Damage to the lateral ligaments of the knee joint
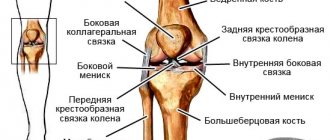
The lateral or collateral ligaments of the knee joint are located, according to their name, along its lateral surfaces.
The external lateral or collateral fibular ligament begins from the external epicondyle (bone protrusion) of the thigh. It covers and strengthens the knee joint from the side. Below this ligament is attached to the head of the fibula. A layer of fatty tissue separates the lateral ligament from the joint.
The external collateral ligament of the knee joint is damaged less frequently than the internal one, but more often the entire ligament is torn completely or the ligament is completely torn from its attachment.
The internal lateral or collateral tibial ligament is subject to traumatic injuries more often.
However, it usually ruptures partially. This ligament starts from the inner femoral condyle. It looks like a wide band, covers and strengthens the inner surface of the knee joint, and below is attached to the tibia. In addition, some of the fibers of the internal collateral ligament are woven into the joint capsule and into the tissue of the internal meniscus of the knee joint. This attachment of the ligament leads to possible damage to the inner meniscus of the knee joint when the ligament is injured.
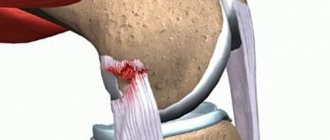
Damage to the collateral ligaments occurs as a result of tension when the tibia deviates. If the shin deviates outward (when walking on an uneven surface, tucking the foot in a heel, etc.), the ligaments are subject to strong tension and are torn or torn. If the tibia deviates outward, the internal ligament ruptures, and if the tibia deviates inward, the lateral collateral ligament of the knee joint is damaged.
When the lateral collateral ligament is torn, an avulsion fracture of the portion of the head of the fibula to which the ligament attaches may occur. Patients complain of pain in the area of the rupture, which intensifies when trying to deviate the leg outward when the internal ligament is torn, or inward when the external ligament is torn. Partial ligament ruptures result in limited flexion in the knee joint, while complete ligament ruptures lead to excessive mobility (looseness) in the joint. The diagnosis is clarified using x-rays taken with special placement of the legs.
Treatment of injuries to the lateral ligaments of the knee joint
The injury site is numbed. If the ligaments are partially torn, a plaster cast called a plaster cast is applied to the leg from the upper third of the thigh to the level of the ankles.
Complete ruptures of the internal collateral ligament, after anesthesia, are also treated conservatively by applying a plaster cast. A complete rupture of the lateral ligament requires surgical treatment, which should be carried out in the first days after the traumatic injury. Usually these ligaments diverge over a considerable distance. They are tightened and stitched with Mylar tape or plastic surgery is performed using the biceps femoris tendon. If an avulsion fracture of the apex of the head of the fibula occurs, the fragment is fixed to the fibula with a screw. Sometimes the ligament not only ruptures, but also separates into individual fibers. Then the ligament is reconstructed using grafts.
The results of treatment are not always satisfactory, because the ligaments grow together with a scar and at the same time they increase in length. Lengthening of the ligaments affects the function of the knee joint, which becomes unstable. If this instability is compensated by other structures of the knee joint (cruciate ligament, other parts of the knee joint capsule), the function of the knee joint can be satisfactory.
In other cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment - reconstruction of the collateral ligaments. Two types of surgical techniques are used: plastic surgery using tendons and grafts to strengthen the ligament, or relocation of the ligament attachment sites. The extent of the operation depends on the severity of the damage.
There are contraindications. Read the instructions or consult a specialist.
Symptoms of Ligament Damage
As a rule, a ruptured knee ligament has established symptoms, including:
- joint pain that worsens with exercise;
- swelling of the knee joint;
- an increase in the size of the knee joint due to blood accumulated in it;
- instability of the knee joint.
Some patients note that the rupture is usually accompanied by a characteristic cracking sound.
Sometimes the injury occurs unnoticed by the patient, and the only symptom is joint instability. If such a sign appears, it is recommended to consult a specialist for a preventive examination.
When a knee ligament rupture , no anatomical changes are observed. For this reason, if you have the symptoms mentioned above, you should consult a doctor who will make a final diagnosis. An X-ray or MRI can show the extent of the ligament damage. It is important to remember that knee ligament injuries can become chronic, which subsequently makes treatment and the recovery period for the ligaments much more difficult.
What to do if a cruciate ligament rupture is suspected?
The first aid for a ligament injury is to immobilize the knee joint. If possible, the ligaments should be numbed. Then you need to apply a splint, which will allow you to transport the patient with minimal concern.
Ligament injuries are a painful injury, and therefore it is important to see a doctor as quickly as possible who will provide qualified assistance.
Cruciate ligament surgery
Almost 50% of knee require arthroscopic manipulation. Only the doctor decides how serious ligament tears . The operation is performed by experienced specialists in specialized clinics.
Treatment of ligament injuries is carried out using the latest technologies. Biodegradable implants are used that can fix the ligaments of the knee joint. This type of implant is made of polyvine and polylactic acids, hydroxyapatite. Damage to the ligaments heals itself, and subsequently the materials independently resolve and are eliminated naturally.
The cruciate ligament can also be restored surgically, using autografts and endoprostheses. With the help of these elements, the restoration procedure is significantly reduced. Over time, the ligament can fully restore its functions.
If the doctor confirms the fact of ligament rupture , then the operation makes it possible to reconstruct the entire damaged area through small incisions. Typically, surgical procedures are performed some time after the diagnosis is confirmed.
Modern medicine makes it possible to effectively treat ligament ruptures even with chronic damage. In this case, an operation is performed on the cruciate ligament according to a scenario similar to that which occurs during an acute injury. But it is worth noting that a chronic type of rupture requires a longer period of recovery.
Surgeries on the cruciate ligament are not performed if knee arthrosis develops when it is damaged. In this case, treatment is postponed until the problems accompanying the injury are resolved.
Treatment of minor ligament tears
In case of minor injuries, conservative treatment methods are used to restore the ligaments. They may include exercise therapy, where the load is gradually increased, as well as massage and physiotherapy.
In some cases, the knee joint ligament can simply be fixed in a certain position using a cast. First, the doctor removes blood from the joint. The duration of wearing a cast can take up to one month. After this, the ligament is restored according to the method described above.
Ligament damage can be repaired using a conservative method in a shorter period of time. At the same time, conservative treatment of knee ligaments is suitable for a larger number of patients, and also has no restrictions on the type of activity and age.
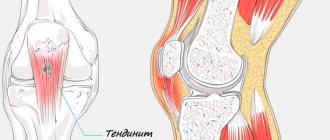
Knee tendon problems
The hamstring is a band of three muscles that is located at the back of the thigh and just behind the knee. Often, it is because of dysfunction of the patellar tendon that people cannot move their legs and arms. A person of any age can have a sprain.
As a result, the elasticity of the hamstring tendon is lost, which entails a pathological alignment of the natural curve of the lumbar and also a loss of elasticity of its muscles. The muscle bundle and tendons play the role of flexor of the leg in the knee joint, raise the heel towards the back, straighten the hip and keep our back in the correct position.
Compression of the tendon in the popliteal region often causes pain in the gluteal region, in the upper and posterior plane of the thighs. Soreness occurs with weakening of the elasticity of the tendon.
How exercises help
Basic exercises that will help you get rid of tendon spasms:
- Starting position, sitting, spread your legs in different directions, but without bending your knees, then clasp your hands behind your back and pull your lower arm up. At the peak point, hold this position for 30 seconds.
- Starting position, stand with the heels of both feet at a slight elevation of about 10 cm. Next, lean forward slightly, but do not allow your hips to turn out. Toes should point in one direction. If you follow all measures, you will feel muscle stretching. You should remain in this position for at least 30 seconds.
Manifestation of inflammation and drug treatment
The inflammatory process, as a rule, has its own external manifestations, namely redness of the skin and the formation of a tumor in the knee area. Physiologically this is felt as pain. Moreover, if rest and local measures do not relieve pain, you should consult a traumatologist.
Among experts, there is a point of view that when treating tendons of the knee area, you should not use corticosteroid drugs, since the risk of tendon rupture increases many times over. If there are no positive indicators during local treatment, surgical intervention should be resorted to. Treatment should begin with painkillers, for example, Naproxen or similar properties. These remedies provide temporary improvement and relief from acute pain. In addition, physical therapy can help alleviate symptoms.
Using the iontophoresis method, namely low-power electrical impulses, the skin is enriched with corticosteroids. Recently, a procedure has become increasingly popular in which plasma enriched with platelets is injected, which forms new tissue connections, which leads to complete restoration of damaged areas.
Knee ligament rupture
The most severe consequences of mechanical damage to the knee joint are ligament ruptures. As a rule, this is accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the circulatory system and blood entering the joint. If there has been a rupture, then fixation of the joint and cold bandages, which will narrow the blood vessels, should be undertaken to stop the hemorrhage.
Treatment of the rupture involves taking anti-inflammatory drugs that do not contain steroids. For external use, including for pain relief, there are various ointments and lotions. After the primary symptoms are relieved, the mandatory use of physiotherapy, a set of special exercises and massage. If we are talking about a complete rupture, then surgical intervention is applicable.
If you contact a specialist in a timely manner, you will receive quick help, and rehabilitation will take the shortest possible time.
If the injury is local, a cast is placed on the thigh and lower leg at an angle of 170°. It is this degree of slope that determines the most effective fusion of tendons. After a minimum of 4 weeks, the cast can be removed. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Prevention of ligament damage
Athletes are now encouraged to warm up before performing exercises and stretch afterwards. Special exercises have also been developed to strengthen the ligaments of the knee joint.
Treatment of ligament injuries at home, unfortunately, is not possible. It must be remembered that a torn ligament injury can only be diagnosed by a professional doctor. They should also treat knee ligaments. It is unacceptable to self-medicate, as ligament damage is a serious problem.
Cost of cruciate ligament surgery
As mentioned above, the main factor leading to cruciate ligament injuries is injury to the knee joint. It is accompanied by severe acute pain and swelling of the knee. Usually, when a ligament ruptures, a cracking sound is heard and a feeling of dislocation appears, and if blood gets into the joint cavity during a rupture, then hemarthrosis occurs. The first days after injury are characterized by pronounced pain and a state of hemarthrosis, in which it is impossible to examine the knee joint by palpation (manual examination). Manual examination is performed after elimination of acute pain and symptoms of hemarthrosis. For comparison, a healthy leg is examined, a traumatologist checks the functionality of the knee joint using special tests (drawer, “Pivot Shift”, Lachman) and makes a diagnosis. To reduce pain and improve the quality of the examination, remove blood fluid from the joint cavity using a syringe. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), x-rays, and ultrasound are performed to rule out other possible injuries (fracture, meniscal or collateral ligament tears).