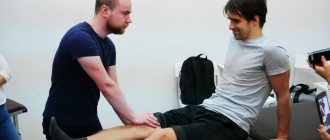
One of the most common reasons for visiting a doctor is pain in the back, namely in the paravertebral muscles, i.e. muscle pain along the spine. According to official data, about 80% of people have experienced back pain at least once in their lives, which makes this pathology an extremely important medical problem.
Most often, this pathology affects people who are forced to remain in a static position for a long time, which leads to overstrain of the muscles that support this position. Examples include office workers who sit for a long time at the computer in the same position, or people after a long flight. After this, one awkward movement is enough for the back to make itself felt. As a result, we feel a sharp or dull aching pain - this is how the body tries to signal to the owner that the muscles and ligaments are not doing well.
Pain is often caused by: poor posture, curvature of the spine, lifting heavy objects with a jerk or one hand, an improperly organized workplace with a poorly selected table or chair.
In other cases, if a person has pathology in the lower extremities, the biomechanics of movement in the spine changes, which leads to overstrain of certain groups of back muscles, and as a result, pain occurs in them. Such pathologies include arthrosis of the hip or knee joint, hallux valgus, etc.
Symptoms of nonspecific pain in the spine
A sharp lumbago in the lumbar region, pain when turning the body, a slight aching pain in the back - these are what patients most often complain about.
Causes
- prolonged uncomfortable position at the desk;
- carrying heavy loads without taking into account the correct biomechanics of the body;
- overweight (body mass index greater than or equal to 25);
- weakened back muscles (lack of physical fitness);
- sudden movements leading to microtrauma of the spine;
- stress and depression.
What diseases cause pain in the back muscles along the spine?
There are many causes of back pain along the spine; most often they develop against the background of diseases of the spine , damage to the nerves of this area; in some diseases, the pain can only radiate to the back.
Lesions of the spinal column
One of the most common causes of pain is compression of nerve processes, which occurs as a result of damage to the spinal column. The pathology may be accompanied by displacement of its structures or segments (vertebral rotation, listhesis, scoliosis, hernia).
The most common cause of back pain is compression of the nerve roots.
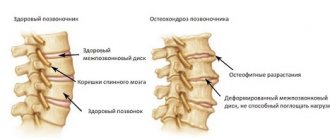
Pain syndrome can also develop due to osteochondrosis, osteoarthrosis , etc. Myalgic manifestations are associated with prolonged stay in a spasmodic state in the area of the pathological process. The body tries to compensate for irritation and compression of nerve endings, which manifests itself in limited mobility of the affected area.
As a result of overexertion, muscles become overtired, and pain develops against this background. A clear clinical picture is observed with radiculopathies; the stability and strength of muscle spasms is so high that in some cases the use of muscle relaxants is required.
Other common causes of back pain:
- Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease accompanied by loss of elasticity and destruction of intervertebral discs. The pathology can affect the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine; the nature of the pain depends on the location of the lesion.
- Curvatures and dysfunctions of the spine (lordosis, kyphosis, scoliosis and others) - such lesions often lead to the development of other diseases.
- Protrusions of the spinal column , hernias, occur against the background of other diseases, for example, osteochondrosis, the disease leads to a change in the position of the vertebrae, resulting in pain and other disorders.
- Inflammatory processes of the sciatic nerve , nerve endings of various parts of the spine. Inflammation of the sciatic nerve, radiculitis, and lumbago are common.
- Fractures and injuries of the spinal column , destabilization of the vertebrae are a very dangerous case, since injuries can be accompanied by damage to the spinal cord and nerve endings located along the spine.
Video: “Causes of acute lower back pain”
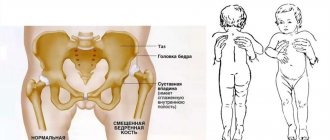
Structural anomalies
Due to the abnormal structure, some muscle groups may be in a state of continuous overstrain, the pain syndrome is persistent and intense.
Types of anomalies:
- joint dysplasia (primarily hip);
- unilateral decrease in pelvic height;
- shortening of the lower limb;
- "Greek foot"
Abnormal development is also considered to be shortening of the shoulder , a decrease in the length of the foot relative to growth indicators, and others. Pain can also occur due to inflammation and injury, the nature of the sensation depends on the type of injury.
Symptoms of specific pain in the spine
Before finding out the cause, more persistent symptoms should be a reason to see a doctor:
- pain in the spine that does not go away for several days;
- deterioration of health when moving;
- irradiation of pain to the limb;
- a feeling of numbness in the affected area.
Thus, lumbago in the legs is characteristic of compression of the spinal cord (this may be a symptom of a herniated disc). A dull local pain near the spine may indicate arthrosis of its joints. The sensation of pain intensity is individual for each patient. Therefore, it is important to consult a competent doctor in time.
Causes
Myositis of the back develops both due to external causes and in connection with the condition of the body:
- physical activity associated with excessive tension in the back muscles;
- exposure to cold and dampness;
- prolonged stay in a static incorrect position (both at work and during sleep);
- traumatic injuries to the back muscles;
- previous colds, flu and some other diseases;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- severe nervous stress.
Diagnostics
Determination of pain characteristics and assumptions about their source are carried out by a doctor during a face-to-face consultation.
What the doctor will tell you:
- onset of dorsalgia and patient age;
- the nature of the pain (does not decrease in a lying position, with rest, or change of position);
- pain is related to previous injury;
- increases over time;
- history of oncology;
- pain due to fever and weight loss;
- “stiffness” in the morning;
- damage to the spinal cord (this is indicated by paralysis, dysfunction of organs, sensitivity).
Next, the necessary list of tests and examinations is compiled to clarify the diagnosis. Our multifunctional center has comprehensive programs for diagnosing back pain. It is recommended for patients:
- whose age is over 65 years;
- early menopause has occurred;
- frequent injuries and fractures occur;
- there is a vitamin D deficiency;
- there are chronic rheumatic diseases or endocrine pathologies, etc.;
- and there are also bad habits (smoking, alcoholism, excessive coffee drinking).
As part of the program, the patient is advised by an experienced rheumatologist. The level of vitamin D, total and ionized calcium and inorganic phosphorus is examined, and osteodensitometry is performed.
How to act in case of severe pain?
- Drink your painkiller right away.
- Contact your doctor immediately.
- Lie down immediately and try to relax as much as possible. Do not get up until the pain subsides.
- You should not sit or lean forward during attacks of pain.
Prevention of back pain
To prevent the development of the disease and attacks of pain, it is enough to follow some recommendations:
- Train yourself to exercise daily. It should not put a lot of stress on the spine. It is enough to twist your body, pull yourself up and twist. Repeat the warm-up every morning and during periods of prolonged sitting.
- Buy a special orthopedic mattress and small pillows. Quality sleep affects the health of your back.
- Don't burden yourself with weights. Try to distribute any weight between two hands. It is best to purchase a backpack in which you can carry heavy things without harm to your health.
- Forget about sudden movements. Perform any action slowly and calmly.
- Train yourself to get up at least every hour after working at the computer for a long time. It is enough to take a break for 5 minutes and do a short warm-up.
- If you lift heavy things from the floor, be sure to bend your knees when doing so. Straight legs put a lot of stress on the spine.
- Pay attention to your posture, walk straight and don't slouch.
Treatment of spinal pain
Effective relief of the patient from dorsalgia is the task of experienced
doctors.
The Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia provides a full range of treatment for neurological diseases using a multidisciplinary approach, individual programs and complexity. Our advantages also include the use of the most advanced diagnostic methods and the ability to provide emergency care for spinal pain.
Conservative
treatment includes various techniques, including the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants, as well as physiotherapeutic effects (amplipulse, darsonvalization, electrophoresis).
The period of subsequent rehabilitation requires mandatory personal participation from the patient. It is necessary to regularly perform a set of therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscular frame of the spine and prevent relapse.
Surgical
treatment is carried out in extremely difficult cases, when conservative treatment options have not led to the desired results, and the pain continues.
Nature of pain
Muscle pain differs in frequency of occurrence, duration, strength, location, and etiology. The last point talks about the causes of pain. They may be associated with spinal pathology.
The following types are distinguished by frequency::
- episodic seizures;
- periodically recurring;
- chronic.
Depending on the strength of the sensation, the pain can be mild or intense.
The nature of pain during inflammatory processes and injuries:
- Continuous aching pain can be a symptom of myositis, a common muscle inflammation that occurs as a result of hypothermia. Similar sensations on the border between pain and itching (in the interscapular region) may indicate the progressive course of osteochondrosis.
- A feeling of “flowing” in the collar area or mild numbness of the lower back accompanied by pain may appear with prolonged sitting. Most often, such symptoms appear in office workers who are forced to sit at the computer for a long time.
- Lacerations and bruises provoke hemorrhages into the muscles, resulting in a painful hematoma, the sensations can be quite intense. Stretches also lead to injury to surrounding tissues and muscles. The back muscles also hurt due to constant and prolonged compression (carrying bags on one shoulder or heavy backpacks).
- Heavy physical activity leads to muscle fatigue resulting from the accumulation of lactic acid in them. The pain syndrome may be accompanied by minor cramps, it disappears after a few days, there is no need for treatment.
Pay attention to possible problems with different types of pain. Nature of pain and disease:
- strong - radiculitis, intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis;
- acute - displacement of spinal discs, sudden movements, falls, renal colic, diseases of the genitourinary system, lung diseases;
- aching - inflammatory processes in the lumbar muscles, myositis;
- chronic - spondylosis, ankylosing spondylitis, metabolic disorders, cancer, osteomyelitis;
- pain radiating to the right or left leg - inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
Get rid of pain and muscle stiffness!
Of course, you could go to a regular clinic, where they will prescribe tablets, ointments and injections for pain in the back muscles. But the effect will last a couple of weeks, and then the question of treatment will arise again. In Savyak’s highly specialized clinic, you will be offered a completely different approach - a safe, modern and most effective approach . The author's technique guarantees that your health will be restored!
Manual massage has proven itself well in relaxing muscles . Thanks to it, blood circulation is normalized and spasms are relieved. It is also useful to undergo a course of manual therapy . Blood flow will improve, pinched nerve endings will relax, and the vertebrae will take the correct position. For muscle pain therapeutic exercises ; specialists from Oleg Savyak’s vertebrology clinic will provide you with an individually designed complex.
Sign up with us for diagnostics and treatment, give yourself a healthy life!
Diagnostic features
The presumable reason why the spine hurts in the middle of the back can be determined by the nature of the discomfort and additional symptoms, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. If you are only concerned about back pain, you should consult a neurologist or orthopedist. If discomfort appears after a bruise or other injury, you need to be examined by a traumatologist. If you have a cough and fever, you may need to consult a phthisiatrician. Various diagnostic procedures allow you to determine the exact causes of pain in the middle of the back:
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- CT;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- ECG;
- lab tests.
MRI or x-rays in several planes reveal curvature of the spine, changes in the width of blood vessels, damage to the intervertebral discs, and displacement of the vertebrae. ECG, ultrasound and tests help detect diseases of internal organs.
Fighting myalgia
Patients often complain of myalgia when visiting a doctor. What is it and how to deal with trouble? Myalgia is considered to be pain of various origins, which can be localized in any muscle group.
The main cause of the disease is spasm of the back muscles caused by pinched nerve endings.
People suffering from chronic fatigue syndrome complain of muscle back pain more often than others. During human life, decay products that have not had time to fully oxidize can accumulate in muscle tissue, which causes pain.
Symptoms
Muscle pain may occur along with other symptoms, which vary depending on the underlying disease. For example, muscle pain that is caused by an injury may be accompanied by bruising and swelling in the area of the injury. Additional symptoms that may accompany muscle pain include:
- Depression
- Diarrhea
- Symptoms of acute respiratory illness (fever, chills, sore throat, fatigue, headache, cough)
- Impaired concentration
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle cramps
- Numbness, tingling or burning (called paresthesia)
- Problems walking
- Sleep disorders
- Swelling at the site of injury
- Sudden weight loss
- Vomit
Serious symptoms that may indicate a life-threatening condition
In some cases, muscle pain may occur in association with other symptoms that may indicate a serious or life-threatening condition, such as a heart attack or meningitis. You should immediately consult a doctor if you have any of these symptoms:
- Changes in consciousness or attention, such as loss of consciousness or sudden memory loss
- Changes in mental state, such as disturbances in perception of one's surroundings
- Chest pain radiating to the arm, shoulder, neck, or jaw
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath
- Inability to move any part of the body
- Impairment (loss) of vision
- Lack of urine
- Progressive weakness and numbness
- Seizure
- Stiff neck with high fever
What contributes to the appearance and progression of myalgia?
There are several important factors here:
hard work (physical);
poor posture;
performing a set of exercises that is not suitable for a particular person for any reason;
regular stress testing of the body and nervous system;
sedentary or sedentary lifestyle;
congenital pathologies of the spine;
an incorrectly performed therapeutic exercise or massage session;
the presence of excess weight, which puts additional stress on the entire body, including the back;
hypertonicity or severe spasms of the muscle corset;
possible hypothermia of the body.
In addition to myalgia, which has a specific cause, there is also arthralgia - pain of an unstable nature, the cause of which has not been identified.
Important: severe pain is a consequence of the inflammatory process in the muscles, and moderate pain may indicate tissue degeneration or chronic inflammation.