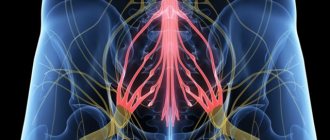
Chest pain can occur due to various diseases; it is sometimes difficult even for a doctor to understand it right away, so patients with such complaints usually undergo additional examination. Chest pain can manifest as diseases of the heart, respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, spine, mediastinum, and central nervous system. All human internal organs are innervated by the autonomic nervous system, the trunks of which arise from the spinal cord. When approaching the chest, the nerve trunk gives off branches to individual organs. That is why sometimes pain in the stomach can be felt like pain in the heart - they are simply transmitted to the common trunk, and from it to another organ. Moreover, the spinal nerve roots contain sensory nerves that innervate the musculoskeletal system. The fibers of these nerves are intertwined with the fibers of the nerves of the autonomic nervous system, and therefore a completely healthy heart can respond with pain in various diseases of the spine.
Finally, chest pain may depend on the state of the central nervous system: with constant stress and high neuropsychic stress, a malfunction occurs in its functioning - neurosis, which can also manifest itself as pain in the chest.
Some chest pains are unpleasant, but not life-threatening, but there are chest pains that need to be relieved immediately - a person’s life depends on it. In order to figure out how dangerous chest pain is, you need to see a doctor. Perhaps this will save your life or calm you down if no serious problems with your health are found.
Clinical manifestation of chest pain
Chest pain caused by the musculoskeletal system is characterized by symptoms similar to those of heart disease. Therefore, to diagnose it, a comprehensive examination is required, and the possibility of an erroneous diagnosis cannot be ruled out. Common chest pains include sternoclavicular pain, sternal angle pain (between the manubrium and the body of the sternum), pectoral muscle syndrome, and pectoralis major pain. If chest pain occurs, it is necessary to examine the musculoskeletal system, since the cause of such pain most often lies there. This can be checked by palpating the muscles and joints around the area where the pain is felt. For pain in the sternoclavicular joint or manubrium of the sternum, move your shoulder to a neutral position and immobilize the joint. Pain occurs if you move your shoulder forward or backward, or rotate your arm to the maximum. In addition, pain will occur if you lower your shoulders or bring your sternoclavicular joints together. Pain also occurs when raising the shoulders, as this raises the manubrium of the sternum. Unlike joint pain, muscle pain does not get worse if the chest wall or shoulders move. Pain when pressing in the pectoralis muscle is accompanied by pain when pressing in the pectoralis major muscle or in the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Muscle-related chest pain is identified by palpation of trigger points rather than movement of the chest wall or arms. For chest pain, examine the pectoralis major, pectoralis, subclavian, latissimus dorsi, and serratus anterior muscles.
Radicular symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
They occur due to the impact on the nerves leaving the spine.
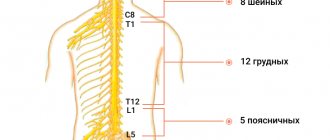
Spinal nerves
There are many nerves coming out of the spine. They are called spinal nerves. Each such nerve gradually branches and follows a specific area of the body with clearly defined boundaries. This area is called the zone of segmental innervation. Each vertebra, disc, nerve and zone are numbered, strictly corresponding to each other. If a nerve is exposed, the symptoms will appear in the zone of segmental innervation corresponding to that nerve, and not just anywhere - in an arbitrary place.
Radicular symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis include:
- Decreased or lost reflexes;
- Impaired sensitivity;
- Muscle weakness;
- Radicular pain.
Innervation zones of the thoracic segments
Osteochondrosis D1–D2
- Causes pain in the shoulder, collarbone and armpit areas.
Osteochondrosis D3–D6
- causes pain of a girdling nature in the upper part of the chest. Simulates pain in the heart, an attack of angina. In women, it causes pain in the mammary glands.
Osteochondrosis D7–D8
- causes girdle pain at the level of the solar plexus. Simulates pain in the stomach, liver, gallbladder or pancreas. Reduces upper abdominal reflexes.
Osteochondrosis D9–D10
- causes pain in the hypochondrium and upper abdomen. Sometimes it imitates the so-called “acute” abdomen - sharp pain in the abdomen. Reduces mid-abdominal reflexes.
Osteochondrosis D11–D12
- causes pain in the groin area. Simulates pain in female diseases, appendicitis, and intestinal diseases. Reduces lower abdominal reflexes.
Treatment for chest pain
Pain relievers or NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can be used to treat chest pain. It should be remembered that most of these symptoms indicate disorders in the cervical spinal nerve. In this case, a simpler and more acceptable method of treatment is peripheral magnetic stimulation of the cervical and thoracic vertebrae, paravertebral drug blockades, carboxytherapy, Multimag, German ZIMMER physiotherapy, MASTER PULS shock wave therapy, etc.
Why does osteochondrosis occur?
There are several reasons affecting the condition of disks. These include smoking and excessive exercise, especially when daily activities involve lifting heavy objects. On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle and poor nutrition are a surefire path to disc destruction. In addition, specific work that forces you to hold your torso in an uncomfortable position, constant load on only one shoulder, as well as sleeping on an incorrectly selected mattress are a risk of developing osteochondrosis.
Sleep correctly on mattresses of moderate hardness so that the spine is in a natural, even position during rest. Soft feather beds only seem comfortable. Lying on a soft bed for a long time causes morning back pain. This happens because the back muscles are stretched when the back bends under its own weight. Stretching the back muscles, which continues throughout the night, leads to pain not only in the lower back, but also along the entire length of the spine.
Flat feet are a risk of developing osteochondrosis, because such a foot cannot fully perform the functions of a shock absorber. The spine, due to this, bears increased loads, and the discs wear out faster.
In addition, people who are overweight put more strain on their spine than those whose body mass index is close to ideal. You need to monitor your shape so that the ratio of weight and height does not put additional stress on the skeleton.
However, completely healthy people who lead a sports lifestyle can have osteochondrosis. The main reason for this is injury. An unfortunate fall or blow to the spine often leads to hernias, protrusion and osteochondrosis.
Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Mizonov Sergey Vladimirovich
The doctor is a neurologist. Chiropractor. Osteopath. Physiotherapist. Experience: 8 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
Dyachenko Ksenia Vasilievna
Head of the center for the treatment of dizziness and balance disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category.
Angioneurologist. Neurorehabilitation specialist. Physiotherapist. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 19 years.Volkova Svetlana Anatolevna
Head of the Center for Parkinsonism and Extrapyramidal Diseases.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Epileptologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 26 years.
How does osteochondrosis hurt: stages of development of the disease
The disease goes through four stages of development, each of which has its own indications and symptoms. Let's look at how osteochondrosis hurts at different stages:
- The first stage is characterized by the initial development of the disease, occurring in the nucleus pulposus and cartilage tissue surrounding the intervertebral disc. In case of increased load, a process occurs that leads to serious dehydration of the core. The parameters of the disc decrease and small cracks appear in the fibrous ring. At this stage, there are practically no symptoms of the disease; only mild discomfort may be felt during intense physical exertion.
- The second stage is characterized by a decrease in the permissible distance between the discs, which leads to a significant weakening of the ligaments and muscles. This, in turn, leads to an increase in the mobility of the already affected vertebrae and to their displacement. Symptoms in the second stage can be expressed in pain during movement or physical activity, as well as more pronounced discomfort.
- During the third stage, protrusions and prolapses may form in the intervertebral discs, which usually lead to the acute development of arthrosis. Against this background, the patient begins to feel tingling in the limbs and even numbness. The necessary mobility is lost, pain appears in the lumbosacral region or in the neck.
- At the fourth stage of the disease, the human body attempts to correct the increased mobility of the discs and adapt to the new conditions of the functionality of the spine. The formation of osteophytes occurs between the vertebrae, designed to improve the fixation of the discs. In this case, osteophytes can provoke injuries to the vertebrae and pinching of nerve endings, and fibrous ankylosis can begin in the vertebrae themselves.
In order to prevent osteochondrosis from progressing to more severe stages , it is advisable to undergo examination at the earliest stages of the disease.
Read also
Pain on the inside of the knee and sphenoid neuralgia
Clinical manifestation of pain on the inside of the knee and sphenoid neuralgia Sphenoid neuralgia is usually observed when the nerve passes through Gunter's canal, or what...
Read more
Chest pain
The first thing a patient thinks about when he feels chest pain is a heart attack. Of course, chest pain is not something that can be ignored. But you need to understand that chest pain is not...
More details
Arm and neck pain
A man's neck hurt. He walks, periodically independently twists it from side to side, kneads it with one hand, then with the other... Brings his neck to the extreme degree of tilt to the left... then to the right... slowly... and...
More details
Pain in the gluteal region
Clinical manifestation of pain in the gluteal region Pain in the gluteal region is quite common. Although this pain can be caused by a number of reasons, it is most often associated with thoracolumbar syndrome,...
More details
Shoulder blade pain
Symptoms of Scapula Pain Symptoms include pain and paresthesia on the inside of the scapula, pain on the outside of the rib cage, limited scapular function, and pain radiating from the shoulder to the arm. These symptoms...
More details
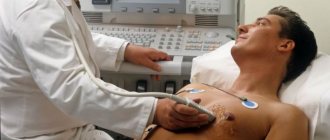
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to differentiate thoracic osteochondrosis due to the similarity of its symptoms with the clinical manifestations of other diseases. Because of this, it was even called the “chameleon disease.” However, the specialists at the CELT clinic have extensive experience in correctly making this diagnosis and have a whole arsenal of modern equipment for this purpose.
Diagnostic studies are carried out in a complex and include the following:
- examination by a Pain Clinic specialist, if required, by related specialists (cardiologist, gastroenterologist, nephropathologist, urologist, rheumatologist, etc.)
- radiography;
- ;
- MRI.
Disease prevention
To prevent serious complications of the pathology, you need to consult a doctor in time. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the opportunity to completely stop degenerative processes.
This is best done with the help of kinesiotherapy. At the initial stage of pathology, as well as during its prevention, this method will help strengthen the muscular corset of the spine and improve blood supply to the disc tissue.
The specialists of our kinesiotherapy center will help prevent the development of degenerative processes in people with a predisposition to them. After all, moderate physical activity is necessary to maintain a healthy spine.
An individually designed daily regimen with special exercises and diet will help avoid disc destruction and complications of this process.