
1) Half push-ups. Lie on your stomach. Without lifting your pelvis from the floor, do push-ups on your hands, arching your back.
2) Roll over onto your back. Press your feet firmly into the floor and bend your knees. Cross your arms and place your palms on your shoulders. Raise your head and shoulders as high as possible, while pressing your lower back and feet toward the floor. Stay in this position until the count of two.
3) Land navigation. Lie on your stomach and raise your left arm and right leg as if swimming crawl. Hold until the count of two, then switch arms and legs as if you were swimming.
4) Visit the pool, but make sure the water is warm. For chronic lower back pain, swimming helps without equal.
All of the above exercises should be performed with a positive emotional attitude, at an average pace, with even breathing. The most important thing: after the tension phase, there must be a phase of complete relaxation, otherwise the exercises will lose their meaning.
When performing any of the above exercises, be careful. If they hurt, stop doing them. But if you feel improvement a day or two after the exercises, then they are safe for you.
Other recommendations
Physical education is physical education, but there are other important nuances that are useful to remember.
Choose a chair that provides good lumbar support. If this option is adjustable, start with the lowest position and move up until you find the most comfortable one.
Try to keep your head straight, without lowering or lifting your chin. If you have to look at the monitor for a long time, place it at eye level.
When it's cold and damp outside, don't forget to wrap your neck with a scarf.
When working sedentarily, even if your work is in Krasnodar, where there is a wonderful climate and excellent working conditions, take short breaks regularly (about once an hour) to warm up. You can just walk along the corridor, climb the stairs two or three floors. But it would be better to stretch and bend.
There is such a very useful invention: fitball. Exercises performed on large (55-65 cm) rubber balls are not only fun, but also extremely beneficial for the back and neck.
Sign up for physical therapy. Modern medicine has reached incredible heights, and your doctor will prescribe precisely and targeted exercises for you. The main thing here is to have less independence.
Try to eat healthy foods and indulge in negative emotions less. Stress is one of the main causes of neck .
It is useful to hang from a bar if possible. Make it at home, for example, in some doorway. Every time you pass by, hang for a few seconds, swinging moderately in different directions. At the same time, the back muscles significantly relax, and the vertebrae strive to return to their normal position.
Visit a chiropractor to have the vertebrae in place. But remember: having a medical center license does not in itself give its employees the right to dig into your back. Each specific therapist must have a personal certificate and permission to carry out medical procedures.
Many neck and back problems begin with an improperly designed sleeping position. It is important to have a firm mattress that does not sag deeply in the middle. The pillow should also not be overly soft; sometimes it is worth abandoning it completely. It is best to purchase a special orthopedic mattress and pillow. Their shape is specially selected to help relax the muscles of the back and neck . On these, you fall asleep sweetly as soon as you lie down, and wake up completely rested.
Source: ekaterinodar.ru
Back exercises
We offer you a set of very easy exercises that can be performed while lying on your back. Its main advantage is that each exercise allows you to stretch the muscles of those parts of the body that are difficult to relax in a normal position. The complex can be used for light stretching and relaxation.
Back exercises #1
Bend your knees, touch the soles of your feet and relax. This pleasant position stretches the groin muscles. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds. Let gravity stretch this area of your body naturally. For greater comfort, you can place a small pillow under your head.
Back exercise option No. 1
Without changing your position, gently swing your legs from side to side 10-12 times. In this case, the legs should act as one part of the body (indicated by a dotted line). Movements are performed easily and smoothly, with an amplitude of no more than 2-3 cm in each direction. The movement should start from the hips. The exercise develops flexibility in the groin and hips.
Back exercises No. 2
Stretch the lower back, upper and side thighs
Bring your knees together so that your relaxed feet are parallel to the floor. Pressing your elbows to the floor, clasp your fingers at the back of your head (Fig. 1). Now cross your left leg over your right (Fig. 2). In this position, use your left leg to push your right leg towards the floor (Fig. 3) until you feel a moderate tension along the outer thigh or lower back. Relax.
Keep your upper back, back of your head, shoulders and elbows on the floor. The stretch lasts 10-20 seconds. Your task is not to press your knee to the floor, but only to stretch the muscles within your capabilities. Repeat the exercise on the other side, crossing your right leg over your left and pushing it to the right. Start the movement with an exhalation and, while holding the stretch , breathe rhythmically.
• Don't hold your breath. • Breathe rhythmically. • Relax.
If you have sciatic nerve problems in the lower back, this exercise may provide relief. But be careful. Give your body only such a load that brings pleasant sensations. Never stretch to the point of pain.
Back exercises #3
Stretching using the PNS method: contraction - relaxation - stretching .
Pressing your right leg with your left, try to pull your right leg towards your body. This way you contract the thigh muscles (Fig. 1). Hold the tension for 5 seconds, then relax and repeat the previous stretch (Fig. 2). This way of doing the exercise is especially useful for people with stiff muscles.
Back exercises No. 4
To relieve tension in the neck
Lying down can stretch your upper spine and neck. Interlace your fingers behind your head at approximately ear level. Begin to slowly pull your head up until you feel a slight stretch in the neck . Hold the stretch for 3-5 seconds, then slowly return to the starting position. Do the exercise 3-4 times to gradually release tension in the upper spine and neck . Relax your lower jaw (there should be a small gap between your molars) and breathe rhythmically.
Back exercises No. 5
Stretching using the PNS method: contraction - relaxation - stretching .
Lying down with your knees bent, clasp your fingers behind your head (not on your neck). Before stretching the back of your neck , gently lift your head up and forward from the floor. Then begin to press your head down toward the floor, but use your arms to counteract this movement. Hold this static contraction for 3-4 seconds. Relax for 1-2 seconds, then begin to smoothly pull your head forward with your arms (as in the previous exercise) so that your chin moves towards your navel until you feel a light, pleasant stretch . Hold the position for 3-5 seconds. Repeat 2-3 times.
Smoothly pull your head and chin towards your left knee . Hold the position for 3-5 seconds. Relax and lower your head to the floor, then pull it towards your right knee . Repeat 2-3 times.
Keeping your head in a relaxed position on the floor, turn your chin towards your shoulder. Rotate your chin just enough to feel a slight stretch in the side of your neck . Hold the position for 3-5 seconds, then stretch to the other side. Repeat 2-3 times. The lower jaw should be relaxed and breathing should be even.
Back exercises #6
Reduction of the shoulder blades
Interlace your fingers behind your head and squeeze your shoulder blades together to create tension in your upper back (your chest should move up as you perform the movement). Hold the position for 4-5 seconds, then relax and smoothly pull your head forward. This way you will also reduce tension in the neck . Try tensing your neck and shoulders, then relax and begin stretching the back of your neck . This will help you relax your neck and turn your head without straining. Repeat 3-4 times.
Back exercises No. 7
Straightening the lower back
To relieve tension in your lower back, tighten your buttock muscles and at the same time tighten your abdominal muscles to straighten your lower back. Hold the tension for 5-8 seconds, then relax. Repeat 2-3 times. Concentrate on keeping the muscles contracted. This pelvic girdle rocking exercise strengthens the muscles of the buttocks and abdomen and helps maintain correct posture while sitting and standing.
Back exercises No. 8
Reduction of the shoulder blades and tension of the gluteal muscles.
At the same time, bring your shoulder blades together, straighten your lower back and tighten your gluteal muscles . Hold the tension for 5 seconds, then relax and pull your head up to stretch the back of your neck and upper back. Repeat 3-4 times and appreciate the pleasure.
Now extend one arm behind your head (palm up) and the other along your body (palm down). Stretch in both directions at the same time to stretch your shoulders and back. Hold the stretch for 6-8 seconds. Perform the exercise on both sides at least twice. The lower back should be straight and relaxed. Keep your lower jaw relaxed too.
Back exercises No. 9
Pulling exercises
Stretch your arms behind your head and straighten your legs. Now stretch your arms and legs in both directions as far as is comfortable for you. Hold the stretch for 5 seconds, then relax.
Now stretch diagonally. As you extend your right arm, simultaneously stretch the toe of your left foot. Stretch as far as you feel comfortable. Hold the position for 5 seconds, then relax. Stretch your left arm and right leg in the same way. Hold each stretch for at least 5 seconds, then relax.
Now stretch again with both arms and legs at once. Hold the stretch for 5 seconds, then relax. This is a good exercise for the muscles of the chest, abdomen, spine , shoulders, arms, ankles and feet.
You can also complement the stretching by drawing in your abdomen. This will help you feel slimmer and at the same time be a good workout for your internal organs. Performing stretching exercises three times reduces muscle tension, helping to relax the spine and the whole body. These stretches help to quickly reduce overall body tension. It is useful to practice them before bed.
Back exercises #10
Leg grip
With both hands, grab your right leg under the knee and pull it towards your chest. When performing this exercise, relax your neck and place your head on the floor or on a small pillow. Hold a gentle stretch for 10>30 seconds. Repeat the same movement with your left leg. The lower back should be straight at all times. If you don't feel tension in your muscles, don't be discouraged. The main thing is that you enjoy it. This is a very good exercise for the legs, feet and back.
Back exercise option No. 10
Pull your knee toward your chest, then pull your knee and entire leg toward your opposite shoulder to stretch your outer right thigh. Hold the gentle stretch for 10-20 seconds. Repeat the same movement with the other leg.
Another option for back exercise No. 10
While lying down, gently pull your right knee toward the outside of your right shoulder . Your hands should clasp the back of your leg just above the knee . Hold the stretch for 10-20 seconds. Breathe deeply and rhythmically. Repeat the same movement with your left leg.
After alternately pulling your legs to your chest, pull both legs at once. This time, concentrate on keeping your head on the floor, then pull it towards your knees.
Lying on the floor, pull your knees towards your chest. Wrap your hands around your shins just below your knees. To stretch your inner thighs and groin area, slowly move your legs outward and downward with your hands until you feel a slight stretch . Hold the position for 10 seconds. The head can rest on the floor or on a small pillow, or it can be lifted off the floor to direct the gaze between the legs.
Stretch your legs and arms again. Stretch and then relax.
Back exercises No. 11
Stretching the lower back and outer pelvis
Bend your left leg at the knee at an angle of 90°, and then use your right hand to pull it up and over your right leg, as shown in the picture above. Turn your head and look at the palm of your left hand, extended perpendicular to your body (do not lift your head from the floor). Then, using your right hand on top of your left thigh (just above the knee ), pull your bent (left) leg toward the floor until you feel a slight stretch in your lower back and outer thigh. The feet and ankles should be relaxed and the shoulder blades should be pressed toward the floor. Hold a gentle stretch for 15-20 seconds on each leg.
To increase the stretch in the buttocks, grab your right leg from below the knee . Slowly pull your right knee toward your opposite shoulder until you feel a moderate stretch. Shoulders should be pressed to the floor. Hold for 15-20 seconds. Repeat the same movement with your left leg.
Back exercises #12
Back stretch
Take a position lying on your stomach, resting your elbows on the floor. In this position, you should feel moderate tension in your lower back and mid-back. Press your hips to the floor. Hold the position for 5-10 seconds. Repeat 2-3 times.
To complete a set of stretching , it is best to take the fetal position. Turn to your side, pull your bent legs towards your chest and place your hands under your head. Relax.
EXERCISE SCHEME FOR THE BACK
It is best to relax your back muscles by performing exercises in the specified order.
Learn to listen to your body. If a movement causes tension or pain, your body is trying to tell you that you have done it wrong or that there is a physical problem. In this case, you should gradually reduce the stretching until you feel comfortable.
10 minute back workout
The main goal of performing exercises to relax the back is to relieve pain, spasms, and fatigue. These manifestations arise from muscle overstrain along the spinal column. Reasons: hypothermia, sudden turn and incorrect seating at the table, incorrect carrying of the bag.
Therefore, it is recommended to do a workout in the morning or evening to relax the back and lower body. Perform each exercise for the specified amount of time (about 1 minute). The total workout time is 10 minutes, but you can always increase the duration of the session if necessary. If an exercise causes pain or severe discomfort, skip it.
We recommend watching:
- Top 100 Stretching and Flexibility Exercises + 8 Day Plan
- Top 50 exercises for longitudinal and transverse splits from scratch
Rotation of the body in a sitting position
How to do it: Sit down on the mat, straighten your legs, bring them out in front of you, put them on the floor, connecting them together. Bend your right leg at the knee and throw it over your left thigh, placing it side by side on your entire foot. Turn your torso to the left and place your left palm behind your buttocks. With your right hand, grab your bent leg (elbow and knee). Make a slight turn with your body and shoulder back towards the outstretched arm, slightly pulling the thigh of the bent leg towards you.
Benefits of the exercise: Reducing overall tension in the body, strengthening the buttocks, thigh muscles, spinal column and popliteal ligaments. Exercise relieves pain in the back and legs, and replenishes energy. Additionally, fat deposits on the sides are removed, brain function is activated, and the shoulder girdle is stretched.
How long to do: 30 seconds on each side.
Knee to chest while lying on your back
How to do it: Lie on your back, straighten up completely and press your body to the floor, stretch your legs, place them close to each other, and leave your arms along your body. Bend one leg at the knee joint, lift it, pull your thigh to your chest, clasping your shin with your hands. Keep your other leg straight. Feel the tension in your muscles. Try to pull your hip as tightly as possible while the stretch allows. Do not lift your head, shoulder blades, lower back, buttocks from the floor.
Benefits of the exercise: Stretching the spine, eliminating pain or tightness in the lumbar region, strengthening the extensor muscles deep inside from the skull to the sacrum. Exercise relieves fatigue in the back and legs. The hamstrings, quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings are gently stretched.
How long to do: 30 seconds on each side.
Lying on your back twist
How to do it: Lie down on the mat, lie on your back, straighten up, place your arms on the floor, stretching them to the sides. Bend one leg at the knee, twist in the opposite direction, place the foot, shin and knee on the floor. Pelvis, roll the other leg onto its side, but do not lift your shoulder blades, shoulders, or head. Leave one hand, on the side of the crossed leg, lying on the floor, with the other, grab the knee of this leg to pull it even stronger.
Benefits of the exercise: Saturation of the vertebrae, discs and nerve bundles with blood, restoration of flexibility and mobility to the spine, stretching of the gluteal and spinal muscles, combating stoop and curvature. To eliminate back pain, training must include this movement. Additionally, massage of internal organs and prevention of obesity are a plus.
How long to do: 30 seconds on each side.
Crossing your legs while lying on your back
How to do it: Lie down on the mat, pressing your pelvis, back, shoulders and head firmly against the surface. Bend your knees, lift them so that your hips are perpendicular to the floor, and a right angle is formed between the thighs and shins. Cross one leg over the other: place your left shin with your ankle on your right thigh, slightly above the knee. Grab the raised thigh from the biceps side with your hands, without lifting your shoulder blades, shoulders and head. Press your lower back tightly.
Benefits of the exercise: Stretching, relaxing the lumbosacral muscles and strengthening the spinal column, increasing blood flow with a lot of nutrients and beneficial substances to bone and cartilage tissue. Flexibility improves, pain and fatigue decrease. Additionally, the buttocks and leg muscles are stretched, the whole body is relaxed and toned.
How long to do: 30 seconds on each side.
Happy Child Pose
How to do it: Lie down, stretch your body straight, and place your arms at your sides on the floor. Raise your legs straight up and keep them close to each other, forming a right angle between your hips and body. Bend your knees and place your thighs on the sides of your stomach, point your shins up, and grab your feet with your hands. Do not lift your lower back and head, stretch your neck. To enhance the stretch, pull your legs down further - you can even touch your knees to the floor on either side of your sides.
Benefits of the exercise: Relaxation of the lumbar muscles and opening, development of the hip joints, general relaxation. The back of the thigh is stretched. This exercise is also great for relieving back fatigue. When lying in the happy child's pose, the body is filled with energy and strength. Flexibility and mobility of the pelvis improves, which preserves the health of the spine and knees.
How long to do: 60 seconds.
Wind Release Pose
How to do it: Lie down on the mat, take your normal position on your back - straighten your legs, place your arms at your sides. Begin to gradually bend your knees and bring your hips towards your chest. Tear off the pelvis, leaving the sacrum and lower back as the lower point of support. Wrap your arms around your legs above your knees, pulling your shins closer to your hips. Raise your head, neck, shoulders, and touch your forehead to your knees so that your nose passes between them. Don't tense up, relax and breathe deeply.
Benefits of the exercise: Relaxation and training of the lower back (sacrum and lower back), reducing tension in the muscles of the hips and pelvic area. The body in the accepted position rests and is saturated with energy. This simple exercise for back pain is great for relaxing your whole body. The functioning of internal organs and blood circulation improves.
How long to do: 60 seconds.
Child's Pose
How to do it: Get on your knees with your feet flat, not on your toes. To take the desired pose, sit down, lower your pelvis onto your heels, spread your hips wide - to a distance greater than the width of your body. Bring your feet together. Bend over, lie as deeply as possible, lower your torso between your thighs. Stretch your arms forward and straighten. Keep your neck in line with your spine and place your head on its side. Slightly round your back at the thoracic region. Relax completely.
Benefits of the exercise: Relieving tension and tightness in the spine, training the back muscles, developing or returning flexibility. Elimination of pain and pressure from discs. Blood flow increases, so nerves and muscles begin to work better. Child's pose is usually located at the end of a back relaxation workout, as it is aimed at relaxation.
How long to do: 60 seconds.
Arc turns while lying on your back
How to do it: Lie on your back, stretch your body, straighten your legs, press firmly to the surface. Place your hands on the floor above your head, elbows slightly bent, palm resting on palm. Cross your legs - place one shin on top of the other and clasp your feet together. Turn your arms and legs to the right side, then do the same in the opposite direction. Keep the amplitude small, feel the stretch in the lower back and thoracic spine. Don't bend your legs, don't lift your pelvis and back.
Benefits of the exercise: Stretching the spine in the thoracic and lumbar region and relieving muscle tension, placing the vertebrae and discs in a natural state. As you do this, the lumbago, tightness, and pain will go away. With regular exercise, your axis will straighten, your posture will improve, and walking, running or other activities will become easier. General health is normalized.
How long to do: 30 seconds on each side.
Lying position with leg to the side
How to do it: Lie on your stomach and stretch out: legs straight at the knees, arms along the body. Take a position to perform. Leave one leg in place, bend the other at the knee at an angle of 90 degrees and move it to the side so that the thigh is perpendicular to the pelvis and the lower leg is perpendicular to the thigh. Press your legs tightly to the surface, do not twist your body. Place your arms bent at right angles at the elbows on either side of your head in a comfortable manner. Relax, feel a gentle stretch in your back and lower back.
Benefits of the exercise: Relieving pain, spasms or tension in the spinal muscles, straightening your posture, relaxation. Exercise eliminates fatigue in the back, legs and arms. The position is not active, so there is time to engage in thoughts and establish a connection between body and spirit.
How long to do: 30 seconds on each side.
Static leg raise against the wall
How to do it: Lie down on a bed or sofa with a flat surface - one edge is near the wall, after which there should be a spacious place to lie down. This version of the exercise can also be performed on the floor with a mat. Lie down, place your pelvis against the wall, stretch your legs straight up, there should be an angle of 90 degrees between them and the body. Place your heels on the wall, straighten your knees, place your head on the surface, arms slightly to the sides. Relax, breathe deeply.
Benefits of the exercise: Relieving discomfort from the back, tension from the legs, buttocks. Puffiness, heaviness, swelling of the feet and legs go away. Daily practice will eliminate back pain, the exercise will gradually calm the nervous system, relieve stress and anxiety. Blood flow to the lower spine and internal organs increases.
How long to do: 60 seconds.