General information
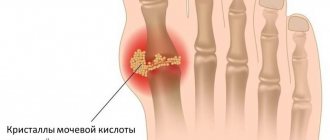
The key reason for the development of gout on the legs is the deposition of uric acid crystals on the surface of the joint structures. In medicine they are called sodium urates. This substance appears as a result of the breakdown of nitrogenous substances - purines, these substances are part of the molecules of protein structures. Uric acid is by its nature a powerful natural antioxidant; under its influence, oxidative processes are inhibited, which negatively affect cells. Uric acid is also a powerful stimulant of brain activity.
Sodium urate deposits can appear in any joint joints, but most often gouty changes are diagnosed in the joints of the lower extremities. Since a person is constantly moving, his lower limbs constantly suffer from high loads. Also in this area there is a slowdown in systemic blood flow. Normally, a small amount of uric acid should be detected in the blood fluid, since if there is an excess, the kidneys actively remove this substance.
Sometimes the concentration of this element in the body rapidly increases, resulting in its crystallization on the surface of the joints. The main provoking factors for the development of gout also include:
- disruptions in metabolic processes;
- various diseases of the urinary system organs of chronic origin, as a result of which their functional activity decreases;
- excess amount of purines that enter the human body along with food. Most often, these are products that contain a large amount of animal proteins and nitrogen: fatty varieties of meat and fish products, seafood, mushrooms, legumes.
Often, specialists diagnose the presence of all of these provoking factors simultaneously, and this is a powerful impetus for gout in the legs to develop much faster. Most often, men undergo such pathological changes, since changes in their hormonal background are observed much more often. In women, this disease is diagnosed much less frequently, its symptoms are less pronounced, the most common manifestation of gouty arthritis is a “bone” on the leg.
Experts have proven that dietary errors are the most common provoking factors in the development of gout. That is why in complex treatment a specially selected diet is mandatory.
Rheumatologists also identify a number of reasons that can provoke gouty changes in the joints:
- genetic predisposition, which is most often associated with metabolic disorders;
- diseases of the urinary system of chronic origin, in which normal kidney function is disrupted and the composition of urine changes;
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of diuretics, without medical supervision, without monitoring health status. The result of long-term use of diuretics is dehydration of the body, blood viscosity increases, and as a result, the concentration of uric acid increases sharply;
- chronic infections and inflammatory processes caused by streptococci. These are tonsillitis, tonsillitis;
- systematic mechanical loads and injuries of articular joints - dislocations, bruises, fractures;
- hypothermia of the lower extremities;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes for a long time, incorrect shoe size.
Gout on the legs is difficult to treat, but if you start taking therapeutic measures in time, you can cure the disease much faster, as well as prevent the development of dangerous health consequences.
What is gout
This disease occurs against the background of hyperuricemia - a pathological increase in the concentration of uric acid in the body. Urate crystals accumulate in joints and other organs. They have an irritating effect on surrounding tissues and provoke the development of chronic inflammation, which results in their proliferation and the appearance of gouty bumps. Tophi usually appear on the fingers, feet, knees, and less commonly on the elbows and forearms. Also, characteristic nodules often appear in other places - on the edge of the outer ear, and sometimes in the tissues of the spine, heart, lungs and other internal organs. The tophi themselves are painless. However, in acute gout, patients feel pain due to inflammation of surrounding tissues, such as tendons or periarticular bursae.
Clinical picture
The key clinical manifestation of gouty arthritis is acute pain in the joint. Most often it occurs at night or early in the morning. An attack of pain appears unexpectedly and can be so intense that a person cannot find relief from the pain and tries to relieve it by changing his body position. During the daytime, pain in the joint may decrease slightly, but with the onset of night it becomes severe again. Such symptoms usually last for about three days, then the attack of pain goes away on its own.
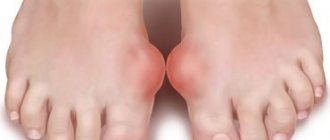
Regardless of the location of the pain, the symptoms of gout are the same. When the disease worsens, redness and swelling of the affected joint is noted, its deformation gradually occurs, and it becomes larger in size. At the same time, there is a local increase in body temperature and limited joint mobility. If a person stands on the sore leg, the pain becomes more intense.
Another clinical manifestation of gouty arthritis is tophi. These are painless subcutaneous nodules that form near the affected joint as the disease progresses. Inside these nodules there is a deposit of uric acid salts. Small tophi appear on the surfaces of the joints of the toes; near large joints they can grow the size of a chicken egg. As the disease progresses, painful ulcers appear on the surface of these nodules, and white, pasty contents flow out. When the exacerbation of the disease passes, the ulcers heal.
If gout of the ankle joint develops, the foot becomes bent and the heel turns out. If the hip joint is affected, the leg also becomes bent.
Classification of the disease
Gout is divided into various subtypes, taking into account the cause of occurrence and the nature of the course. It can be primary, that is, caused by genetic factors, or secondary, arising as a result of certain diseases or external causes that provoked a violation of the excretion of uric acid.
In 80% of cases, gout has classic manifestations. At the same time, in practice, atypical forms of the disease are often encountered: pseudophlegmonous, asthenic, rheumatoid-like, periarthritic and other types.
According to the prevalence, gouty arthritis is divided into two types:
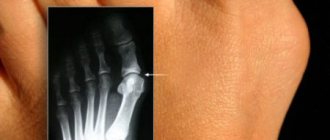
- Monoarticular - the lesion affects only one joint. This type is typical for middle-aged patients when the disease is first diagnosed. In approximately 60% of cases, the gouty nodule is localized at the joint of the big toe. Less commonly, tophi and other symptoms of the disease appear on the knees or ankles.
- Polyarticular - the lesion spreads to two or more joints. Usually occurs in older people or with a chronic course of the disease. During the initial manifestation of the disease, several joints become inflamed at once only in 10–20% of cases. The polyarticular form affects the feet, hands, wrists, elbows and ankles.
Stages
Experts classify several stages of development of gout on the legs, each of them is characterized by its own clinical picture:
1. At the first stage, there are no pronounced changes in the joints. Any pathological changes are visible in a biochemical blood test, since an increased concentration of uric acid is determined.
2. When the disease passes into the second stage, an acute form of gouty arthritis of the joints develops. This is accompanied by swelling and inflammation. First, the joint of the big toe is affected, then the neighboring joints begin to suffer.
3. At the third stage, attacks of pain occur; they do not last long, but they are intense. The remission period may last several months. As the disease progresses, it decreases, and relapses occur more often.
4. At the fourth stage of gout development, pathological changes in the joints are visible to the naked eye - the joint is deformed, tophi are visible.
Gout symptoms
Gout is characterized by the presence of autoinflammatory features and regular acute attacks. Most often, pathology develops in the joints of the feet and in the area of the big toe, but gout on the hands, elbows, and knees can also make itself felt. Acute gouty arthritis usually begins with sudden, sharp pain (often at night). The most common type of gouty arthritis is the first joint of the big toe where the toe joins the foot. The finger swells, its skin at this moment acquires a red and sometimes purple-violet hue. Touching it causes severe pain. The onset of gouty arthritis from lesions of other joints is observed much less frequently (mainly in older people), and therefore sometimes there is a need for differential diagnosis with other inflammatory arthropathies.
In addition to the phalanges of the foot, the joints of the metatarsus, ankle, knee, wrist and elbow joints can become inflamed. The shoulder, hip, sacroiliac, and sternoclavicular joints are rarely affected. From the onset of the attack, the pain usually intensifies within several hours, often becoming unbearable. Signs characteristic of acute arthritis: swelling, local hyperthermia, severe pain suggest an infectious process. The skin over the affected joint is tight, hot to the touch, shiny, red or purple. Sometimes there is an increase in body temperature, chills, tachycardia, general weakness and leukocytosis.
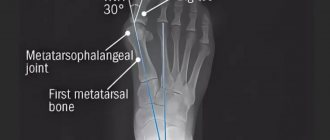
The diagnosis is made on the basis of at least six of the following symptoms and diagnostic signs: more than one acute attack of arthritis in the anamnesis, maximum inflammation of the joint already in the first day; monoarticular nature of arthritis; redness of the skin over the affected joint; swelling or pain localized to the first metatarsophalangeal joint; unilateral damage to the joints of the arch of the foot; nodular formations resembling tophi; hyperuricemia (increased uric acid levels); unilateral lesion of the first metatarsophalangeal joint; asymmetric swelling of the affected joint; detection on radiographs of subcortical cysts without erosions; absence of bacterial flora in the joint fluid.
If untreated, the most intense phase of the first attack usually lasts 3-4 days; over the next 3-4 days the pain gradually subsides. The pain and inflammation of gout usually resolves spontaneously.
Diagnosis of gout on the legs
Diagnostic measures begin with an external examination by a specialist. The doctor collects anamnestic data and conducts a survey regarding complaints. It is important to find out how severe the pain syndrome is, determine the intensity of joint swelling, and detect whether there are tophi. Next, the doctor refers the patient to the following types of diagnostics:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- synovial fluid samples;
- radiography;
- scintigraphy;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- blood chemistry.
In the general blood test, if there is gout, there is an increase in the concentration of leukocytes, the leukocyte formula changes, and an increase in the level of uric acid is visible. Any changes in the urine are diagnosed only if the inflammatory process has affected the organs of the urinary system.
When puncturing the synovial fluid, specialists find urate crystals in it. These deposits are also visible on X-ray images.
Gout on the legs: treatment
With the development of gouty arthritis, hospitalization of the patient in a hospital is required in extremely rare cases, if pathological changes have affected the kidneys. With the development of the articular form of pathology, outpatient treatment of gout on the legs is recommended.
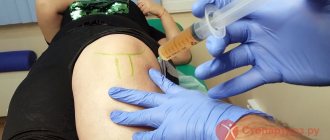
Conservative treatment of gout on the legs is prescribed with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Butadione, Reopirin, Indomentacin. They are produced in the form of tablets, ointments, and injections for intramuscular administration. These drugs effectively relieve the inflammatory process and reduce the severity of pain.
Among the specific drugs for the treatment of gout on the legs, due to which it is possible to stop attacks of gout on the legs and have a positive effect on metabolic processes, one can highlight: Allopurinol, Allomeron, Colchicine, Urodane. Colchicine is administered intravenously. This drug is very effective during an attack of illness.
During complex treatment of gout on the legs, in addition to medications, physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated. Thanks to such procedures, it is possible to improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in pathologically modified joints. The following physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed by doctors:
- irradiation with ultraviolet light;
- ultra-high frequency currents;
- shock wave therapy;
- balneology;
- use of paraffin applications;
- ozokerite applications;
- electrophoresis.
When the inflammatory process is stopped and pain is eliminated, the patient is indicated for massage and physical therapy. Such procedures contribute to the normal restoration of joint mobility. Massage of the foot, knees, and hip joint helps improve microcirculation of blood fluid, helps reduce the size of tophi, accelerates the removal of uric acid salts from the body, eliminates muscle spasms, and prevents the development of muscle contracture.
It is recommended that you learn foot massage under the guidance of a physical therapist so that you can perform this procedure yourself at home. Therapeutic exercise can also be performed at home after prior consultation with a physiotherapist.
Stages of development of gout
Gouty arthritis is a sluggish disease that inevitably progresses in the absence of proper treatment and periodically worsens. The natural development of the disease has 4 stages:
- Asymptomatic hyperuricemia. At this stage, a person does not have any external manifestations of the development of gout. However, there is an increased level of uric acid in the blood. There is no specific treatment for gout at this stage. After all, up to 30 years can pass from the first case of increased uric acid to the development of the disease. In addition, hyperuricemia does not always lead to gout.
- Acute gouty arthritis. At this stage, the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints becomes critical. The result is swelling and severe pain. Severe intoxication of the body and the appearance of febrile fever may also occur. An acute attack of gout usually occurs at night after exposure to trigger factors and can last for several weeks.
- Intercritical period. At this stage, the disease develops asymptomatically. The joint has normal mobility, the person is not bothered by pain or other unpleasant sensations. At the same time, uric acid salts continue to accumulate in tissues. The next gout flare-up may occur several months or even years later. However, it can be avoided altogether by controlling uric acid levels in the body through diet or medication.
- Chronic gouty arthritis. This stage occurs in the absence of adequate treatment and control of uric acid levels in the previous stages. The disease progresses, affecting an increasing number of joints, as well as the bladder, kidneys and other internal organs. Tophi grow, which can result in ruptures of cartilage and ligaments, severe deformation of bones, and even complete destruction of joints.
Completing a course of treatment and following the doctor’s recommendations during the intercritical period can reduce cases of exacerbation or completely eliminate them. Otherwise, gout will be accompanied by multiple attacks, alternating at short intervals and accompanied by severe pain.
Radical methods
If the conservative treatment of gout on the legs prescribed by the doctor does not bring results, the disease is diagnosed in an advanced form, there are complications, doctors consider the advisability of radical treatment of gout on the legs. Minimally invasive and invasive techniques can be used. A minimally invasive technique allows you to remove tophi, open the joint cavities in order to remove purulent contents from them if an acute inflammatory process develops. This operation is performed using local anesthesia.
In advanced situations, the patient is indicated for endoprosthetics, which involves removing the joint affected by the disease. A prosthesis is installed instead. But in the majority of cases, gout on the legs can be treated with conservative methods, and it is possible to extend the period of remission for a long time.
Symptoms of the disease
At the initial stage of development, gout is diagnosed very rarely, since the patient does not have pronounced manifestations of the disease and, accordingly, there is no reason to see a doctor. The only sign that may indicate the likelihood of developing the disease is renal colic, a symptom of urolithiasis that often precedes gouty arthritis.
Symptoms of the disease appear during the exacerbation period:
- severe swelling of the affected joint;
- hot, shiny red skin over the area of inflammation;
- moderate local pain with intensification in the evening and morning;
- limited joint mobility;
- deterioration in general health (fever, loss of appetite, weakness, etc.).
If left untreated, the acute phase resolves on its own within a few days or weeks. In this case, the disease becomes chronic, in which severe symptoms weaken and hard nodes form in the joints.
Unconventional methods
Any alternative medicine can only be used in combination with conservative therapy prescribed by a doctor. The following means are used:
- ointment based on poplar buds;
- St. John's wort decoction;
- larkspur ointment;
- cinquefoil decoction;
- propolis ointment;
- lubricate damaged joints with a mixture of iodine and crushed aspirin tablets;
- ointment based on red pepper.
Proper nutrition is required; the diet should contain a low amount of purines. Those patients diagnosed with gout on the legs are not allowed to eat mushrooms, legumes, fatty fish and meats, offal, fried, salty and spicy foods. It is recommended to consume large amounts of fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables and fruits.
These foods contain low levels of purines. It is not recommended to consume any oil - butter, sunflower, so as not to burden the kidneys and organs of the digestive system.
With complex treatment of gout on the legs, with the help of medication, folk treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures and proper nutrition, you can achieve a quick recovery, reduce the number of attacks, reduce the severity of their symptoms, and achieve stable and long-term remission.