- Treatment options
- Conservative treatment
- Surgery
- Arthrotherapy
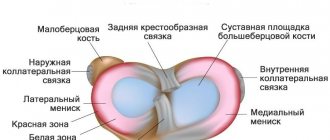
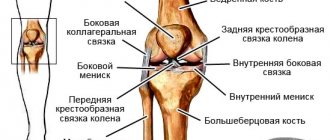
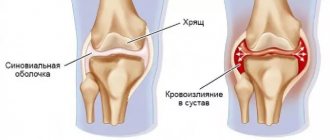
Rupture of the lateral (collateral) ligaments of the knee joint occurs through an indirect mechanism. The damaging factor does not affect the ligament itself. The cause is the deviation of the lower leg inward or outward. In this case, the lateral ligament of the knee, located on the opposite side, is torn. Both conservative and surgical methods are used to treat injury.
Treatment options
Treatment methods
The consequences of incorrectly chosen treatment tactics can be sad for the patient. He develops permanent disability. After the end of the acute period, the pain goes away. But instability of the joint remains. When the medial collateral ligament is torn, the knee easily tilts outward because there is no force holding the joint in the correct position. To be able to walk normally, a person fixes his knee either with a bandage or with special orthoses. But this only temporarily solves the problem. Over time, atrophy of the lower leg muscles develops, and long-term instability of the joint leads to gonarthrosis.
To avoid such problems in the future, the correct choice of treatment method is required. For this purpose, instrumental studies are carried out: not only X-rays, which allow us to establish the fact of a rupture, but also MRI, which provides the doctor with clarifying information. The patient is monitored after conservative treatment. If instability of the joint persists, it is operated on.
Causes of ligamentitis
Infantile ligamentitis occurs mainly due to the fact that some components of the hand go through stages of development over different time periods. This is what contributes to the faster development of tendons compared to the annular ligament on the fingers. Due to this discrepancy in growth, the ligaments interfere with the normal functioning of the tendons, on which thicker areas appear, and when the ligament passes through these areas, a click is created. Subsequently, the tendon loses its ability to slide easily, and the finger ceases to function normally.
In the adult population, the principle of the appearance of stenosing ligamentitis is the same. Occurs due to overload while working with hands. Rheumatism, arthritis, diabetes and gout also contribute to the appearance of ligamentitis.
Conservative treatment
The essence of conservative treatment is that the internal (tibial) ligament of the knee is provided with complete functional rest. As a result, the necessary conditions are created for the splicing of broken fibers. At the same time, during the acute period, there is a fight against symptoms (pain relief, elimination of swelling).
In the acute period, immediately after injury, the person is carefully examined. Typically, the lateral medial ligament is torn by a blow to the lateral aspect of the knee. Typically this is a sports injury. It may be accompanied by damage to other intra-articular structures (menisci, joint capsule, ligaments).
Sometimes surgery is performed shortly after injury. But if only the internal collateral ligament is damaged, conservative therapy is used. The knee is punctured, washed, and the blood is removed. Local anesthetics are injected internally to relieve pain. Typically 0.5% procaine is used. A plaster splint is applied for 1 week. After eliminating the swelling of the joint, it is changed to a circular plaster cast from the groin to the fingers.
When the medial collateral ligament of the knee joint is torn, the tibia is placed in an adducted position. This fixation ensures reduced mobility of the leg in the damaged joint. The position of the limb helps reduce the load on the injured ligament. It remains in a relaxed state for a long time, which ensures the normal course of regenerative processes.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
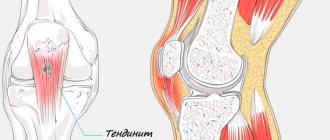
Ligamentitis is manifested by aching pain in the leg, which intensifies with movement. When the patellar ligament is inflamed, pain is localized on the front surface of the knee, the inner lateral on the medial side, and the outer lateral on the lateral. In case of damage to the cruciate ligaments, the pain is usually of uncertain localization and diffuse in nature.
Ligamentitis cannot be recognized by clinical symptoms alone. The disease can be easily confused with ligamentosis, sprain or rupture of ligaments, meniscal damage, etc. These diseases can only be distinguished with the help of additional research methods.
Table 1. Methods used to diagnose ligamentitis
| Method | Diagnostic capabilities |
| Radiography | Allows you to identify bone fractures, cracks, calcification of ligaments, etc. X-rays are taken for all patients with pain in the knee joint. The purpose of the examination is to exclude severe injuries and serious bone damage. |
| Ultrasound | Allows you to clarify the nature of pathological changes in the ligaments. An experienced doctor will be able to distinguish between inflammation, thickening, calcification, degenerative changes, partial and complete ruptures |
| MRI | Provides a clearer and more detailed image than ultrasound, but ultrasound is almost as informative as magnetic resonance imaging |
Do not confuse ligmentitis and ligamentosis. These are different diseases. Ligamentosis is a dystrophic disease of ligaments that causes them to ossify at the point of attachment to the bones. Most often, patients suffer from cruciate ligaments. Their damage leads to severe limitation of knee mobility.
physiotherapy
physiotherapy
Additional treatment methods:
- physiotherapy – many methods are used that can improve blood circulation in the joint, accelerate the elimination of swelling, and normalize regenerative processes;
- physical therapy - static gymnastics is prescribed from the third day, in the recovery period (after removing the cast) they move on to dynamic exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the limb;
- arthrotherapy - injections of hyaluronate and platelet-rich plasma into the joint, accelerate tissue regeneration and prevent cartilage degeneration.
Ligamentitis and ligamentosis: what is the difference?
Sometimes after an X-ray of the knee joints in the conclusion you can read that a diagnosis of “ligamentosis” has been made. What is the difference between ligamentosis and ligamentitis? With ligamentosis, there is a thickening of the ligamentous tissue, an increase in its fragility due to excessive mineralization or salt deposition. This process of calcification of ligaments most often occurs when calcium metabolism in the body is disturbed, for example, with pathology of the parathyroid glands. Knee ligamentitis will be a “transparent” pathology during X-ray examination, and with ligamentosis, radiopaque shadows of the ligaments will appear. What other ways can you make a diagnosis?
Massage for nephroptosis
Surgery
Surgical treatment of a rupture of the internal ligament of the knee is required if it is completely torn, if instability of the joint persists. It can be partially compensated with the help of special restrictive orthopedic devices. However, sooner or later the disease will cause gonarthrosis and muscle atrophy. Therefore, the earlier surgery is performed, the better the results.
Ligament plastic surgery
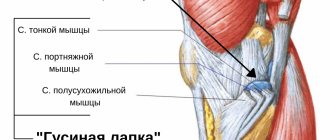
There are several ways to stabilize a knee when the medial ligament is torn. One of them is plastic. The material for it is an autograft. That is, tissues of the human body that are similar in their properties are taken. They are implanted at the site of the torn ligament. Often, a fragment of the fascia lata of the thigh is taken for this purpose.
Autoplasty with the tendon of the tender muscle is used. In the area of the medial epicondyle of the femur, the osteoperiosteal cusp is formed. A tendon is placed under it. The sash is then strengthened with sutures. The wound is sutured. The limb is immobilized with a plaster cast for 4 weeks. The bandage is applied from the upper third of the thigh to the toes. In this case, the knee should be bent at an angle of 170 degrees.
Ligament suture
Often this operation is performed in the acute period of injury - no later than 8 days after receiving it. It can also be carried out within the first three days. That is, almost immediately after the injury, although swelling and hematoma still persist. Early intervention improves surgical results.
When the superficial layer of the medial collateral ligament of the knee ruptures, the rupture site is sutured. The doctor discovers a hematoma at the site of the rupture. In addition, he can detect this place by abducting and adducting the lower leg: the ends diverge. The doctor stitches the ligament in the transverse direction, covering 1 cm above and below the damaged area. After this, the ligament is stitched longitudinally along its entire length. When a bone fragment is torn off, it is fixed with a screw and washer.
After surgery, the limb is immobilized with an orthosis. Duration – up to one and a half months. In the postoperative period, a person is prescribed antibiotics and painkillers. In most cases, within 3 months after surgery, a person’s lameness completely disappears, and after 6 months, the function of the joint is completely restored.
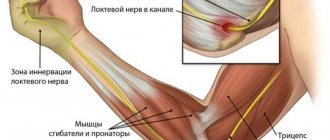
Causes of collateral ligament rupture
Isolated rupture of the lateral collateral ligament is extremely rare due to anatomical features and other typical mechanics of injuries. Typically, when the lateral collateral ligament is torn, the traumatic force is so great that it damages the so-called posterolateral complex, which includes the lateral collateral ligament, the popliteus tendon, and the posterolateral capsule of the knee. joint Although such injuries are, fortunately, rare, they occur among young patients when engaging in active sports associated primarily with the active use of the entire range of motion of the knee joint. Among these sports are game types: football, basketball, volleyball; extreme sports: alpine skiing, skydiving, parkour, bike trials and the like.
A rupture of the lateral collateral ligament or damage to the entire posterolateral complex cannot be overlooked. It is accompanied by a noticeable “click” or “crunch”, acute pain and limited ability to support. After some time, significant swelling occurs in the entire area of the injured knee joint.
Diagnosis of the disease
Currently, the basis of diagnosis is imaging studies such as joint ultrasound and MRI. If the presence of stones and calcification is suspected, this will be clearly visible when performing conventional radiography in two projections.
In the last decade, such a modern method of diagnosis and treatment as arthroscopy has been widely introduced into clinical practice. With this examination, you can not only see how the ligaments work and what condition they are in, but also carry out certain diagnostic and therapeutic measures, such as tissue biopsy and instillation of medicinal drugs into the joint.
Quite important methods for diagnosing inflammatory joint damage are clinical and biochemical studies. The doctor evaluates:
- level of total protein and globulin fraction;
- C-reactive protein level;
- rheumatoid factor.
During a clinical blood test, attention is paid to the level of leukocytosis and ESR. All this together gives certain reasons to continue research or search for a systemic connective tissue disease, or suggests a traumatic or physical genesis of ligamentitis.